BIO
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Viruses
⭐ Acellular → not cells
No metabolism, cannot grow
Must use a host cell to replicate
Ultimate parasite → uses host machinery
Origin uncertain; may be pieces of nucleic acid collected from other sources
Can infect almost all life forms, often species- and tissue-specific
1892: Tobacco mosaic virus
→ filtered plant extract still caused disease → smaller than bacteria ⭐
1930s: Electron microscope (EM)
makes viruses visible
Most viruses too small for light microscope (~20 nm)
EM magnification: 500,000x, resolution ~0.05 nm ⭐
Virus Evolution Hypotheses
Devolution: from free-living cells
Escape: nucleic acids escaped from cells
Self-replicating molecules: started as independent RNA/DNA
Devolution
from free-living cells
Escape
nucleic acids escaped from cells
Self-replicating molecules
started as independent RNA/DNA
Virus Structure
Core: DNA or RNA (⭐ one type only)
Single or double-stranded
Circular or linear
One piece or segmented
Protein capsid → protects genome ⭐
Envelope (optional) → similar to cell membrane
Shapes: helical, polyhedral, complex ⭐
Core
DNA or RNA (⭐ one type only)
Single or double-stranded
Circular or linear
One piece or segmented
Protein capsid
→ protects genome
Envelope (optional)
→ similar to cell membrane
Shapes
helical, polyhedral, complex ⭐
Bacteriophage T4
Host | Features | Most Tested |
Bacteria (E. coli) | DNA genome, tail fibers attach to host | DNA virus, bacteriophage |
Adenovirus
Human respiratory tract | Non-enveloped, spikes on capsid | Non-enveloped virus |
⭐HIV (Retrovirus)
Humans | RNA → DNA via reverse transcription, enveloped | Retrovirus, envelope |
Virus Genome Notes
DNA → host makes new viruses
RNA → can be directly transcribed or replicated first
RNA viruses mutate faster → more errors ⭐
Virus Classification (4 main ways)
Nucleic acid type & function ⭐
Capsid structure ⭐
Enveloped or non-enveloped ⭐
Genome structure (linear, circular, segmented)
Baltimore classification
based on type of nucleic acid + how it makes mRNA
First virus discovered
→ Tobacco mosaic virus ⭐
Virus vs cell: name 3 differences
→ acellular, no metabolism, needs host ⭐
Bacteriophage T4 infects?
→ E. coli ⭐
HIV unique feature?
→ RNA → DNA (retrovirus), envelope ⭐
RNA viruses mutate faster because…
→ replication enzymes make more errors ⭐
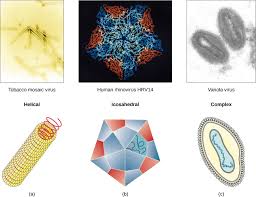
Capsid shapes?
→ helical, polyhedral, complex ⭐
Enveloped vs non-enveloped virus example?
→ Envelope: HIV; Non-envelope: Adenovirus ⭐
Virus genome can be…
→ DNA or RNA, single/double-stranded, circular/linear, segmented ⭐
Three virus origin hypotheses?
