Veterinary Parasitology - Final Exam Review
1/173
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Compilation of all answers to multiple choice questions and open response questions on the previous 3 exams.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
174 Terms
When larval nematodes shed their cuticle and grow bigger and more mature, this is called _______.
molting
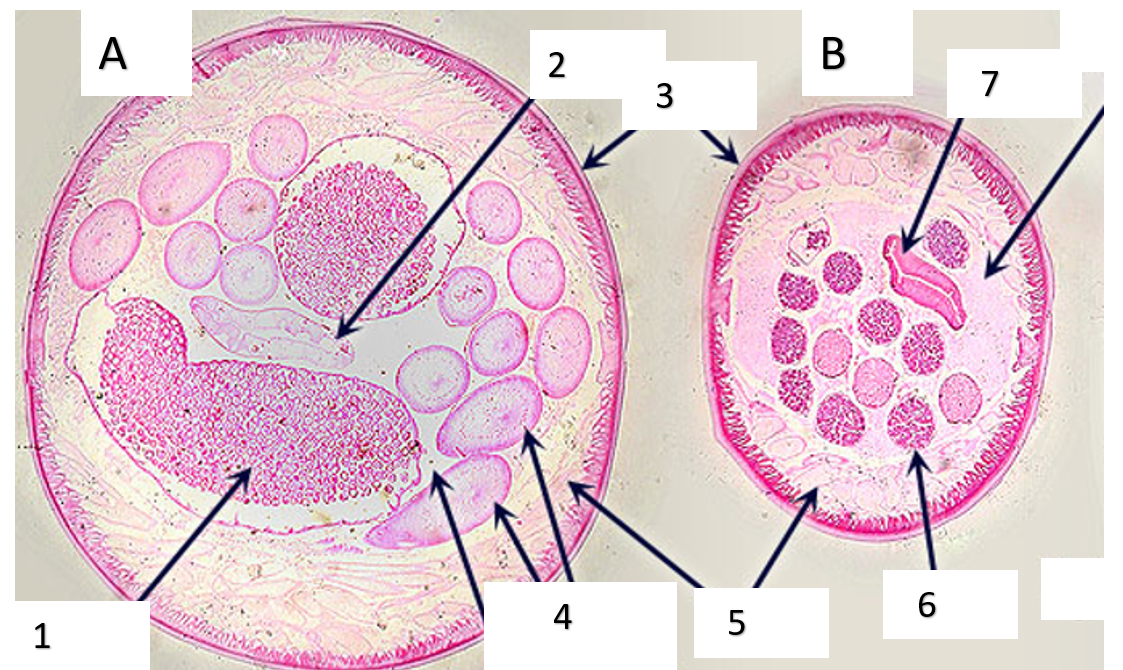
Look at the two cross-sections of parasites and answer the questions.
Which one is male A or B?
How do you know?
Based on the structure seen below, what phylum of parasite is represented?
Write numbers 1-7 and list the anatomical structures next to their number.
B
smaller, no eggs
nematoda
1. eggs 2. digestive tract 3. cuticle 4. ovaries 5. muscle 6. testes 7. digestive tract
When Bayliscaris procyonis leads to zoonotic infections, it is most likely to cause:
neurologic larva migrans
Which of the following is NOT true about Elaeophora schneideri?
it is a common parasite in dogs, cats and horses
it can cause dermatitis on the face and head
it can cause obstructions in the carotid arteries
it is carried into the host by horse flies
it is a common parasite in dogs, cats and horses
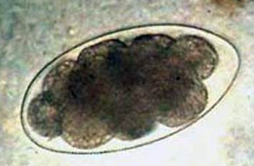
List the egg TYPE for the nematode egg shown.
Strongly
How long is the prepatent period for Dirofilaria immitis?
6 months
All of the following are members of Kingdom Protista except:
flagellates
apicomplexa
amoeba
annelids
ciliates
annelids
The mosquito is the _____ host for Dirofilaria immitis, while the dog is the ______ host.
intermediate; definitive
Why is it important for a veterinary professional to be able to understand and describe the life cycles of various parasites in their practice?
It is important so that they can identify the parasites, know the signs & symptoms, know if/when the animal was infected or infested, know how the animal could have gotten infected or infested, and whether they can treat it or not.
Why could broken tail hairs be a common sign of Oxyuris equi in horses? What is the best way to diagnose this parasite?
It could be from the horse swishing their tails constantly and rubbing against things to relieve itching. Eggs can be found on fecal scraping or scotch tape test.
