Cells and lymphoid organs
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
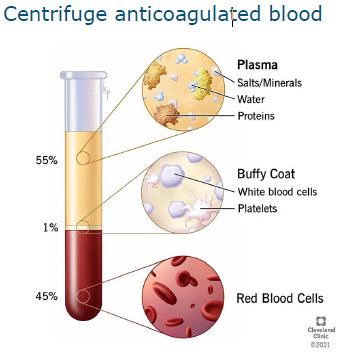
Isolation of immune cells form blood
Centrifuge anticoagulated blood
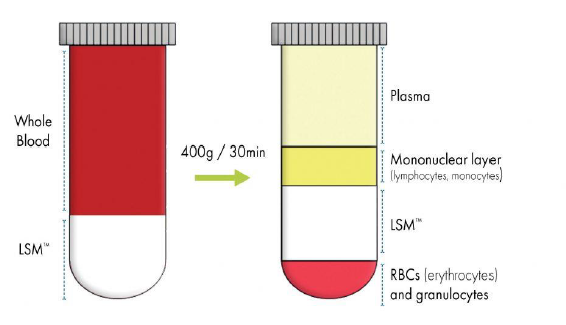
Isolation of leukocytes iwth density gradient
Cells of the immune system
Innate system comprises
Monocytes (macrophages)
granulocytes
Platelets
Dendritic cells
Natural killer cells
Cells of the immune system
Specific system comprises
T Cells or T lymphocytes
B cells or B lymphocytes
Sites of haematopoiesis
Before birth in the yolk sac, up to 2 months in humans
Liver and splee, 6-9 months
Bone marrow in vertebrate species, primary site of haematopoiesis and lymphopoeisis in adult life
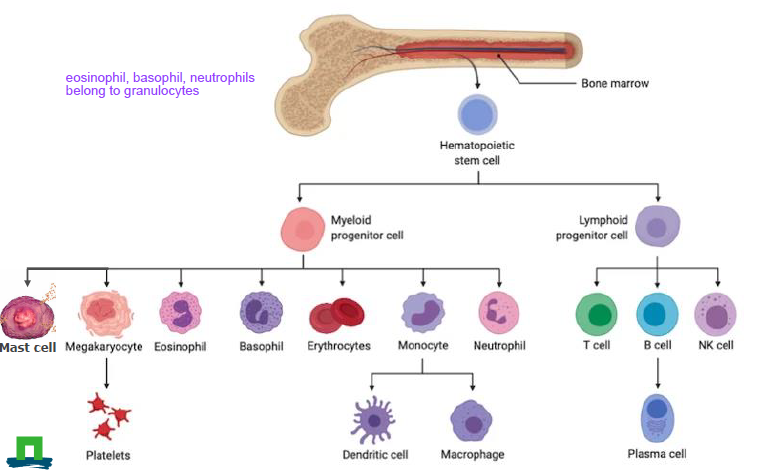
Haemmatopoiesis of white blood cells
Hematopoietic stem cell
myeloid progenitor cell
Mast cell
Megakaryocyte -→ platelets
Easoinophil
Basophil
Erythocytes
monotye → dendritic cell, macrophige
neutrophil
lymphoid progenitor cell
T cell
B cell → plasma cell
NK cell
Myeloid lineage
Granulocytes
nuetrophils (also konwn as polymorphonucelar cells (PMN;s)
eosinophils
basophils
Monocytes
macrophages
dendritic cells
Granulocytes: neutrophils
Major phaocytic cell
First cells that infiltrate an area of infection (bacterial infections)
Induce acute inflammation
MIlk white blood cell count in mastitis mainly due to neutrophils
Granules contain anitbacterial substances (e.g. lysozyme and proteases
granulocyte colony stimulating facto (G-CSF)
Pus contains many dead neutrophils
Granulocytes: eosinophils
Phagocytic cell
Target mainly helminth parasites, but plays also a role in allergic disease (asthma)
granules contain acid hydrolases (azurophilic granules)
degranulation stimulates also degranulation of other immune cells
located in blood, lungs, stomach, gut, skin
granulocytes: basophils
present in blood
least common granulocyte, around 1% of circulating white blood cells
