Leaving Cert Chemistry - Assignment 1 (LC HL Q5)
1/156
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Atomic Structure and Periodic Table, including trends, bonding, Radioactivity
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
157 Terms
what is diffusion?
the spontaneous spreading out of a substance due to the natural movement of its particles
briefly outline the contributions of greek philosophers to the discovery of the atom
all matter is made of tiny particles called atoms
no experiments
four elements - earth, fire, air, water
atomos - indivisible
briefly outline the contributions of john dalton (1766-1844) to the discovery of the atom
experiments on gases
atomic theory:
all matter is made of atoms
atoms are indivisible and small
atoms cannot be created or destroyed
elements are made of one of a kind atoms
atoms can join together to form compounds
briefly outline the contributions of william crookes (1832-1919) to the discovery of the atom
investigated cathode rays in a vacuum tube
two experiments
the maltese cross - saw something was hitting the back of the glass
the paddle wheel
concluded that radiation was coming from the negative terminal - cathode rays
they moved in straight lines towards anode
cathode rays cause the glass to fluoresce
briefly outline the contributions of george stoney (1826-1911) to the discovery of the atom
named electrons
briefly outline the contributions of jj thomson (1856-1940) to the discovery of the atom
investigated cathode rays
attracted to positive plate
cathode rays consist of negatively charged particles - electrons
plum pudding model
briefly outline the contributions of robert millikan (1868-1953) to the discovery of the atom
measured charge of electron
oil drop experiment - charged oil drop suspended between two charged plates
e/m calculated (charge/mass)
briefly outline the contributions of ernest rutherford (1871-1937) to the discovery of the atom
scattered alpha particles at a thin sheet of gold foil
nucleus
briefly outline the contributions of james chadwick (1891-1974) to the discovery of the atom
bombarded beryllium with alpha particles
observed a chargeless radiation emitted from the nucleus - neutrons
state two assumptions of daltons atomic theory
electrons revolve around the nucleus in fixed paths called energy levels
electrons normally occupy the lowest available energy level
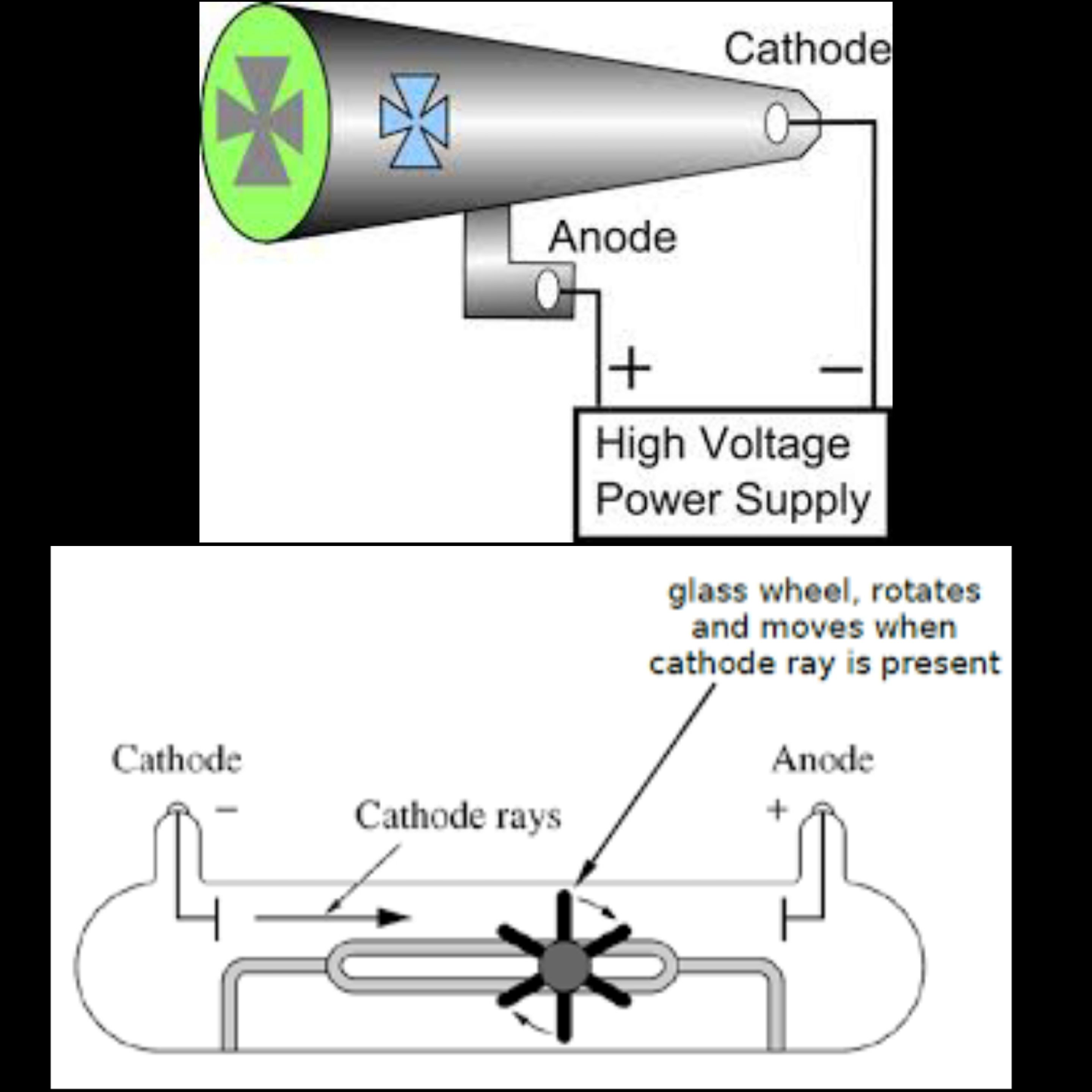
outline the experiment performed by crookes to discover cathode rays
maltese cross
saw something that was hitting the back of the glass
investigated the negative terminal of a - bettery in a vacuum tube (empty space)
the paddle wheel
established cathode rays
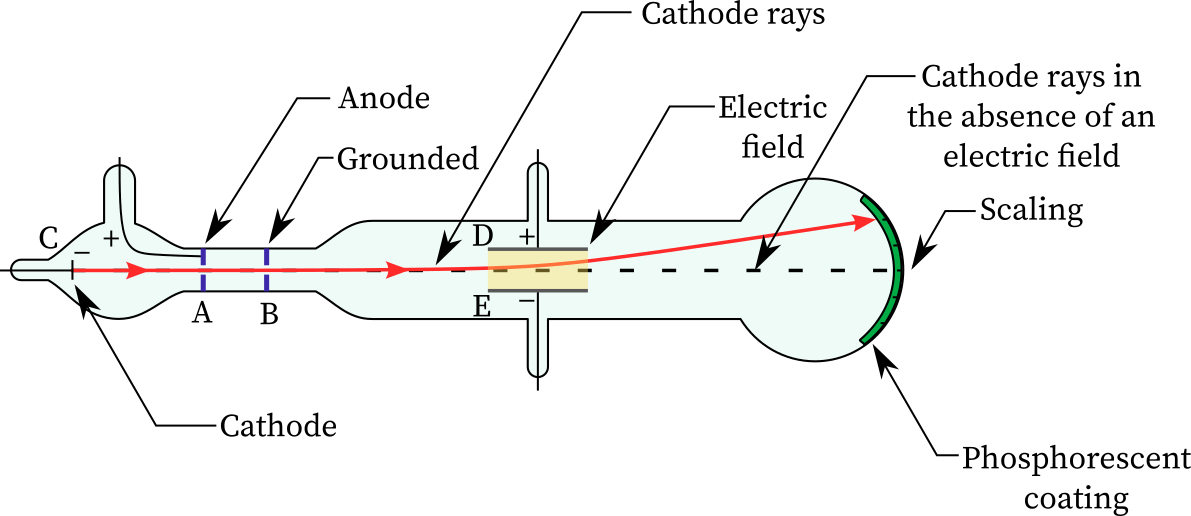
outline the experiment performed by jj thomson to discoverthe charge on cathode rays
investigated if cathode ray consisted of charged particles
observed cathode rays attracted to positive plate
concluded that cathode rays consist of negatively charged particles - electrons
what are cathode rays?
