Exam 1 Lec 3 Plasma Proteins and Dysproteinemia
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Hundreds of proteins, with many structures and functions.
What are plasma proteins comprised of?
Liver (most plasma proteins)
Lympohoid organs (immunoglobulins)
Where are plasma proteins synthesized?
Water, albumin, globulins, fibrinogen
Total blood - RBCs
What is Plasma made of?
Plasma - serum
water, albumin, globulins
What is Serum made of?
Transport (nutrients, small hormones, waste, drugs), colloid osmotic effects, acid-base, regulatory (cell production, inflammation), immune defense, hemostasis
What is the function of plasma proteins?
4-6 g/dL
how much total plasma concentration do neonates have?
6-8 g/dL
how much total plasma concentration do adults have?
Physical (refractometric)
Biochemical (spectrophotometric)
Fractionation (electrophoresis)
What are the three ways to measure protein?
PCV or Hct
Packed cell volume
Leukocytes and platelets
what makes up the buffy coat?
free hemoglobin
hemolysis means
chylomicrons/VLDL
lipemia of plasma appearance means
Specific gravity (urine) and total plasma proteins (plasma/serum)
A refractometer is used to quickly screen urine or plasma/serum for:

1. Hemolysis in the sample
2. Lipemia (interferes with light transmission)
3. marked increases in nonprotein solids (like glucose in diabetics or urea nitrogen in kidney disease)
What are three ways your plasma protein concentration can be erroneously increased? (with refractometer)
no
Is hemoglobin a plasma protein?
separately using 2 different spectrophotometric assays
Total protein and albumin concentrations in serum (or plasma) are measured
subtracting albumin concentration from total protein concentration
[total protein] - [albumin]
Total globulin concentration is calculated:
Various alpha-, beta-, and y- globulin bands.
stain proteins for protein, carbs, and lipids
What categories are serum/plasma proteins separated into by protein electrophoresis?
for it to migrate the farthest
In a serum protein electrophoresis what do you expect from albumin?
Ponceau S stain
What kind of stain is used here?
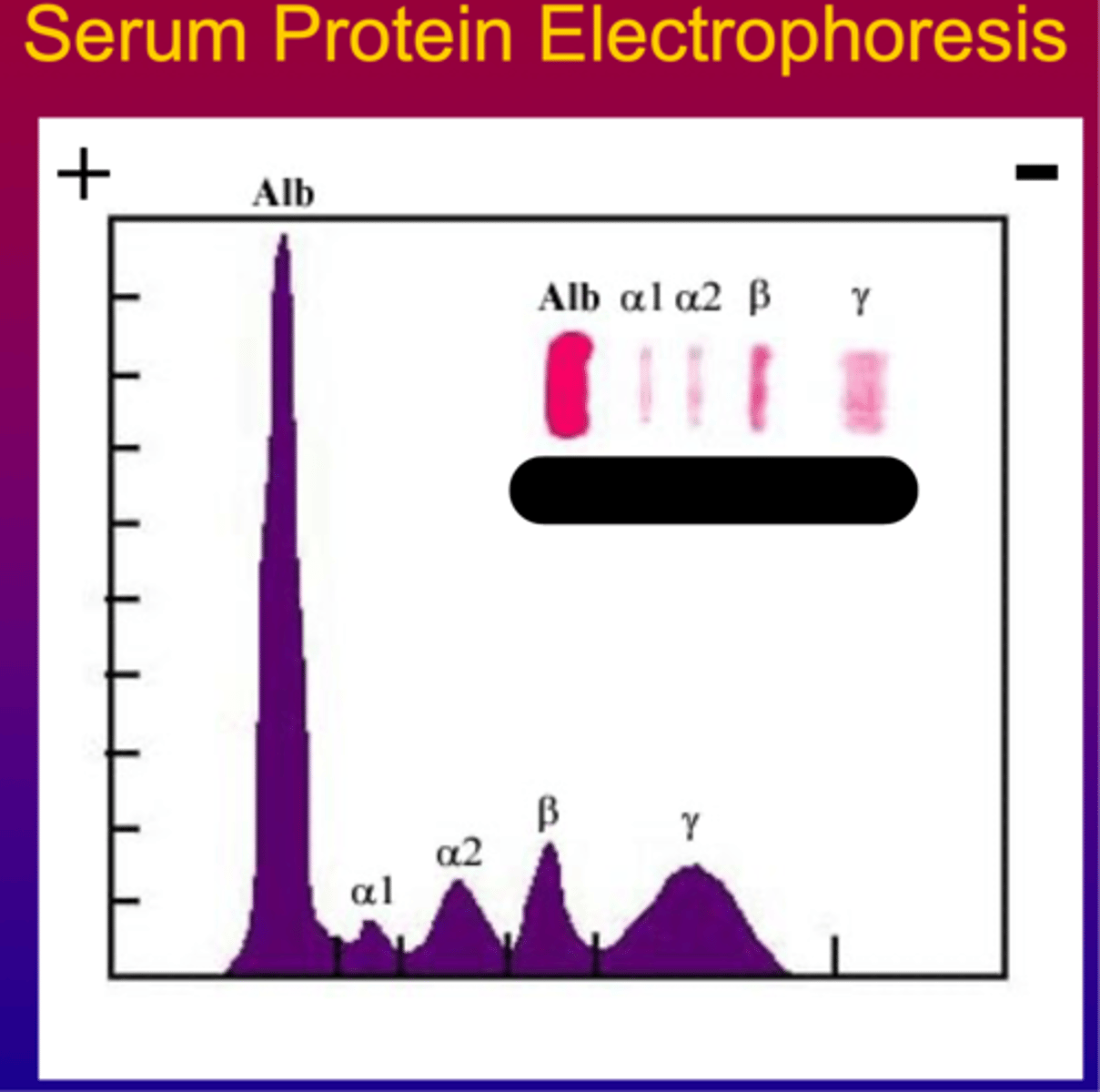
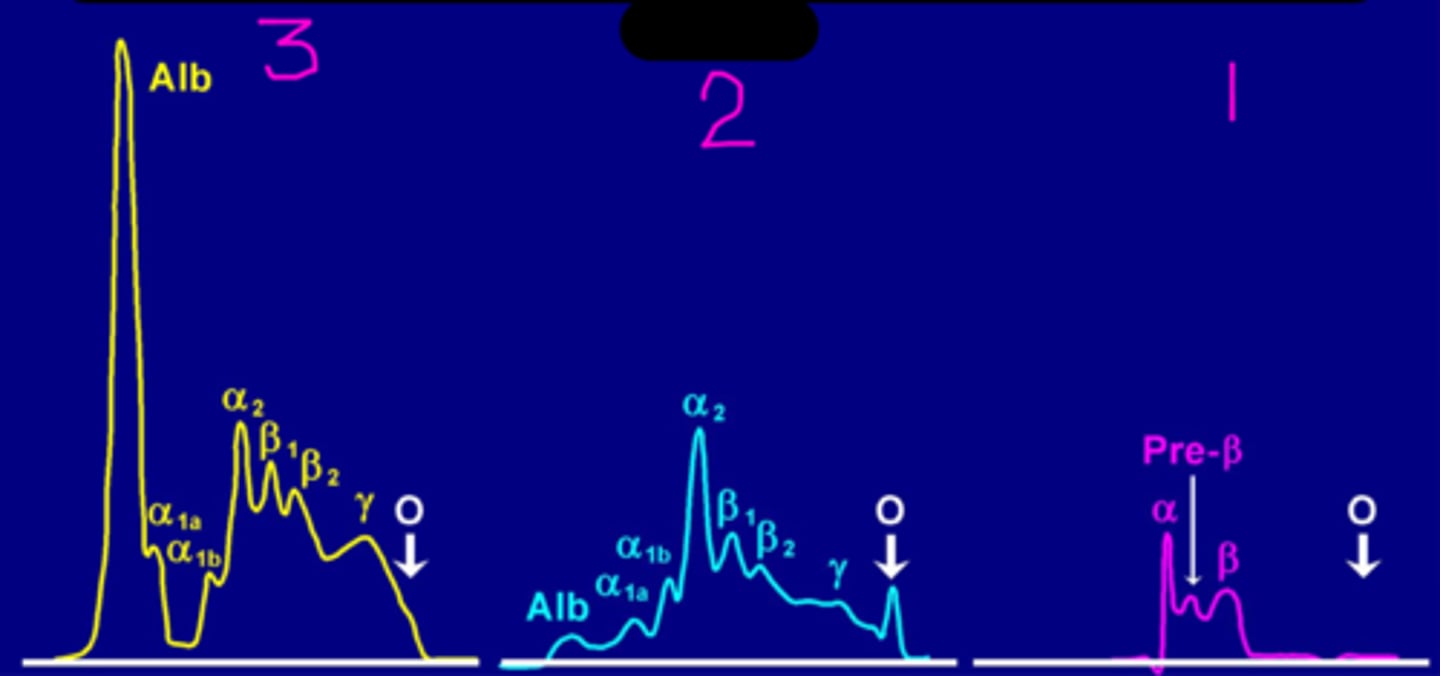
Protein stain on a serum protein electrophoresis
What is 3?
