Herpesviridae: Types, Structure, and Veterinary Significance
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
What is the family name of viruses that includes herpes simplex viruses?
Herpesviridae
How many herpesviruses have been identified so far?
130 herpesviruses
What is a common characteristic of herpesviruses in relation to their hosts?
They co-evolved with their hosts.
How many herpesviruses are isolated from humans?
9 herpesviruses
What are the three subfamilies of Herpesviridae?
Alphaherpesvirinae, Betaherpesvirinae, Gammaherpesvirinae
What is a key biological property of Alphaherpesvirinae?
They have a variable host range and efficiently destroy infected cells.
What is a characteristic of Betaherpesvirinae?
They have a restricted host range and infected cells become enlarged.
What is a defining feature of Gammaherpesvirinae?
They replicate mainly in lymphoblastoid cells and are usually specific for T or B lymphocytes.
What is the structure of herpesviruses?
Spherical, icosahedral capsid, enveloped, and contains dsDNA.
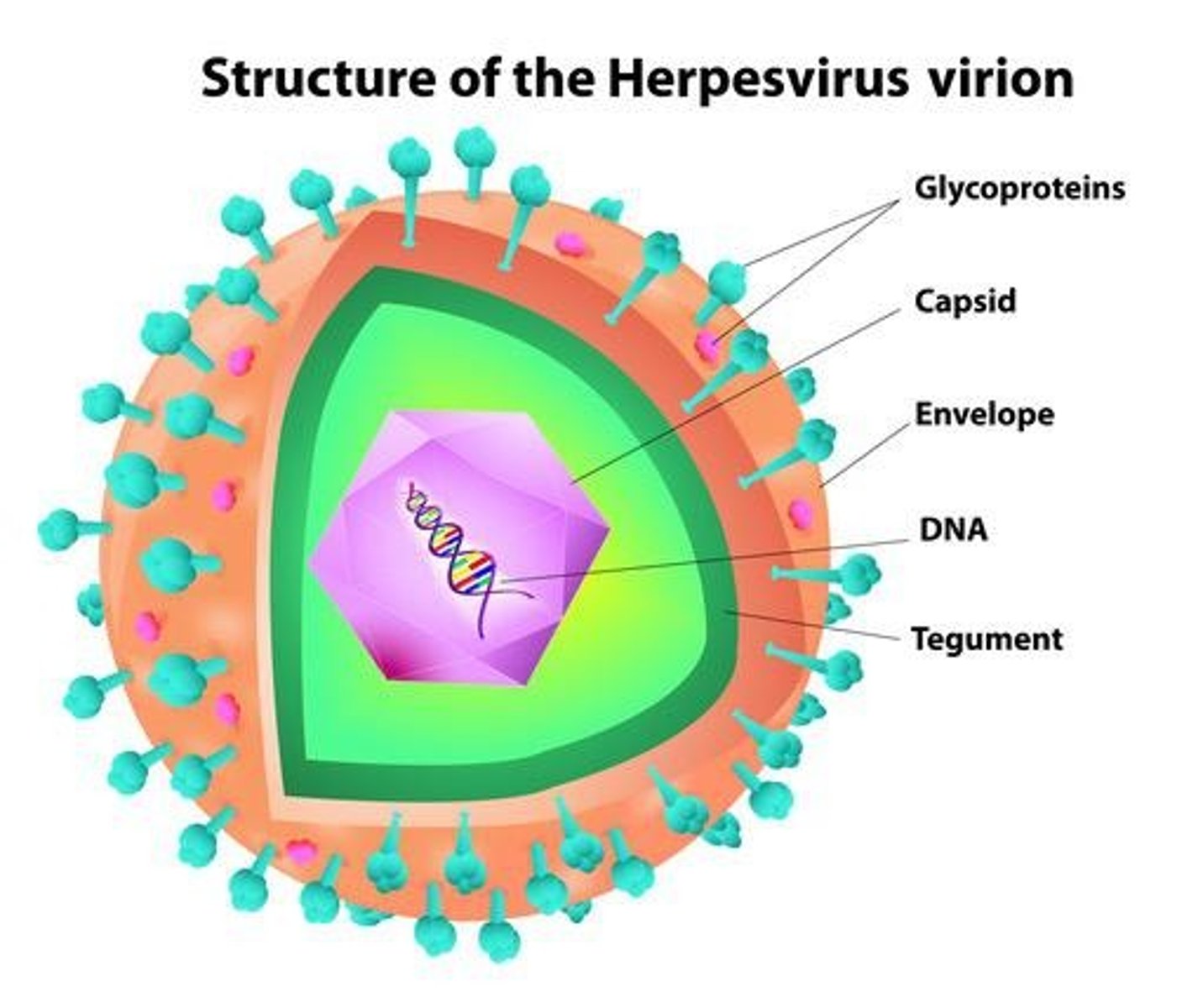
What is the size range of herpesvirus particles?
