Understanding the Nursing Process and Diagnostic Reasoning
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
Nursing Process
Systematic method for planning patient care.
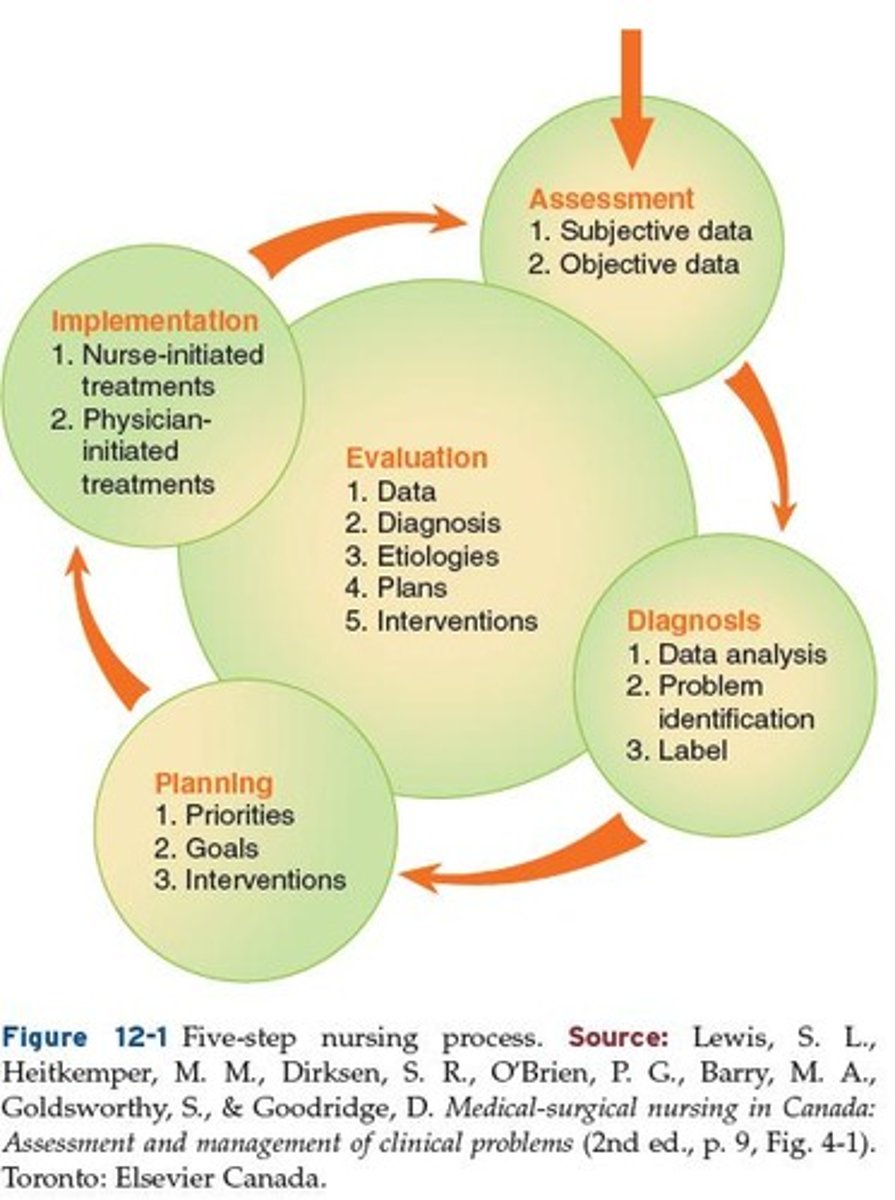
Assessment
Data collection regarding client's health status.
Diagnosis
Analysis of data to identify key health issues.
Planning
Prioritizing strategies and creating care plans.
Implementation
Execution of the nursing care plan.
Evaluation
Assessment of outcomes to determine effectiveness.
