16 Bariatric Surgery, 17 Orthopedic Surgery, 18&19 Critical Care/Ventilation
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
THANKS ERIN FOR QUESTIONS <3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Which of the following best describes the anatomic and absorptive differences between Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding?
A. Roux-en-Y bypasses the duodenum and proximal jejunum, leading to malabsorption of iron and calcium, while lap banding preserves normal GI anatomy and absorption
B. Both procedures remove a portion of the small intestine, leading to similar risks of nutrient malabsorption
C. Lap banding limits absorption by delaying gastric emptying and bypassing the pylorus
D. Roux-en-Y only restricts stomach volume and has minimal impact on nutrient absorption
A. Roux-en-Y bypasses the duodenum and proximal jejunum, leading to malabsorption of iron and calcium, while lap banding preserves normal GI anatomy and absorption
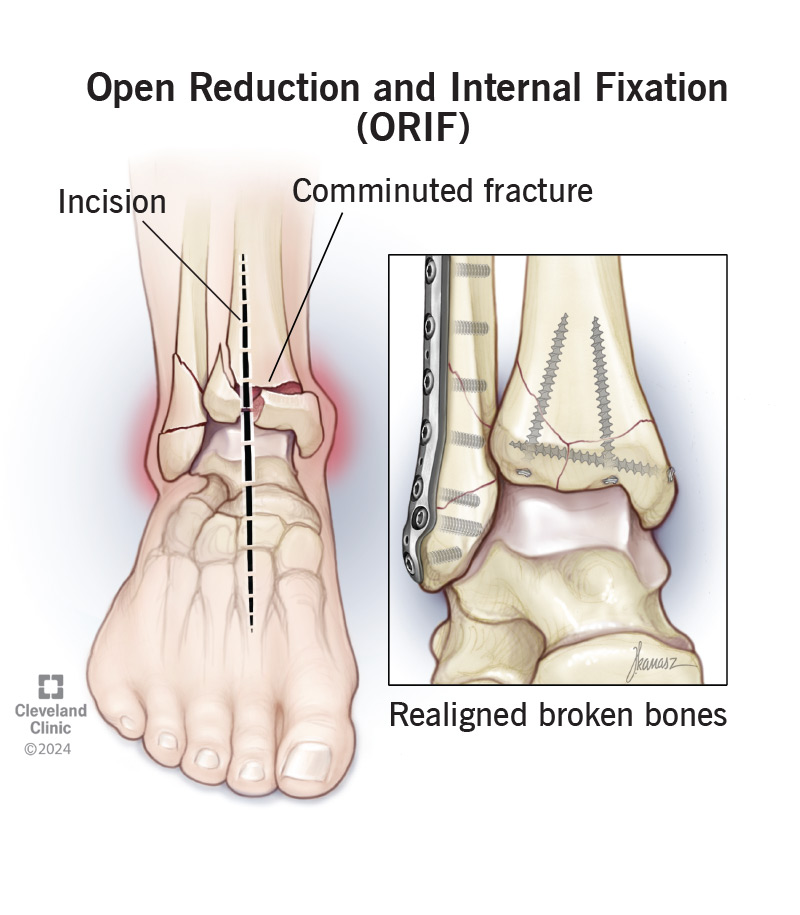
What is the gold standard treatment for unstable, displaced fractures involving joints?
A. Percutaneous pinning
B. External fixation
C. ORIF
D. Arthrodesis
C. ORIF open reduction internal fixation
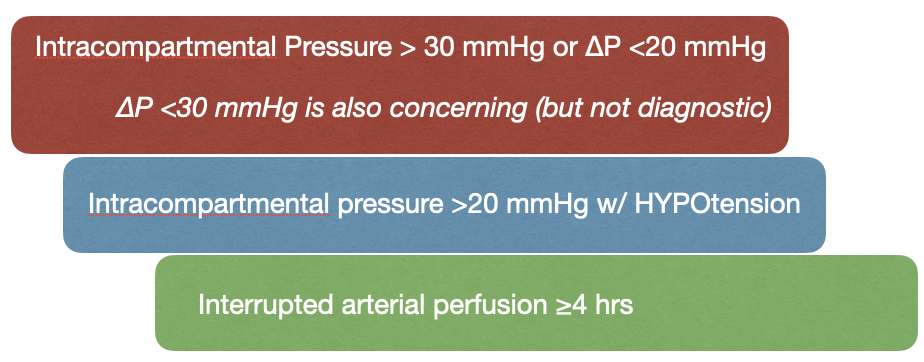
What is the diagnostic threshold pressure for compartment syndrome?
A. >10 mmHg
B. >20 mmHg
C. >30 mmHg
D. <10 mmHg
C. >30 mmHg
What is the typical treatment for mallet finger?