involved in inflammatory immune responses and in acute and chornic allergic diseases
cells contain basophilic granules
granules contain histamin, heparin and serotonin
mast cells
look like basophils, but form a differen heamopoietic lineage
tissue resident cells (brain, blood brain barrier) intestines
contain granules with large amounts of histamin
involved in pathogen protection, allergy, angiogenesis, nut also involved in tissue repair
high affinity receptor fo immunoglobulin E (IgE)
Monocytes
found in blood
can diffferentiate into macrophages or dendritic cellsMa
macorphages
tissue resident cells
show a range of phenotypes from pro-inflammatory to anti-inflammatory
M1 and M2 paradigm
ANtigen presenting cells
dendritic cells
antigen presenting cells
monoctes respond via chemotaxis to
dead cell material (apoptotic cells)
microbes
complement deposition (C5a)
immune complexes
recruitment factors from T cells
M1 phenotype
bactericidal activity
inflammation
immunostimulation
anti-tumoral activity
LPS TNFA, IFNY
M2 phenotype
tissue repair
matrix remodeling
angiogenesis
immunosuppression
pro-tumoral activity
IL4/IL13, IL10, TGFB
Toll like receptors
innate cells, able to sense for conserved structres of pathogens
Opsonisation
Coating of a micorbe with either complement C3b, fibronectin, specific, or natural anitbodies to facilitate phagocytosis
Mechanisms of opsonization
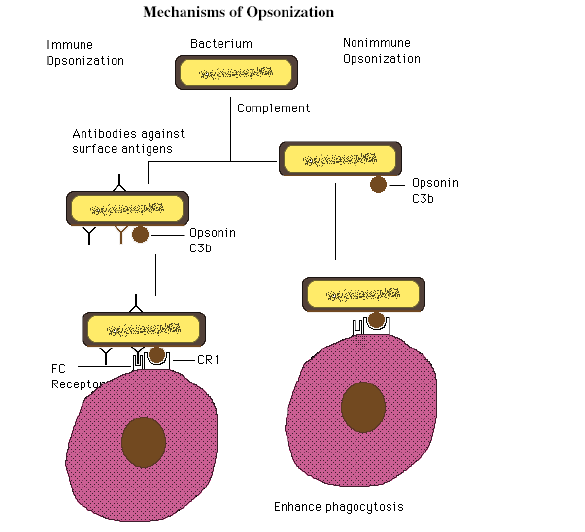
Opsonization: by complement factor C3b and immunoglobulines
Mac proteins, produced by streptococcus pyogenes, block attachment of C3b and immunoglobulins to receprors on macrophages
Phagocytosis process
Atttachemtn of the phagocyte to the pathogen
Ingestion of the pathogen
Fomration of phagosome
FOmration of phagolysozome
Destruction of pathogen and formation of residual body
Elimination of waste materials
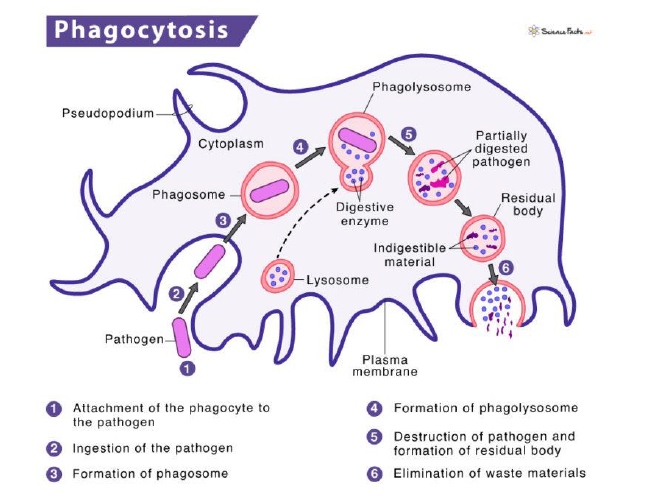
content phagolysozyme
about 50 different degraditve enzymes + other molecules, e.g.