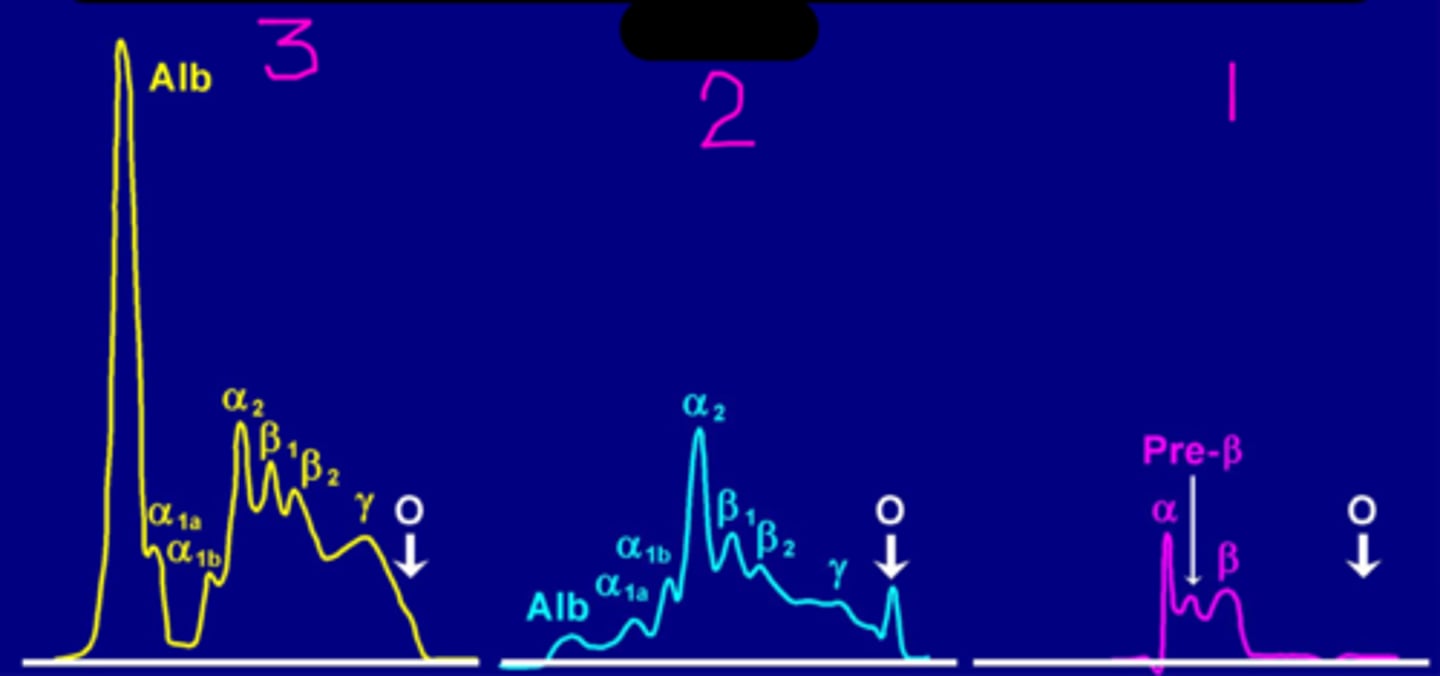
Carbohydrate stain on a serum protein electrophoresis
What is 2?
