Fermentation
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
2/10/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Why does anaerobic respiration occur?
After glycolysis produces pyruvate
With no oxygen, pyruvate cannot go into mitochondria
Oxygen cannot be used as the final electron acceptor
No etc needed
Organic compound is used as final electron acceptor
Produces less atp than aerobic respiration: no figure, less and less overtime
Waste products besides CO2 and water accumulate in extracellular space
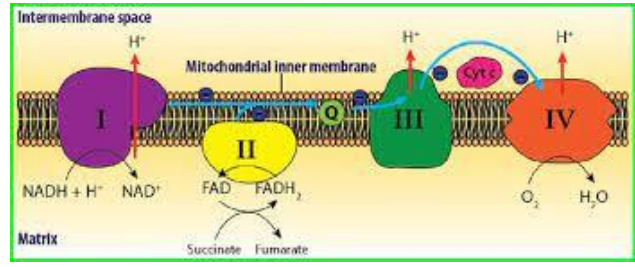
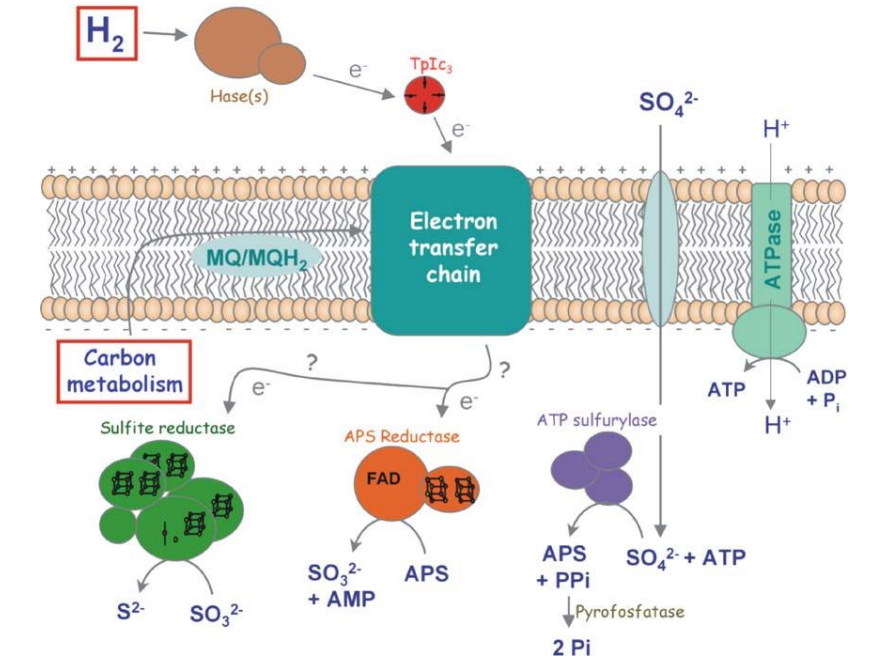
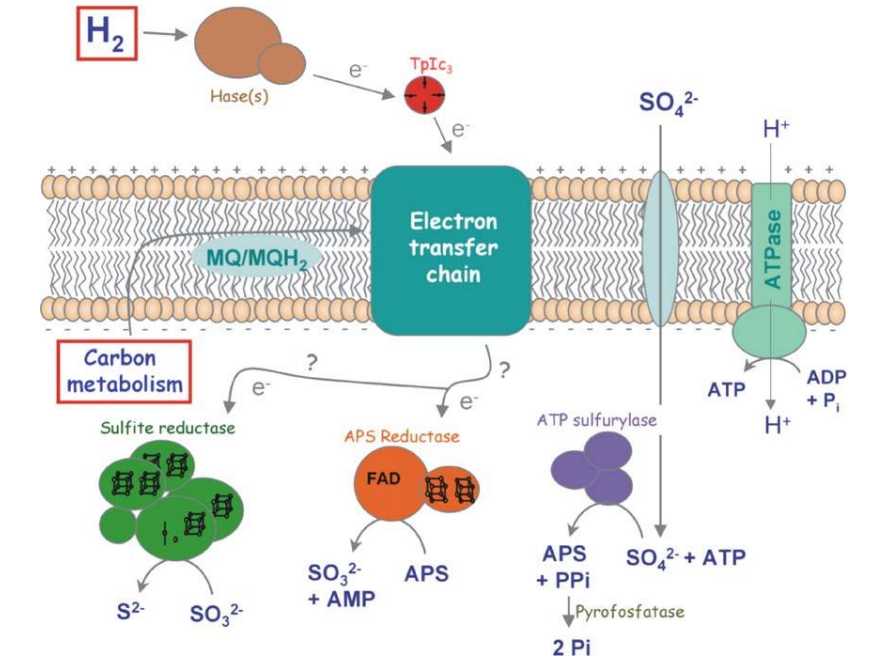
What is the electron receptor here?
