Music Theory Vocabulary Terms Unit 3-4
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Alto (voice)
Typically a low female voice. This voice is below the soprano.

bass (voice)
lowest voice in music

closed position
notes placed as close as possible on the staff, within an octave.

doubling
to duplicate the same note in another octave
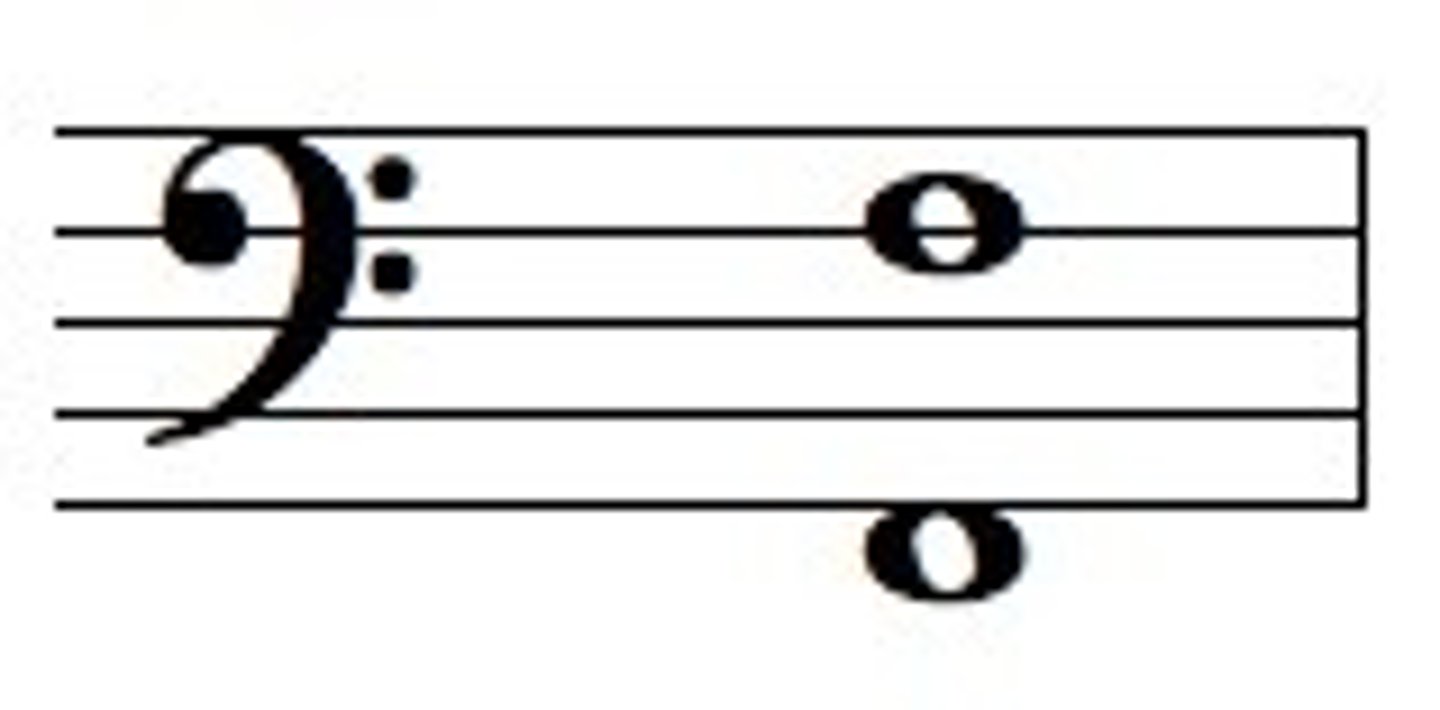

Inversion
rearranging the notes of a chord or melody, flipping them upside down relative to a central point or bass note
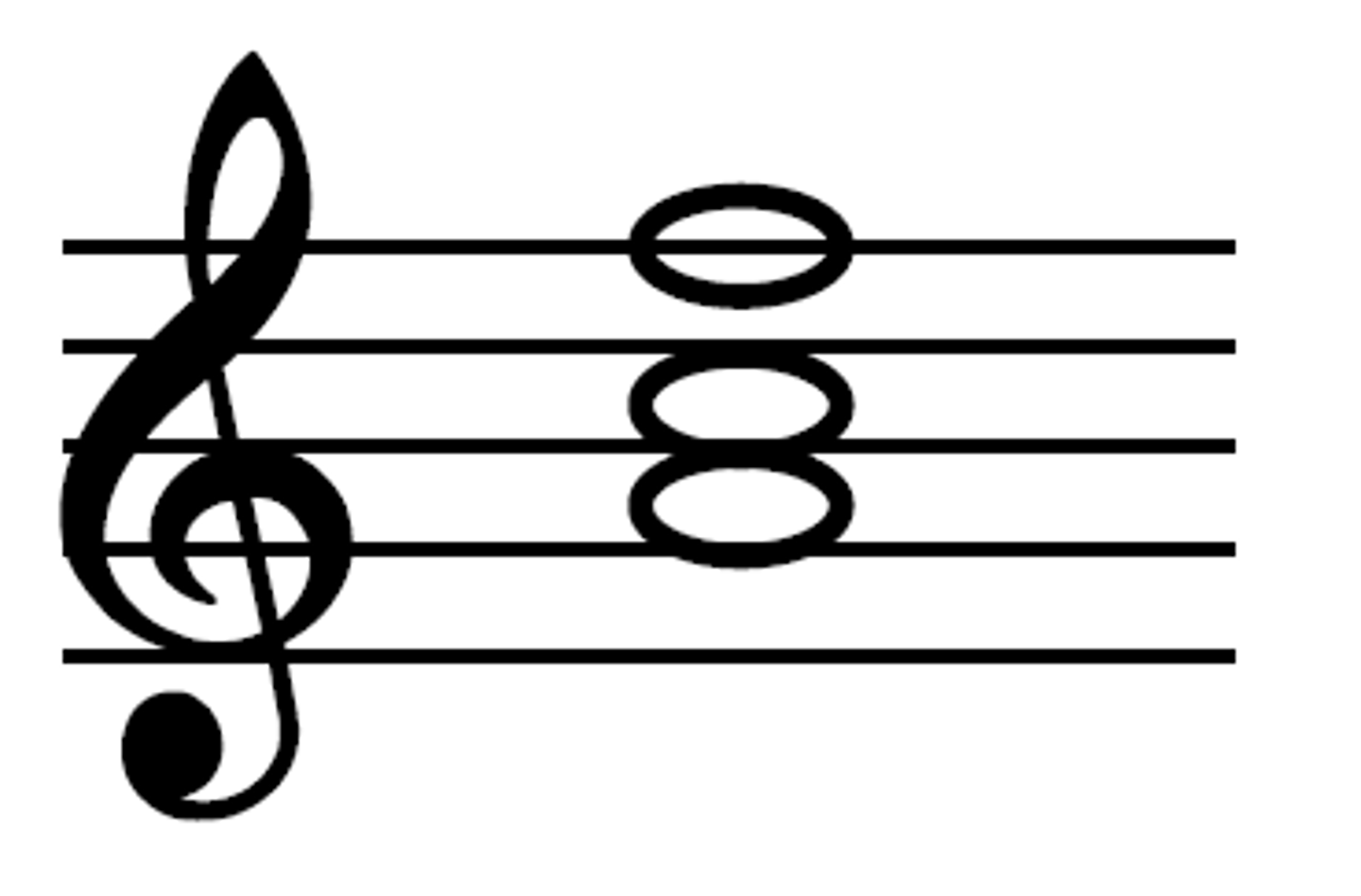
Soprano (voice)
The highest female voice
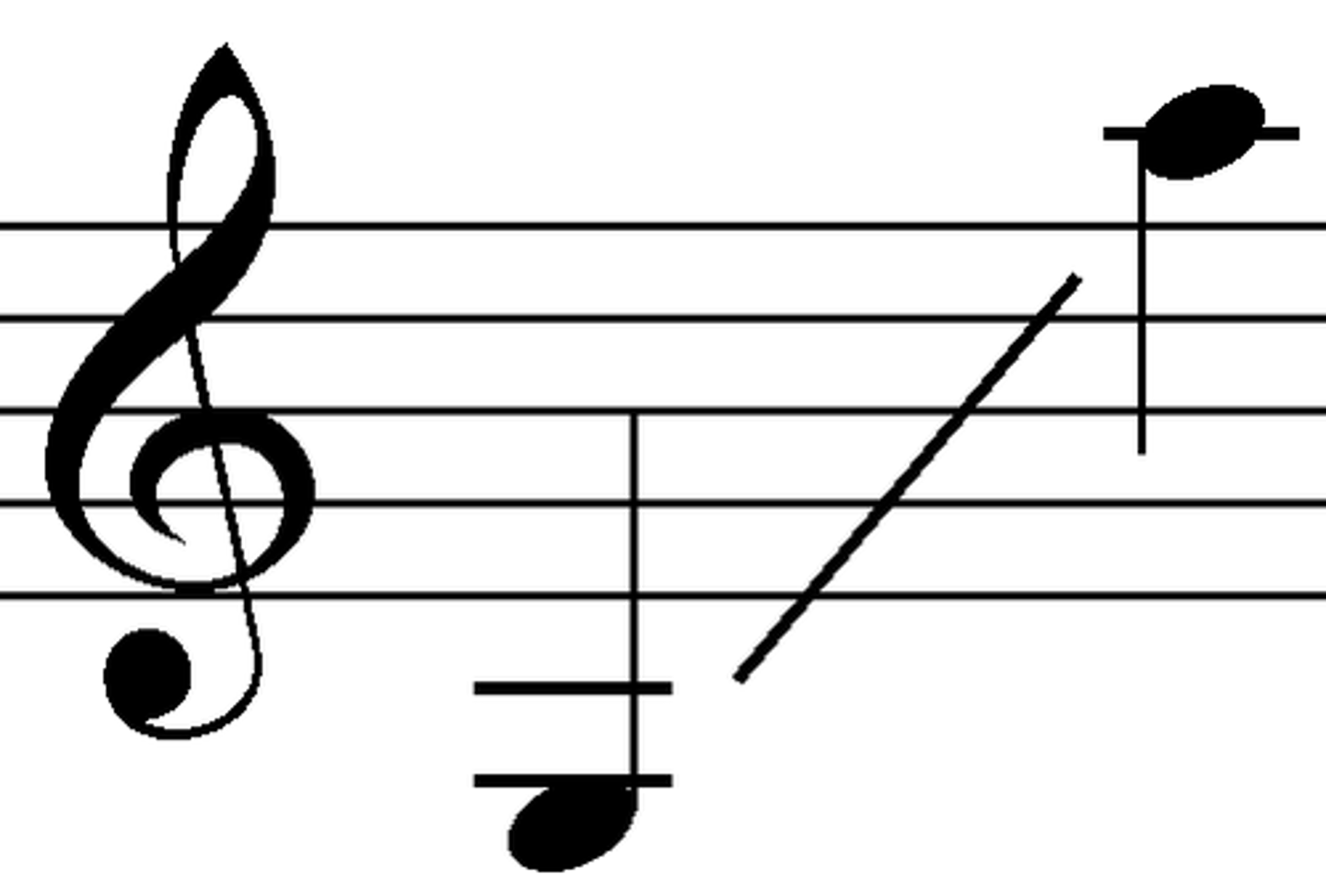
Tenor (voice)
Highest male voice

