BY 124- Gibbons Ch 27- Bacteria and Archaea
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
What is a key difference between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes?
A. Eukaryotes are smaller than Prokaryotes
B. Prokaryotes have membrane bound organelles and Eukaryotes do not
C. Prokaryotes have circular chromosomes and Eukaryotes have linear chromosomes
D. Prokaryotes have a nucleus and Eukaryotes have a nucleoid
C. Prokaryotes have circular chromosomes and Eukaryotes have linear chromosomes
Prokaryote Characteristics
Prokaryote characteristics:
Single celled
Smaller than eukaryotes
Variety of shapes
Cocci (circular)
Bacilli (rod-shaped)
Spiral
Can achieve all of life’s functions in a single cell
Prokaryote Cell Wall
In Bacteria, cell walls contain peptidoglycan
In Archaea, cell walls have no peptidoglycan
Eukaryote Cell Wall
Fungi cell walls are made of chitin
Plant cell walls made of cellulose
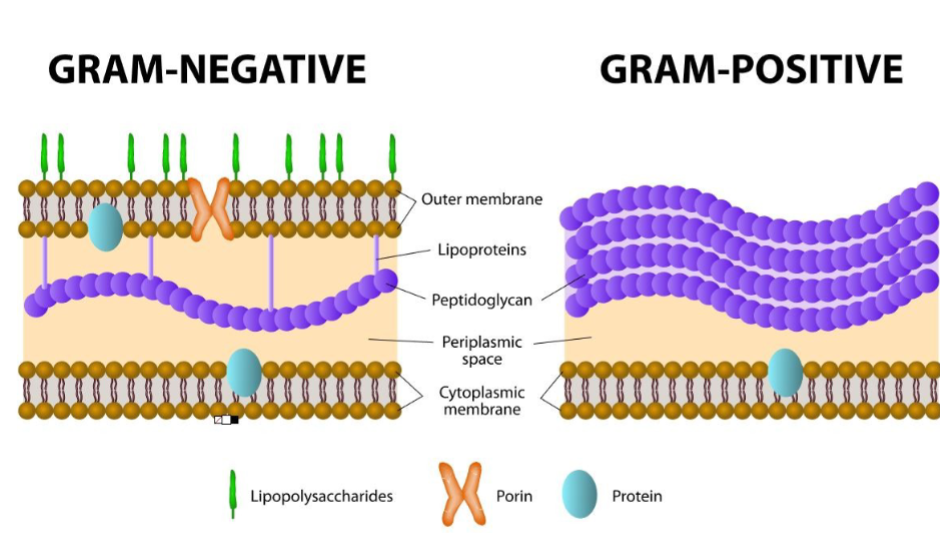
Gram-positive vs Gram-negative
Gram-positive: simple cell wall structure, thick layer of
peptidoglycan
Gram-negative: less peptidoglycan, more complex with
an outer membrane
Actions of antibiotics are different for gram-positive and –negative bacteria (gram negative are usually more resistant)
Antibiotics usually affect peptidoglycan, so don’t impact
human cells
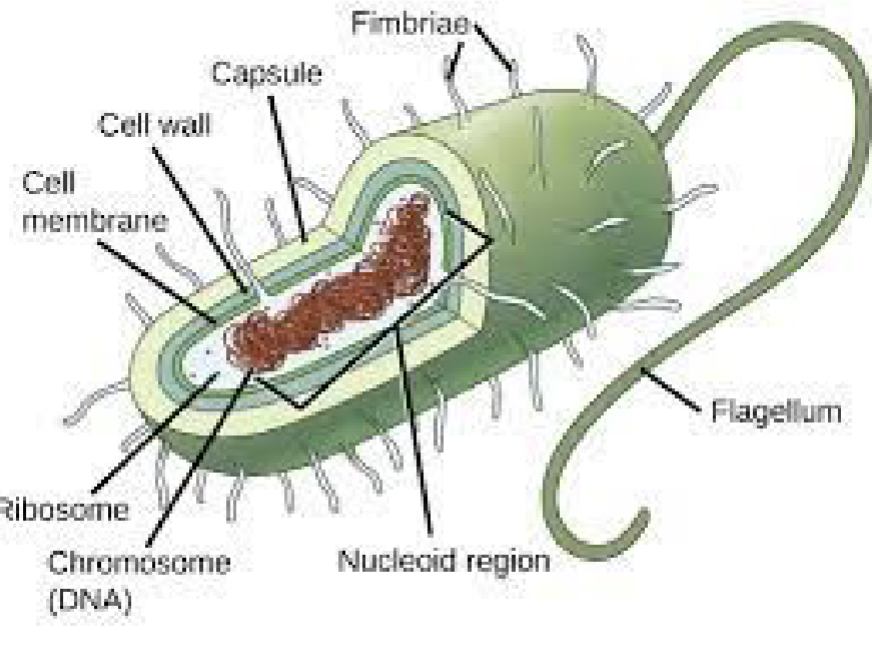
Prokaryote Capsules and Endospores
Capsule/slime layer
outer layer allowing adherence to substrate or other bacteria
Endospore:
Chromosomes copied and surrounded by protective structure
Formed when bacteria become inactive in sparse conditions
Withstands extreme conditions
Prokaryote Fimbriae and Sex Pili
Fimbriae:
hairlike appendages
allow them to stick to their substrate/other individuals
• Pili (or sex pili):
longer than fimbriae
pull cells together for exchange of DNA
Prokaryote Motility and Movement
Taxis: the ability to move toward or away from a stimulus
Flagella: structure used by prokaryotes for movement.
