3.5 lipids
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
how are triglycerides formed
Formed by condensation one molecule of glycerol and three molecules of fatty acid, ester bond form and one water molecule released per ester bond (three molecules of water per ester bond)
Structure of fatty acids
Long made from chain of hydrocarbons with 4-36 carbon atoms, tail variable but most contain 12-18 carbons, glycerol links to the central carbon atom on fatty acids.
Types of fatty acid
Saturated or unsaturated
Functions of triglycerides
Energy release, double amount of energy per gram than carbohydrates (lipid micelle in other flash cards)
Why do triglycerides repel water
Lipid micellle, insoluble fatty acid tails hydro phobic, osmotic balance not affected, could make swell
Structure of phospholipids
Three fatty acid tails, one hydrophilic phosphate group attached to glycerol, hydrophilic and hydrophobic (amphipatic molecule)
Hydrophobic tail
Phospholipids are hydrophobic, can't interact with water, in membranes fatty acid tails face inside of cell, water soluble substances can't easily diffuse through bilayer
Hydrophilic head
Phosphate group is hydrophilic, interact with water, in membrane phosphate group face outside
lipids such as triglycerides and phospholipids are examples of what
macromolecules
glycerol is in what group
alcohols
fatty acids are in what group
carboxylic acids (carboxyl group and hydrocarbon chain attached
Functions of triglycerides
three hydroxyl groups interact, form bonds between fatty acids and the glycerol molecule, form three water molecules (condensation)
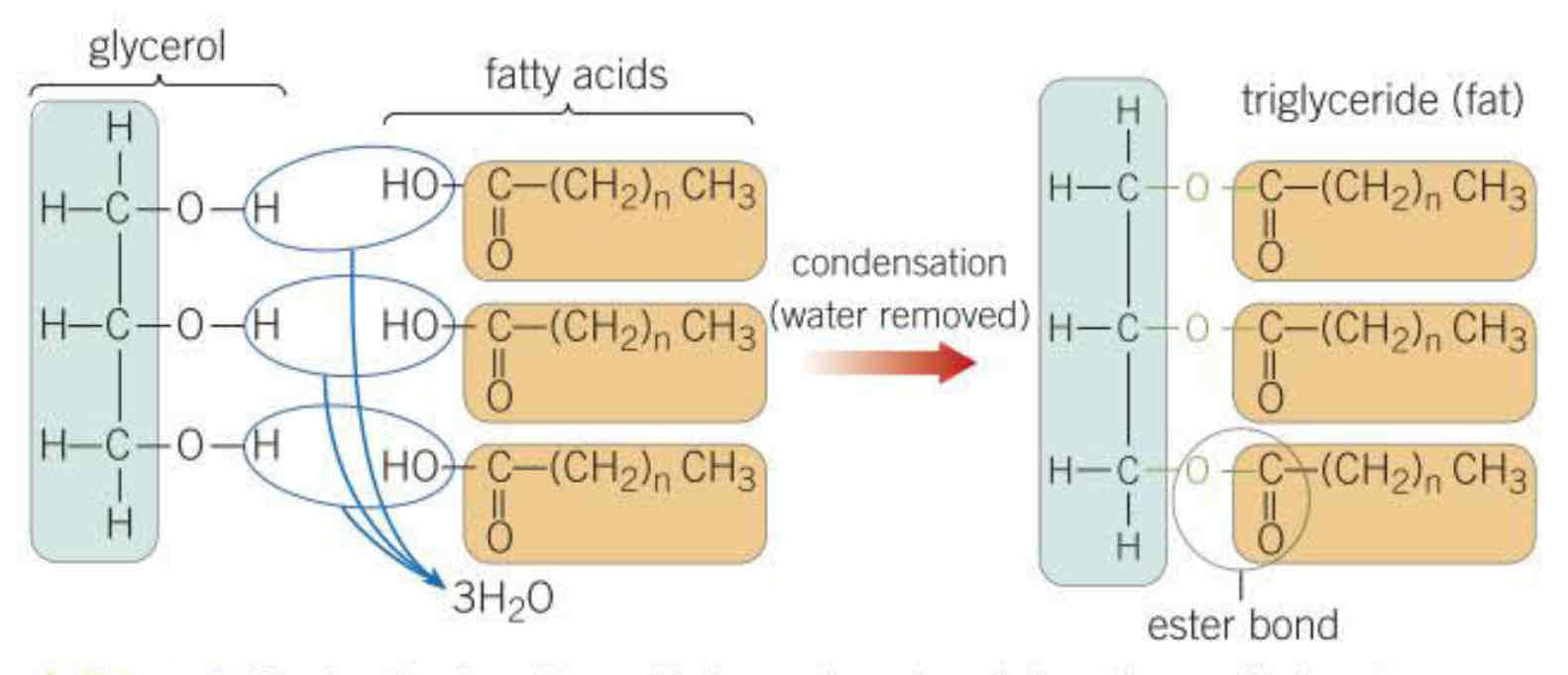
how to break an ester bond
three water molecules supplied, reverse reaction (hydrolysis)
structure of saturated fatty acids
only single bonds between carbon atoms in hydrocarbon chain, number off H atoms attached to carbon maximised
function of saturated fatty acids
solid at room temperature, usually animal origin, linked to increased risk of cardiovascular disease
structure of unsaturated fats
with double bonds, cause molecule to kink/bend, cannot pack closely together
function of unsaturated fats
remain liquid at room temperature, from plant origin, tend to be more healthy than saturated fats
what are sterols
complex alcohol molecules, four carbon ring structure with a OH group at one end, polar like phospholipids
what is cholesterol for
made in the liver and intestines, important role in formation of cell membranes, add stability and regulate fluidity
roles of lipids
membrane formation, hydrophobic barriers, hormone production, electrical insulation (impulse transmission), waterproofing (bird feathers and plant leaves), thermal insulation, cushioning to vital organs, buoyancy for aquatic animals
examples of things that are made using cholesterol
vitamin D, steroid hormones and bile
what is the test for lipids
emulsion, sample mixed with ethanol, white emulsion forms add layer on top, presence of lipid