voice leading
How notes in a chord move to the following chord
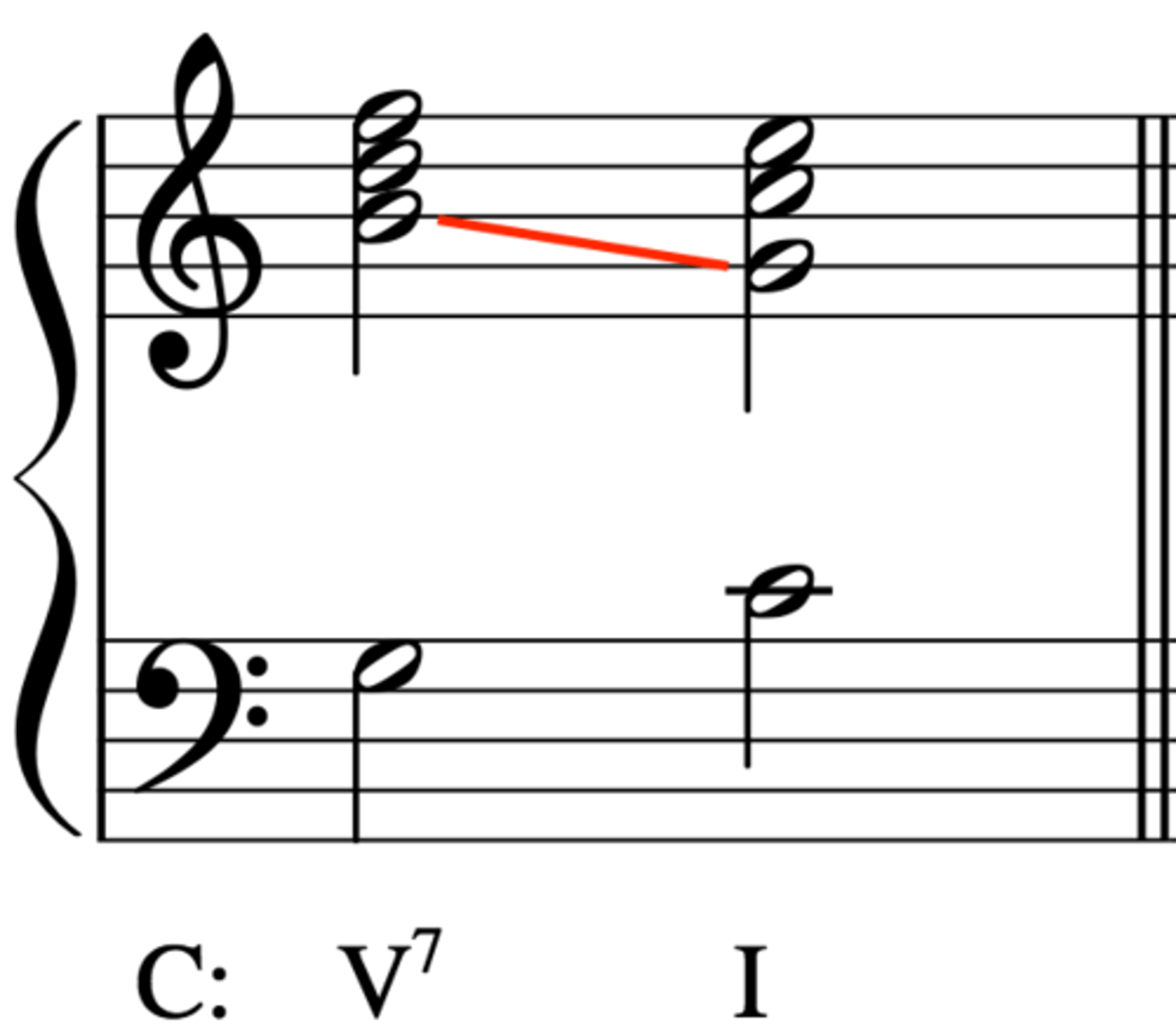
common tone
In a chord progression, a note which belongs to both chords
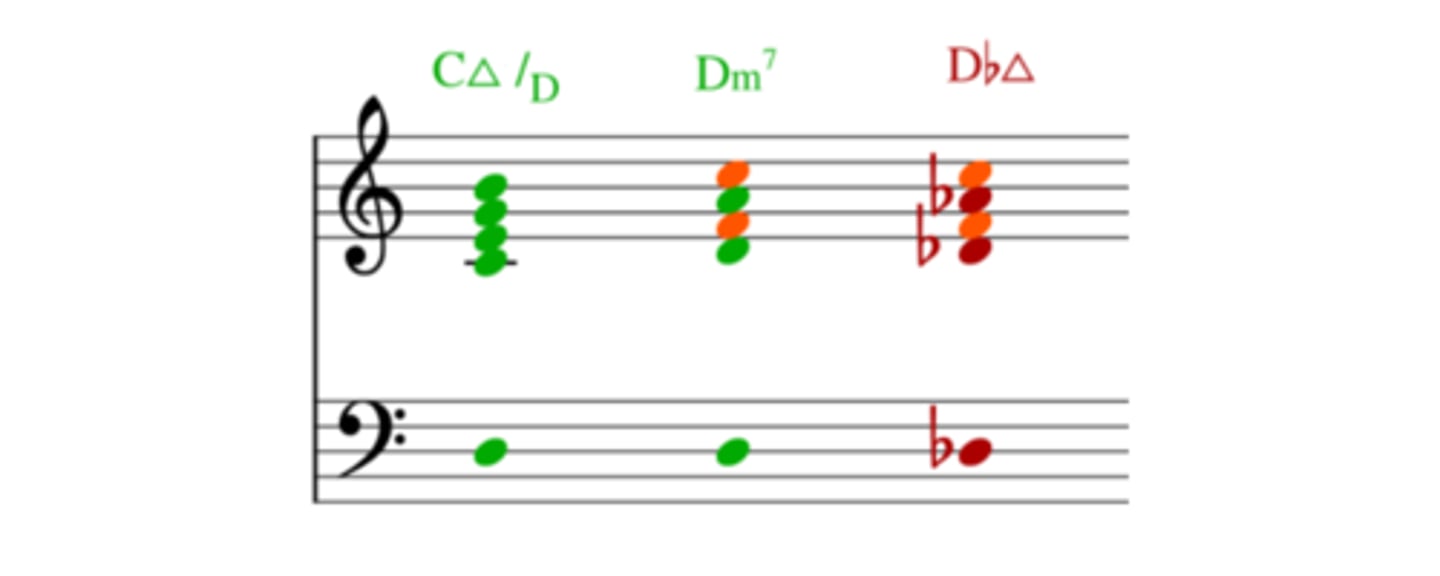
contrary motion
voices move in opposite directions

cross relation
When a note and a chromatically altered version of that same pitch (e.x F and F#, or C and C♭) appear in close succession or simultaneously in different voices or parts, creating a momentary contradiction.
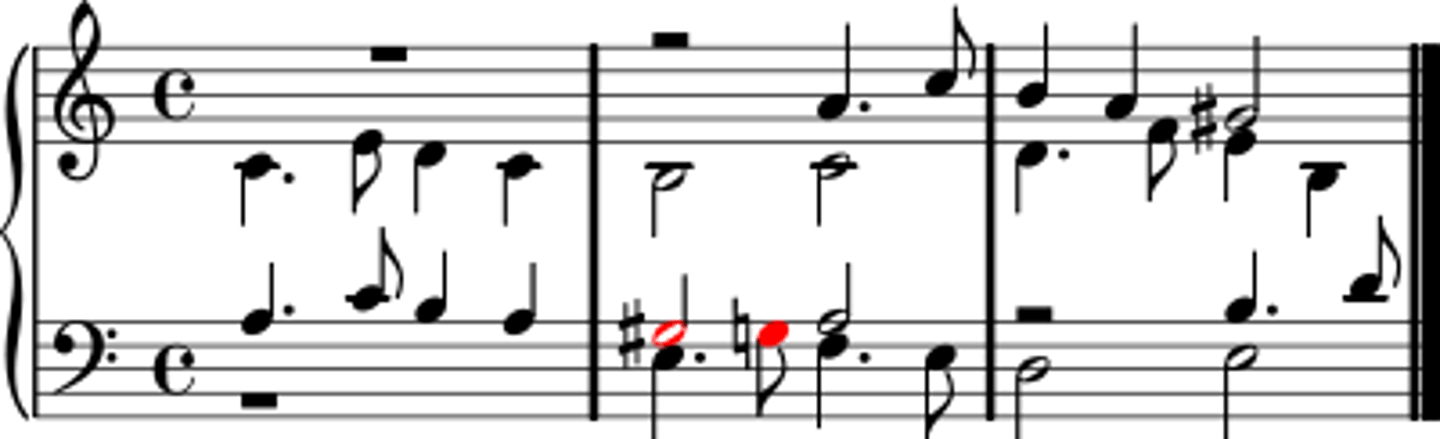
voice crossing
In four-part writing, one voice written higher than the part above it or lower than the part below it; considered poor voice-leading in common-practice SATB style.