Prokaryote Internal Organization
Simple structure, no membrane-bound organelles
Smaller genome (less DNA) than eukaryotes
One circular chromosome; eukaryotes have multiple linear chromosomes
Lack a nucleus; the chromosome is in the nucleoid
May have plasmids: small rings of DNA
Differences in DNA replication, transcription and translation from Eukaryotes
Allow antibiotics to kill or inhibit bacterial cell growth without harming human cells
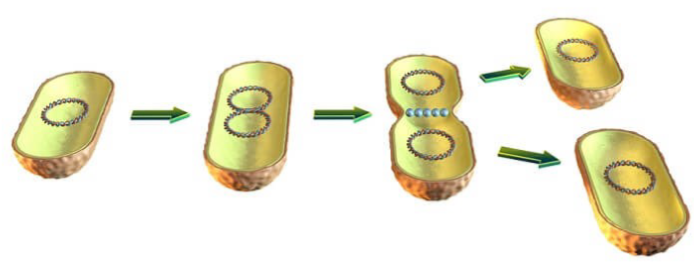
Prokaryote Reproduction
Binary fission (as fast as every 1–3 hours!!)
There are three key features of rapid prokaryote reproduction:
They are small
They reproduce by binary fission
They have short generation times
Genetic Diversity in Prokaryotes
Prokaryotes are incredibly diverse in forms and adaptations
Three factors are responsible
Rapid reproduction
Mutation
Genetic recombination
Prokaryote Reproduction and Mutation
Variations arise through mutation
Mutation rates are low, but can accumulate quickly in large populations with rapid reproduction
Leads to natural selection/adaptation in challenging environments
Prokaryote Genetic Recombination
Genetic Recombination: combining of DNA from 2 sources
Transformation
Transduction
Conjugation
Horizontal gene transfer
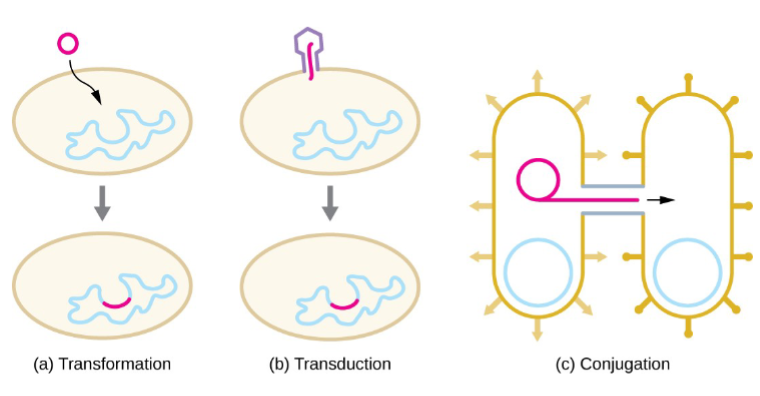
Prokaryote Genetic Recombination - Transformation
Incorporation of foreign DNA
Prokaryote Genetic Recombination - Transduction
Viruses carry genes from one host cell to another
Prokaryote Genetic Recombination - Conjugation
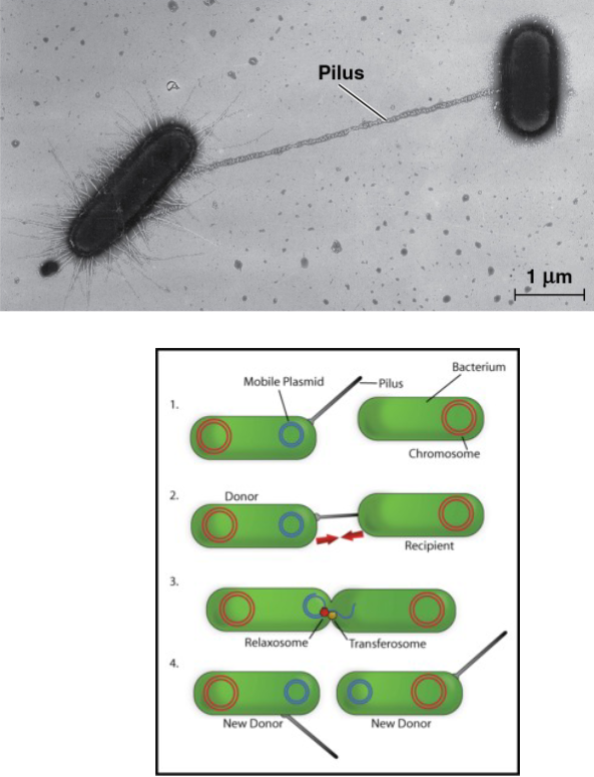
Conjugation: DNA is transferred between two prokaryotic cells
E. coli steps:
pilus of the donor cell attaches to the recipient
pilus retracts
DNA is transferred through a temporary structure called the “mating bridge”
Which of the following forms of genetic recombination in Prokaryotes involves viruses?
A. Transformation
B. Transduction
C. Conjugation
D. Binary Fission
Transduction
Prokaryote Genetic Recombination - Horizontal Gene Transfer
movement of genes from one organism to another (different species)