Ancylostoma can develop in the environment and infect the definitive host through the skin without going into an intermediate host. This is called a/n:
direct life cycle
Which of the following describes a parasite with a narrow host range?
erratic
stenoxenous
pseudoparasite
euryxenous
stenoxenous
The common opening that male nematodes use to pass urine, feces and copulate is called the _____.
cloaca
Write the Latin Genus and species names of the parasite next to its picture and description:
This nematode, often found in the muscle of pork and wild game can be zoonotic and infect humans.
Trichinella spiralis, roundworm.
Which of the following does NOT describe the morphology of nematodes?
dorsoventrally flattened
unsegmented
bilaterally symmetrical
elongated
dorsoventrally flattened
Musca autumnalis is the intermediate host of what dog parasite?
Thelazia californiensis
Flukes like Clonorchis or Fasciola are characterized as:
trematodes
Mites and ticks are:
arthropods
Which of the following nematode eggs can be identified by bipolar plugs at both ends?
Trichuris
Toxocara
Ancylostoma
Physaloptera
Strongyloides stercoralis
Trichuris
Which of the following is the “giant kidney worm” of dogs?
Ancylostoma caninum
Toxocara leonina
Dipylidium caninum
Dioctophyma renale
Dioctophyma renale
Which of the following would be used to treat cattle with Trichostrongyles?
antihelminthic
insecticide
antiprotozoal
acaricide
antihelminthic
Animals like dogs and cattle that sleep or roll in fields or hay can get cutaneous infections of ____, a facultative parasite in soil that can sometimes look like Dirofilaria on deep skin scrapings.
Rhabditis strongyloides
The most common symptom in ruminants of Dictyocaulus species would be:
coughing
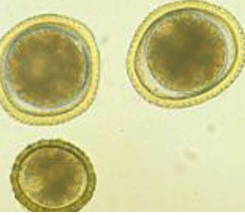
List the egg TYPE for the nematode egg shown.
ascarid
List the egg TYPE for the nematode egg shown.
thrichurid
Define the following types of parasites and give an example of each: definitive, facultative, periodic and give an example of each.
Definitive: Parasite that has a definitive host that it lives in during its adult life. Example: Dirofilaria immitis.
Facultative: Don't need a host to live, they can be free living. Example: Rhabditis strongyloides.
Periodic: Only visits the host for a short period of time for their meals. Example: Mosquito.
Which of the following is the hookworm of dogs?
Ancylostoma caninum
Toxocara canis
Haemonchus contortus
Dioctophyma renale
Ancylostoma caninum
Baylisascaris procyonis is commonly called the:
raccoon roundworm
Tapeworms are all member of the Phylum:
Platyhelmenthes
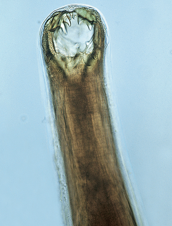
Write the Latin Genus and species names of the parasite next to its picture and description:
This common roundworm in dogs, especially puppies, is known for its barbed mouth parts shown below.
Ancylostoma caninum, hookworm.
Explain how and why good pasture management helps prevent nematode infections in ruminants, equids and swine.
It reduces the chances of reinfection and the passing of parasites to other members of the herd/flock.
Which of the following would be used to treat an animal with Dictyocaulus or Trichuris?
antihelminthic
insecticide
antiprotozoal
acaricide
antihelminthic
The mosquito is the intermediate host for which ruminant nematode that we studied?
Setaria cervi
Which of the following is not a taxonomic Domain?
Fungi
Eukaryota
Bacteria
Archaea
Fungi
Dracunculus insignus is commonly called:
the Guinea worm
The biting midge or “no see em” is the intermediate host of what horse parasite?
Onchocerca cervicalis
Which of the following would be used to treat your new puppy who has contracted Giardia?
antihelminthic
insecticide
antiprotozoal
acaricide
antiprotozoal
If your animal became infected with a Strongyloides species that has a free-living stage, the roundworm would be considered a ______ parasite
facultative
A __________ is an antihelminthic drug that paralyzes the adult nematode so it can pass out in feces.
vermifuge

Write the Latin Genus and species names of the parasite next to its picture and description:
The canine whipworm, a non-zoonotic parasite that releases eggs only every third day.