Sulfate
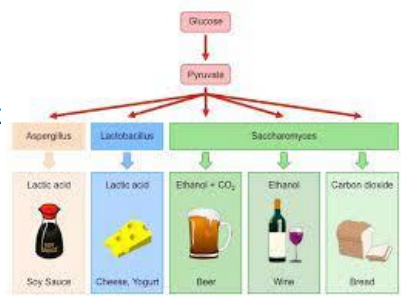
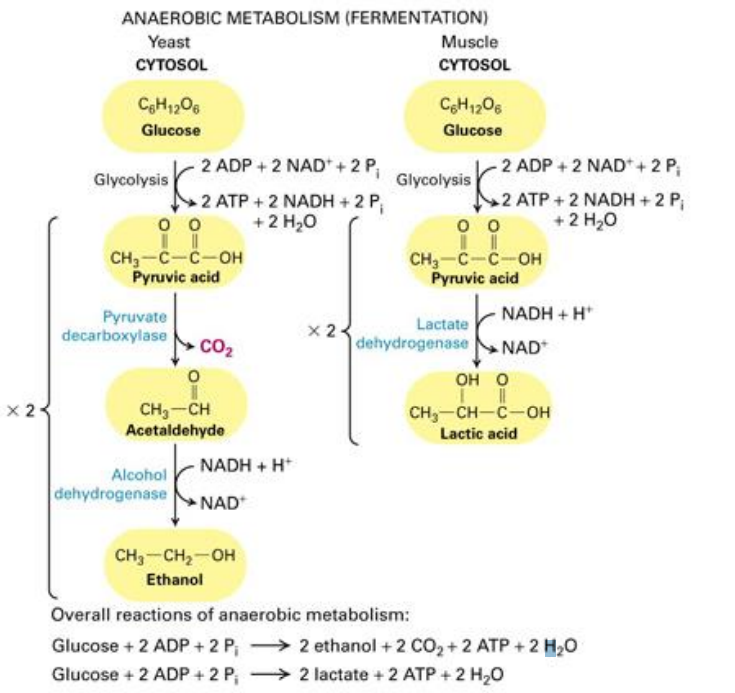
Glycolysis with and without oxygen
With oxygen: cellular respiration
Without oxygen: fermentation allows glycolysis to continue
Fermentation types
Lactic acid fermentation: in mammals and bacteria
Alcohol fermentation: producing ethanol, in yeast, beer, wine
Mixed acid fermentation: many different acids, in e. Coli
Depends on
availability of nutrient
Tolerance of waste product
Energy yield
Type of organism
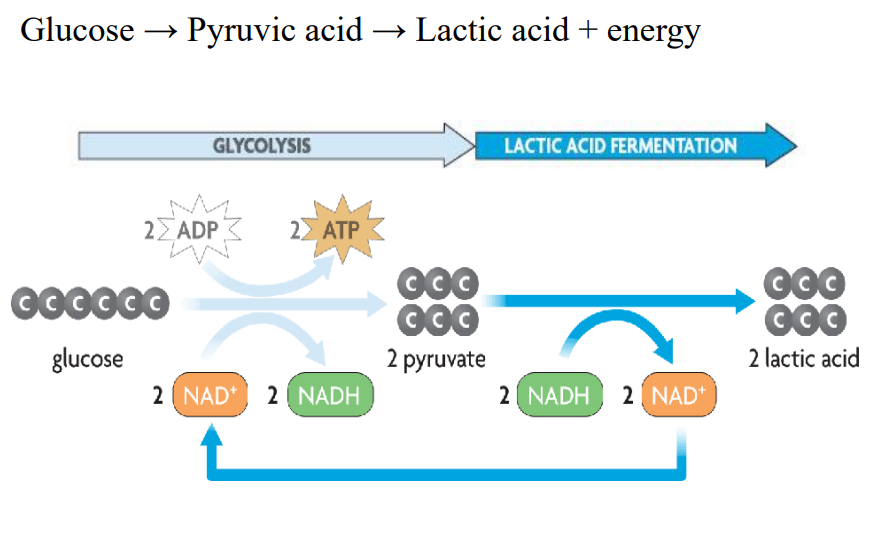
Lactic acid fermentation
Occurs during intense physical movement when oxygen is not available for our cells
Muscle cells switch from respiration to fermentation
Glycolysis occurs, 2 pyruvate formed
2 pyruvate -> 2 lactic acid
With no oxygen, NADH cannot be oxidized and travel to etc
Potential energy from pyruvate conversion to lactic acid used to change NADH -> NAD+ (oxidation)
Waste (lactic acid) accumulates in muscles preventing muscle function and causing burning, painful sensation
Clears up about one hour later with proper oxygen intake
formula: glucose → pyruvic acid → lactic acid + energy
What build up causes burning and pain?