can occur through transformation, transduction, or conjugation
can spread genes associated with virulence to normally harmless bacteria (E. coli)
Nutritional Modes of Prokaryotes
Photoautotroph: Light as energy source, photosynthesis (uses CO2)
Chemoautotroph: Inorganic chemicals as energy source (e.g., H2S), uses CO2
Thermal vents!
Photoheterotroph: Light as energy source, but takes in organic compounds through “eating” for Carbon source
Chemoheterotroph: Organic compounds for energy and source of Carbon
Most bacteria are in this category
Diversity of Prokaryotes: Archaea versus Bacteria
The use of ribosomal RNA as a marker for relationships (1970s)
Some “bacteria” were more closely related to eukaryotes than others (now categorized as Domain Archaea)
Horizontal gene transfer has played a large role in bacterial diversity!
Most genes in bacterial genomes (75-80%) have been transferred horizontally at some point
Which Domain is more closely related to Eukaryotes?
A. Bacteria
B. Archaea
B. Archaea
Extremophile Archaea
Many Archaea inhabit extreme conditions unsuitable for other
species
Extreme halophiles- occupy environments (lakes) with very high amounts of salt
Extreme thermophiles- occupy environments with very high temperatures
Ecological Roles of Prokaryotes include:
decomposers
symbiosis
host or parasite
mutualism
commensalism
parasitism
pathogens
Beneficial Prokaryotes
Mutualistic Bacteria in the gut: up to 1000 species of bacteria
Help us digest food
Synthesize vitamins and carbohydrates, etc
Involved in signaling absorption of nutrients from small intestine
We have 10x more bacteria than human cells in our body!
Harmful Prokaryotes
Pathogenic Bacteria release endotoxins, causing:
Tuberculosis (lung disease)
Lyme disease (tick-borne)
Cholera (digestive)
Botulism, Salmonella, Typhoid fever, etc.
Ability of Prokaryotes to rapidly evolve, especially in challenging environments, has led to _________ ________ by many bacteria
antibiotic resistance
Choose the list below that contains the substances required by typical nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria.