catalase, O2, H2O2, OH-, NOX, myeloperoxidase, lactoferrin, colalgenase, elastase, lysozyme
Macrophages in tissues can be either derived from
blood monocytes or tissue resident macrophages are developed from the embryonic yolk sac and fetal liver
Lymphocyte-dendrite interaction
Dendritic cells activate lymphocytes in the secondary lymphoid organs
Antigen presenting cells
Dendrites, macrohpages, B-cellsA
Antigen presentation
Phagocytosis of microbe or macromolecule
partial degradation
presentation of parts via MHC class II molecules
To fitting TCR from T cellsL
Lymphoid lineage
B cells, T cells, NK cells
Lymphocytes, B and T cells can not be distinguished by light microscopy
B cells differentiate into plasma cells, which are the factoreis of antibodies
B cells mature in bone marrow or in Bursa of Fabricius in birds
T cells mature in the thymus
How ot distinguish between T cells and B lymphocytes
Using serological methods and monoclonal antibodies
monoclonal antibodies, recognize cell specific differentiation molecules: cluster of desingation CD
immunochemistry on cells or tissues
cytokine producton
cytokine mRNA
Lymphoid system
All are connected via blood and lymph vessels
Spleen, thymus, bone marrow, lymph nodes, peyers path, adenodis and appendix
drain tissues
Primary lymphoid organs
Production, maturation and education of lymphocytes
bone marrow, thymus, fetal liver, fetal yolk sac, bursa of fabricius(birds), kdiney (fish) peyers patches (in the intestines in sheep)
Secondary lymphoid organs
spleen
lumph nodes
mesenteric lymph node
intestines
tonsils
Secondary lymphoid organs are the sites where immune responses are initiated. Their main function is to facilitate the interaction between lymphocytes (B and T cells) and antigens — allowing the body to recognize and respond to pathogens effectively.
Head kidney in fish
priamry organ for haematopoiesis
