Special sense organs
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
neurology, opthalmology and special senses
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
list all special sense organs
nose- olfaction
vomeronasal organ- phermomone detection
tongue- taste
eye- vision
ear- hearing and balance
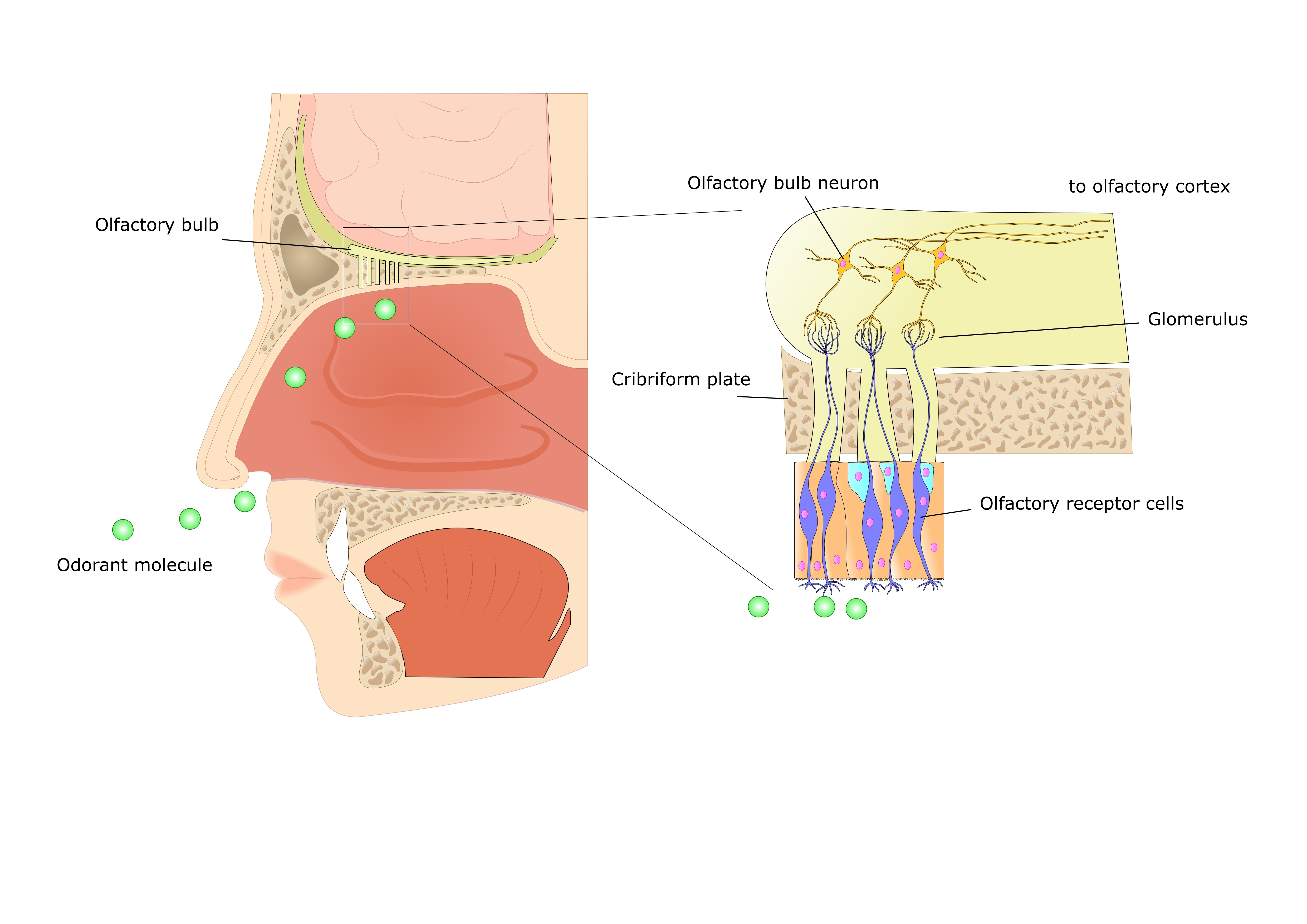
olfaction
detected by special cells in muscosa of nasal cavity
mucose= olfactory epithelium, contain sensory receptors
neurons (bipolar) pass through epithelial surface to olfactory bulb in cranium after passing through bony cribiform plate (separate cranial cavity from nasal cavity)
cribiform plate has small pores
olfactory epithelium held by supporting cells that secrete lipid rich mucus, odorants dissolve in this fliod and reach the sensory receptors
signal tranduction takes place through neurons
vomeronasal organ
found on the floor of the nasal cavity
ducts link nasal and oral cavities caudal to incisor teeth
are blind ending caudal sacs
flehmen reaction- pump air in and out (sexual and social behaviour)
aroma is the combined effect of neural inputs from the sense o smell and taste
gustation
gustatory receptors found on the tongue mucosa
sensory neurons carry info to the brain
receptor cells have one single receptor type so each receptor can only detect one form of taste
gustatory inputs link directly to centres involving ingestion, food avoidance, insulin release, diuresis when water in pharynx
vision
eye has transparent media that conducts light to stimulate photoreceptor cells
vitreous humor is gel like substance filling the eye
sclera is a tough connective tissue to maintain integrity and strength- continuous with membrane covering the brain.
ear
outer middle and inner
the eye
Transparent media- Cornea, aqueous humour, lens and vitreous humour direct and converge light on the photoreceptor cells on the retina
Non-Transparent media- Choroid, Uvea, Sclera- Support transparent media
The photosensitive layer - retina made up of rod and cones receptor cells. Cones for daylight vision and rods for night vision.
Light splits chemical compound -Rhodopsin in cones and rods and triggers signal transduction thru optic nerve. The signals are transmitted to the optic cortex of the brain.
outer ear
sound collected from external auditory canal to the tympatic canal and tympatic membrane
middle ear
maleus, incus and stapes conducts sound to oval window. also connected to eustachian tube to the nasopharynx
inner ear
oval window transmits waves to the cochlea which contain sensory receptor cells known as hair cells from where signals are transmitted to the brain via CN VIII
Ear- balance and motion
inner ear has semicircular canals that detect angular movement while the saccule and utricle (maculae) detect linear acceleration
cochlea
basilar membrane
organ of corti
hair cells
CN VIII
fluid movement in the cochlea caused by sound vibration on the oval window cause a standing wave to travel in cochlea canals.
so hair cells on basilar membrane bends against tectorial membrane
then signals are generated and sent to the brain
hair cells bend due to fluid movement and discharge electrical signals to the brain
semi circular canal
cupula
hair cell
CN III
hair cells of the cupula bend due to fluid movement in the semicircular canals and discharge electrical signals to the brain
saccule and utricle
detection of linear acceleration
hair cells
CN VIII
hair cells (otoliths) bend due to fluid movement caused by inertia in the saccule and utricle causing them to discharge electrical signals to the brain
two are in right angles to each other so can only detect linear movement in one plane