Lactic acid build up in tissues
Lactic acid fermentation can also be called
a Fate of pyruvate under anaerobic condition
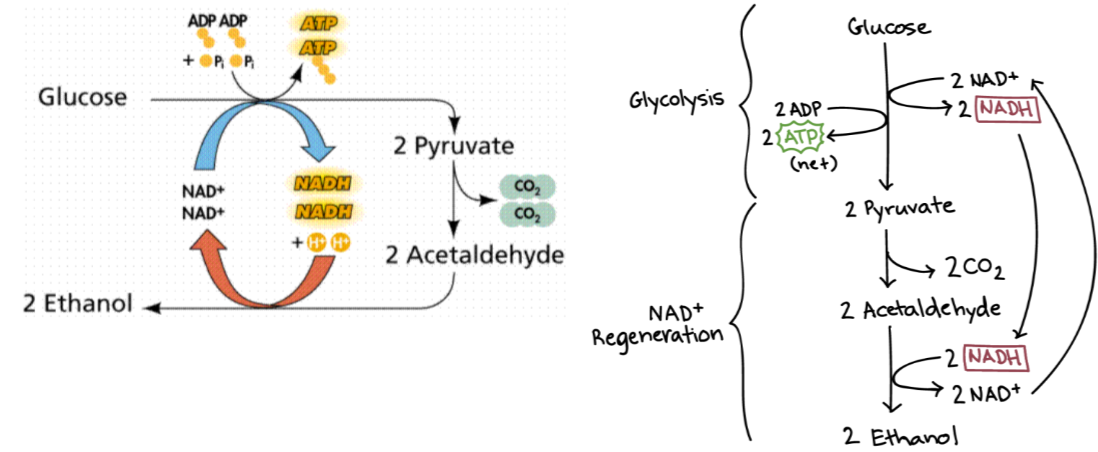
Alcohol fermentation
Occurs in yeasts and some bacteria
2 Pyruvate converted to 2 acetaldehyde converted to 2 ethanol
Acetaldehyde is intermediary step
Potential energy from acetaldehyde -> ethanol used to oxidize NADH to NAD+ (can also be called NAD+ regeneration)
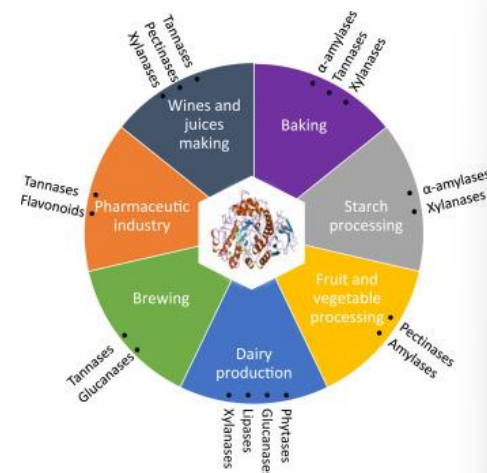
Applications of fermentation SPALD
Alcoholic beverages: wine, beer, ethanol makes it intoxicating
Acidic dairy products: yogurt, accounts for sour taste
Spoilage of food
Lactic acid build up in muscle cells
Pharmaceutical medical purposes
Baking: yeast, yeast rises and releases CO2
Starch, fruit and veggies processing
Difference between yeast/alcohol fermentation and muscle/lactic acid fermentation
Yeast fermentation has the extra step of converting pyruvate -> acetaldehyde
Lactic acid fermentation: glucose -> pyruvate -> NADH
Yeast/alcohol fermentation: glucose -> pyruvate -> acetaldehyde -> ethanol
What is NADH?