streams of negatively charged electrons which travel from the cathode to anode
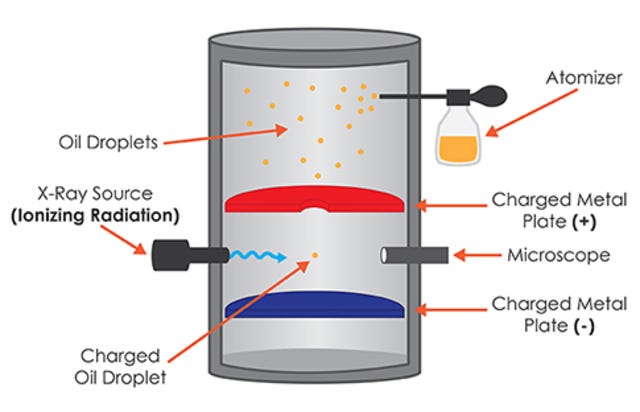
outline the experiment performed by millikan to measure the charge on an electron
oil drop experiment
investigated the size of a charge on the electron
charged oil drop suspended between two charged plates
e/m calculated (charge/mass)
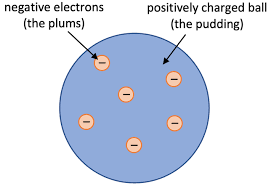
outline thomsons plum pudding model of the atom
sphere of positive charge with negatively charged electrons embedded in it
state three observations that rutherford made during his gold foil experiment
most alpha particles passed through the gold foil
some were deflected at large angles
a very small amount were deflected back along their own path - hit the nucleus head on
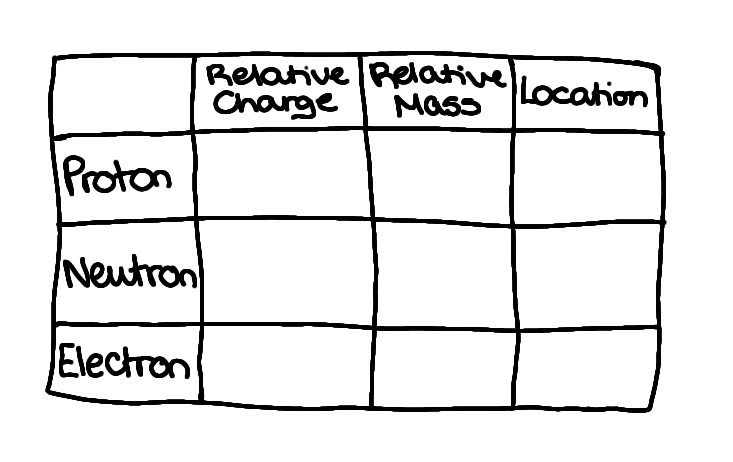
complete the table, which shows the properties of sub-atomic particles
proton: +1, 1, nucleus
neutron: 0, 1, nucleus
electron: -1, 1/1860, space outside the nucleus
outline bohrs atomic theory based on the hydrogen emission spectrum
electrons revolve around the nucleus in fixed paths called energy levels
while in a particular energy level, the energy of the electron is fixed/quanised
electrons normally occupy the lowest available energy level. they are said to be in their ground state
when an atom absorbs energy, electrons jump from a lower energy level to a higher energy level. they are then said to be in an excited state, which is temporary and unstable
state the characteristic colour given off by lithium when heated in the flame test
crimson
state the characteristic colour given off by potassium when heated in the flame test
lilac
state the characteristic colour given off by barium when heated in the flame test
green
state the characteristic colour given off by strontium when heated in the flame test
red
state the characteristic colour given off by copper when heated in the flame test
blue-green
state the characteristic colour given off by sodium when heated in the flame test
yellow
define energy level
a region of definite energy within the atom that electrons occupy
what is meant by the ground state of an atom
the lowest energy state for an electron
what is meant by the excited state of an atom
when an electron occupies a higher energy state than the ground state by absorbing enough energy
state what each symbol represents in the equation E2 - E1 = hf
E2 = energy of electron in excited state
E1 = energy of electron in ground state
h = Plancks constant
f = frequency of the light emitted
define atomic orbital
a region in the space of an atom where the probability of finding an electron is relatively high
name the following series of lines in emission spectrum of hydrogen: electron transitions are from higher energy levelsto n=2 and give rise to lines in the visible spectrum
balmer series
name the following series of lines in emission spectrum of hydrogen: electron transitions are from higher energy levels to n=1 and give rise to lines in the ultraviolet region of the spectrum
lyman series
name the following series of lines in emission spectrum of hydrogen: electron transitions are from higher energy levels to n=3 and give rise to lines in th infrared region of the spectrum
paschen series
how is an atomic absorption spectrum produced?
created when electrons transition from a low energy level to a high energy level since they absorb energy
what is a sublevel?
a subdivision of an energy level containing one or more atomic orbitals, all of equal energy
state heisenberg’s uncertainty principle
it is not possible to measure both the position and velocity of an electron, since doing one affects the other
state two limitations of bohr’s theory
only worked for hydrogen
subsequent discoveries:
energy sublevels
wave nature of the electron
uncertainty principle
orbitals
name this
s orbital
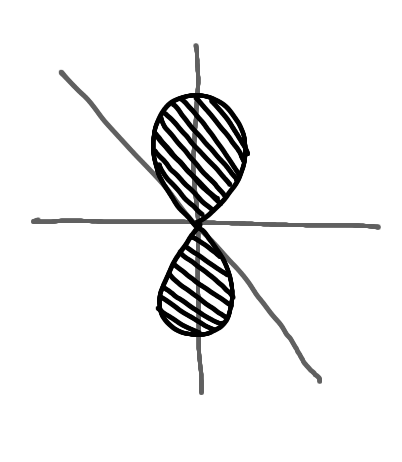
name this
p orbital
define an element
a simple substance that cannot be broken into anything simpler
what method did humphrey davy use to discover new elements?
passed electric current through a number of compounds. compounds split into their component elements
what contribution did dobereiner make to the systematic arrangement of the elements?