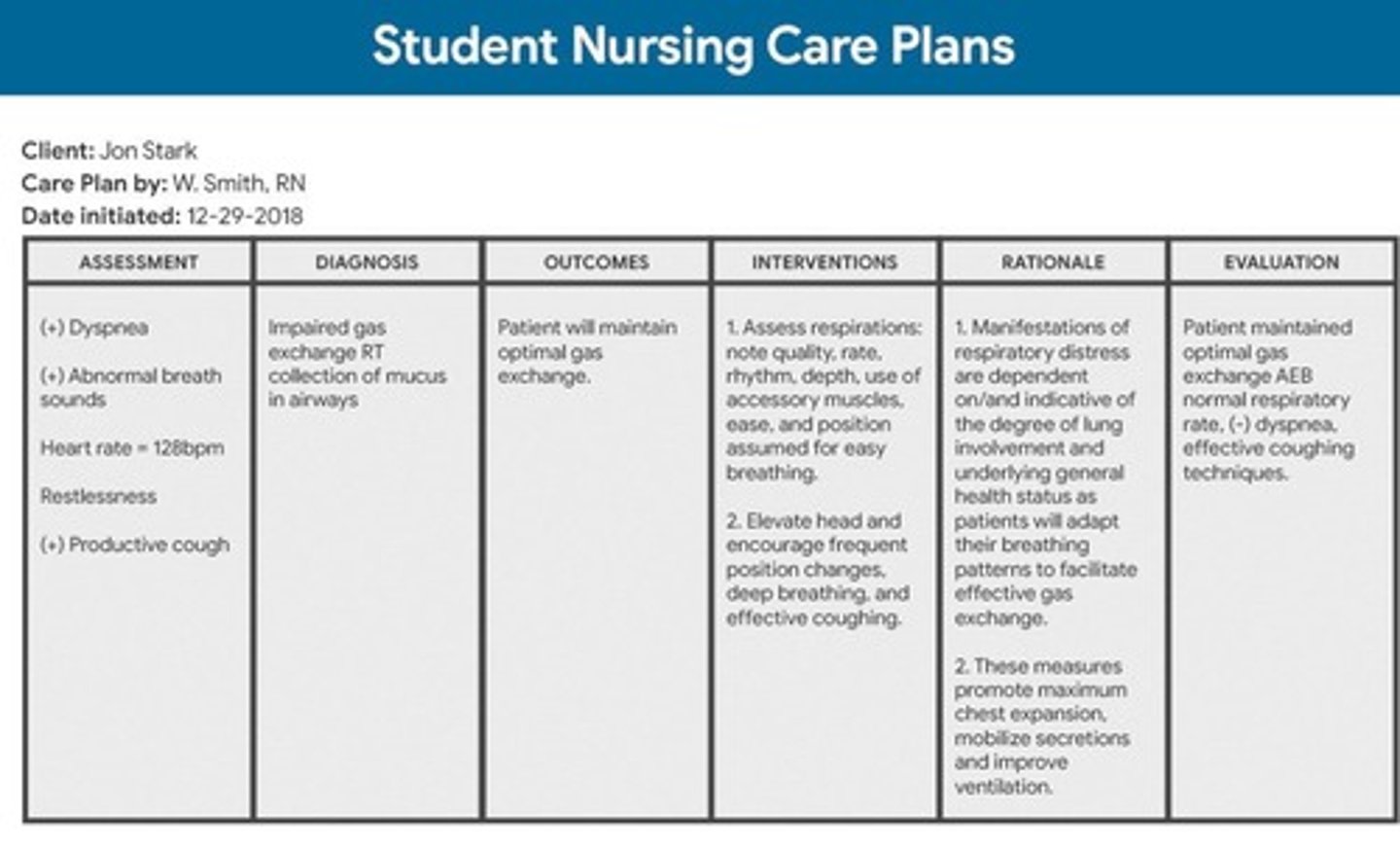
Nursing Care Plan (NCP)
Document outlining nursing diagnosis and interventions.
Collaborative Problems
Issues requiring interdisciplinary team involvement.
Diagnostic Reasoning
Process of analyzing data to reach conclusions.