→ Devolution, Escape, Self-replicating ⭐
Virus Classification by Genome (Core)
Viruses are classified by genetic material (DNA/RNA), strands, shape, and segments:
Core Type | Strand | Shape | Segments | Examples |
DNA | ss | Linear | Non-segmented | Herpesvirus, smallpox |
DNA | ds | Circular | Non-segmented | Papillomavirus, many bacteriophages |
RNA | ss | Linear | Non-segmented | Rabies, retroviruses |
RNA | ss | Linear | Segmented | Influenza |
RNA | ds | Linear | Non-segmented | Parainfluenza |
⭐ Most Tested
Rabies = ssRNA, enveloped helical;
Smallpox = dsDNA, complex;
Influenza = segmented ssRNA
Icosahedral (20 faces)
Polio virus (naked)
Epstein-Barr virus (enveloped)
Helical
Tobacco mosaic virus (naked)
Mumps virus (enveloped)
Complex
Herpesvirus
Bacteriophage T4
Tip: Capsid + genome type =
most common exam Q
Virus Effects on Cells (Cytopathic Effects)
Viruses can damage host cells:
Lysis → Cell bursts ⭐
Apoptosis → Programmed cell death
Immune response → Symptoms
Budding → Virus leaves without killing cell
Lysis
→ Cell bursts ⭐
Apoptosis
→ Programmed cell death
Immune response
→ Symptoms
Budding
→ Virus leaves without killing cell
Steps of Virus Infection
Attachment
Entry
Replication and Assembly
Egress (Release)
Attachment
Virus binds host cell receptors
Very specific to species/tissue ⭐
Entry
Bacteriophages → DNA injected directly
Eukaryotic viruses → Endocytosis or membrane fusion if enveloped
Replication & Assembly
Virus Type
Process
DNA
Make mRNA → viral proteins; duplicate DNA → new genomes
RNA
Make complementary RNA if needed; transcribe mRNA → proteins; copy RNA → new genomes
RNA retrovirus
Reverse transcribe RNA → DNA → integrate into host; host makes viral proteins/genomes
Egress (Release)
Lysis → kills host
Budding → host survives
Most Tested
Influenza cycle: glycoproteins attach → engulfed → RNA/proteins made → new virions
Bacteriophages (Phages)
Viruses that infect bacteria
Tail fibers inject DNA into host
Have two cycles
Lytic cycle
Virus replicates → cell bursts
Lysogenic cycle
Viral DNA integrates → replicates with host; stress triggers lytic cycle ⭐
Rabies virus has which genome type?
ssRNA, enveloped helical ⭐
Smallpox virus capsid type?
dsDNA, complex ⭐
Steps of viral infection?
Attachment → Entry → Replication/Assembly → Egress ⭐
Latent
Virus hides in tissue; may reactivate | Herpes simplex, Varicella-zoster (chickenpox → shingles) ⭐ |
Oncogenesis
Can cause cancer | Hepatitis B & C, HPV ⭐ |
Varicella-Zoster Virus (Chickenpox/Shingles)
Childhood → chickenpox → latent in nerves → may reactivate → shingles
dsDNA, enveloped, icosahedral capsid
HPV (Human Papillomavirus)
Naked icosahedral capsid, dsDNA
Sexually transmitted → can cause cervical cancer ⭐
Influenza Virus
Infects lungs → fever, cough, aches
Responsible for 1918 Spanish flu (20–50M deaths worldwide)
3 types:
Type A → serious
Type B & C → mild
Proteins: H = entry, N = exit
Antigenic changes:
Drift → small mutations, yearly flu vaccine needed
Shift → new strain from 2+ viruses combining → may cause pandemic ⭐
HIV (Retrovirus)
Enveloped, icosahedral, ssRNA
Attaches to CD4 receptor → fuses with cell → RNA → DNA (reverse transcription) → integrates into host genome ⭐
Plant Viruses – Transmission & Effects
Horizontal: Enters via damaged tissue, pollen, insects
Vertical: Parent → offspring
Effects:
Hypoplasia (stunted growth)
Necrosis (death of tissue)
Human impact: Can indirectly affect food supply via crops
Vaccines – Preventing Viral Infection
Boost immune protection
Types:
Attenuated live virus ⭐
Killed virus
Molecular subunits
Small risk of infection with live vaccines
Prions – Infectious Proteins
Very small, no nucleic acid
Cause fatal neurodegenerative diseases:
Mad cow (BSE), Creutzfeldt-Jakob (humans), Kuru (humans), Scrapie (sheep), Chronic wasting disease (deer, moose, elk)
Resistant to cooking
Mechanism: Abnormal PrP → converts normal PrP → abnormal PrP ⭐
Viroids – Plant RNA Pathogens
Tiny circular RNA
Infect only plants
Replicate inside cells but do not make proteins
Spread via infected tools or plant parts
Can cause crop failures ⭐
Which virus causes shingles?
Varicella-zoster (latent dsDNA virus) ⭐
Difference between antigenic drift and shift?
Drift = small mutations; Shift = new viral subtype
Name 2 prion diseases in humans
Creutzfeldt-Jakob, Kuru ⭐