Bone marrow (hallow bones)
haematopoiesis and lymphopoeisis and maturation (B cells)
filtratoino f blood, by macrophages, dendrites
containes mature T and B cells, antigen presenting cells (APC) and plasma cells
Bursa of Fabricius
primary lymphoid organ in birds
Proliferation and maturation of B - cells
contains follicles
degrades after a while
bursectomy results in
an impaired humoral immune ssytem
less circulating B cells
fewer specific antibodies
no formation of memory B cells
vulnerable for infectious diseases
Maternal IgG repertoire acts as
memory of infection history
Induction of specific IgM in offspring
early life protection
Specific serum IgM levels are decreased by bursal duct ligation at 2 weeks post hatch
Athymic mice and dogs
nude mice, lack T cell immunity
Mexican hairless dog, involution of thymus at veyr young age, no impaired immunity
human thymus with lobular structure
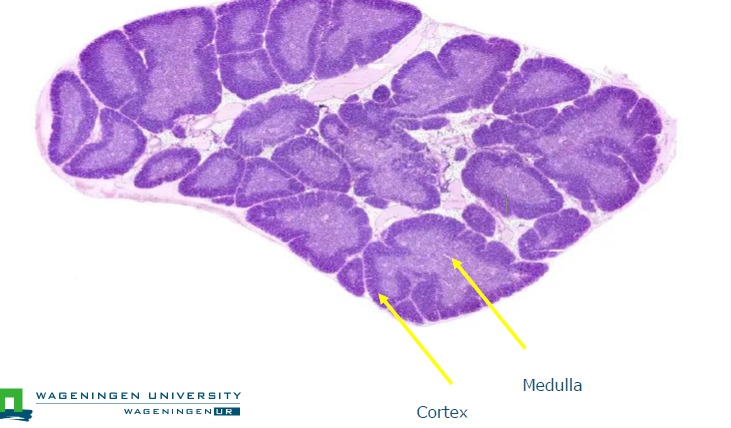
medulla and cortex
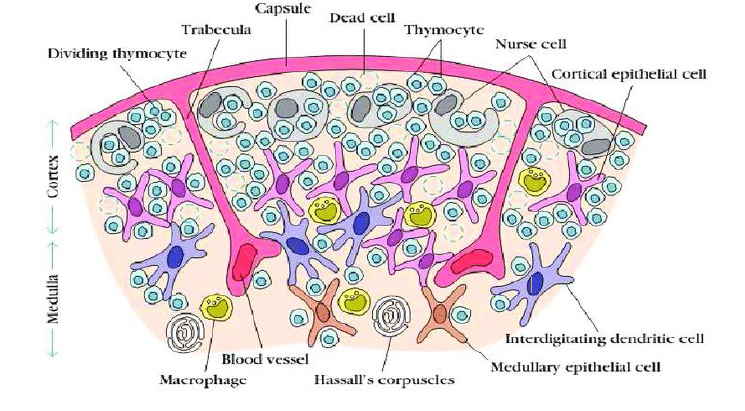
Histology of the thumus

Hassal’s bodies
concentrically arranged epithelial cells. probably play a role in producing regulatory T cells (Treg), may be also production of growth factors for T cells

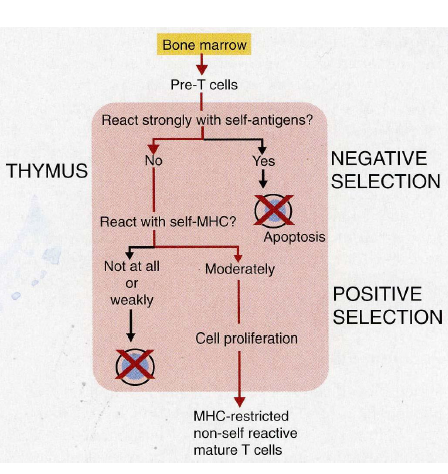
Positive and negative selection
Positive selection precedes neg selection, no correct order in figure
pos selection in corte
neg selection in medulla
AIRE
autoimmune regulator
expression of every self antigen by epithelial cells
Bone marrow: pre T cells (thymocyte) migrates towards thymus
proliferation >90% apoptosis
10% enter periphery
Migration of T cells from cortex to medulla
positive selection: TCR fits MHC
if not: death by apoptosis
negative selection: TCR fits MHC plus self-antigen: death by apoptosis
result: TCR fits MHC plus non-self: migration to periphery
Immunology thumsu
no access of foreign antigens into thymus