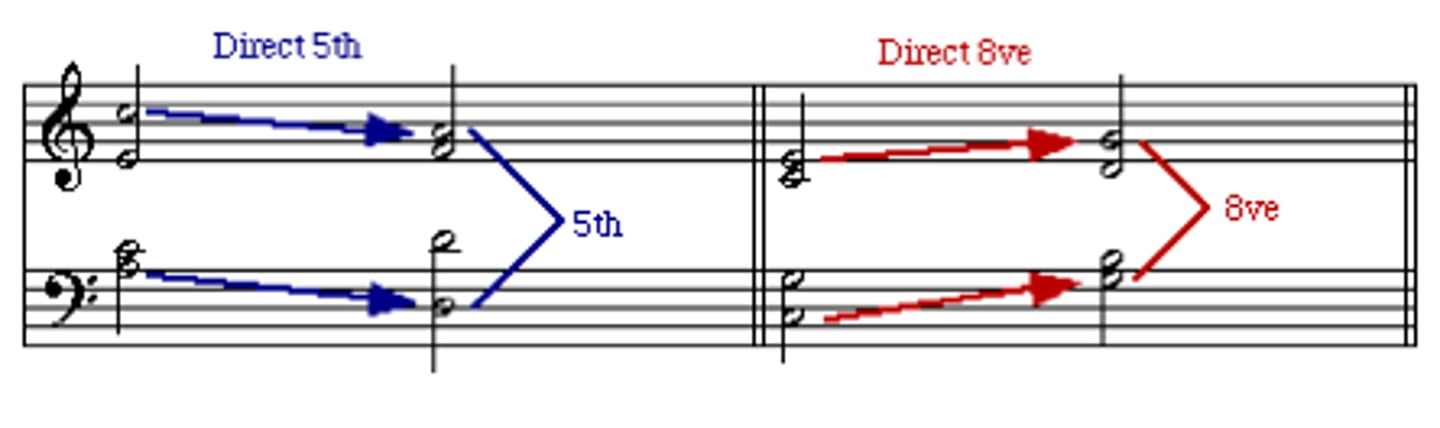
direct fifths (hidden fifths)
outer parts move in the same direction into a perfect fifth with a leap in the soprano
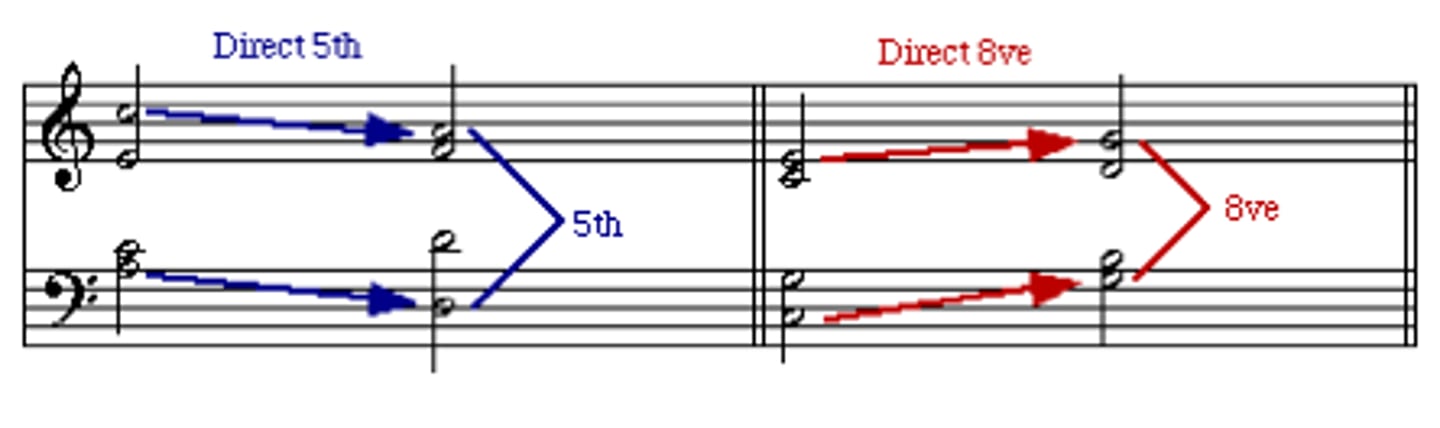
hidden fifths
Similar motion into a perfect interval, permitted only in inner voices or if the soprano moves by step.
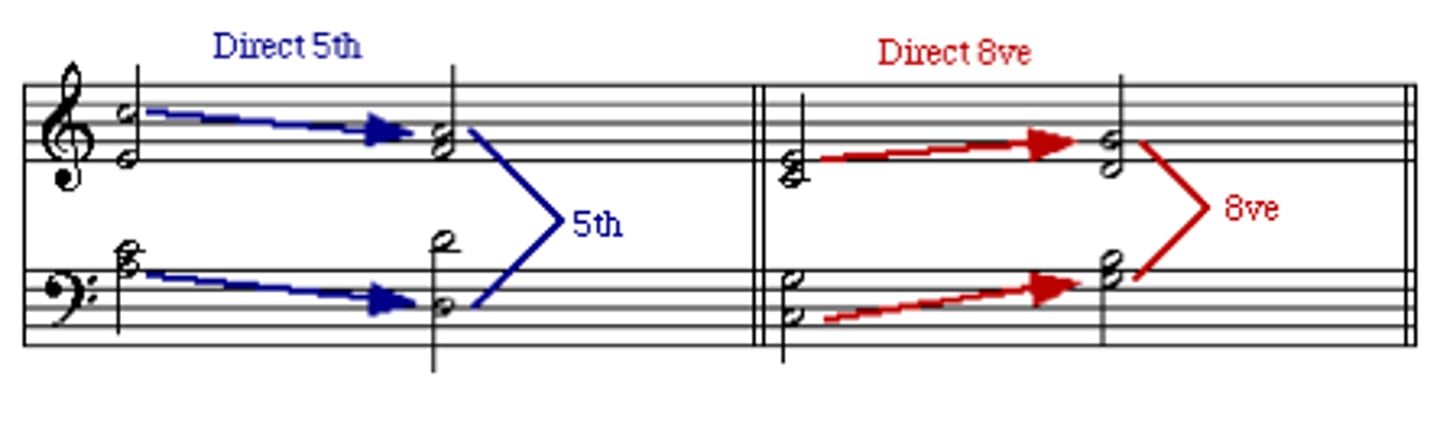
direct octaves (hidden octaves)
a voice-leading error where two parts move in the same direction (similar motion), the upper part leaps, and they end on a perfect octave, reducing voice independence and creating a hollow sound, especially in outer voices (bass/soprano)
Oblique motion
one voice stays the same, the other moves

overlapping voices
Part-writing error where one voice crosses above or below the previous note of another voice
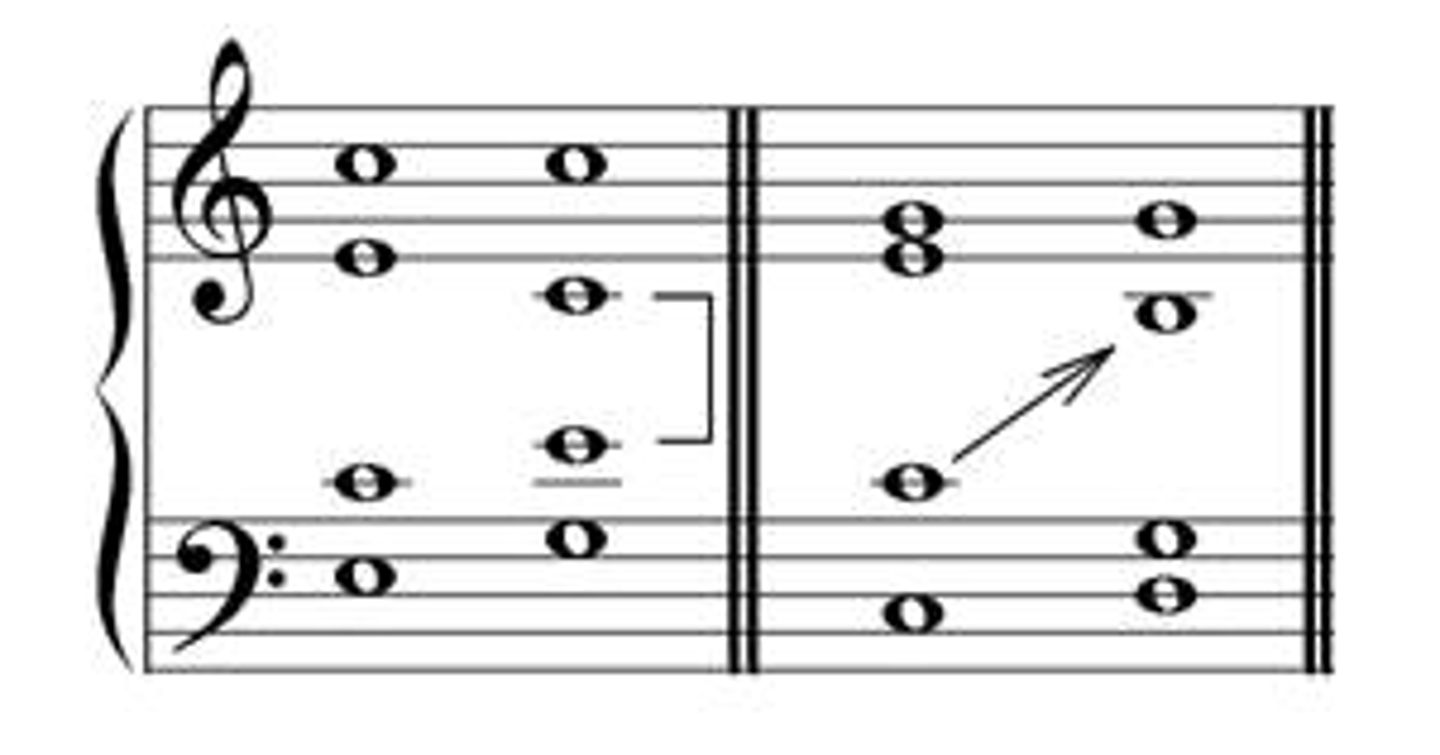
parallel motion
Voices move in the same direction by the same interval
parallel intervals
Two or more adjacent intervals made by parallel motion.
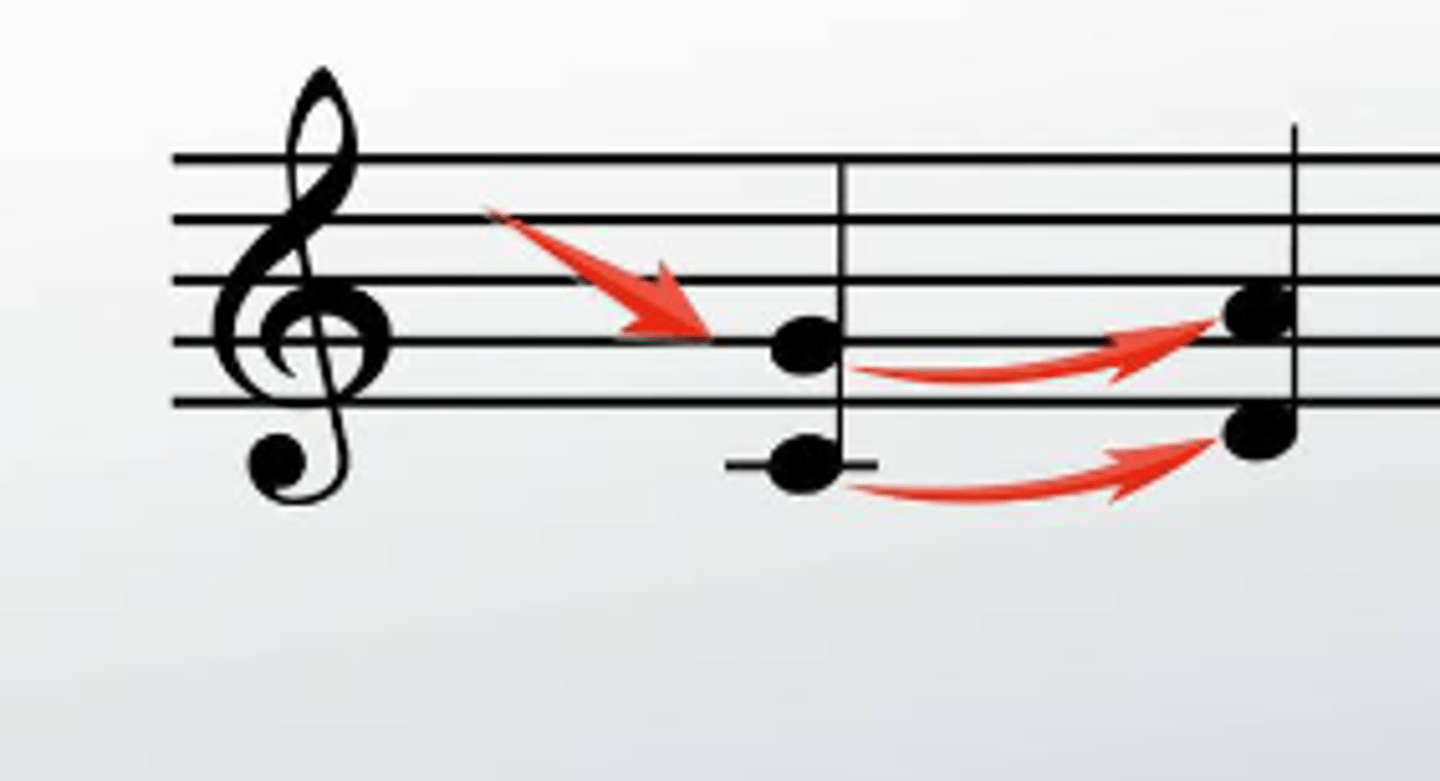
parallel fifths
Part-writing error where two voices that are a P5 above each other move to another P5
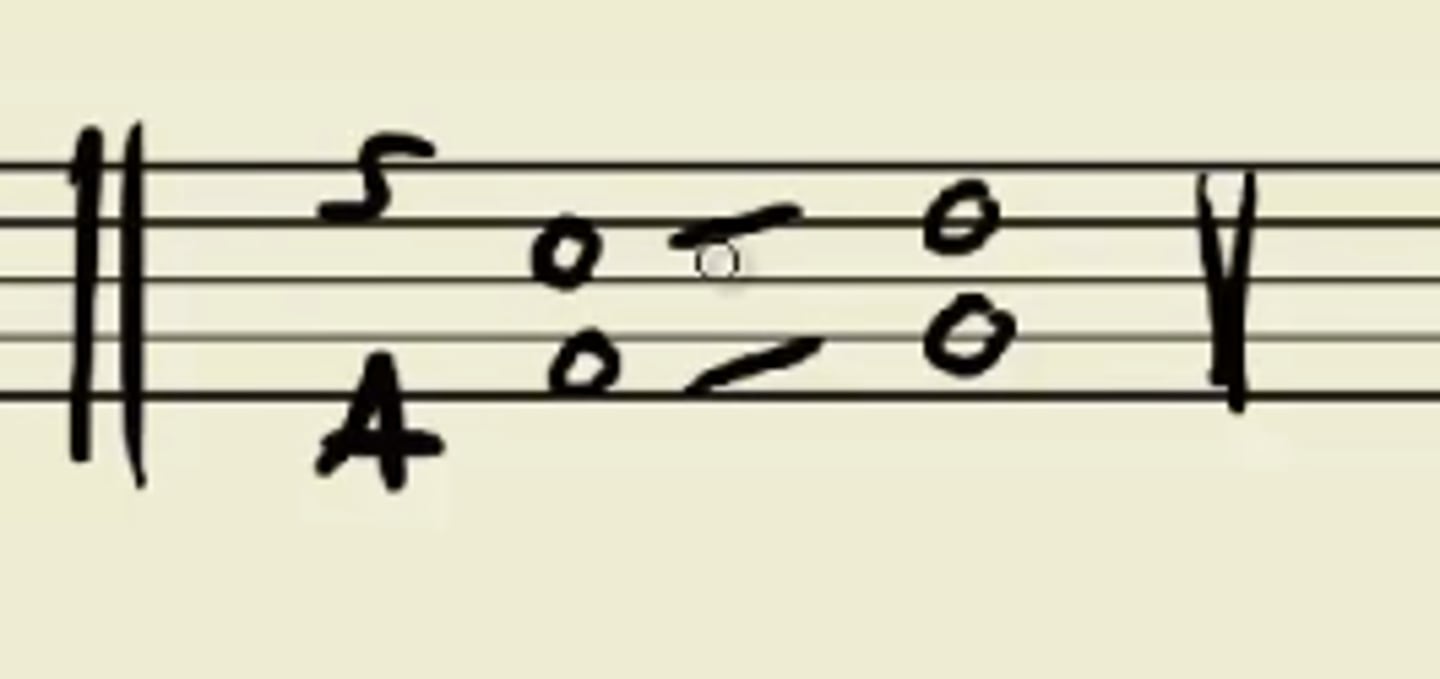