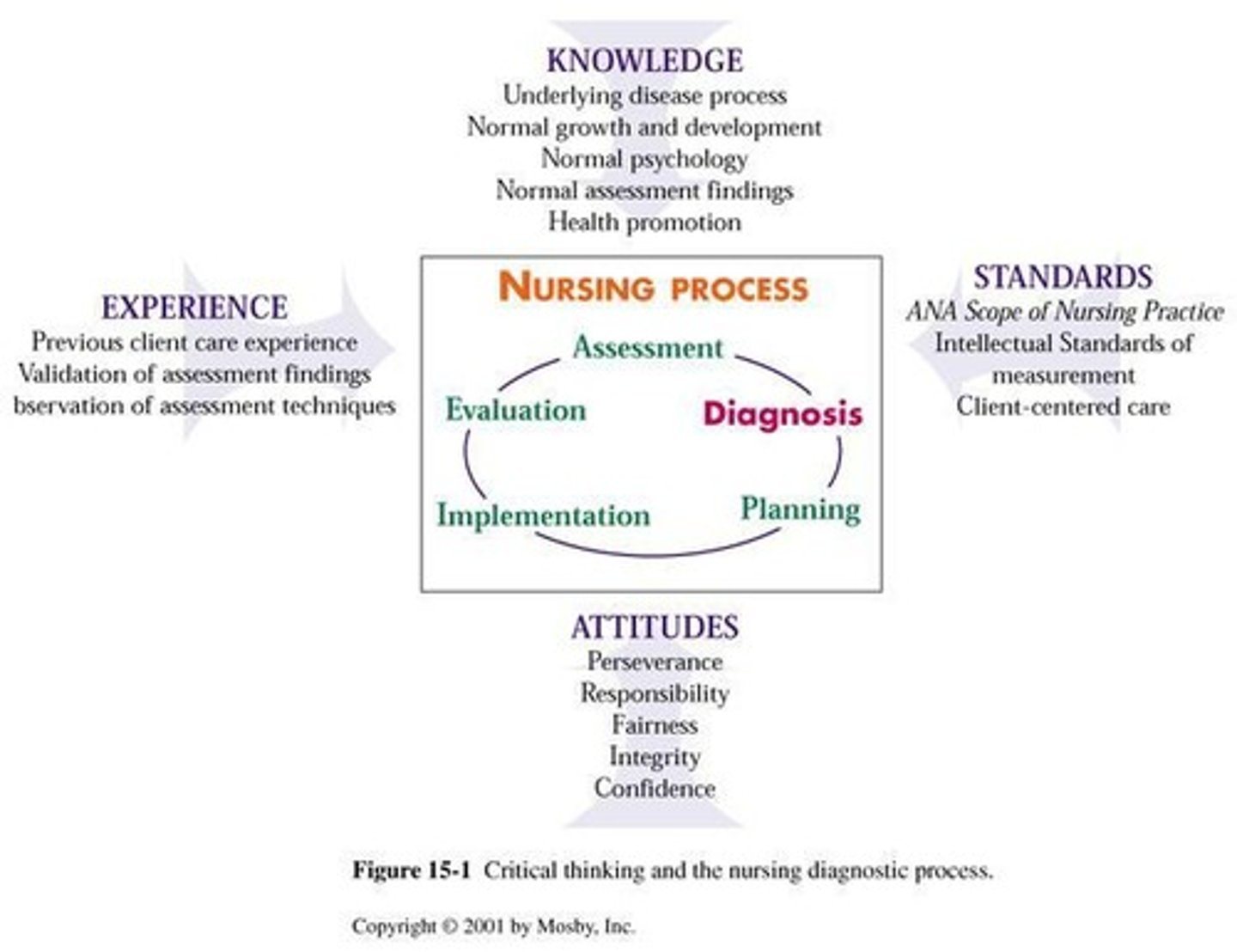
Diagnostic Errors
Mistakes in identifying patient health issues.
Critical Thinking
Objective analysis to make informed decisions.