Trichuris vulpis
Which of the following describes a hookworm egg?
single pigmented cell with a thick sometimes roughened shell
small, smooth egg with larva inside at time of release
thin walled oval shell with multicelled morula inside
thick walled yellow or brown shell with bipolar plugs
thin walled oval shell with multicelled morula inside
Which of the following would be used to treat an animal that has mites?
antihelminthic
insecticide
antiprotozoal
acaricide
acaricide
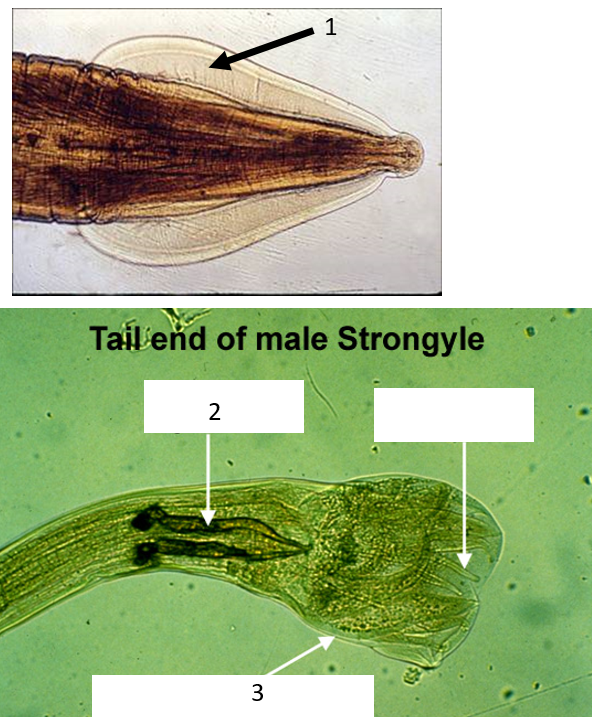
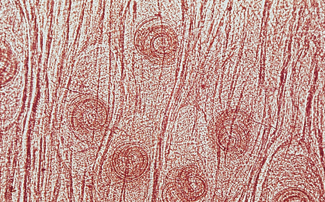
List the numbers 1-3 and write the anatomical structure labeled on the nematodes shown below.
alae
spicule
copulatory bursal rays
Nematodes are all part of Kingdom ____________.
Animalia
Acanthocephalans are more commonly referred to as:
thorny-headed worms
What is the common name of cutaneous Hebronema infection in horses?
summer sores
Once the _____ larval stage is reached, the now-infective nematode must find its way into the definitive host in order to full mature.
third
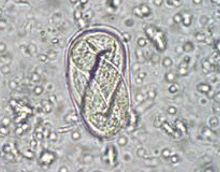
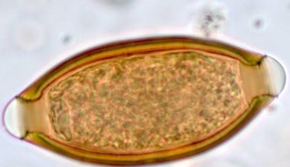
List the egg TYPE for the nematode egg shown.
spirurid
Which of the following is the heartworm of dogs and cats?
Toxocara cati
Trichuris ovis
Ascaris lumbricoides
Dirofilaria immitis
Dioctophyma renale
Dirofilaria immitis
Dirofiliaria immitis is normally found in the heart of the dog or cat, but can often be found in ______ sites like brain, eye or skin.
aberrant
Musca autumnalis is the scientific name for the:
face fly
Which of the following is the roundworm of pigs?
Trichuris vulpis
Ancylostoma caninum
Ascaris suum
Haemonchus contortus
Toxocara leonina
Ascaris suum
Pearsonema feliscati is a nematode found in the _________ of cats that uses the _________ as an intermediate host.
bladder; earthworm
Tapeworm larvae are called hexacanths because they:
have six hooks to penetrate their intermediate host
Schistosomes are unique flukes in that they infect the ____________ of the host and all ____________.
circulatory system; have both male and female adults
The Moniezia expansa egg is what type?
pyriform apparatus-type ova.
The segmented sections of the tapeworm body are called its:
strobili
Choose the correct order of the lifecycle of Taenia pisiformis.
egg, miracidium, sporocyst, rediae, cercariae, metacercariae
proglottid, egg, hexacanth, rabbit, cysticercus, dog
egg, hexacanth, flea, cysticercoid, dog
egg, hexacanth, grain mite, cysticercoid, cow
egg, coricidium, crustacean, procercoid, fish, plerocercoid, dog
proglottid, egg, hexacanth, rabbit, cysticercus, dog
Explain the causative agent of Swimmer’s Itch and how a human could possibly be exposed and what symptoms they would be likely to have.
Humans become infected by swimming in water containing avian blood flukes, the cercarie migrate into the skin. Symptoms include itching, burning, and rashes/small red bumps on the skin.
Simplified answer:
Schistosoma in bird feces that gets into water supply and swimmers get cercaria through the skin.
What subclass do pseudotapeworms belong to?
Cotyloda
You’re vacationing in the Caribbean and can’t go home without rescuing a stray animal that you that befriends you in your hotel courtyard. You discover that your new family member has Platynosomum fastosum and must be treated before you can bring him back to the U.S. Describe the life cycle of this fluke below. Include the: definitive host, intermediate host(s) and stages of the life cycle of this parasite.