parallel octaves
Part-writing error where two voices that are a P8 above each other move to another P8
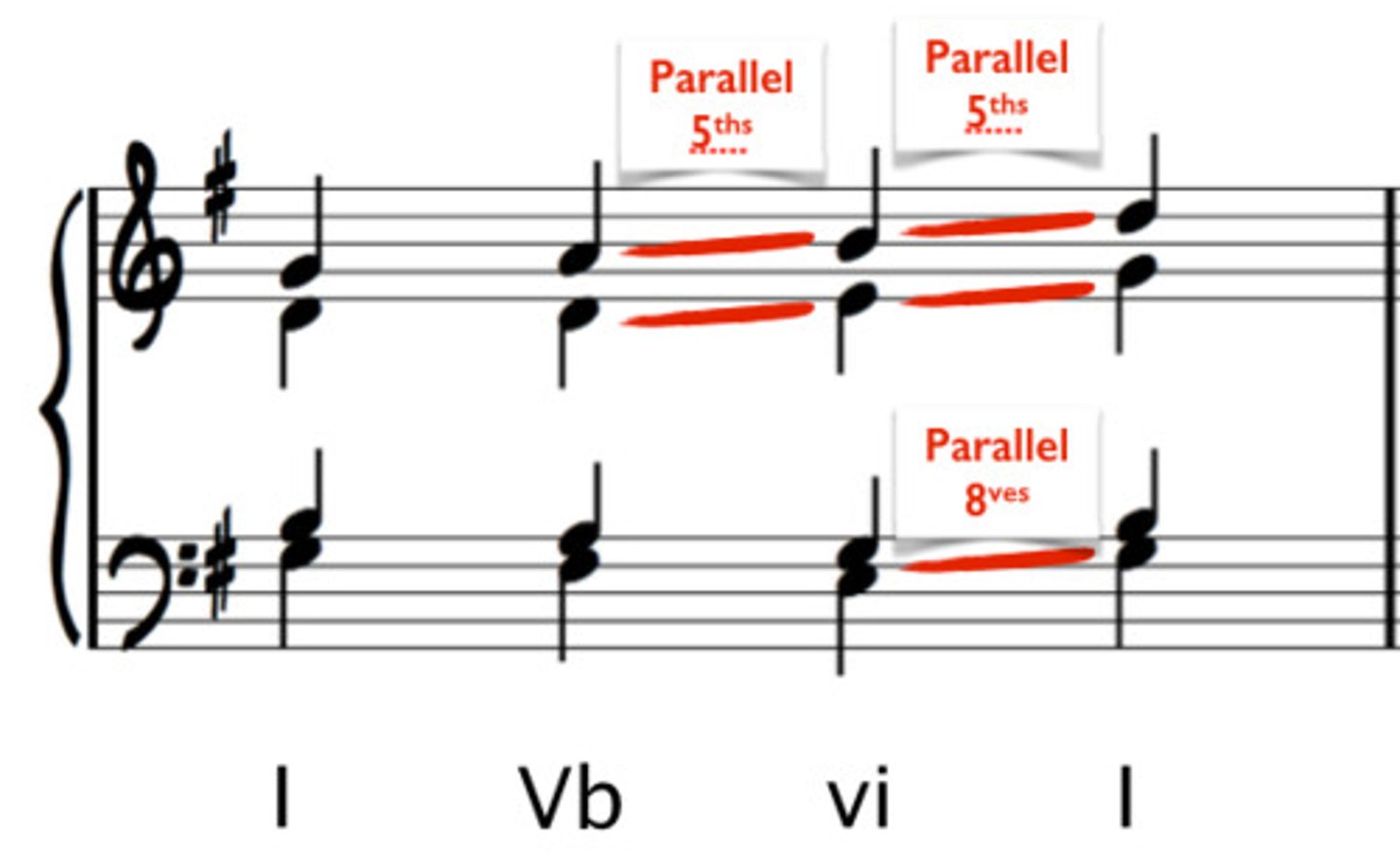
similar motion
both voices move in the same direction