otherwise, induction of tolerance
so, there is no immune response int he thumus
or inducing holes in the repertoire by depletion of T cells
Peyers patches in lambs are
primary lympod organs
Function and anaotymy of the spleen
antigen filter for the blood (blood-borne pathogens)
therefore, no afferent lymphatic vessels, in contrast ot lymph nodes
encapsulated and compartmentalized viseral organ
trabaecula, connective tissue: framework for splenic structure
red pulp: resrvoir of erythrocytes and platelets
white pulp: lumphoid tissue
drains and filters blood
consists of white and red pupa regions
degradation old erythoryctes and thrombocytes (red pulpa)
no drainage by lymphatic vessels
Spleen - overview picture
white pulpa
rreservoir for red blood cells and platelets
contains periarteriolar lymphatic sheaths (PALS) - T cellr egion close to arteriolar blood vessels
Red pulp
reservoir for red blood cells and platelets
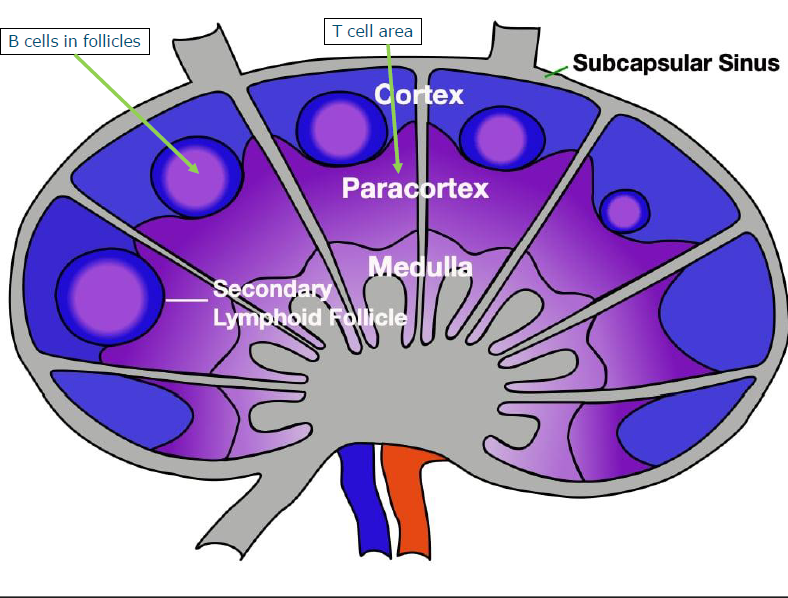
Lymph nodes
encapsulated
strategically located aruond the body
conected - network
filters atnigens in lymph fluid
lymph fluid contains also antigen presenting cells (dendritic cells)
cortex contains primary and secondary follicles and is surrounded by paracortex
germinal centers: secondary follicles with activated and maturing B cells
Migration of dendritic cells
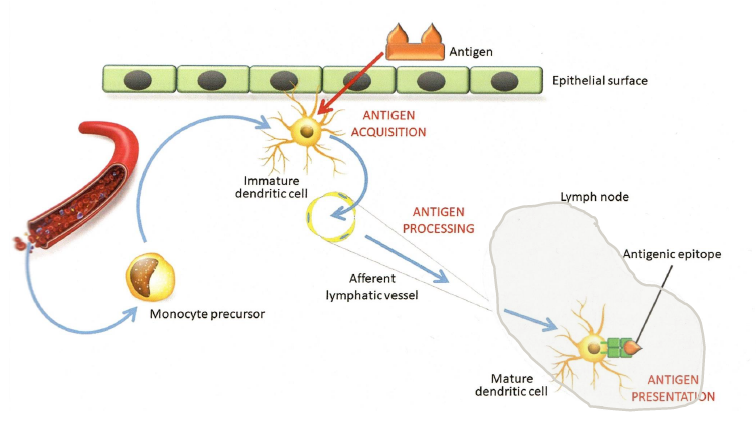
Homing of lymphocytes
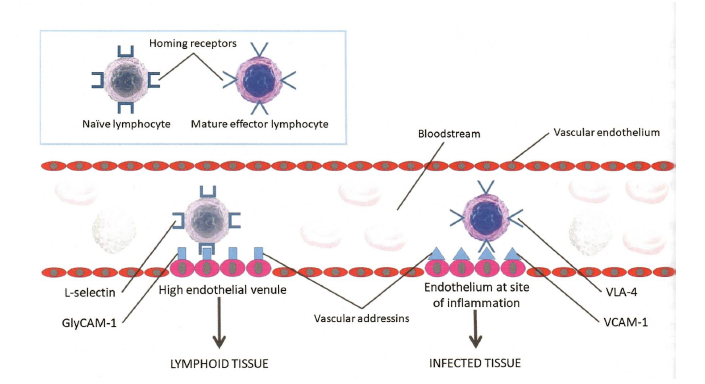
Model for homing of lymphocytes
HOming receptors deterine migration pattern
type of homing receptors depends on developmental stage of the lymphocyte
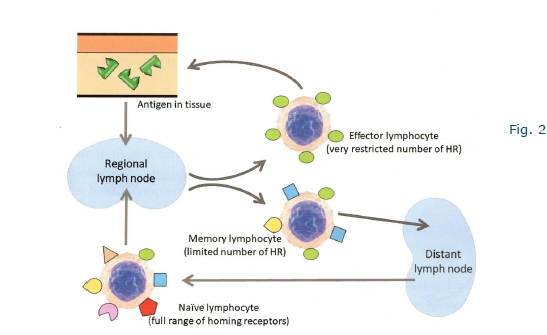
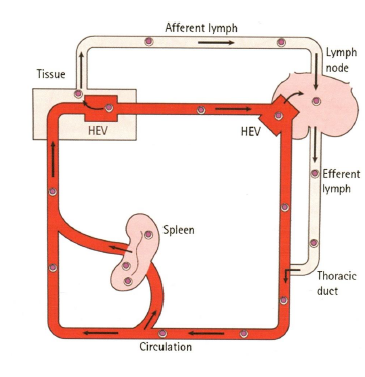
lymphocyte recirculation
HEV’S high endotelial venules
exhcange between bloodstream and lymphatic system
allows immune surveillance, naive lymphocytes enter the secondary lympod organs via HEV’S