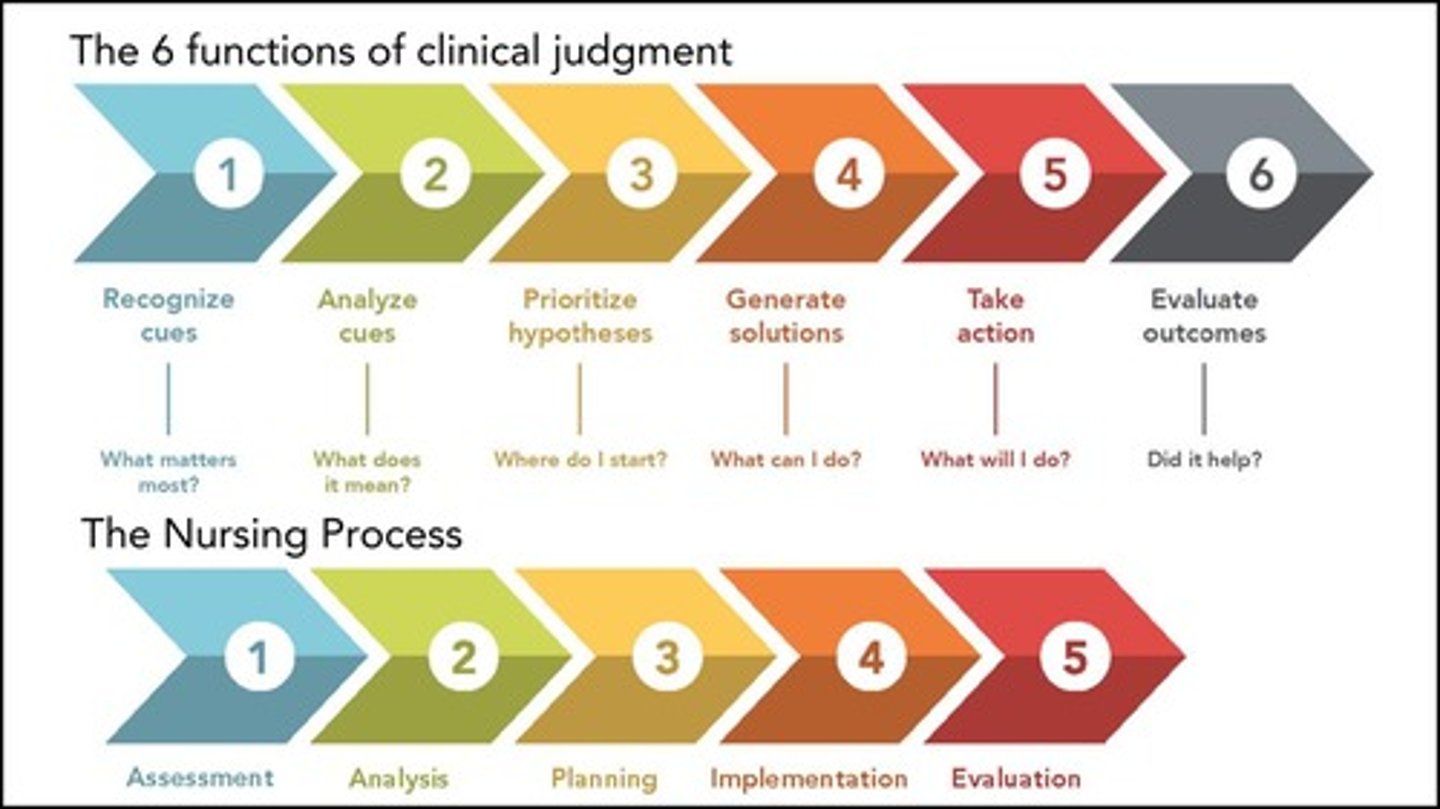
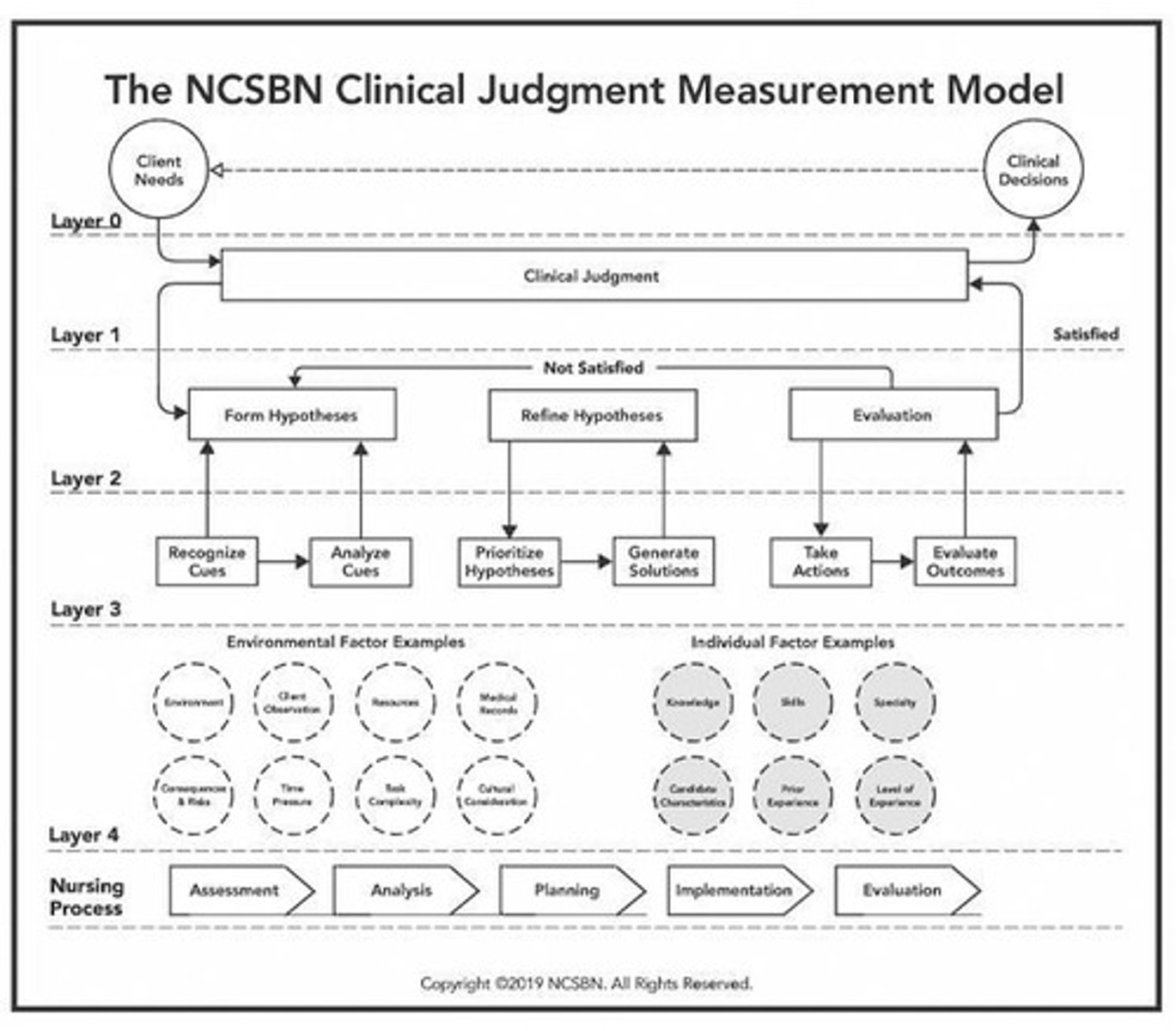
Clinical Judgment
Nurse's decision-making based on patient data.
Three-part Diagnostic Statement
Format including problem, etiology, and symptoms.
Two-part Diagnostic Statement
Format including problem and etiology only.
Actual Nursing Diagnosis
Current health issues identified in patients.
Potential Nursing Diagnosis
Possible future health issues based on risk.
At-risk Nursing Diagnosis
Identified risks for developing health issues.