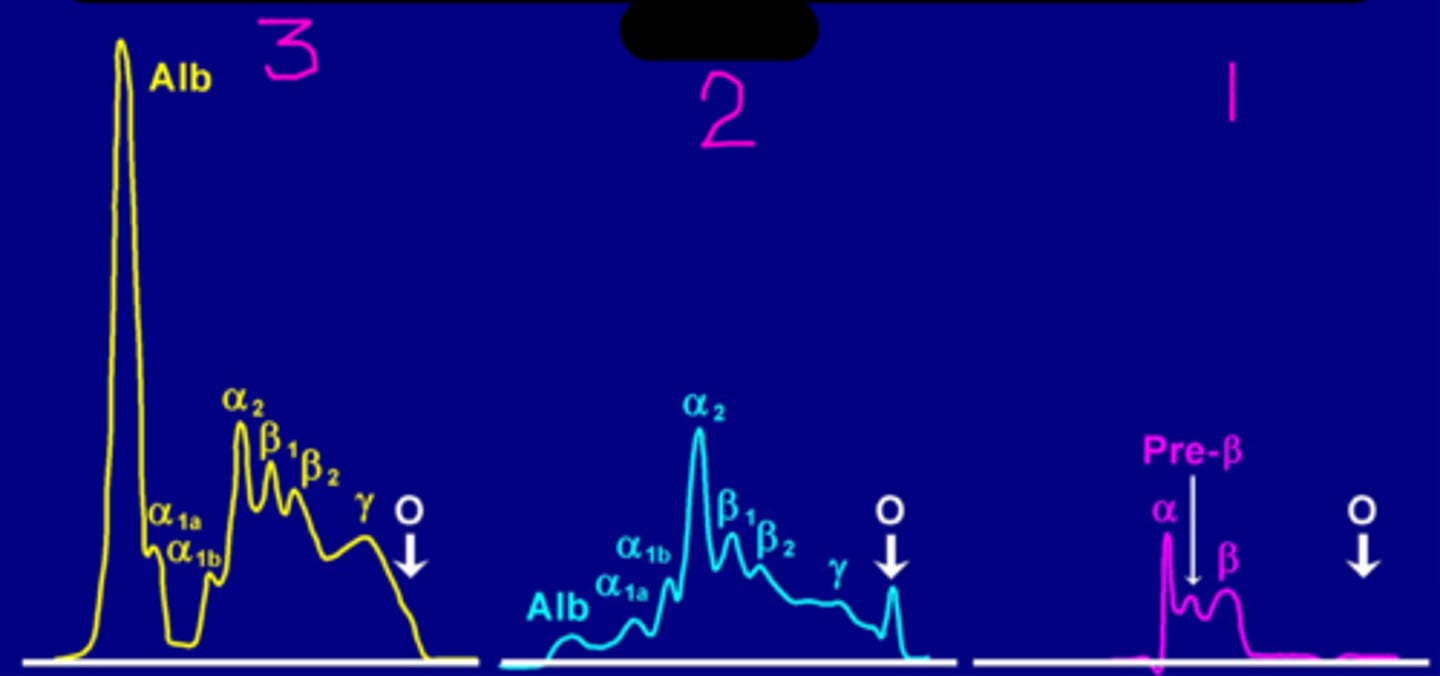
Lipid stain on a serum protein electrophoresis
What is 1?
edema and low total Ca+ in blood
hypoalbuminemia can result in
APP - respond to inflammation
What are acute phase proteins?
Serum Amyloid A (SAA)
Which positive APP doe all common domestic mammals have/
c-reactive protein
Dogs and humans have what positive APP?
Haptoglobin
What positive APP do cow, sheep, goat, and pig have?
Fibrinogen
This is classified as a coagulation factor. It is optimal platelet aggregation. Is considered a moderate APP that increases inflammation.