Suspension
a harmonic device where a note from a previous chord is held over (suspended) into a new chord, creating temporary dissonance (a "clash") that resolves by stepping down
Cadence
a chord progression or melodic/rhythmic pattern that signals the end of a musical phrase, section, or piece
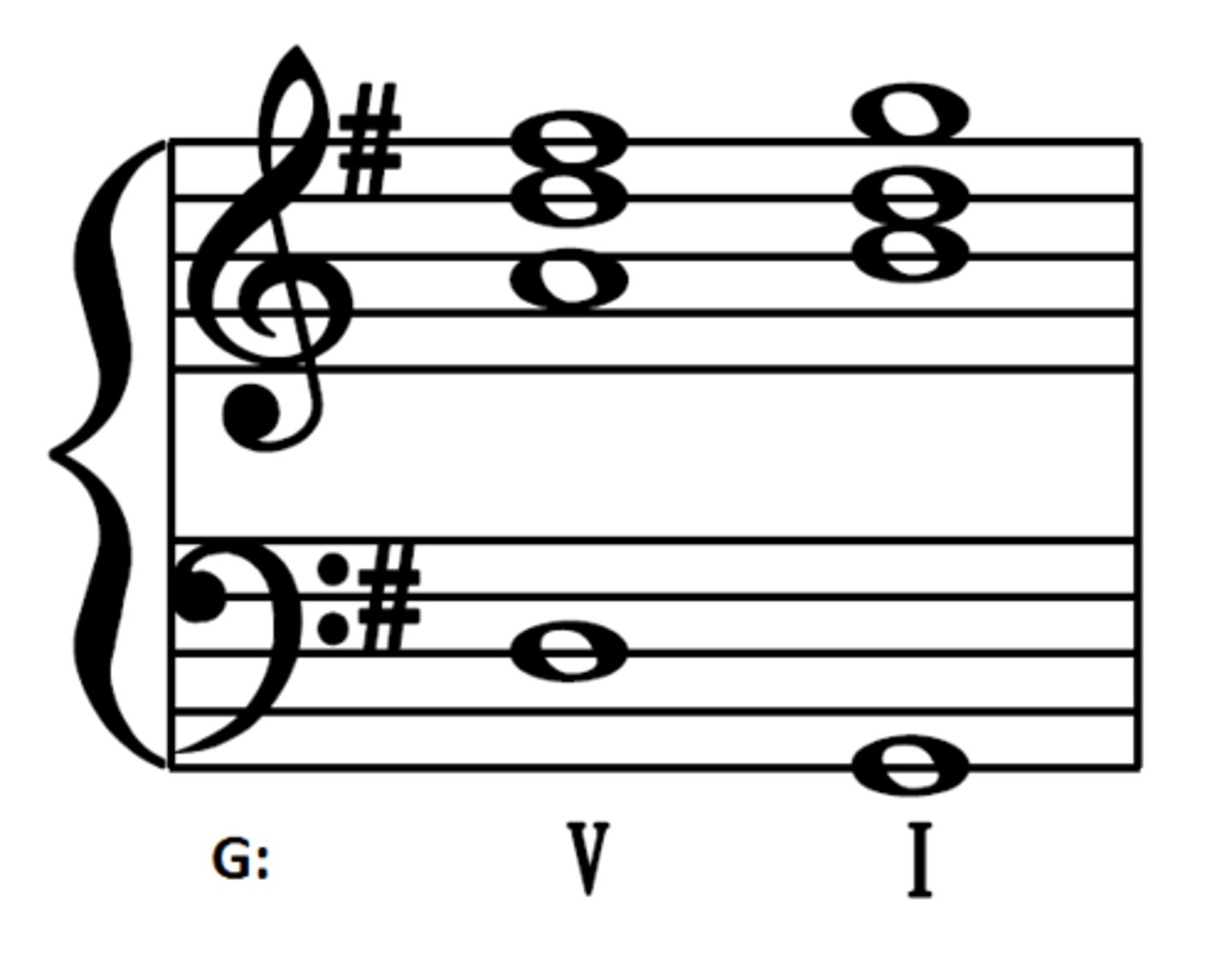
Perfect Authentic Cadence (PAC)
V to I; in root position; soprano ends on tonic
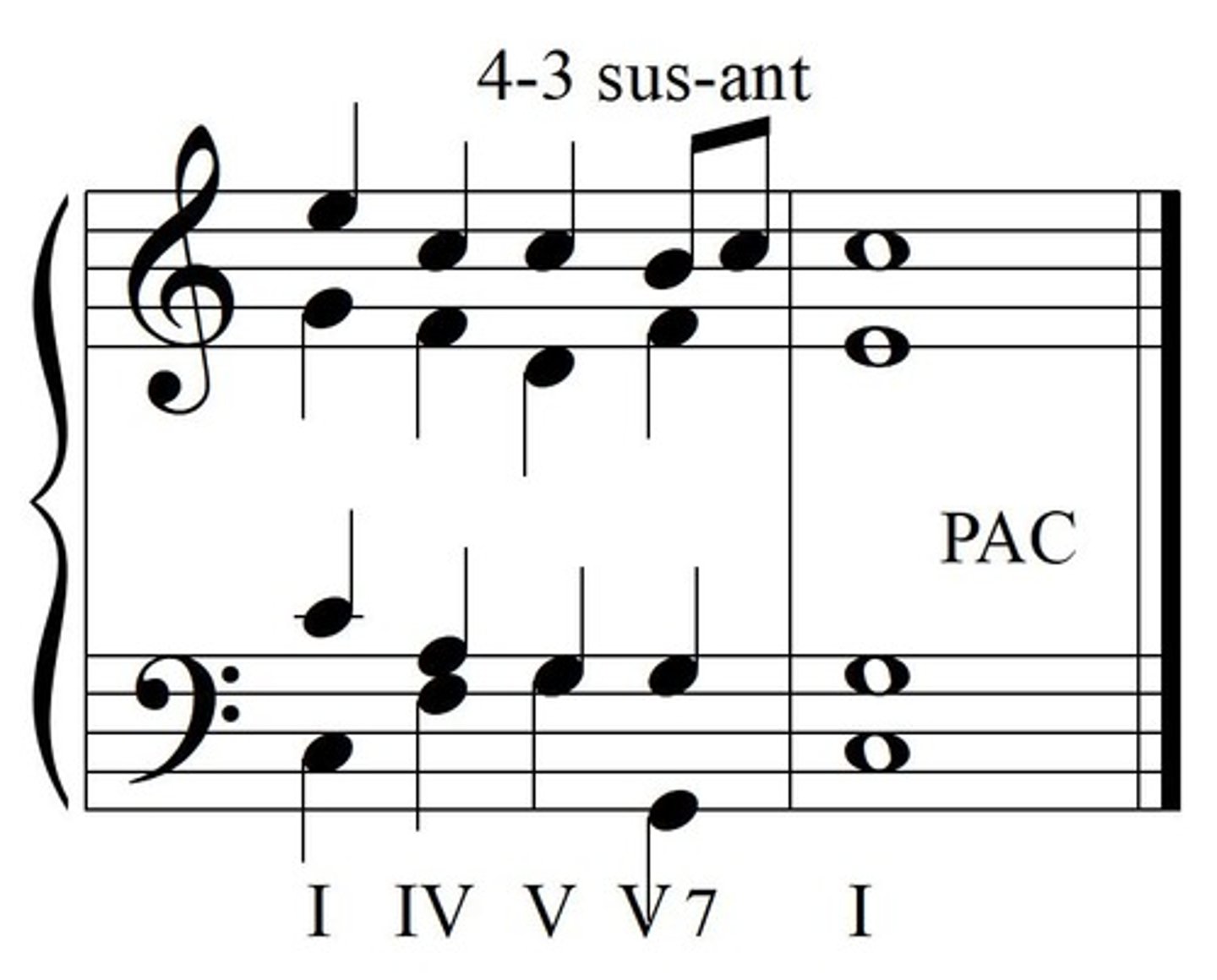
Imperfect Authentic Cadence (IAC)
V - I, but with either an inverted chord, or soprano not ending on the tonic.
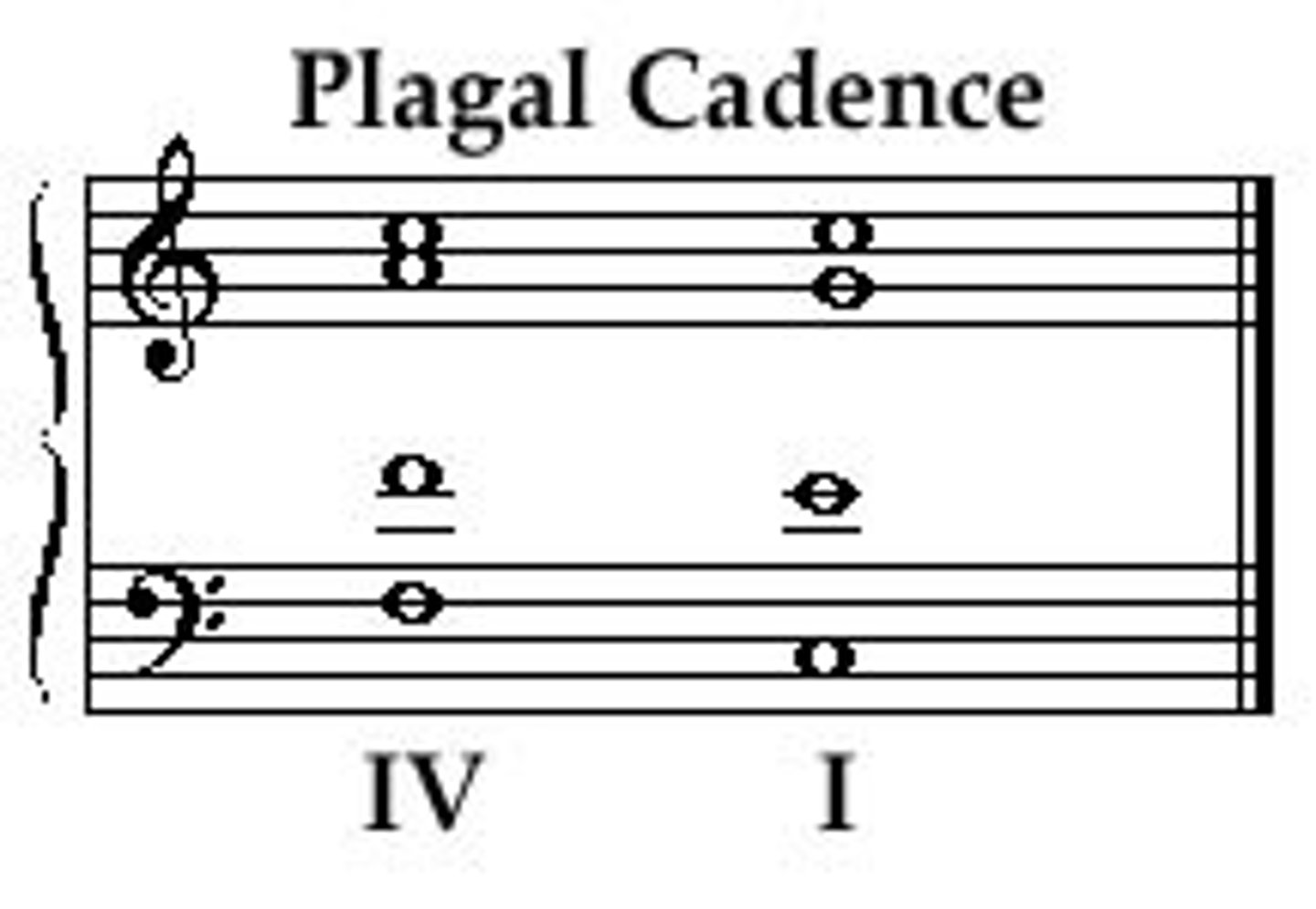
Plagal Cadence (PC)
A IV-I progression. Known as the "Amen" cadence.
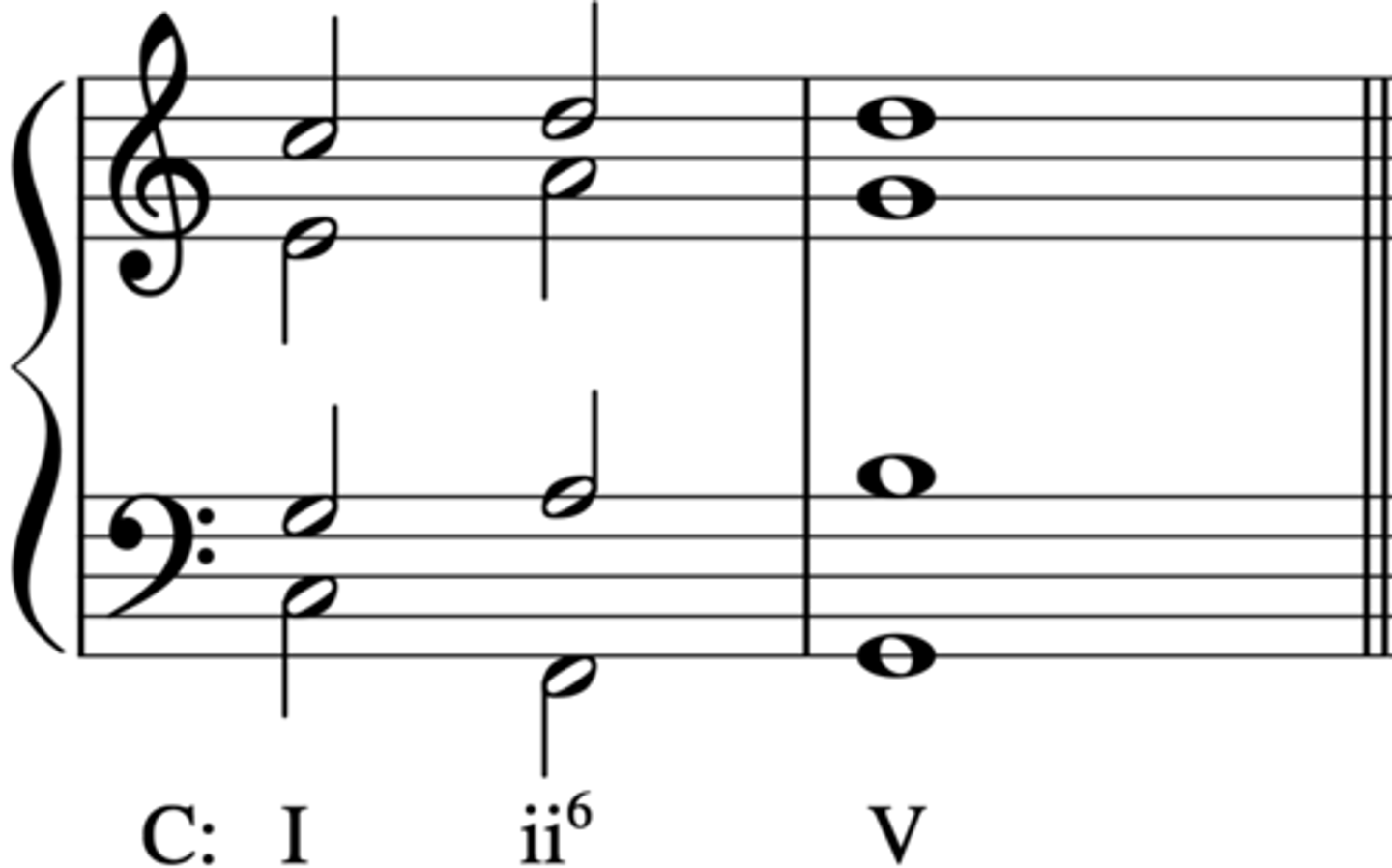
Half Cadence (HC)
a cadence that ends on V
Tendency Tones
Pitches that have strong inclination to move in a specific direction.
re-do
fa-mi
la-sol
ti-do
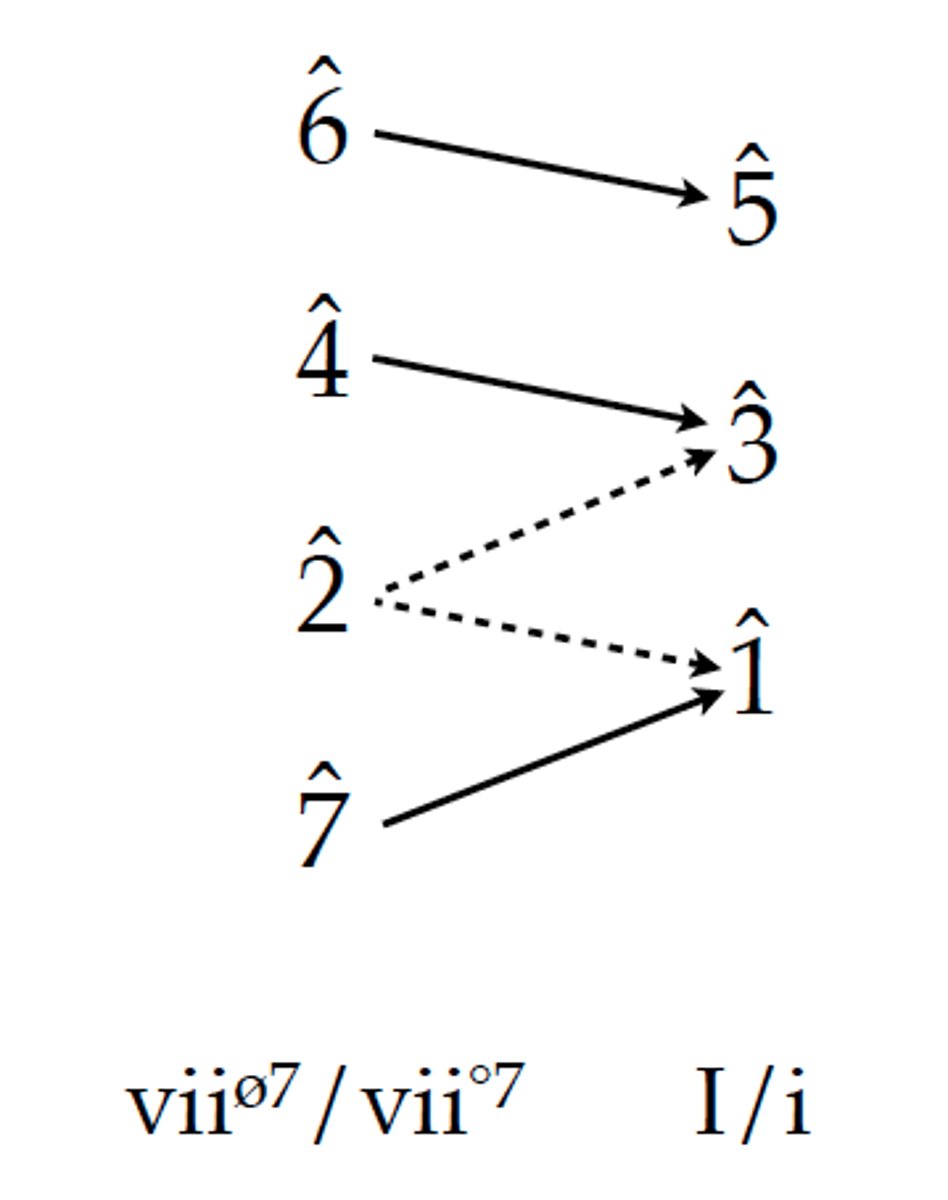
unresolved leading tone
Instead of moving to the tonic, the note stays put, moves elsewhere (like down a step), or the piece ends before it resolves, leaving that tension lingering.
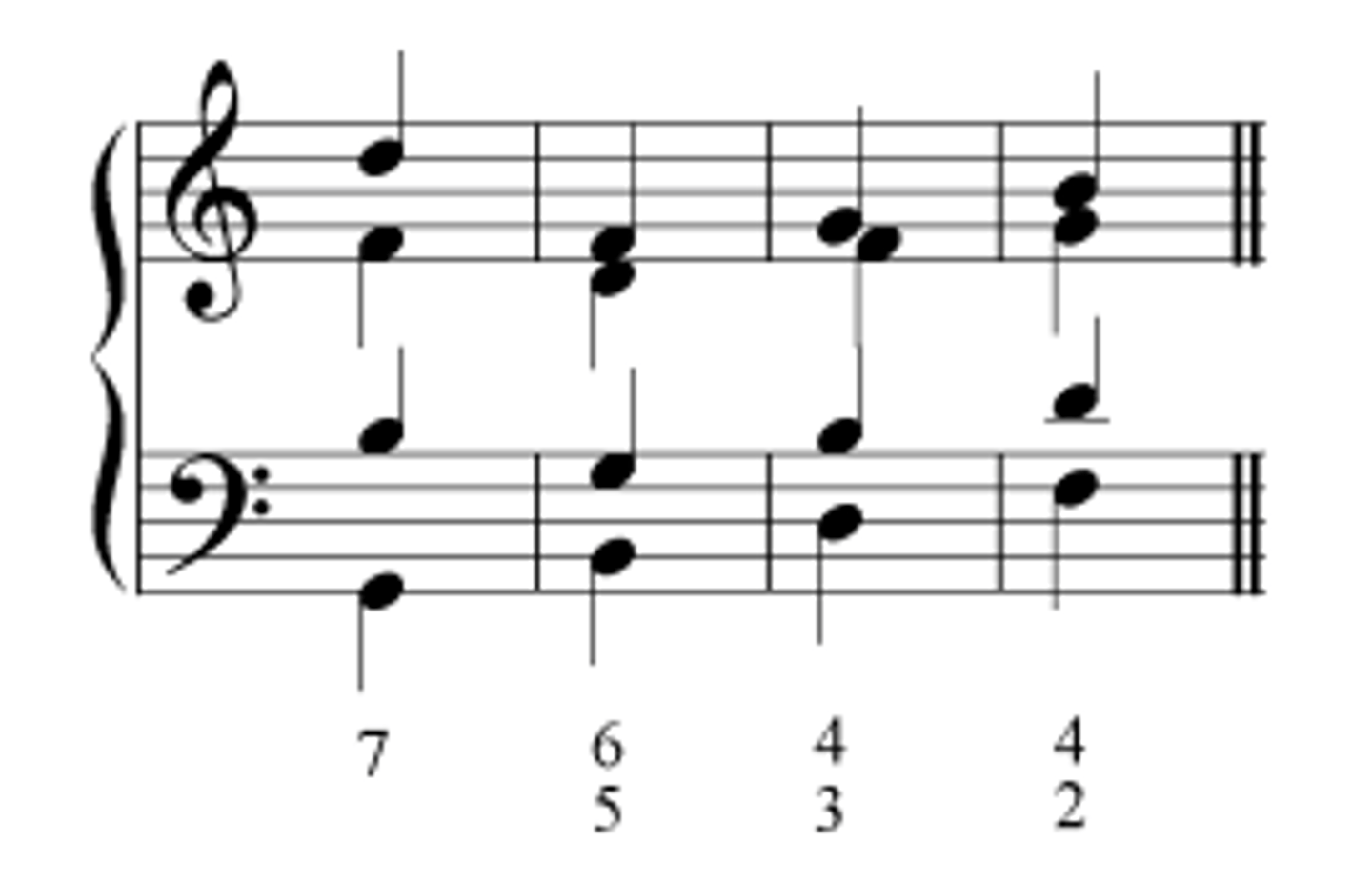
figured bass
in musical notation, a numerical shorthand that tells the player which unwritten notes to fill in above the written bass note

