Ch. 15: Monopoly
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Definitions, concepts, and practice questions for Ch. 15 of Principles of Economics by Gregory Mankiw.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Monopoly
A firm that is the sole seller of a product with no close substitutes
Q: What is the fundamental cause to monopoly?
Barriers to entry (other firms cannot enter the market and compete)
Three main sources of barriers to entry
Monopoly resources
government regulation
the production process
Barrier to entry: Monopoly resources
One firm has sole access to a key resource
Barrier to entry: Government regulation (Government-created monopolies)
The government gives one person/firm the exclusive right to sell a good/service
(ex. patent and copyright laws)
Barrier to entry: The production process (Natural monopoly)
A single firm can provide a good/service to a market at a lower cost than could two or more firms
(ex: supplying water to a town)
Q: Some government grants of monopoly power are desirable if they
A: provide incentives for innovation
Q: A firm is a natural monopoly if it exhibits _________ as its output increases.
A: decreasing average total cost
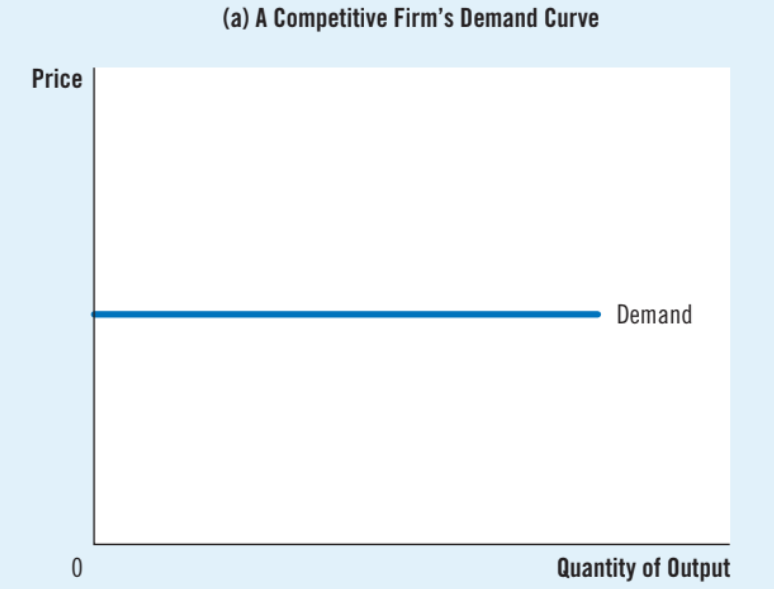
Demand curve of a competitive firm