Health Promotion Diagnosis
Focus on enhancing patient well-being.
Wellness Diagnosis
Diagnosis indicating optimal health status.
Nursing Intuition
Nurse's instinctive understanding of patient needs.
Evidence-informed Practice
Care based on research and clinical evidence.
Client-centered Approach
Care tailored to individual patient needs.
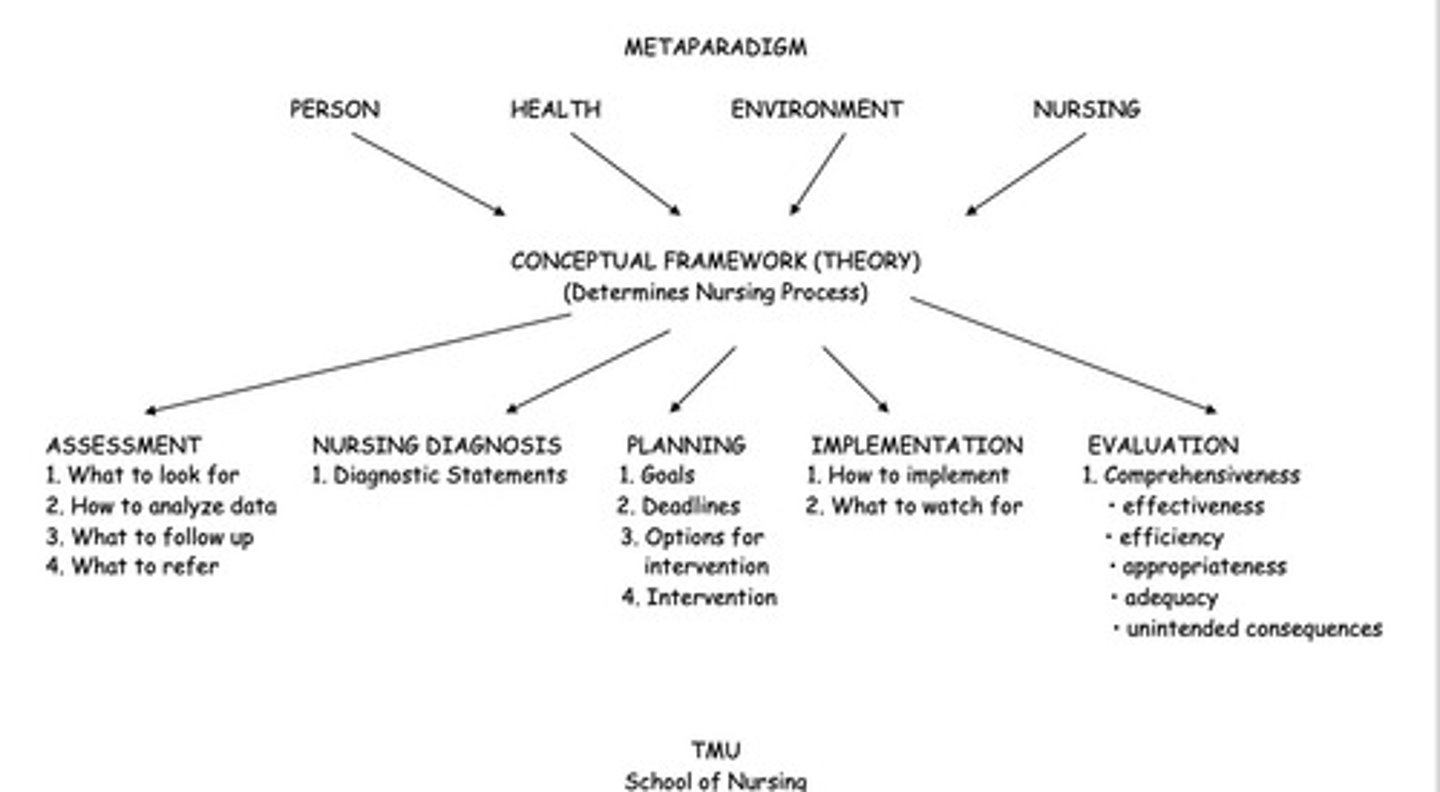
Assessment
Process of gathering client information for understanding.
