The Human Gait | Exam 2
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
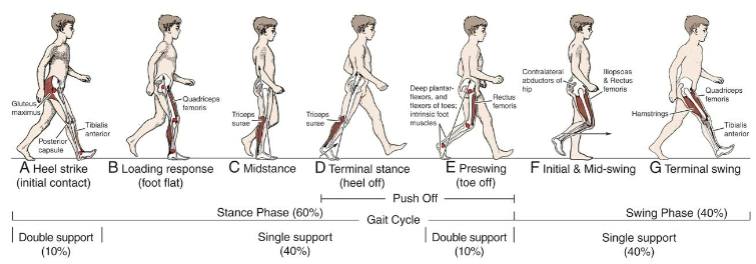
What two phases are in a single gait cycle
Stance phase and swing phase
What percentage of a single gait cycle is the stance phase?
60%
What percentage of a single gait cycle is the swing phase?
40%
What components are part of the stance phase?
heel strike
foot flat
toe of
what components are part of the swing phase
acceleration
deceleration
Draw the gait cycle
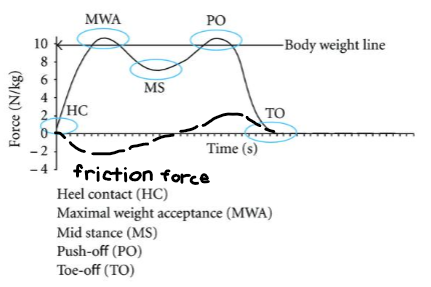
Draw the graph for a normal gait cycle and its ground reaction forces. Label/explain the grab
What variables are most commonly used to describe gait patterns
step length
stride length
velocity
walking base
cadence
foot angle
what is step length
the distance between the point of one foot and the point of initial contact of the opposite foot.
In a normal gait, R and L have similar step length.
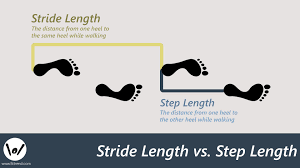
what is stride length
distance between successive points of initial contact of the same foot
L and R are normally equal
what is velocity
product of cadence and step length
what are the units of velocity
distance/time
what does “free speed” mean
the individual’s comfortable walking speed
what is walking base
the sum of the side-to-side distances from the points of initial contact of the right and left feet
what is cadence
walking rate
what are the units for cadence
steps/min
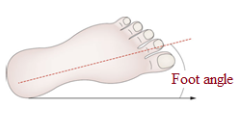
what is foot angle (toe out)
an angle between the line of progression and a line drawn between the midpoints of the calcaneus and the second metatarsal head
external forces acting on a runner (draw the diagram)
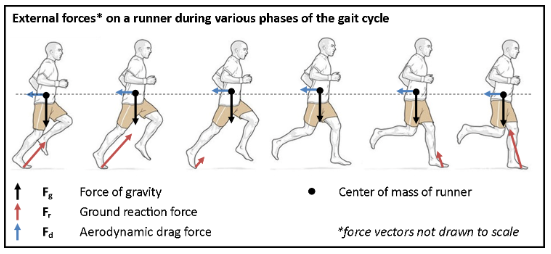
The six determinants (features of the movement pattern that minimize displacement in the body’s center of gravity during gait)
pelvic rotation
lateral pelvic tilt
knee flexion in stance
knee ankle foot interactions
hip and knee interactions
physiological genu valgus
kinematic features that produce an efficient walking pattern
double limb support
pelvis rotated forward on the side
mid-stance and mid-swing
pelvis tilted downward laterally toward the swing limb
what happens during double limb support
the center of gravity is at its lowest point
lower extremity lengths are maximized
what happens when the pelvis is rotated forward on the side
the limb is in loading response
backward on the limb which is in pre-swing
what happens during mid-stance and mid-swing
center of gravity is highest
the stance limb’s hip, knee, and ankle are all flexed 5 degrees
what happens when the pelvis is tilted downward laterally toward the swing limb
minimizes the center of gravity’s upward excursion
keeps COG lower than if the individual were standing erect
COG during walking
COG is propelled forward
COG also moves laterally and vertically
gait is most energy efficient when vertical and lateral displacement is minimized
What is Trendelenburg?
When the left hip drops, it’s a positive right trendelenburg sign
cause of trendelenburg?
weakness of the abductor muscles (gluteus medius and minimus)
lesion of superior gluteal nerve
What is steppage equines gait
the walking gait of patients with foot drop
causes of steppage equines gait
peroneal fibular nerve injury
weakness of the tibialis anterior muscle
what is antalgic gait
the way to avoid pain while walking