120-300 nm
What is the role of the tegument in herpesviruses?
It is a protein-filled region between the capsid and envelope containing 20 proteins.
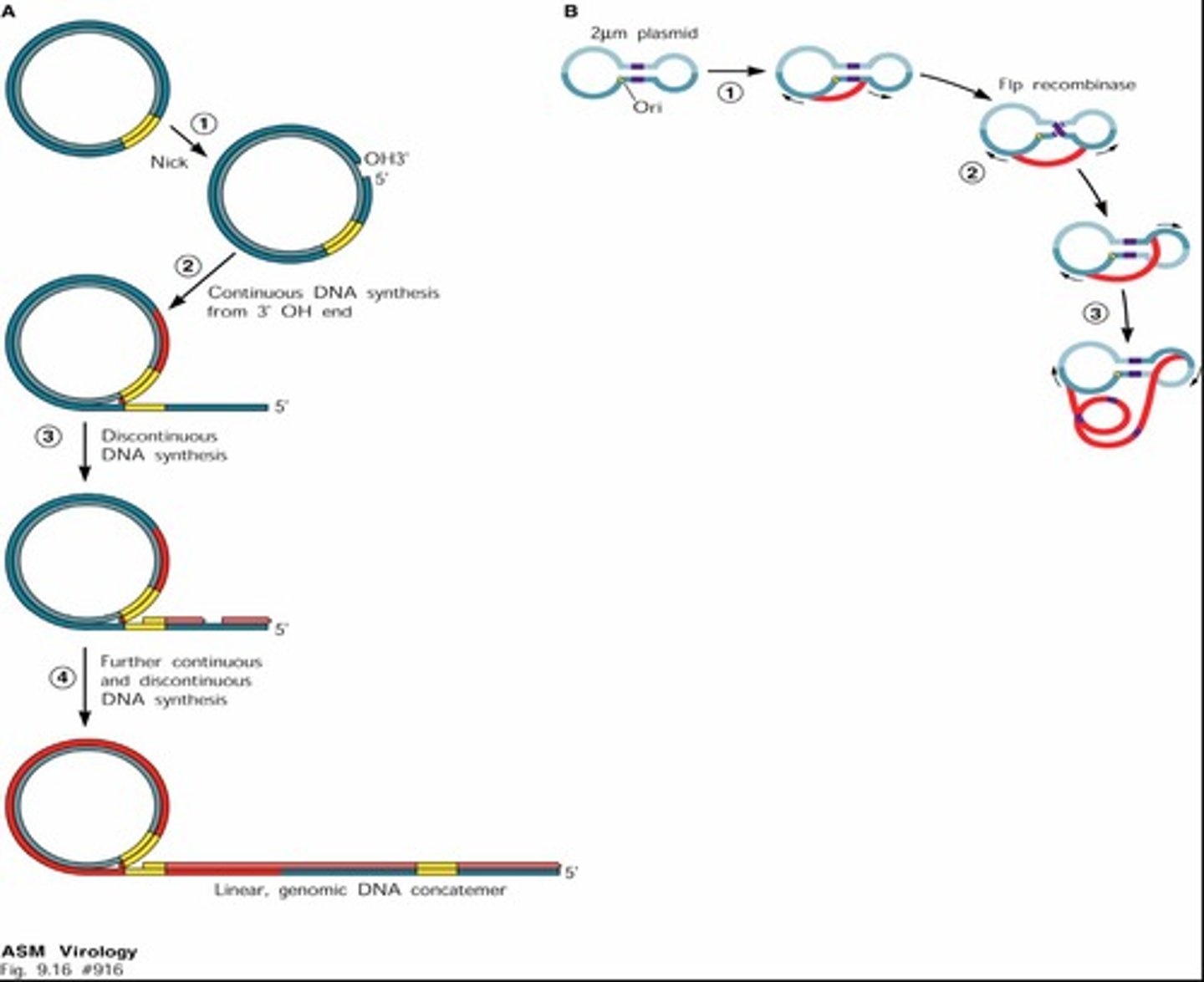
What type of replication do herpesviruses undergo?