Data Collection Tool
Framework used to gather assessment data.
Subjective Data
Information reported by the client about feelings.
Objective Data
Observable and measurable data collected by the nurse.
Primary Sources
Direct information from the client.
Secondary Sources
Information from family and healthcare team.
Tertiary Sources
Data from medical records and literature.
Interview
Conversation to gather information from the client.
Nursing Health History
Comprehensive account of client's health background.
Physical Examination
Assessment of the body for health status.
Comprehensive Assessment
Detailed evaluation of all human functioning spheres.
Problem Based Assessment
Focused assessment on a specific health issue.
Cues
Observations or signs indicating client's condition.
Inferences
Conclusions drawn from collected assessment data.
Emerging Patterns
Trends identified from assessment data analysis.
Mrs. Brady
Case study patient with hip fracture and confusion.
Fluid Intake
Amount of fluids consumed by the client.
Dietary Preferences
Client's specific likes or dislikes regarding food.
Allergy Information
Known allergies to peanuts and shellfish.
Height and Weight
Mrs. Brady is 1.6 meters tall and weighs 50 kg.
Appetite Issues
Client reports decreased appetite since her fall.
Skin Condition
Thin and dry skin resembling tissue paper.
Data Validation
Verifying data accuracy before analysis begins.
Data Clustering
Organizing data into meaningful groups for analysis.
Inferential Reasoning
Attaching meaning to clinical data through analysis.
Normal Values
Client's baseline data for comparison during analysis.
Diagnostic Phase
Identifying and analyzing patient information for conclusions.
Diagnostic Reasoning
Using assessment data to explain clinical judgments.
Clinical Inference
Drawing conclusions from evidence before diagnosis.
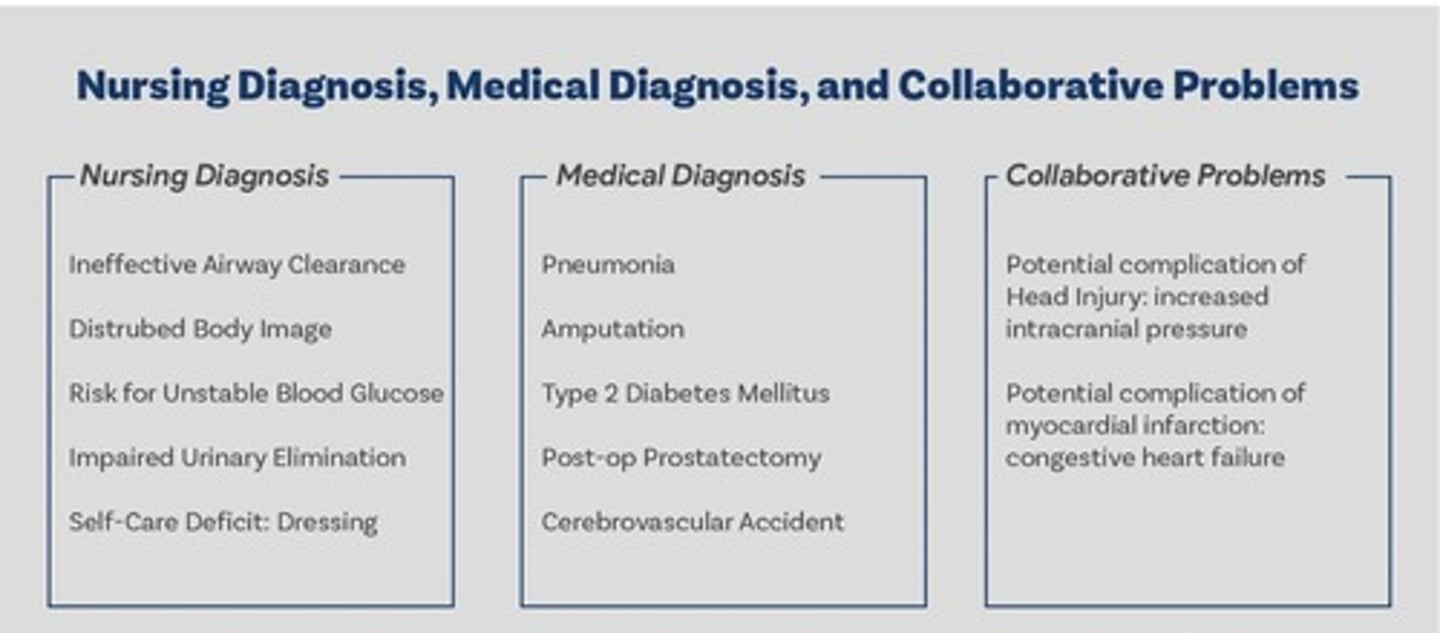
Nursing Diagnosis
Clinical judgment on responses to health problems.