Carbon, nitrogen, light, water, and some minerals
Oxygen, sulfur, light, water, and some minerals
Carbon dioxide, sulfur, light, water, and some minerals
Carbon dioxide, ammonium, water, light, and some minerals
Carbon dioxide, nitrogen, water, light, and some minerals
Carbon dioxide, nitrogen, water, light, and some minerals
Portions of the genomes of certain prokaryotic species are very similar to portions of the genomes of distantly related prokaryotes. The process that most likely accounts for this genetic similarity is __________.
convergent evolution
identical mutations occurring independently in these distantly related lineages
genetic variation arising from binary fission
genetic variation arising from meiosis
horizontal gene transfer
Horizontal gene transfer
What is the structural feature of gram-positive bacteria that results in their retaining a crystal violet dye stain and thereby being distinguished from gram-negative bacteria in a Gram-stain technique?
Gram-positive bacteria have thicker cell walls.
Gram-positive bacteria have structurally more complex cell walls.
Gram-positive bacteria lack cell walls.
Gram-positive bacteria have additional outer membranes.
Gram-positive bacteria lack peptidoglycan in their cell walls.
Gram-positive bacteria have thicker cell walls.
Which subgroup of proteobacteria contains many species that are closely associated with eukaryotic hosts in mutualistic or parasitic relationships?
Gamma
Alpha
Epsilon
Beta
Delta
Alpha
Which of the following characteristics is a reason why a Gram-stain to distinguish gram-positive from gram-negative bacteria is an important tool in a medical diagnosis of a bacterial infection?
The outer membrane of a gram-negative bacterium helps protect it from the body’s defenses.
None of the listed characteristics is a reason why a Gram-stain is important in medicine.
Certain gram-positive bacteria are resistant to antibiotics.
All of the listed characteristics are reasons why a Gram-stain is important in medicine.
The cell walls of many gram-negative bacteria are toxic.
All of the listed characteristics are reasons why a Gram-stain is important in medicine.
Bacterial flagella have a very complex structure composed of 42 distinct proteins. What is the most likely explanation for the evolution of these complex structures?
Exaptation
Endosymbiosis
Early bacterial species needed to be able to locomote and thus developed complex flagella to facilitate this motility
They evolved from earlier, simpler organisms
Flagella evolved as extensions of other bacterial appendages such as pili and fimbriae
Exaptation
Which of the following statements about cyanobacteria is true?
It can be said that nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria are the most self-sufficient of all organisms.
All of the listed responses are correct.
Some species may carry on nitrogen fixation.
They are the only prokaryotes that perform plantlike, oxygenic photosynthesis.
Some are single cells, whereas others live in filamentous colonies.
All of the listed responses are correct.
Which of the following is a structure that bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes have?
Plasma membrane
Membrane-enclosed organelles
Nuclear envelope
Circular chromosome
Peptidoglycan cell wall
Plasma membrane
Which of the following mechanisms is/are (a) means of genetic recombination in prokaryotes?
Transduction
None of the listed mechanisms is a means of genetic recombination.
Transformation
All of the listed mechanisms are means of genetic recombination.
Conjugation
All of the listed mechanisms are means of genetic recombination.
Antibiotics administered in human medicine work against bacterial infections by __________.
providing resources to lure bacteria away from human cells
interfering with an aspect of bacterial metabolism or structure that differs from that of eukaryotic cells
raising the host’s body temperature to make a less favorable environment for bacteria
stimulating the host’s immune system to mount defenses against the bacteria
preventing any cells from dividing
Interfering with an aspect of bacterial metabolism or structure that differs from that of eukaryotic cells
What are biofilms?
A biofilm is a location where nitrogen has been made available in the environment by bacterial decomposition.
Biofilms are any resource upon which bacterial colonies can grow.
A biofilm is the sticky layer surrounding a bacterial cell wall.
Biofilms are an antibacterial treatment.
Biofilms are cooperative colonies of bacteria.
Biofilms are cooperative colonies of bacteria.
In an experiment, a microbiologist put equal numbers of each of the following organisms into a flask of sterile broth, consisting mostly of sugar and a few amino acids. She then placed the flask in the dark.
Which of the following organisms would be most likely to survive?
Chemoheterotrophic bacteria
Photoautotrophs
Thermoacidophilic bacteria
Photoheterotrophs
Cyanobacteria
Chemoheterotrophic bacteria
What is a difference between the cell walls of prokaryotes and the cell walls of eukaryotes?
The cell walls of prokaryotes are made of molecules different from those comprising the cell walls of eukaryotes.
There are no cell walls in eukaryotes.
The cell walls of prokaryotes do not play a role in structural support.
Differences in prokaryotic cell wall composition are difficult to discern in the laboratory.
The cell walls of prokaryotes do not resist osmotic pressure.