Rolling cycle replication.
What is the primary treatment for herpes simplex infections?
Acyclovir, a nucleoside analog.
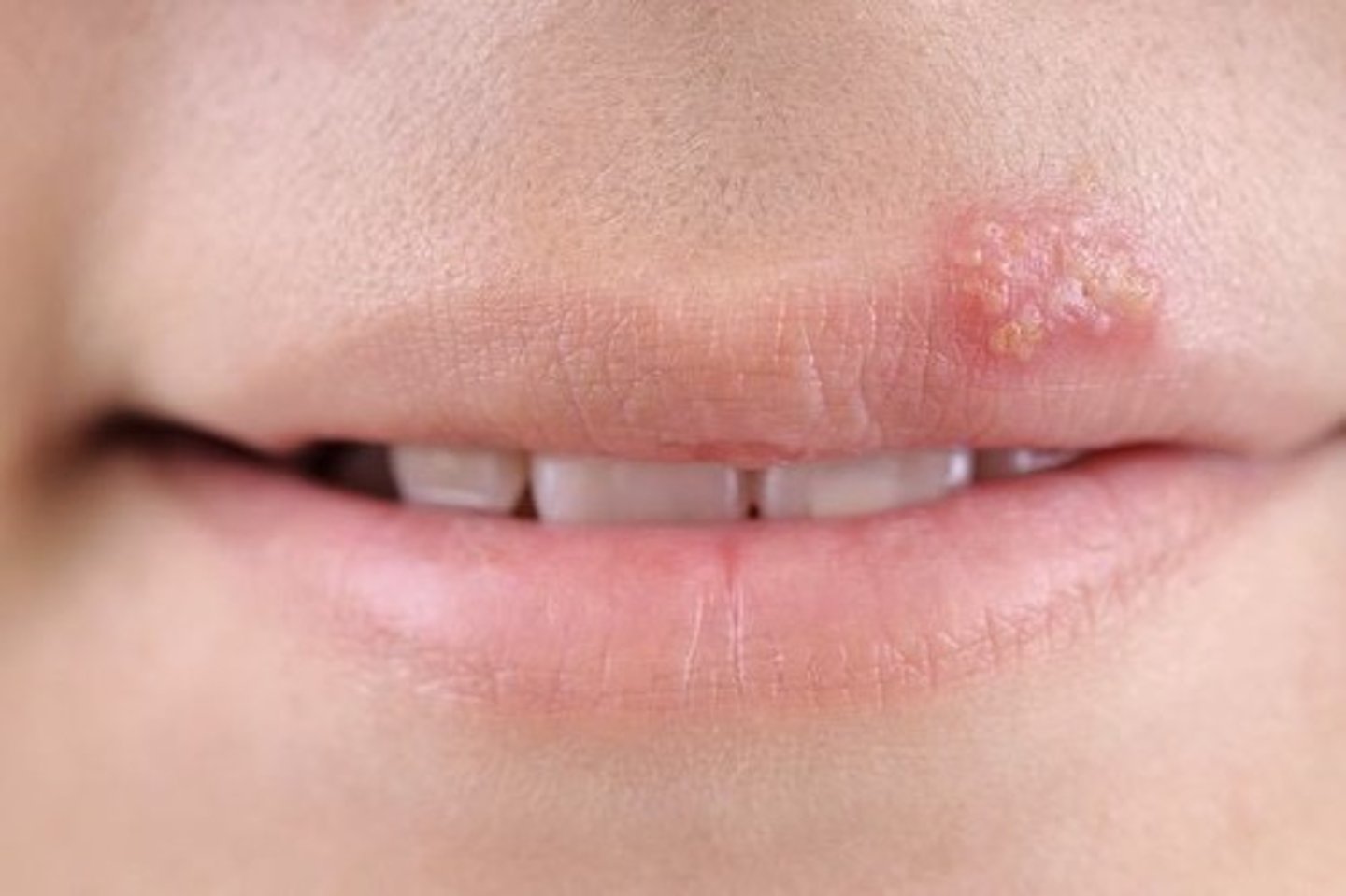
What are the clinical manifestations of Herpes Simplex Virus 1 (HSV-1)?