Active inflammation (cattle, goats, and horses).
Dehydration (all plasma proteins increase)
Fibrinogen will increase with:
Disseminated intravascular coagulation
DIC stands for
DIC
Liver failure
Some snake venoms
Fibrinogen will decrease with:
Ceruloplasmin
This transports copper. has ferroxidase activity that facilitates iron mobilization from tissue stores. Is also a plasma antioxidant and alpha2-protein.
Transferrin
This is an iron-binding metalloprotein. Correlated with total iron binding capacity (TIBC). Transports iron throughout the body. Is a negative acute-phase protein.
Ferritin
This correlated with total body iron stores. It is also an iron-containing protein, primarily found inside cells. It is found in low concentrations in the blood. High values could reflect inflammation.
Hormone Binding Proteins
Bind small molecular weight hormones, preventing them from being rapidly filtered by the kidney:
1. corticosteroid-binding
2. Thyroxine-binding globulin
3. sex hormone-binding globulin
List three Hormone binding proteins
Antithrombin
This protease inhibitor inhibits thrombin and certain other coagulation factors. Required GAGs (e.g. heparin) for optimal activity.
Albumin and transferrin
What are two negative acute-phase proteins?
Dehydration or hyperglobulinemia
If you have hyperproteinemia what disorder would you expect?
Dilution (overhyration), decreased production, increased loss, sequestration in body cavities.
If you have hypoproteinemia what disorders would you expect?
Increased vascular permeability (edema) and increased tissue catabolism