Horizontal, perfectly elastic due to many perfect substitutes (price taker)
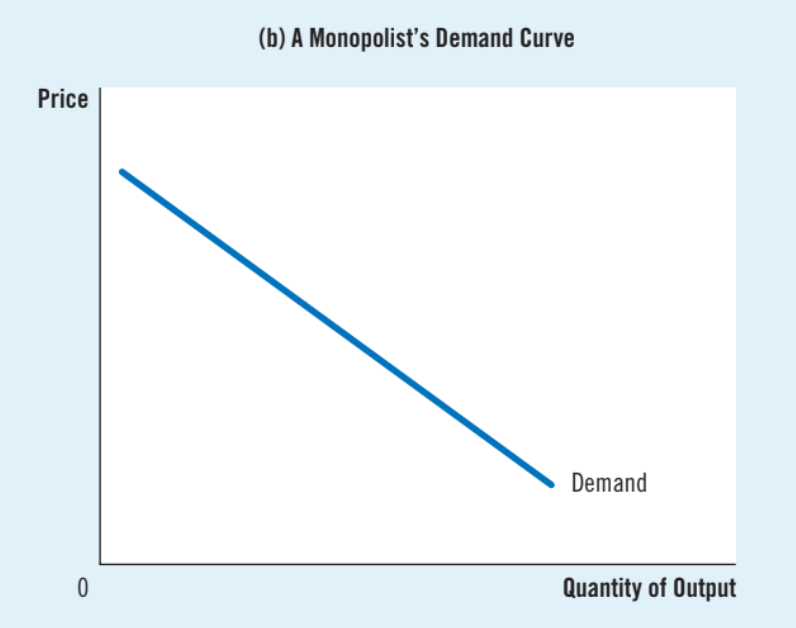
Demand curve of a monopoly
Slopes downward, it is the market demand curve because the firm is the sole producer in the market
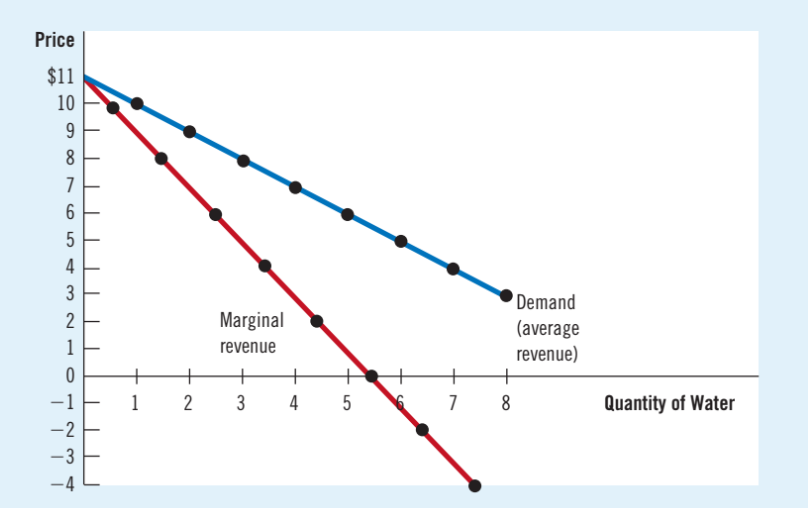
Q: A monopolist’s marginal revenue is _______ the price of its good
A: less than
The output effect
When more output is sold, Q is higher, which increases total revenue
The price effect
The price falls, so P is lower, which decreases total revenue
Q: Is a competitive firm affected by the price effect?
A: No. When production is increased by one unit, they receive market price, and do not receive less for units they were already selling. (Marginal revenue = price)
Q: Is a monopoly affected by the price effect?
A: Yes. When production is increased by one unit, they must charge less for every unit they sell, and receive less revenue for units they were already selling (Marginal revenue < price)
Monopoly profit maximizing
Profit is maximized at the intersection of the marginal revenue and marginal cost curve
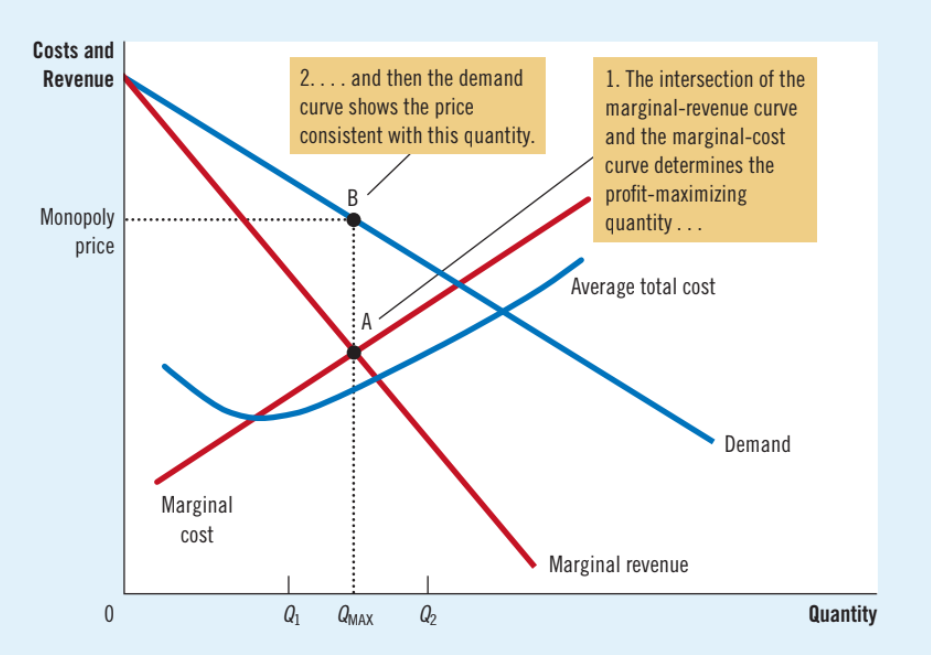
Q: In a competitive firm, price _____ marginal cost. In a monopolized market, price _______ marginal cost.