triads - placed elements with similar chemical properties into groups of three
the atomic weight of the middle one was approximately halfway between that of the other two
what contribution did newlands make to the systematic arrangement of the elements?
the law of octaves - arranged elements in order of atomic weights
noticed every eight element repeated properties
what is mendeleev’s periodic law?
when elements are arranged in order of atomic weight, their properties vary periodically
outline mendeleev’s work to construct a periodic table of elements
prioritised chemical properties over atomic weight
left gaps to ensure elements fit into the correct columns
predicted the properties of undiscovered elements
reversed the order of some elements to make them fit their column
state two differeces between mendleev’s periodic table and the modern periodic table of elements
mendeleev - in order of weight, modern - in order of atomic number
mendeleev - gaps for undiscovered elements, modern - no gaps
what contribution did henry moseley make to the systematic arrangement of elements?
used x-rays to discover the number of protons in the nuclei of atoms - atomic number
placed elements in order of increasing atomic number - no reversing
define atomic number
number of protons in an atom of that element
define mass number
average mass of the isotopes of the element
define relative atomic mass
the average mass of the isotopes of that element, taking their abundances into accouunt, compared to the carbon-12 isotope
a sample of chlorine is found to consist of 75% Cl-35 and 25% Cl-37. Calculate the average mass of an atom of chlorine
35.5
what is an isotope?
atoms of the same element (atomic number) with different mass numbers due to different numbers of neutrons in the nuclei
name the five processes that occur in a mass spectrometer
vapourisation
ionisation
acceleration
separation
detection
describe the five processes that occur in a mass spectrometer
vapourisation: the sample is turned into a vapour or gas
ionisation: electrons are removed from the atoms to form positive ions
acceleration: through a magnetic field
separation: the ions are separated according to their mass
detection: both the type and abundance of each type of ion is detected
state the principle of mass spectrometry
positive ions are accelerated through a magnetic field and separated according to their mass
state the aufbau principle
electrons always occupy the lowest available energy level first
state hund’s rule of maximum multiplicity
where two or more orbitals are available, electrons will occupy them singly before filling them in pairs
state the pauli exclusion principle
no more than two electrons may occupy an orbital and they must have opposite spin
write the electron configuration of hydrogen
1s1
write the electron configuration of helium
1s2
write the electron configuration of lithium
1s2 2s1
write the electron configuration of berryllium
1s2 2s2
write the electron configuration of boron
1s2 2s2 2p1
write the electron configuration of carbon
1s2 2s2 2p2
write the electron configuration of nitrogen
1s2 2s2 2p3
write the electron configuration of oxygen
1s2 2s2 2p4
write the electron configuration of fluorine
1s2 2s2 2p5
write the electron configuration of neon
1s2 2s2 2p6
write the electron configuration of sodium
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1
write the electron configuration of magnesium
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2
write the electron configuration of aluminium
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p1
write the electron configuration of silicon
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p2
write the electron configuration of phosphorous
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p3
write the electron configuration of sulphur
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4
write the electron configuration of chlorine
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p5
write the electron configuration of argon
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6
write the electron configuration of potassium
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1
write the electron configuration of calcium
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2
write the electron configuration of scandium
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d1 4s2
write the electron configuration of titanium
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d2 4s2
write the electron configuration of vanadium
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d3 4s2
write the electron configuration of manganese
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d5 4s2
write the electron configuration of iron
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d6 4s2
write the electron configuration of cobalt
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d7 4s2
write the electron configuration of nickel
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d8 4s2
write the electron configuration of copper
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s1
write the electron configuration of zinc
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2
write the electron configuration of gallium
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p1
write the electron configuration of germanium
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p2
write the electron configuration of arsenic
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p3
write the electron configuration of selenium
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p4
write the electron configuration of bromine
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p5
write the electron configuration of krypton
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6
write the electron configuration of chromium
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d4 4s1
define atomic radius
half the distance between the nuclei of two atoms of the same element that are joined together by a single covalent bond
give two reasons why the values of atomic radius increase as you go down a group in the periodic table
addition of a new energy level
screening effect of inner electrons
give two reasons why the valus of atomic radius decrease as you go across a period in the periodic table
increase in nuclear charge
no increase in screening effect
define first ionisation energy
the minimum energy required to remove the most loosely bound electron from a netural gaseous atom in its ground state
give two reasons why the values of first ionisation energy decrease as you go down a group in the periodic table
increasing atomic radius
screening effect of inner electrons
give two reasons why the values of first ionisation energy increase as you go across a period in the periodic table
increasing nuclear charge
decreasing atomic radius
explain why there are some exceptions to the general trend in first ionisation energy as you go across a period in the periodic table
a completely filled outer sublevel or half-filled outer sublevel gives an atom extra stability. thus it makes it more difficult to remove the most loosely bound electrons, resulting in higher ionisation energy