Oral cold sores, dermatitis, and encephalitis.
What are the clinical manifestations of Herpes Simplex Virus 2 (HSV-2)?
Genital herpes and encephalitis.
What virus causes chickenpox?
Varicella zoster virus (VZV).
What is the primary symptom of shingles caused by VZV?
Painful blisters along a dermatome.
What is the vaccination strategy for preventing chickenpox?
Live attenuated virus-based vaccine.
What is the association between the recombinant shingles vaccine and dementia?
It is associated with a reduced risk of dementia within 6 years of vaccination.
What is the role of LAT in herpesviruses?
It stands for latent-associated transcript, involved in latency.
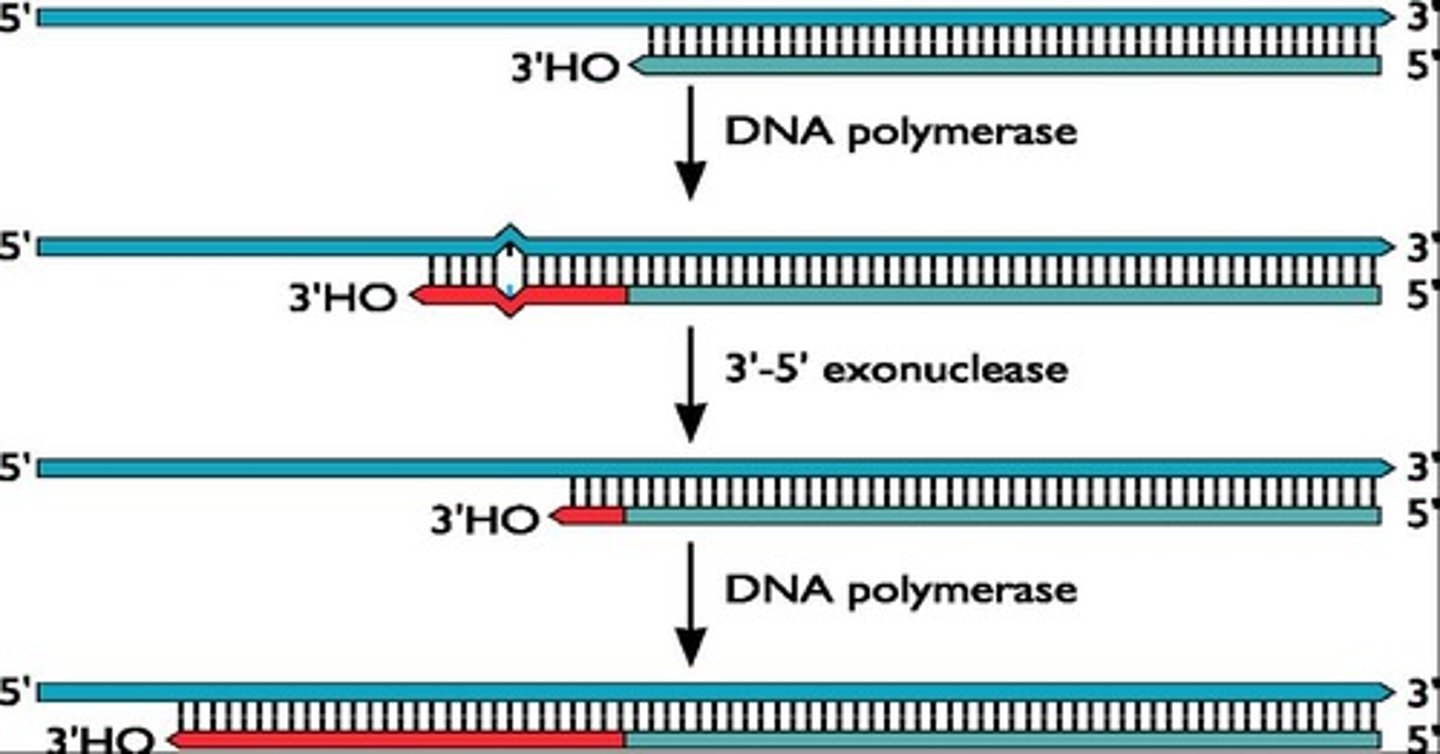
What is the function of herpesvirus DNA polymerase?
It is involved in proofreading during DNA replication.
What is the typical latency location for Alphaherpesvirinae?
Sensory neurons.
What are the common symptoms of chickenpox?