A: equals, exceeds
Profit formula
P = (P - ATC) X Q
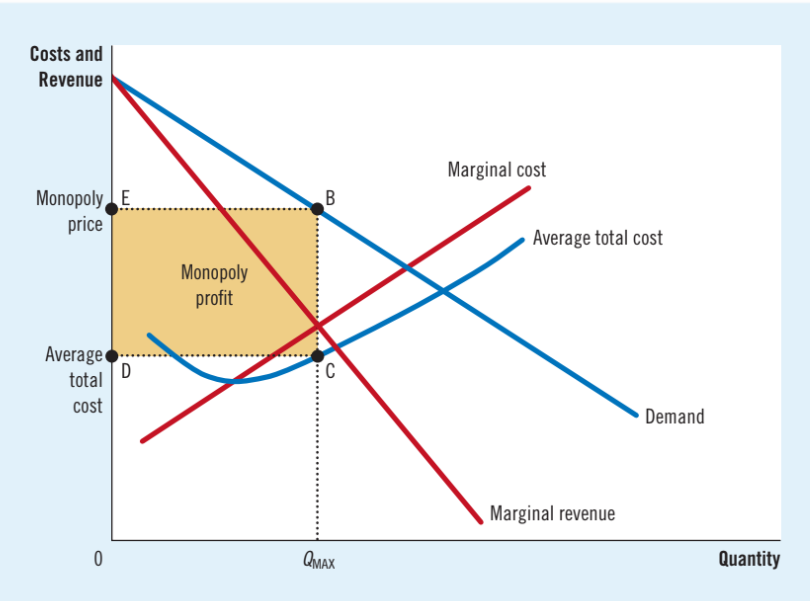
Profit maximizing rules for a monopolized firm
1. Derive the MR curve from the demand curve.
2. Find Q at which MR = MC.
3. On the demand curve, find P at which consumers will buy Q.
4. If P > ATC, the monopoly earns a profit.
Q: If a monopoly’s fixed costs increase, its price will ________ and its profit will _________.
A: Stay the same, decrease
Q: The monopolist produces ____ than the socially efficient quantity of output.
A: less
Q: Is monopoly profit a social cost?
A: Monopoly profit is not a social problem: producers are better off and consumers are worse off, but there is no change in total surplus.
Social cost of monopoly inefficiency
Monopolies produce and sell a quantity below the level that maximizes total surplus (inneficiently low amount of output)
Price discrimination
the practice of selling the same product at different prices to different consumers
Perfect price discrimination
The monopolist knows each customer’s exact willingness to pay and can charge each customer a different price, receiving all surplus
Q: When a monopolist switches from charging a single price to practicing perfect price discrimination, it reduces __________.
A: consumer surplus
Four ways the government responds to monopoly
Increasing competition through antitrust laws
Regulating behavior of monopolies
Public ownership
Doing nothing
Horizontal merger
a merger between two firms in the same market (more scrutinized)
Vertical merger
merger between firms at different points in the production process (less scrutinized)
Antitrust laws
group of statutes aimed at curbing monopoly power (Sherman Antitrust Act, Clayton Antitrust Act)
Synergies
benefits from a merger (lower administrative costs, lower production costs, etc)
Regulation
Government agencies regulate the price of monopolies
Problem with regulation
marginal cost and average total cost pricing both generate deadweight loss
Public ownership
Government-run monopoly
Problem with public ownership
The profit motive does a better job of ensuring firms are well run than the government system
Q: If regulators impose marginal cost pricing on a natural monopoly, a possible problem is that _________.
A: the firm will lose money and exit the industry