The cell walls of prokaryotes are made of molecules different from those comprising the cell walls of eukaryotes.
The Desulfovibrio bacterium breaks down organic matter (which it must have) and uses sulfate (not oxygen) as an electron acceptor. As a result, it produces hydrogen sulfide (H2S), accounting for the "rotten egg" smell of swamp muck. Oxygen is a deadly poison to Desulfovibrio.
We would call Desulfovibrio a(n) __________.
obligately anaerobic chemoautotroph
There is insufficient information to answer this question.
facultatively aerobic chemoheterotroph
obligately anaerobic chemoheterotroph
facultatively anaerobic chemoautotroph
Obligately anaerobic chemoheterotroph
Plasmids __________.
All of the listed responses are correct.
are transferred from one bacterium to another by conjugation
allow bacteria to survive adverse conditions
replicate independently of the main chromosome
often contain antibiotic resistance genes
All of the listed responses are correct.
What is the function of a bacterial endospore?
To facilitate persistence in temporarily harsh environments
To store the genetic material of the cell
To adhere to a substrate or other bacteria
To fix nitrogen
To transfer DNA from one cell to another
To facilitate persistence in temporarily harsh environments
Which of the following does not contribute to bacteria’s ability to evolve rapidly?
Large populations
Genetic recombination
Short generation times
Sexual reproduction
Mutation
Sexual reproduction
Why is salt a good preservative to use for foods such as pork and fish?
Salt is a toxin to prokaryotic cells and leads to their death.
Salt breaks down the chitin contained in the cell walls of prokaryotes.
Salt breaks down the peptidoglycan found in the capsule of prokaryotes.
Prokaryotes living in the food products will take in excess water and explode.
Prokaryotic cells living in the food will shrink from their cell walls, impacting their ability to reproduce.
Prokaryotic cells living in the food will shrink from their cell walls, impacting their ability to reproduce.
Bacteria that __________ tend to have abundant internal membranes.
are pathogenic
are gram-negative
All of the listed responses are correct.
are photosynthetic
have flagella
are photosynthetic
Which of the following is not a true statement concerning bacterial flagella?
Bacterial flagella originate in and extend from the cell wall and plasma membrane.
There can be more than one flagellum on each bacterial cell.
Bacterial flagella enable bacteria to move.
Bacterial flagella are not covered by the plasma membrane as eukaryotic cells are.
Bacterial flagella are homologous to the flagella of eukaryotic cells.
Bacterial flagella are homologous to the flagella of eukaryotic cells.
Which of the following is not one of the most common prokaryotic cell shapes?
Spherical
Spiral
Cuboidal
Rod-shaped
All of the listed cell shapes are very common.
Cuboidal
Some prokaryotes stick to their substrate or to one another by means of hairlike appendages, each called a __________.
capsule
heterocyst
nucleoid
fimbria
pilus
fimbria
Acquiring an R plasmid would allow a bacterium to do what?
Reproduce
Resist high temperatures
Conjugate
Reduce its metabolic rate
Resist antibiotics
Resist antibiotics
Bacteria function primarily in which ecological role?
Commensalism
Bacteria are common in all of the listed ecological roles.
Parasitism
Mutualism
Decomposition
Bacteria are common in all of the listed ecological roles.
Bacteria that use light for their energy source and CO2 for their Carbon source are called __________.
photoautotrophs
photochemoheterotrophs
chemoautotrophs
photoheterotrophs
chemoheterotrophs
photoautotrophs
An F+ bacterial cell __________.
has many antibiotic resistance genes
uses fimbriae to transfer DNA
acts as a donor during conjugation
acts as a receptor during conjugation
transfers DNA by way of transduction
acts as a donor during conjugation
Which of the following is a disease caused by bacteria?
Smallpox
Measles
Tuberculosis
Common cold
Aids
Tuberculosis
Which subgroup of proteobacteria contains many species that are predators of other bacteria?
Delta
Beta
Alpha
Gamma
Epsilon
Delta
Which group of bacteria is unusual in that they lack peptidoglycan in their cell walls?
Cyanobacteria
Gram-negative bacteria
Chlamydias
Epsilon proteobacteria
Spirochetes
Chlamydias
Prokaryotes found inhabiting the Great Salt Lake would be __________.
extreme halophiles
extreme thermophiles
methanogens
extremophiles
cyanobacteria
Extreme halophiles