If you have increased loss of some proteins (especially albumin) what should you expect?
Positive acute-phase proteins and immunoglobulins
If you have increased synthesis of some proteins due to altered cytokines, what might you expect?
Negative actue phase proteins (albumin and transferrin)
If you have decreased synthesis of other proteins due to altered cytokines, what might you expect?
you have dehydration and causes relative hyperproteinemia and erythrocytosis
When only the fluid component of blood is lost:
panhypoproteinemia
When AG (albummin and globulin) is normal but is expected to be abnormal?
External hemorrhage
This is when fluid is replaced more rapidly than protein and cells. This will cause hypoproteinemia and anemia.
Hypoalbuminemia
This can occur with excessive fluid therapy, decreased synthesis, or loss from body (protein losing glomerulopathy).
hyperalbuminemia
This can occur with dehydration, artifacts, and in dogs that have hepatocellular carcinoma that produces albumin
Hemorrhage, protein-losing enteropathy, failur of passive transfer, overhydration, decreased production of immunoglobulins
When would you expect hypoglobulinemia?
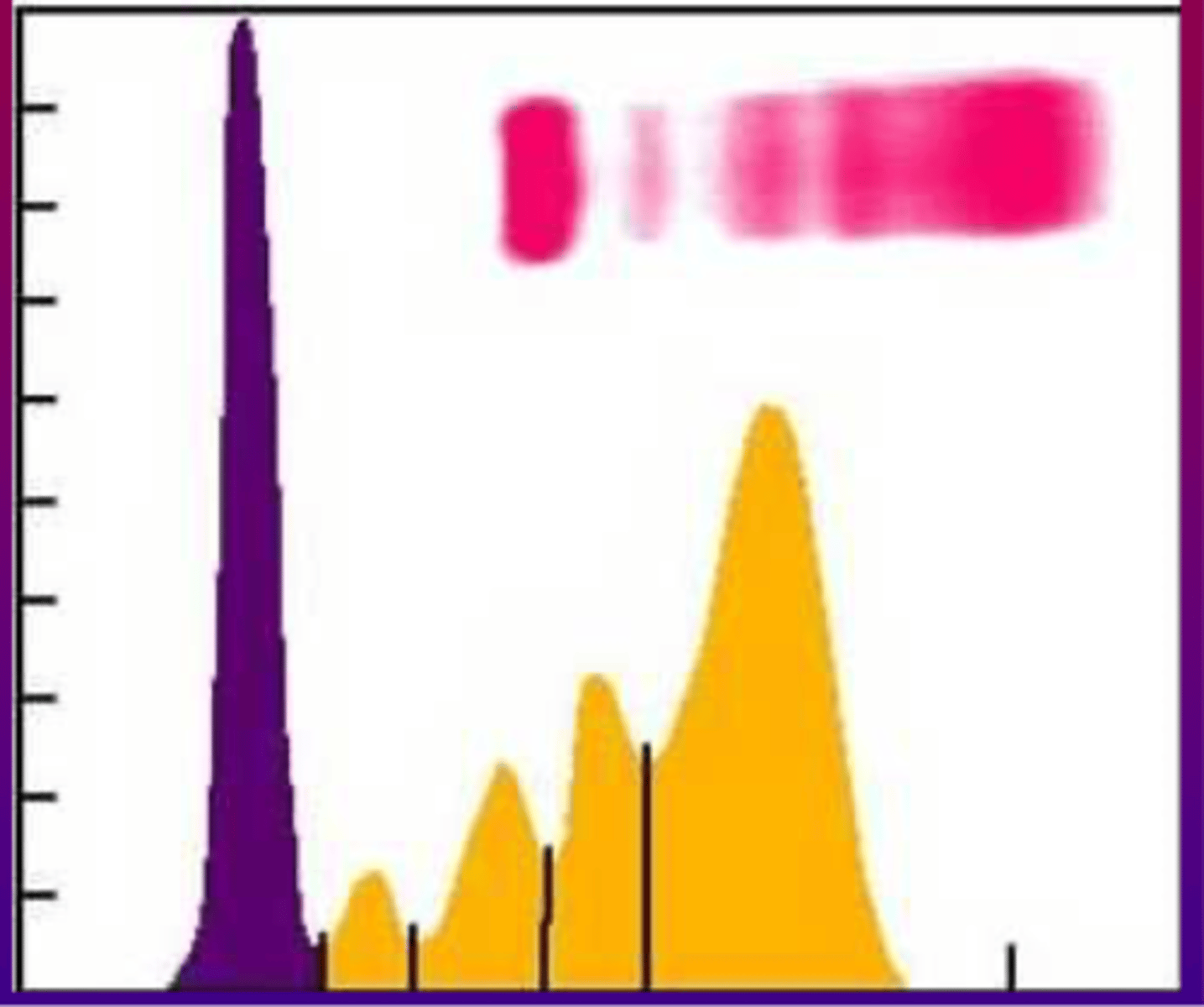
Blunt broad peak, Ig from many lympoid clones.
in serum protein electrophoresis. if you have hyperglobulinemia and its polyclonal-
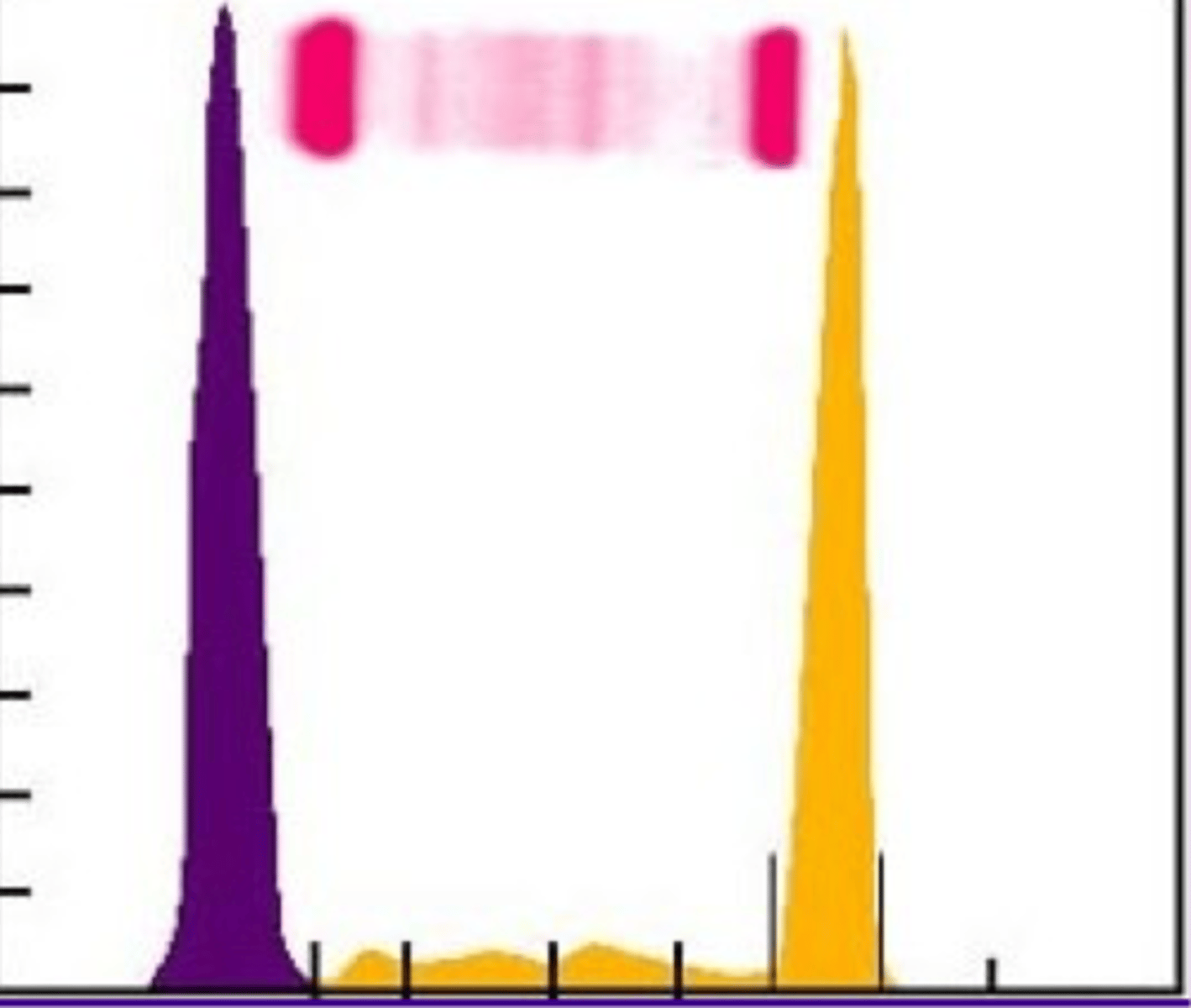
Narrow sharp peak. Ig (or Bence Jones protein) from a single lympoid clone.
In serum protein electrophoresis. If you have hyperglobulinemia and it is monoclonal-
Neoplasia (multiple myeloma, mymphoma/leukemia)
Rarely non-neoplastic