Coenzyme and electron carrier
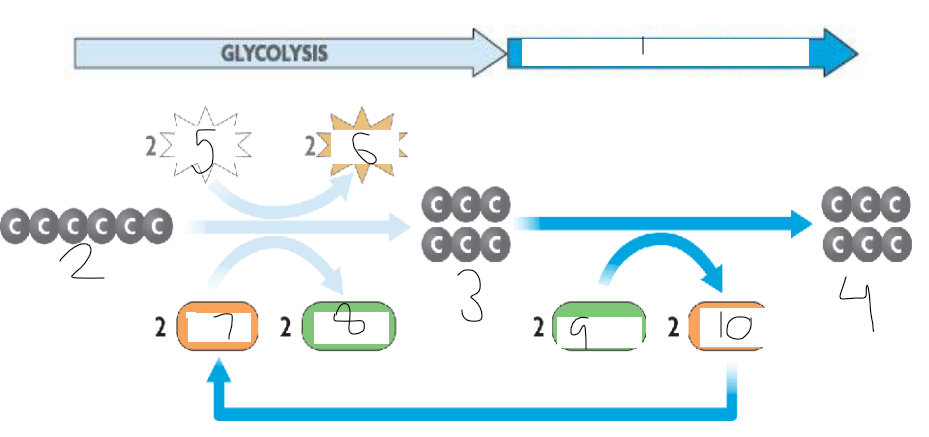
label
1 = lactic acid fermentation
2 = glucose
3 = 2 pyruvate
4 = 2 lactic acid
5 = 2 adp
6 = 2 atp
7 = 2 nad+
8 = 2 nadh
9 = 2 nadh
10 = 2 nad+
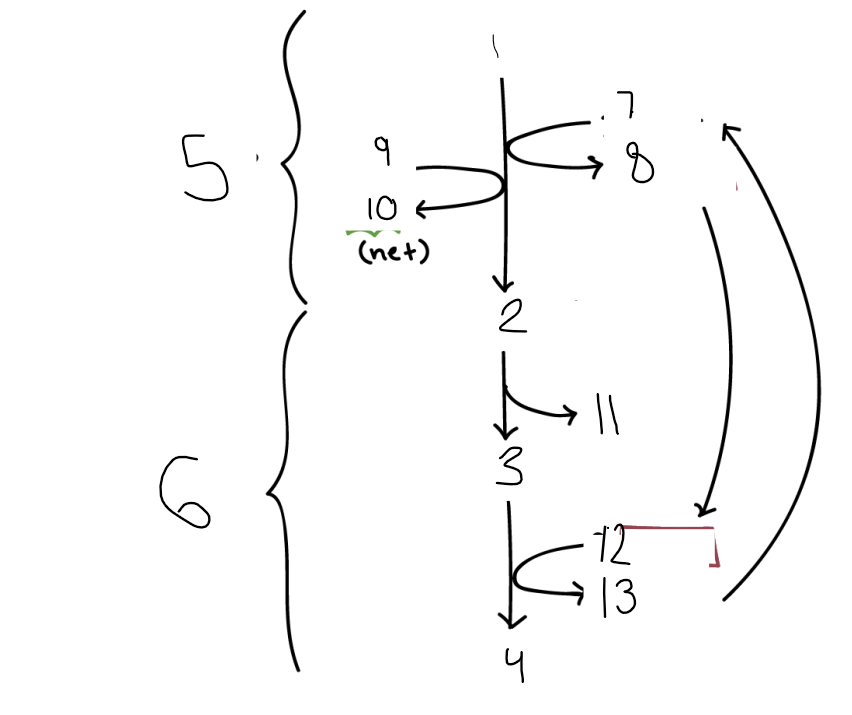
label
1 = glucose
2 = 2 pyruvate
3 = 2 acetaldehyde
4 = 2 ethanol
5 = glycolysis
6 = NAD+ regeneration
7 = 2 NAD+
8 = 2 NADH+
9 = 2 ADP
10 = 2 ATP
11 = CO2
12 = 2 NADH
13 = 2 NAD+