09 stress-stain, hookes law
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
density for steel
7.84 g/cm³
density for aluminum
2.7 g/cm³
density for polycarbonate
1.20-1.40 g/cm³
aluminum modulus in psi
10 × 10^6
steel modulus is psi
30 × 10^6
polycarbonate
500 × 10³
what is hookean?
the elastic part of the graph, usually linear
what is proportional limit (PL)
the maximum stress it can handle before it deviates from linear
what 3 things can happen after a proportional limit?
line is STILL elastic, but in a way it is deformed but NOT PERMANENTLY
linear
flat
non linear
ex: after stretching rubber band a few times, it goes back the way it was but wonky
what is recoverable strain?
elastic (material is not PERMANENTLY deformed, can still go back to before)
what is nonrecoverable strain?
plastic (deformed, no way to go back to original state)
what is yield stregth?
the point where plastic (permanent) deformation begins
after this point material DOES NOT return to original state
CANT be reversed
Stress us NECESSARY
What is UTS (ultimate tensile strength)
The highest stress a material can withstand
necking happens afterwards
What is ROA (reduction of Area)
Measures the material’s ductility, or ability to withstand plastic deformation before breaking
%ROA = (A0-Af)/A0 × 100
delta(area)/original area x 100
strain to failure
strain at which specimen is breaking
total strain at failure
elastic + plastic
stress strain curve in ceramics
linear behavior
high stress = low strain
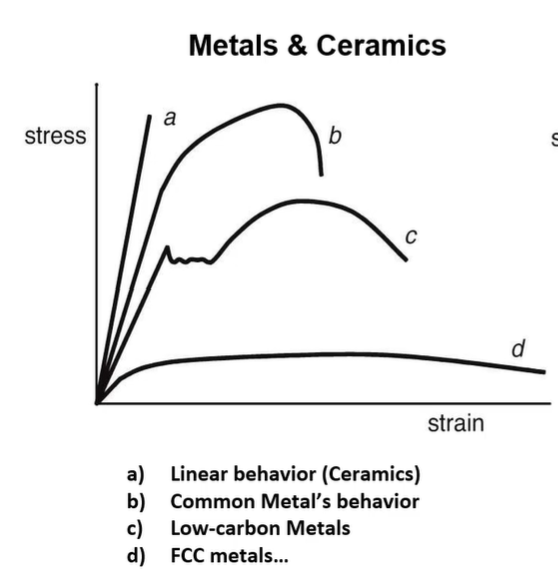
stress strain curve in common metal’s
curve
elastic, plastic, and breaking
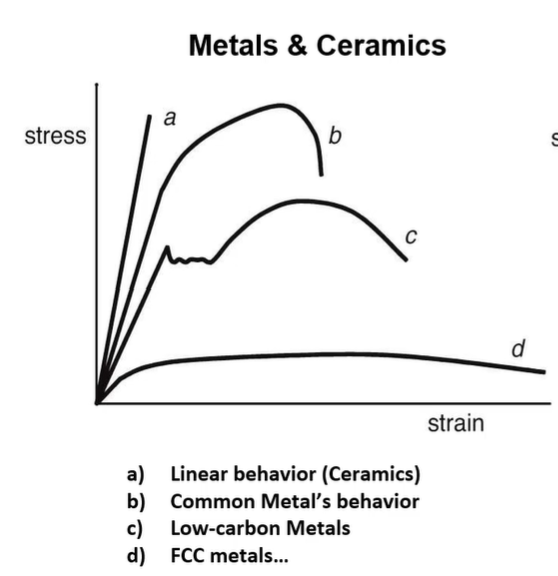
stress strain curve in low carbon metals
ups and down after yield point
curve → break
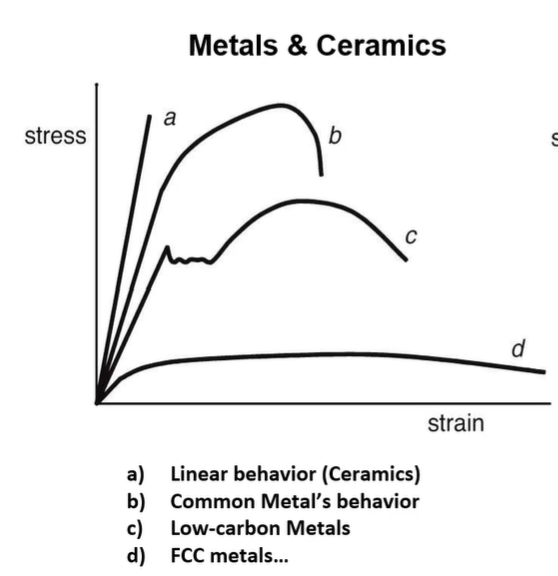
stress strain curve in FCC metals
low stress = high strain

What are the effects of temperature and strain rate in stress vs strain graphs?
As temperature increases = material gets softer (stretchy) = less stress to deform
higher temperature = more ductile, less brittle
What happens when strain rate is high?
atoms don’t have enough time to rearrange themselves, so it makes material stronger = stiffer
harder to deform
requires more stress
elastic deformation is due to ____?
applied stress
bond stretching
volume is NOT constant
because when stretched or compressed = atoms/shape is changing
usually v=0.3
plastic deformation is due to ____?
slipping of dislocations
volume WILL be constant
the only thing happening is the rearranging of atoms
v = 0.5
young modulus?
stress/strain
stretching/compression
what is strain?
HOW MUCH IT CHANGED
amount of deformation material experiences compared to its original size
change in length / original length
what is stress?