conjunct
describes melodic motion that moves by small, stepwise intervals (like a half or whole step), creating smooth, connected lines
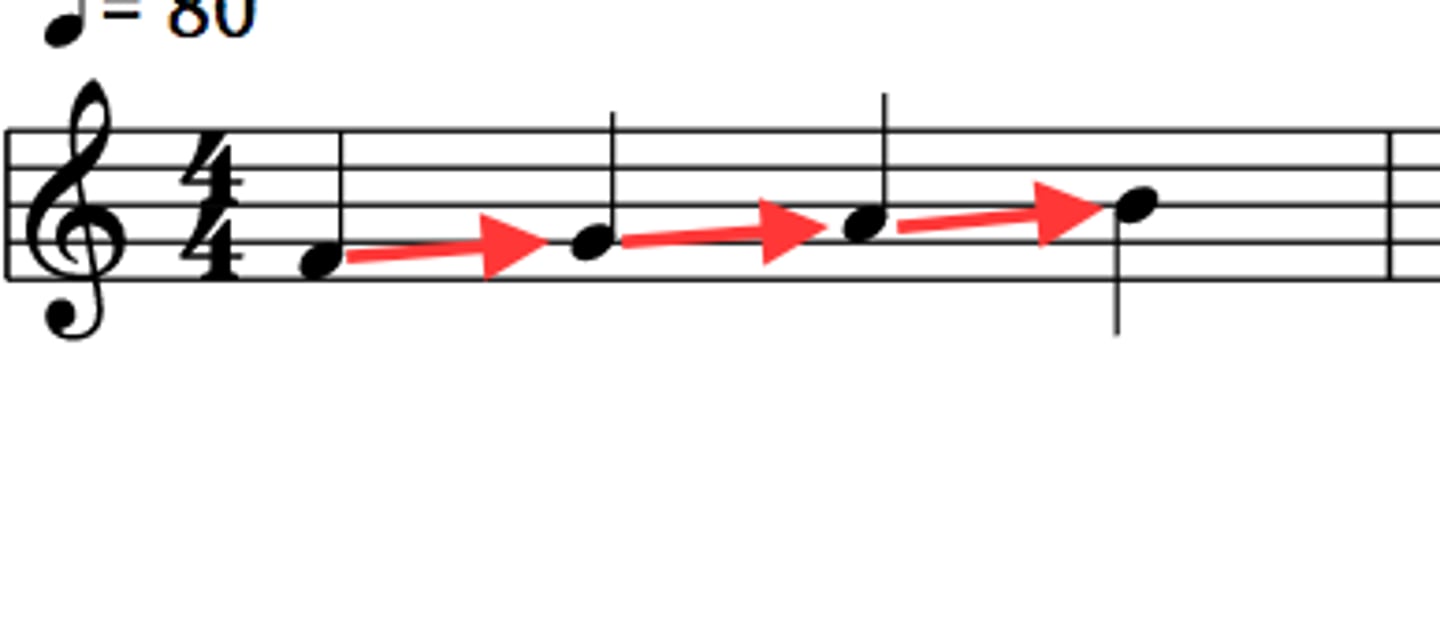