Fever, rash, and itchy blisters.
What is the significance of the phylogenetic tree of herpes viruses?
It is based on amino acid sequences of homologous genes.
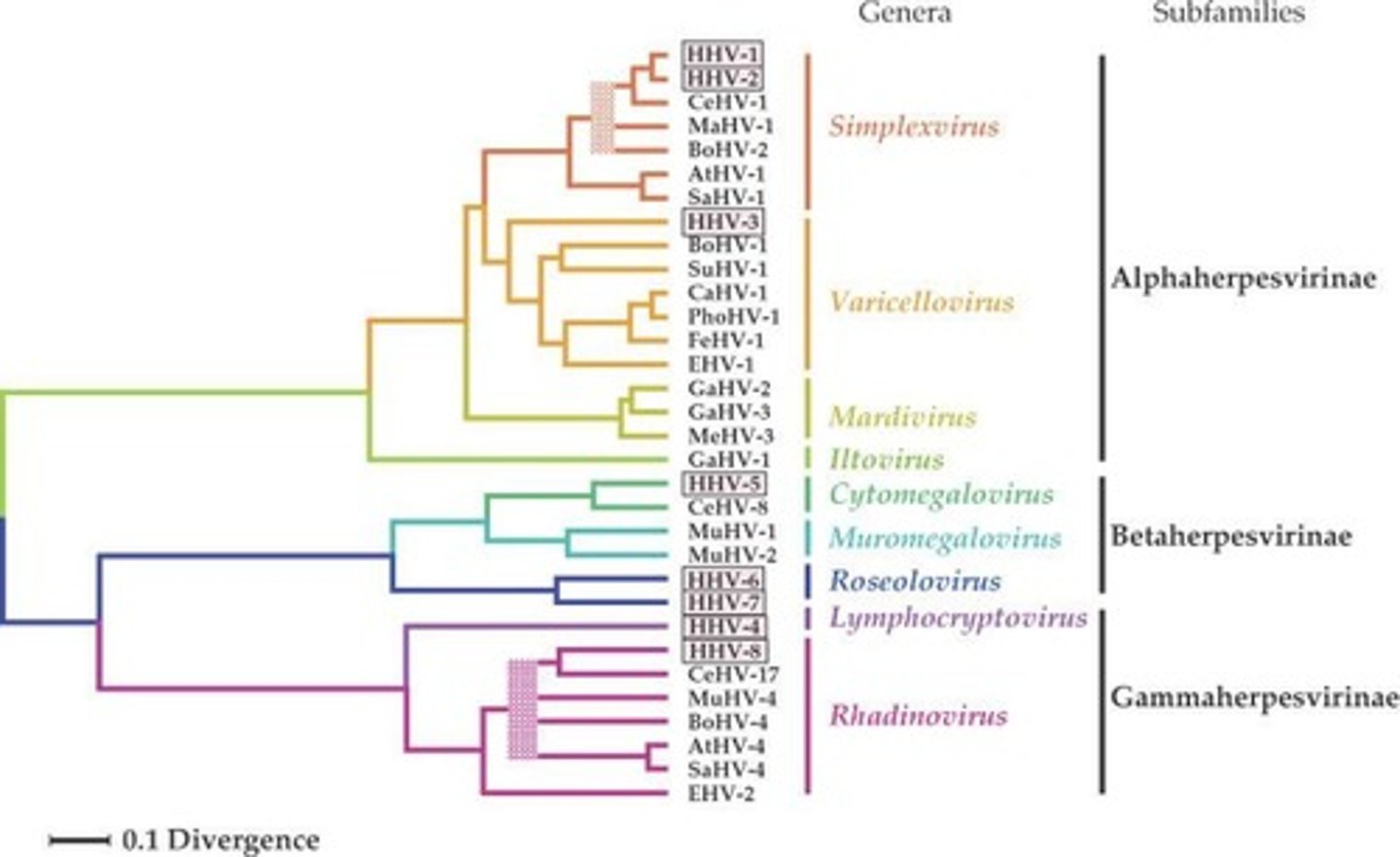
What is the most common infection at daycares?
Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV)
What is the typical symptomatology of HCMV?
Usually asymptomatic but can cause serious diseases in congenital infections.
What are the potential consequences of congenital HCMV infections?
Birth defects and damage to the developing brain, including encephalitis and multiple organ system diseases.
In which patient populations is HCMV particularly dangerous?
