Population and genetics - Evolution and speciation
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What are the facts that the Darwin-Wallace theory of evolution is based on?
1. Organisms produce more offspring than is needed to replace the parents
2. Natural populations remain stable however
3. Individuals in a population show variation
What are the conclusions that Darwin-Wallace made on account of their observed facts?
- That there must be competition for survival (otherwise the population would increase)
- That best selected for individuals would survive
Define evolution.
Change in the allele frequency in a population (due to natural selection)
What does evolution result in?
Speciation
What is speciation?
Formation of new species from a pre-existing species due to evolution (this is as a result of a type of separation of two population)
Genetic isolation is needed for speciation to occur
Describe briefly how evolution led to all the species we have today.
1. There was one species
2. Species evolved into different species due to selection pressures and different mutations
3. These species would then divide further and further due to different mutations and selective pressures
What are the two types of speciation?
- Allopatric
- Sympatric
What makes two species different?
When they can no longer interbreed to produce fertile offspring
What is reproductive separation?
When changes in the alleles and phenotypes of some individuals in a population prevent them from successfully breeding with other individuals in the population who do not have the changed alleles and phenotypes
What changes can cause reproductive separation?
- Seasonal (temporal)
- Mechanical
- Behavioural
- Geographical
Describe seasonal reproductive separation
Some individuals in a population may develop different mating or flowering seasons to the rest of the population
Describe mechanical reproductive separation.
Where some individuals in a population develop changes in their genitalia that prevent them from mating with the opposite sex
Describe behavioural reproductive separation.
Some individuals in a population may develop changes in their courtship behaviours meaning they can no longer attract individuals of the opposite sex for mating
Describe geographical reproductive separation.
Changes that develop due to populations being separated by physical barriers
What is the most common type of speciation?
Allopatric
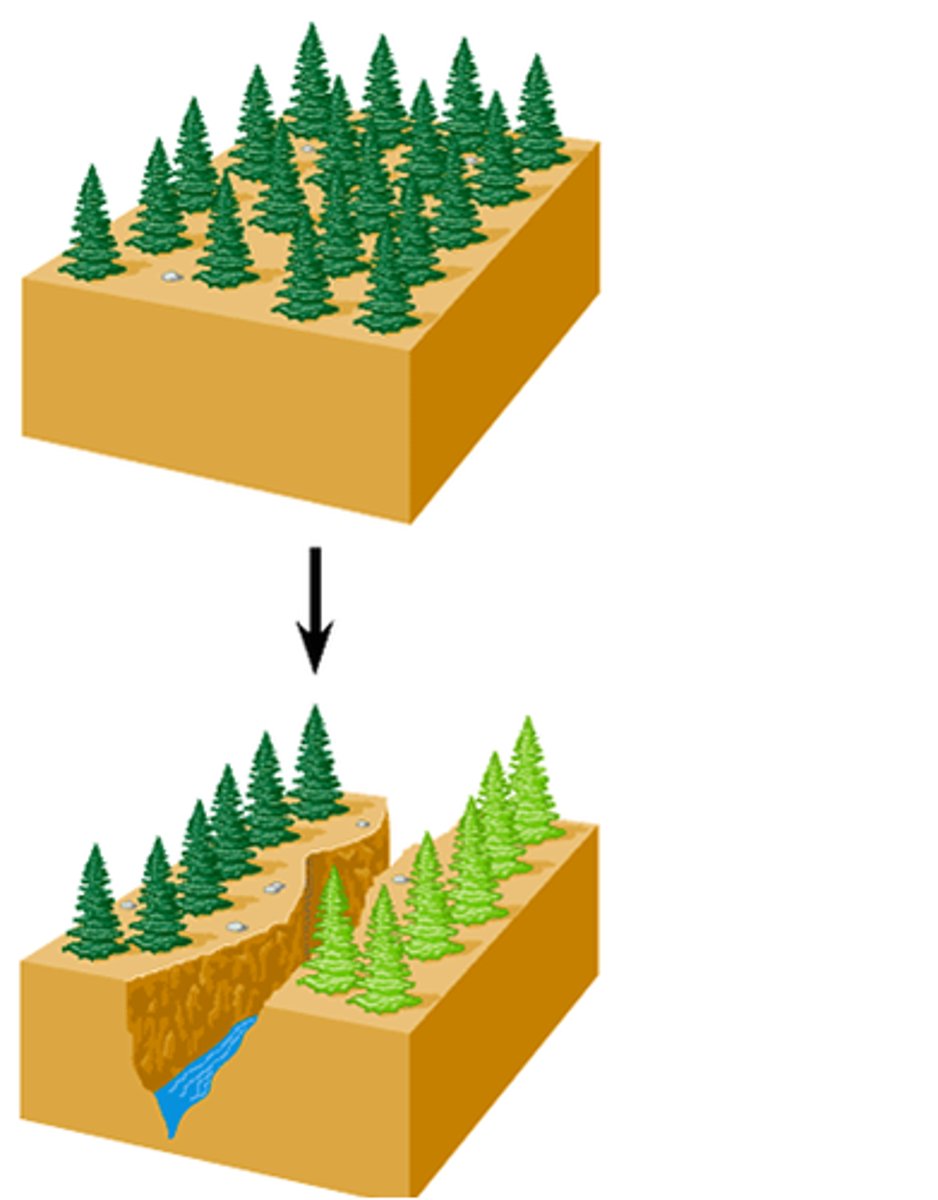
Describe allopatric speciation.
- Speciation as a result of geographical isolation
- Arises when a natural barrier develops that separates a population
- Population undergos different selection pressures which leads to genetic change
- Phenotypes of both populations are effected
Describe sympatric speciation.
- Speciation that occurs without a geographical barrier
- Ecological separation can occur - separation by living in different habitats in the same area
- Behavioural separation can occur - populations separated due to different behaviours e.g. in feeding or courtship/mating behaviours
(also mechanical separation occurs)