Rarely biclonal
What disorders are monoclonal?
Antigenic stimulation- infections, immune-mediated, immune response to neoplasia
What disorders are polyclonal?
Bence Jones Proteins
What are Ig light chains referred to as:
Polyclonal
What is going on here?
Monoclonal
What is going on here?
Synthesis of lipoproteins occurs in GI and liver.
Transport of water insoluble lipids in blood.
Where are lipoproteins made and what is their function?
apolipoproteins
High MW water-miscible complexes of lipids and proteins called:
Chylomicrons
These are very large lipoproteins of low density that remain at the origin when electrophoresis is performed
In the mucosal cells of the duodenum and jejunum following digestion of fat in diet.
Where do chylomicrons form?
White cloudy plasma becasue of chylomicronemia after eating a meal containing fat.
Define postprandial lipemia
Very Low Density Lipoproteins VLDLs
These are primarily synthesized by the liver, transport the bulk of the endogenous triglycerides.
Low density lipoproteins LDL
These arise as metabolic products from VLDLs. They are the major mechanism by which cholesterol is transported to peripheral tissues.
High density lipoproteins HDL
These are the most dense lipoproteins. Their precursors are formed in the liver and complete molecules are formed in the plasma by addition of remnants from other lipoproteins. They transport cholesterol from tissues back to the liver.
Caused by hypertriglyceridemia but NOT hypercholesterolemia. Increased chylomicrons and/or VLDL
If you have lipemia in plasma or serum (cloudy/milky):