A. ORIF
B. Closed reduction
C. Stack splint for 10–12 weeks
D. Percutaneous pinning
C. Stack splint for 10–12 weeks
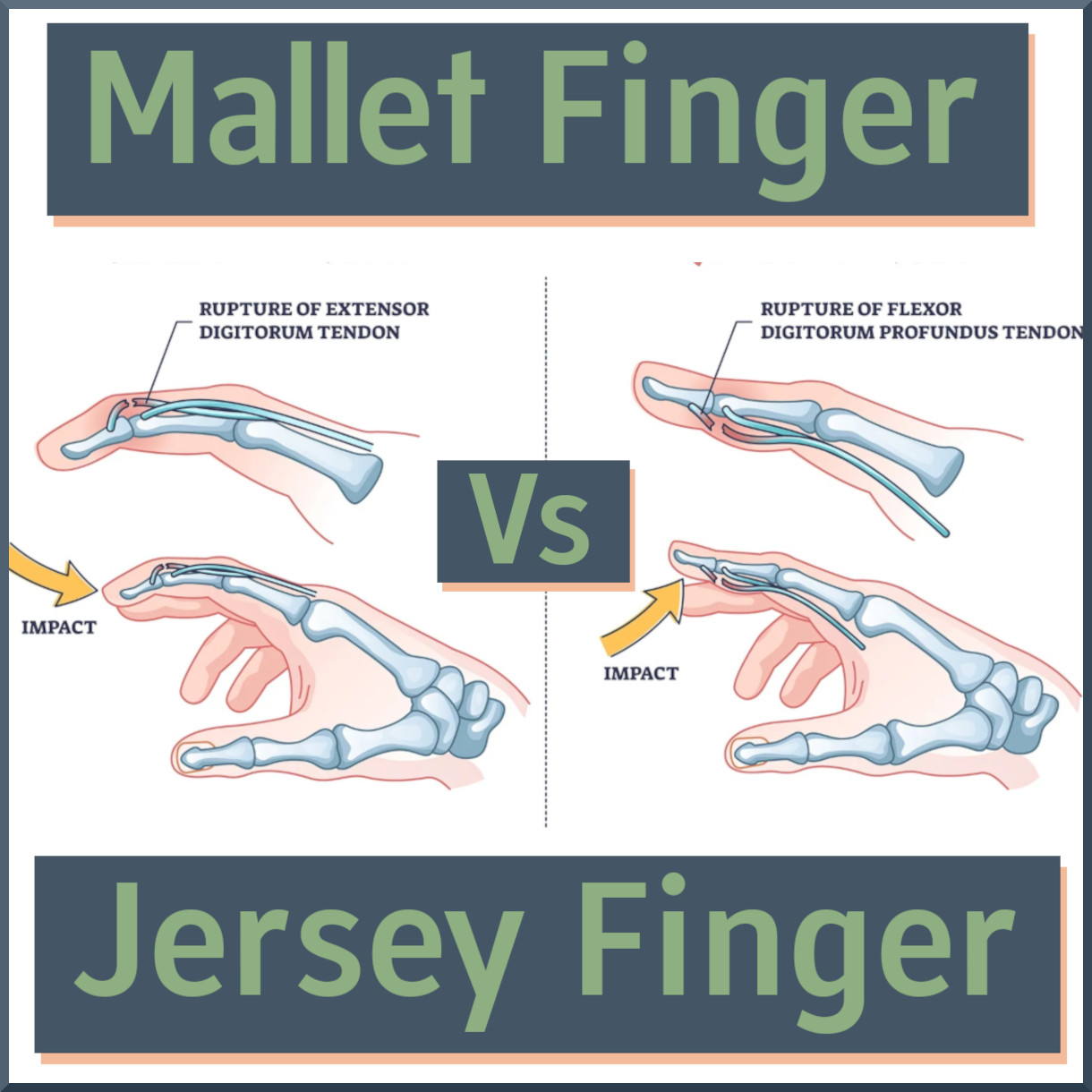
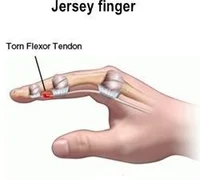
Jersey finger involves rupture of which structure?
A. ECRB
B. Extensor DIP
C. FDP tendon
D. Collateral ligament
C. FDP tendon
Which of the following is NOT a common indication for arthroscopy?
A. Meniscus repair
B. Loose body removal
C. Joint tumor resection
D. Synovial biopsy
C. Joint tumor resection
Which physical finding is associated with DIP joint osteoarthritis?
A. Bouchard nodes
B. Swan neck deformity
C. Heberden nodes
D. Boutonniere deformity
C. Heberden nodes
What is the most common primary cancer site metastasizing to bone in adults?
A. Prostate
B. Pancreas
C. Colon
D. Liver
A. Prostate
What is the most common cause of poor prosthesis fit post-amputation?
A. Muscle spasm
B. Phantom pain
C. Infection
D. Stump edema or contracture
D. Stump edema or contracture
Which of the following is an indication for Non-Invasive Positive Pressure Ventilation (NIPPV)?
A. Inability to protect airway
B. Active vomiting
C. Increased work of breathing
D. Untreated pneumothorax
C. Increased work of breathing
Which medication is commonly used as an induction agent for intubation?
A. Ketorolac
B. Succinylcholine
C. Etomidate
D. Atropine
C. Etomidate
💡 Explanation:
Etomidate is a sedative-hypnotic induction agent used during rapid sequence intubation (RSI):
Onset: 30–60 seconds
Duration: 5–10 minutes
Hemodynamically stable (little effect on BP or HR)
Often used in critically ill or unstable patients
❌ Incorrect Answers:
A. Ketorolac – NSAID for pain; not used in intubation.
B. Succinylcholine – Paralytic agent, not an induction/sedative. Often used after giving etomidate.
D. Atropine – Anticholinergic; may be used in pediatric intubation to prevent bradycardia, but not an induction agent.
Which paralytic is used during rapid sequence intubation (RSI)?
A. Etomidate
B. Propofol
C. Succinylcholine
D. Fentanyl
C. Succinylcholine