disjunct
describes a melody that moves by leaps and large intervals (larger than a whole step), creating a "jumpy" or exciting contour
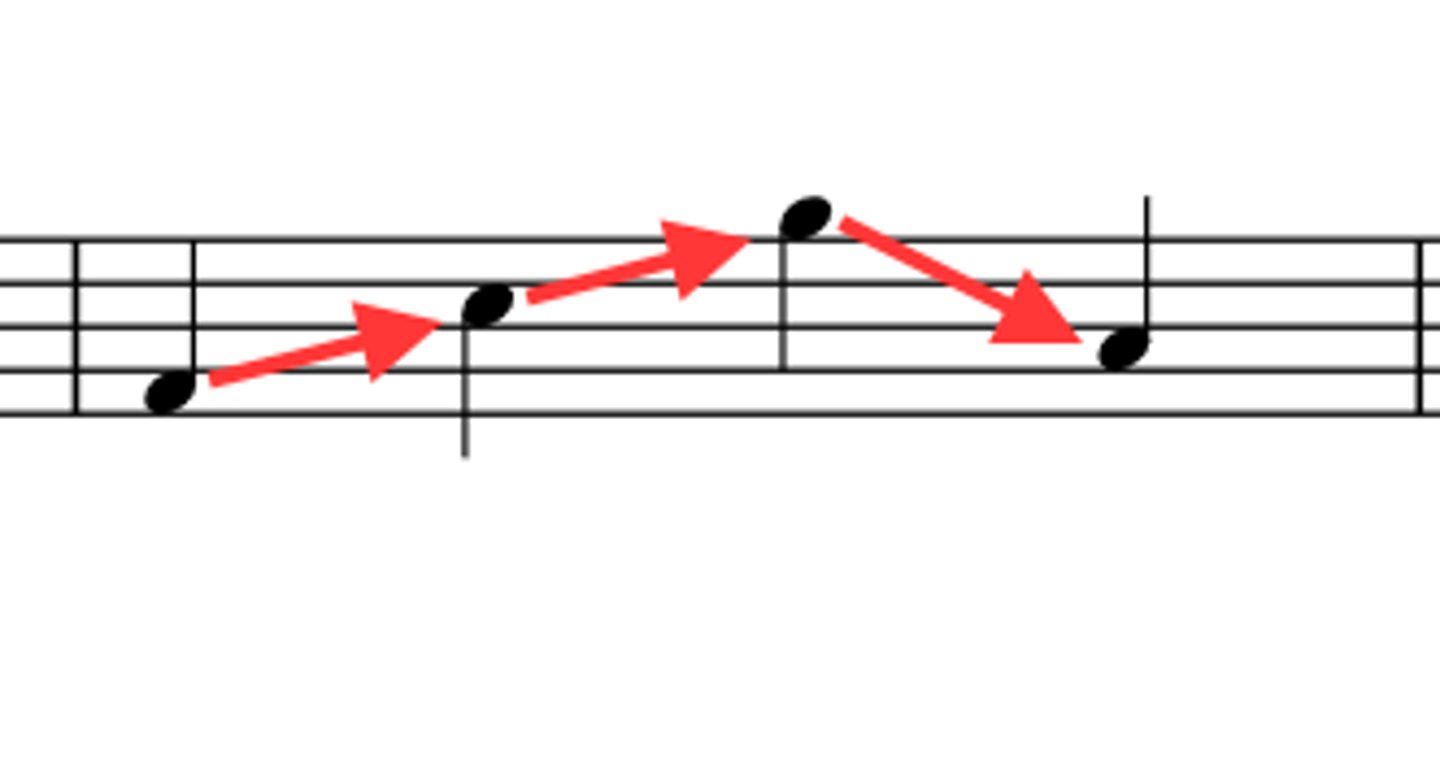

Retrogression
means moving backward harmonically, away from the tonic (like V-IV or IV-I), creating tension
Resolution
movement from a dissonant sound to a consonant (stable) sound. Often from the dominant (V) chord to the tonic (I) chord, creating a sense of arrival and finality
Tendency Tone
scale degrees that create tension and have a strong "pull" to resolve to a more stable pitch. Usually the tonic of the key
Anticipation
non-chord tone that arrives early, usually on a weak beat, as a preview of a note that will become a chord tone in the next harmony
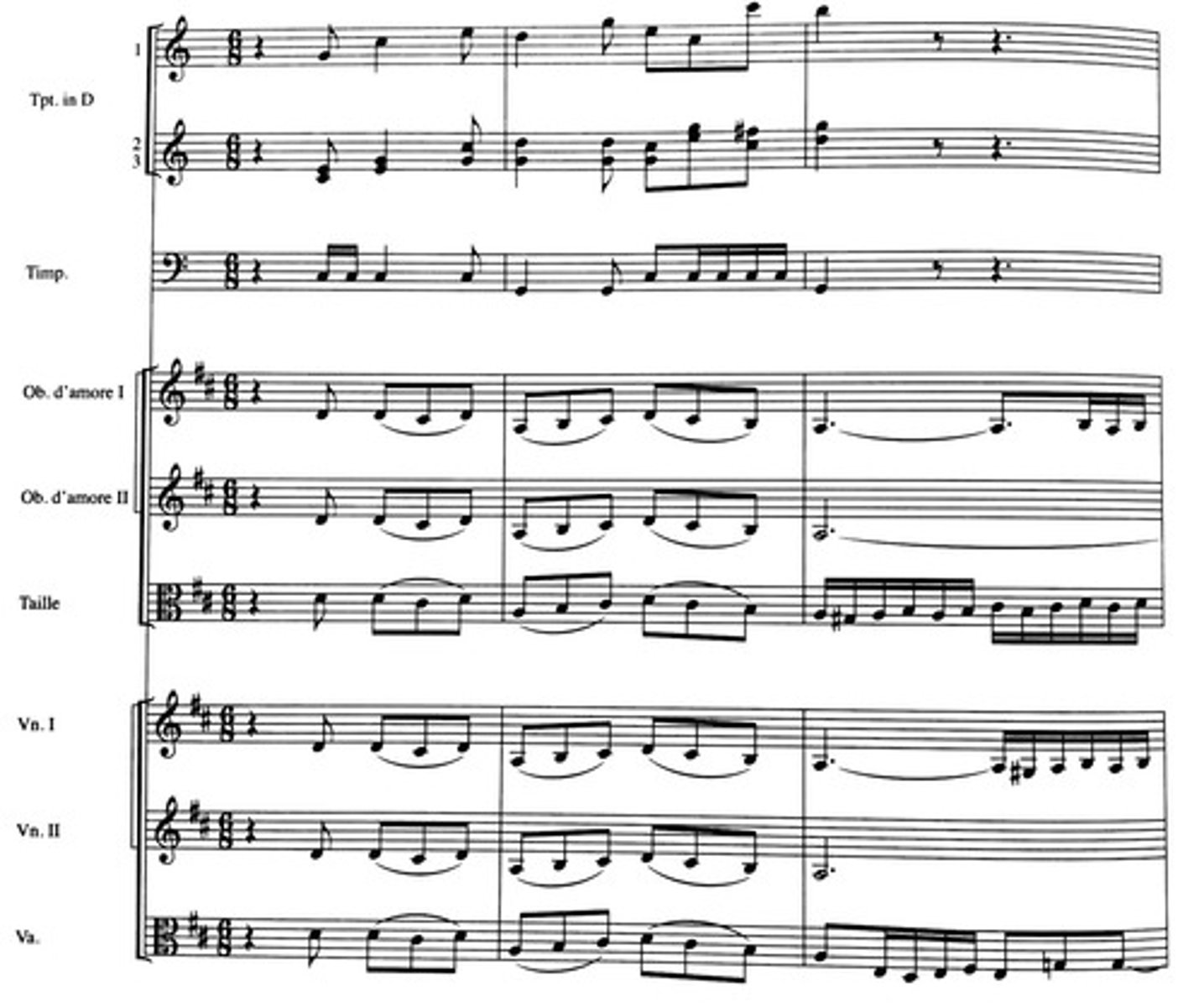
compound melody
A melody created by the interaction of two or three voices, usually separated by register. Often features large leaps.