HOW MUCH FORCE IT TAKES before breaking
FORCE
what is yield behavior?
the point where a material starts to deform permanently
what causes yield behavior?
shear stress
yield behavior is the point where a material starts to deform, which shear stress is exactly that
shear stress = slipping of atoms that cause permanent deformation
Hooke’s law?
S = E x e
Stress = Young modulus (stress/strain) x strain
ONLY FOCUSED ON LINEAR PART OF GRAPH
When tension is happening what happens to Area?
gets smaller
When compression is happening what happens to Area?
area gets bigger
what happens when area gets smaller?
Force gets affected = gets smaller
Stress = rises
F = S (stress) x a (area)
Changing Area during test
S = F/Ao
Ao is inaccurate because it doesnt take into mind area changing after deformation
True Strain ?
ln (delta L / Lo) = Ln(1+e)
takes into mind that length is NOT constant (constantly changing)
True stress?
S (1 +e)
engineering stress = f/a
What is the main factor for slip step?
dislocations
what is the actual mechanism of plastic deformation?
dislocation movement through crystals
movement of dislocations cause slippage
Breaking INDIVIDUAL bonds NOT all at once
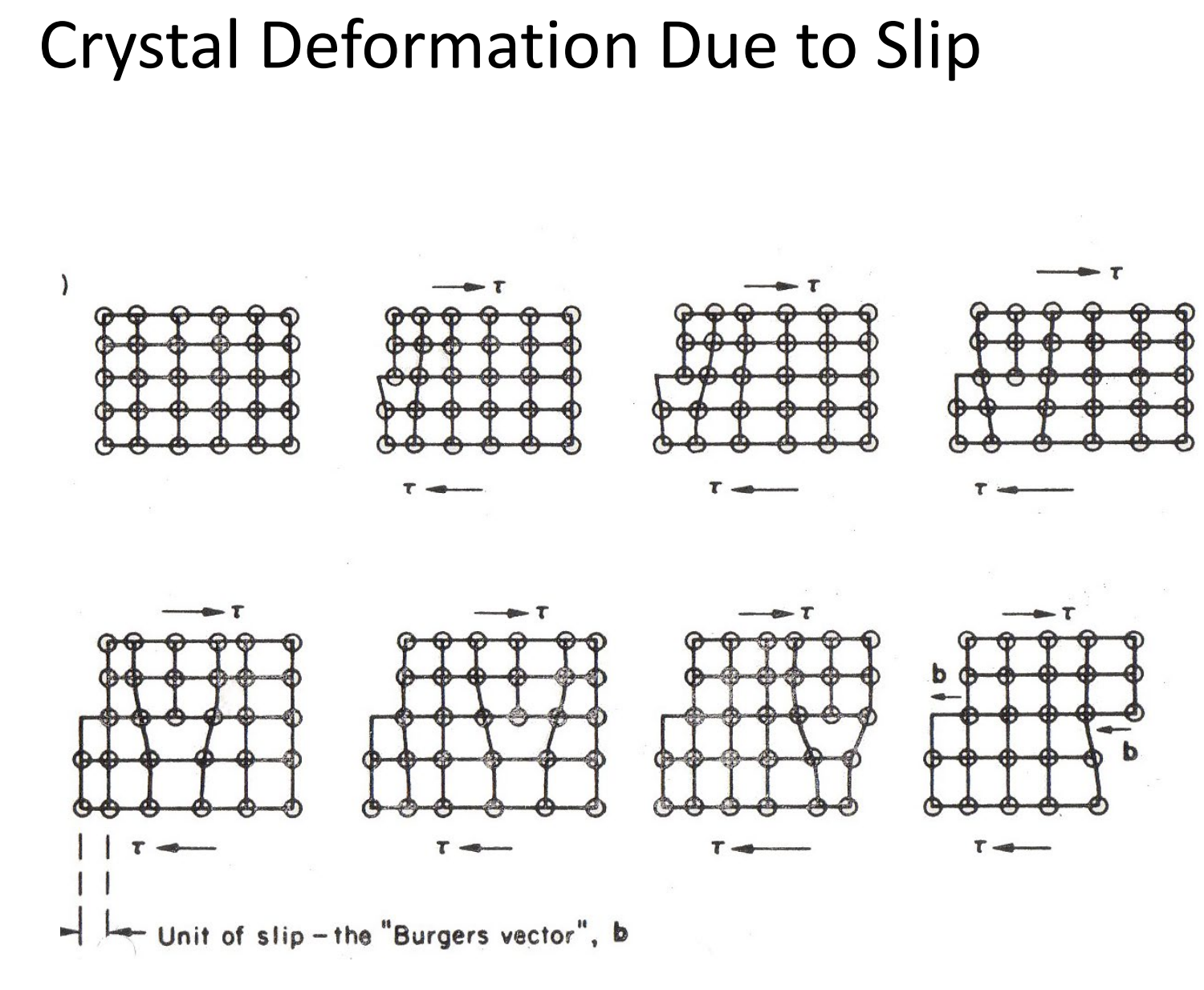
Where does slip happen on?
Slip systems
What are the requirements for slip to happen?
CLOSED PACKED PLANES
closed packed directions
what is dislocation?
extra half planes on crystal
if it moves = shear stress (slip)
Relation between FCC and Slip:
has MANY crystal planes (slip systems)
Very ductile = easy for ductility
Relation between BCC and Slip:
has an average amount of slip systems
not as ductile = harder for slip to happen
Relation between HCP and Slip:
very few slip systems
LESS ductility = hard to deform plastically
what happens to area in compression?
it expands (increases)
what happens to area in tension?
it decreases
what does true stress show?
shows real material behavior
Force ÷ changing (instantaneous) area