CSA Test 1 Review Definitions
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Algorithm
A step-by-step description of how to accomplish a task.
Program
A list of instructions to be carried out by a computer.
Digital
Based on numbers that increase in discrete increments, such as the integers 0, 1, 2, 3, etc.
Binary Number
A number composed of just 0s and 1s, also known as a base-2 number.
Program Execution
The act of carrying out the instructions contained in a program.
Compiler
A program that translates a computer program written in one language into an equivalent program in another language (often, but not always, translating from a high-level language into machine language).
Java Virtual Machine (JVM)
A theoretical computer whose machine language is the set of Java bytecodes.
Java Runtime
A program that executes compiled Java bytecodes.
Java Class Libraries
The collection of preexisting Java code that provides solutions to common programming problems.
Console Window
A special text-only window in which Java programs interact with the user.
Class
A unit of code that is the basic building block of Java programs.
Method
A program unit that represents a particular action or computation.
Statement
An executable snippet of code that represents a complete command.
Identifier
A name given to an entity in a program, such as a class or method.
Comment
Text that programmers include in a program to explain their code. The compiler ignores comments.
Decomposition
A separation into discernible parts, each of which is simpler than the whole.
Iterative Enhancement
The process of producing a program in stages, adding new functionality at each stage. A key feature of each iterative step is that you can test it to make sure that piece works before moving on.
Static Method
A block of Java statements that is given a name.
Method Call
A command to execute another method, which causes all of the statements inside that method to be executed.
Flow of Control
The order in which the statements of a Java program are executed.
Data Type
A name for a category of data values that are all related, as in type int in Java, which is used to represent integer values.
Expression
A simple value or a set of operations that produces a value.
Evaluation
The process of obtaining the value of an expression.
Operator
A special symbol (like + or *) that is used to indicate an operation to be performed on one or more values.
Precedence
The binding power of an operator, which determines how to group parts of an expression.
Variable
A memory location with a name and a type that stores a value.
Declaration
A request to set aside a new variable with a given name and type.
String Concatenation
Combining several strings into a single string, or combining a string with other data into a new, longer string.
Control Structure
A syntactic structure that controls other statements.
Scope
The part of a program in which a particular declaration is valid.
Local Variable
A variable declared inside a method that is accessible only in that method.
Localizing Variables
Declaring variables in the innermost (most local) scope possible.
Infinite Loop
A loop that never terminates.
Pseudocode
English-like descriptions of algorithms. Programming with pseudocode involves successively refining an informal description until it is easily translated into Java.
Class Constant
A named value that cannot be changed. A class constant can be accessed anywhere in the class (i.e., its scope is the entire class).
Class Header
public class MyClass{}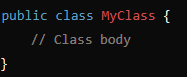
Method Header
public static void MyMethod{}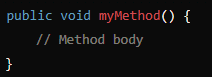
string precedence
string → double → intInitializing Variable
assigning a value to the variable
Declaring Variable
showing the variable exists without assigning a value