Double neighbor tone
When a chord tone is decorated by both an upper and a lower neighbor tone before returning to the original chord tone
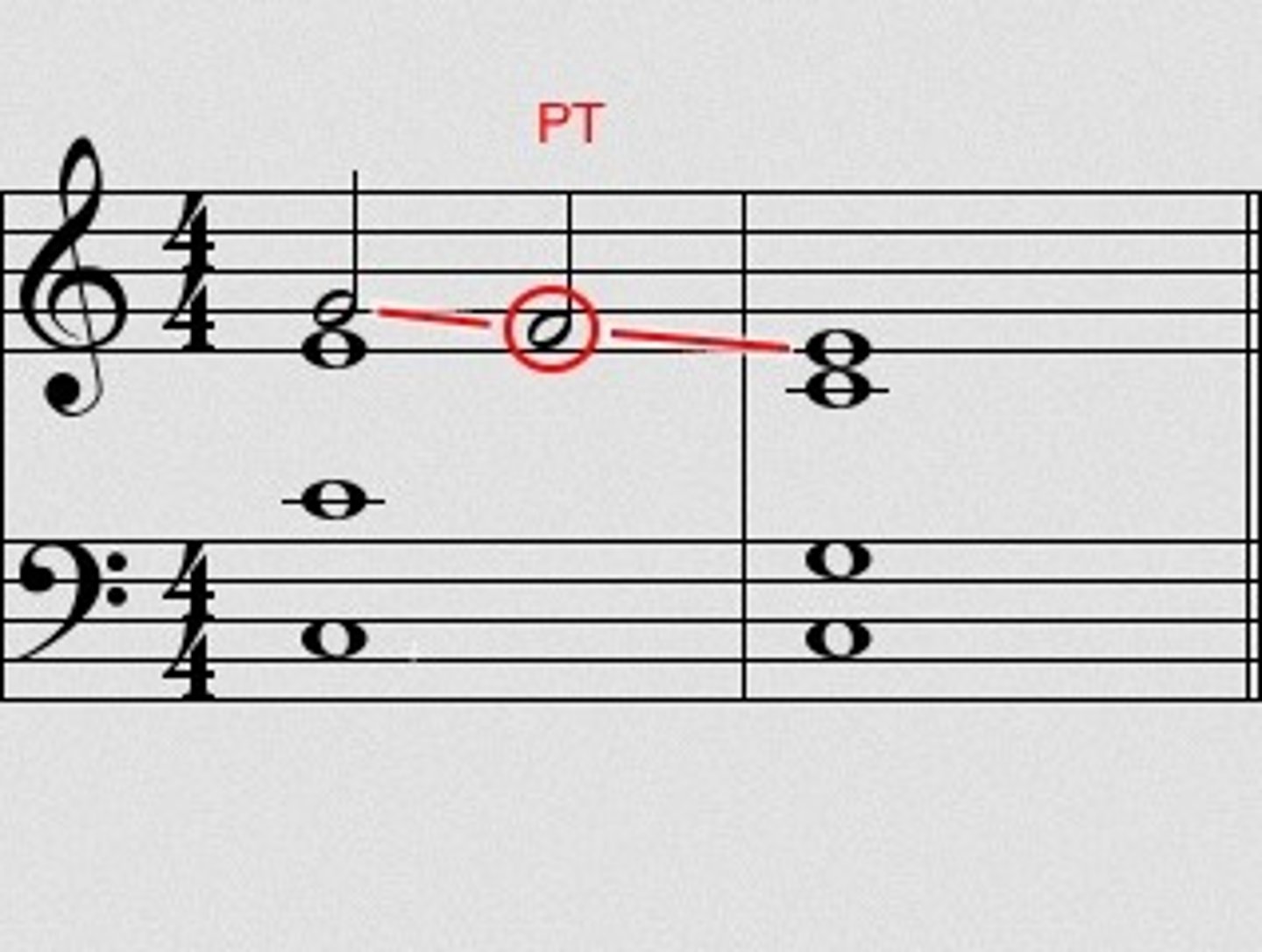
Passing Tone (PT)
Approached by step and then continues by step in the same direction
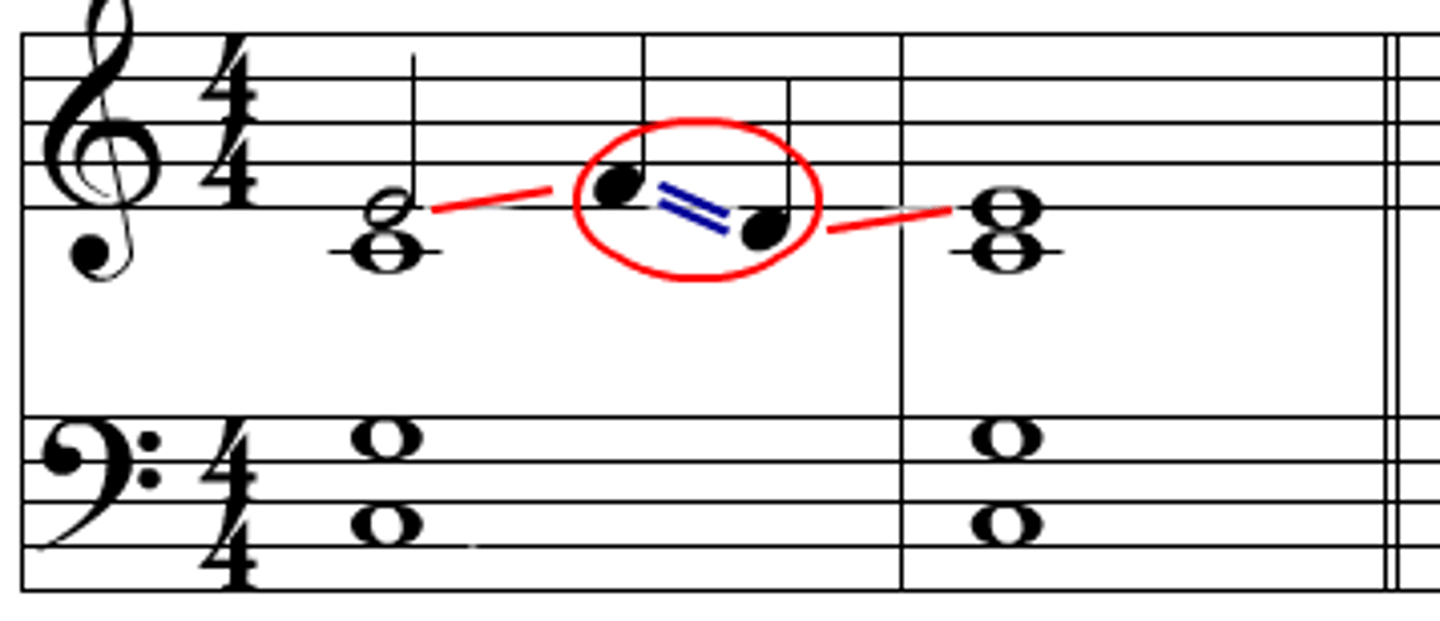
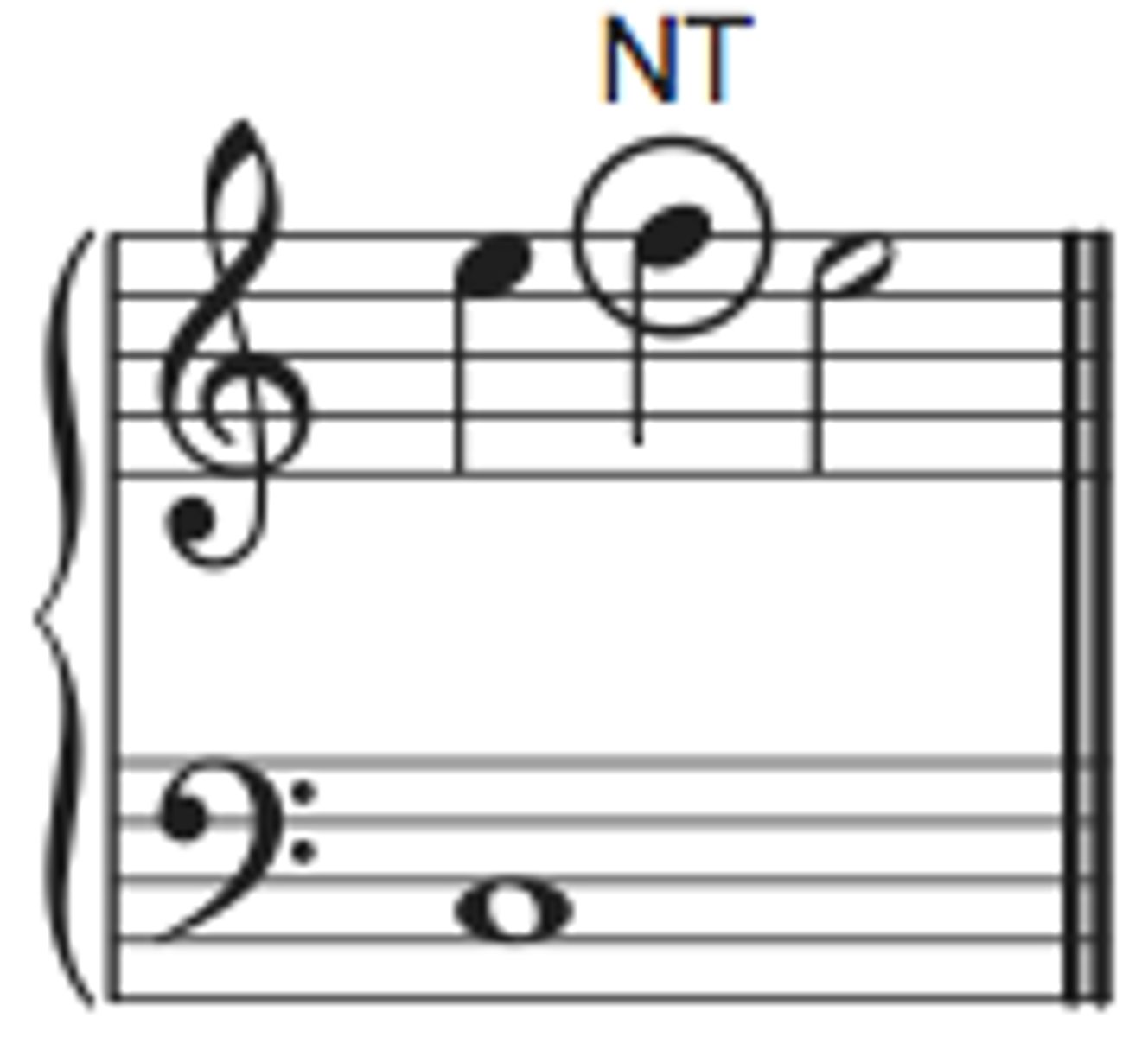
Neighbor Tone
a non-chord tone that decorates a melody by moving one step (half or whole) from a chord tone to an adjacent note (upper or lower neighbor) and then stepping back to the original chord tone, creating a temporary melodic embellishment that adds movement and interest

Pedal Point
a sustained note over which harmonies change