Recurrent infections in immunosuppressed patients, such as organ transplant and AIDS patients.
What antiviral drug is primarily used for treating HCMV?
Ganciclovir, a nucleoside analog with significant toxicity.
Is there a vaccine available for HCMV?
No, there is currently no vaccine for HCMV.
What virus infects both B cells and epithelial cells and is associated with glandular fever?
Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)
What are the common symptoms of infectious mononucleosis caused by EBV?
Malaise, fatigue, and sore throat.
What is a significant complication of EBV in regions with high malaria incidence?
Burkitt's Lymphoma.
What is the relationship between EBV and multiple sclerosis?
EBV has been associated with a high prevalence of multiple sclerosis.
What are the characteristics of HHV-6 and HHV-7?
Usually asymptomatic, associated with T lymphocytes, and can cause roseola infantum in infants.
What is the primary disease associated with HHV-8?
Kaposi's Sarcoma in AIDS patients.
What type of cells does HHV-8 target?
Endothelial cells and mesenchymal stem cells.
What are the clinical signs of Bovine herpesvirus 1 (BoHV-1.1)?
Upper respiratory tract disease and infectious b. rhinotracheitis (IBR).
What disease does Bovine herpesvirus 2 (BoHV-2) cause?
Bovine mammilitis and pseudo lumpy skin disease.
What are the clinical signs of Porcine herpesvirus 1 (Pseudorabies)?
Neurological disease in piglets and respiratory disease in older pigs.
What is the prevention strategy for Pseudorabies in pigs?
Vaccination with a gene-deleted marker vaccine.
What are the clinical signs of Equine herpesvirus 1 (EHV-1)?
Abortion in mares and neurological disease.
What is the primary prevention method for Equine herpesviruses?
Inactivated and modified live vaccines with frequent revaccination.
What is the pathogenesis of Canine herpesvirus 1 (CHV-1)?
Generalized viremia in puppies under 4 weeks of age, leading to high mortality.
What disease does Feline herpesvirus 1 (FHV-1) cause in kittens?
Upper respiratory tract disease, rhinotracheitis, and keratitis.
What are the potential consequences of corneal ulcers and keratitis in animals?
They can lead to blindness.
What types of vaccines are used to control herpesvirus infections?
Inactivated and modified live vaccines (MLV).
What is Cercopithecine herpesvirus 1 commonly known as?
Herpes B virus.
Which primates are natural hosts for Herpes B virus?
Old World Monkeys, specifically Rhesus and Cynomolgus monkeys.
What is a significant risk associated with Herpes B virus in humans?
It can cause encephalitis with an 80% mortality rate.
What is the treatment for Herpes B virus infection in humans?
Acyclovir or gancyclovir.
What is Gallid herpesvirus 1 also known as?
Infectious Laryngotracheitis virus (ILTV).
What is the morbidity and mortality rate associated with Gallid herpesvirus 1 in chickens?
100% morbidity and 20-70% mortality.
What is Marek's Disease virus (MDV) known for?
It is oncogenic and can cause several syndromes in chickens.
What are the four syndromes associated with Marek's Disease?
Neurolymphomatosis, classic Marek's, acute Marek's, and ocular lymphomatosis.
How is Marek's Disease virus transmitted?
It grows in feather follicles and is shed in dander.
What is Anatid herpesvirus 1 responsible for?
Duck plague in waterfowl.
What is the morbidity rate of Anatid herpesvirus 1 in ducks?
5-100%, affecting both wild and domestic ducks.
What is the primary disease caused by Alcelaphine herpesvirus 1?
Bovine Malignant Catarrhal Fever (MCF).
What are the clinical signs of Bovine Malignant Catarrhal Fever?
Fever, nasal and ocular discharges, mucosal ulcers, and CNS signs.
What is the incubation period for Alcelaphine herpesvirus 1?
Approximately 3 weeks.
What factors contribute to the outbreaks of MCF in cattle?
Close contact with wildebeest or sheep.
What is the primary issue with Koi herpesvirus?
It can cause high mortality in farmed catfish under warm conditions.
What are the conditions that predispose fish to herpesvirus diseases?
Dense stocking and poor environmental conditions.
What is the effect of Salmonid herpesvirus-1 on rainbow trout?
It causes acute die-off in hatcheries.
What is a common symptom caused by Salmonid herpesvirus-2 in fish?
Epithelial tumors in survivors.