Medical Diagnosis
Identifying disease based on signs and tests.
Collaborative Problems
Monitoring potential physiological complications in clients.
Data Interpretation
Understanding data patterns to identify problems.
Reasoned Conclusion
Logical deduction based on data analysis.
Interrelationships
Connections between different data points in analysis.
Positive Functioning Areas
Identified strengths in patient health during assessment.
Risk of Problems
Identified areas where health issues may arise.
Plan of Care
Strategy based on identified patient problems.
Cues
Data points that indicate patient health status.
Evidence-Based Practice
Using research evidence to inform clinical decisions.
Assessment Data
Information collected to evaluate patient health.
Health Problems
Actual or potential issues affecting patient well-being.
Nursing Interventions
Actions taken to achieve desired patient outcomes.
Collaborative Problems
Issues managed with health care team collaboration.
Diagnostic Process
Steps include data clustering and inferential reasoning.
Data Clustering
Grouping cues to identify patterns in assessment.
Defining Characteristics
Clinical criteria confirming a nursing diagnosis.
Accepted Norms
Standard values for comparison in client data.
NANDA
Taxonomy for nursing diagnoses by North American Nursing Diagnosis Association.
Diagnostic Label
Name of the nursing diagnosis in two-part format.
Related Factors
Etiology or facts related to the nursing diagnosis.
Actual Nursing Diagnosis
Response to existing health conditions in individuals.
Risk Nursing Diagnosis
Potential responses to health conditions in vulnerable clients.
Health Promotion Nursing Diagnosis
Judgment on motivation to enhance health behaviors.
Wellness Nursing Diagnosis
Judgment to enhance levels of wellness.
Nursing Diagnostic Statement
Two-part statement linking diagnostic label and related factors.
Acute Pain
Example of an actual nursing diagnosis.
Vulnerable Individual
Client at risk for developing health conditions.
Physiological Factors
Body-related aspects increasing health condition risk.
Psychological Factors
Mental aspects affecting health condition vulnerability.
Health Behaviors
Actions taken to improve or maintain health.
Optimal Level of Health
Desired state of health for clients.
Readiness for Enhanced Coping
Example of a wellness nursing diagnosis.
Lack of Exposure to Instruction
Example of related factor in nursing diagnosis.
Surgical Incision
Example of risk factor for infection.
Nursing Diagnostic Statement
Describes patient response to health condition.
Descriptors
Words like impaired or decreased to clarify meaning.
Related Factors
Etiology or cause of patient response.
NANDA dx statement
Standardized language for nursing diagnoses.
Treatable Etiology
Identifiable cause that can be addressed.
Client's Problem
Focus on patient's issues, not nurse's.
Legally Suspect Statements
Avoid ambiguous or judgmental language.
Single Problem Statement
Refer to one issue per nursing diagnosis.
Activity Intolerance
Inability to perform activities due to health issues.
Inactivity
Lack of movement due to lifestyle choices.
Lack of Motivation
Reduced drive to engage in activities.
Increased Metabolic Demands
Higher energy needs due to assistive devices.
Decreased Muscle Strength
Reduction in muscle power and flexibility.