Platynosumum fastosum is also called the Lizard Poisoning Fluke. These flukes use land snails as the first intermediate host, which is then ingested by the second intermediate host, lizards. Infected lizards are then ingested by cats, which are the definitive hosts. The adult worms are found in the bile ducts of cats. Eggs are found in feces/fecal flotation about 4-5 weeks after reaching the bile duct of an infected cat. Symptoms include diarrhea, vomiting, and jaundice. These worms are not zoonotic.
The first intermediate host of pseudotapeworms are tiny crustaceans called:
copepods
What is the definitive host of Fasciola magna?
white tail deer
The trapdoor at one end of the trematode egg where the immature fluke comes out is called the:
operculum
The fluke stage that is covered in cilia and can swim in a watery environment is called the:
miracidium
One unique feature of the pseudotapeworms compared to tapeworms is that their life cycle includes:
two intermediate hosts
Which proglottids of the true tapeworm are furthest away from the scolex?
gravid
Which of the following is the double pore or cucumber seed tapeworm of dogs and cats?
Echinococcus multilocularis
Dipylidium caninum
Taenia hydatigena
Multiceps multiceps
Dipylidium caninum
The site of the adult Paragonimus kellicotti in the definitive host is the:
lung
This parasite is the fringe tapeworm that uses tiny book lice as an intermediate host.
Thysanosoma actinoides
What is the intermediate host for the equid tapeworm Anoplocephala perfiolata?
grain mites
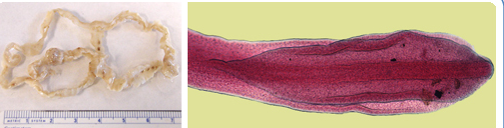
This is the broad fish tapeworm, a wide flat, ribbon-like pseudotapeworm that uses fish as the second intermediate host and can infect dogs as the definitive host.
Dipyllobothrium latum
Which of the following flatworms has unique lappets behind its acetabula to aid in attachment to the host?
Mesocestoides
Spirometra
Anoplocephala
Moniezia benedini
Taenia pisiformis
Anoplocephala
Which of the following organisms produces large hydatid cysts that can damage surrounding tissues in the host?
Multiceps multiceps
Moniezia expansa
Echinococcus granulosus
Taenia pisiformis
Hymenolepis diminuta
Echinococcus granulosus
What larval stage of the tapeworm is called the bladder worm?
cysticercus
One way to tell T. saginata from T. solium is:
they have a different number of uterine branches
All flukes in the Subclass Monogenea:
are ectoparasites
The eggs of the pseudotapeworms look very much like ______ eggs?
Trematode
What immature form of Dipylidium caninum infects the intermediate host?
cysticercoid
Explain how both Multiceps serialis and Dicrocoelium dentiticum larvae change the behavior of their intermediate host in order to make it more likely for a definitive host to ingest them.
Multiceps makes rabbit slow so dog can catch them.
Dicrocoelium makes ants climb up grass so they're eaten by ruminants.
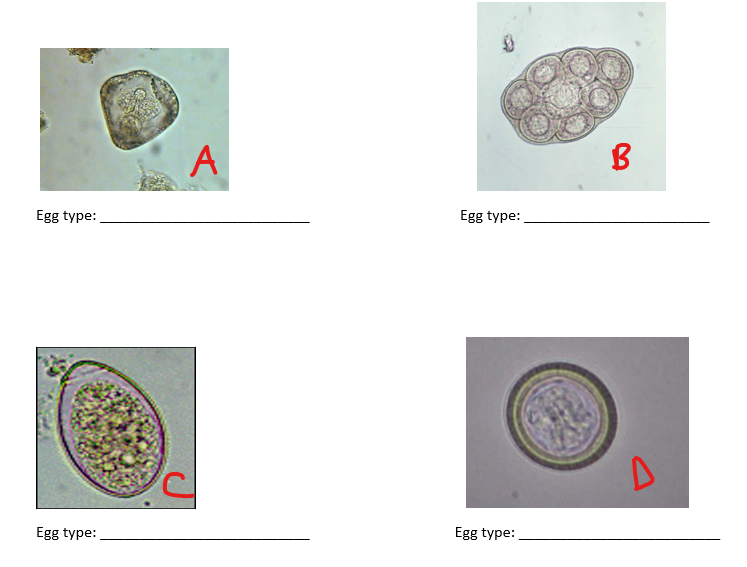
Write the letters A-D. Write the name of the egg type next to its letter and give an example of a parasite we've seen that has each type of egg.
A: Pyriform - Parasite example: Anoplocephala
B: Dipylidium - Parasite example: Dipylidium caninum
C: Pseudophyllidium - Parasite example: Diphyllobothrium latum
D: Taenia - Parasite example: Taenia solium
Which of the following is NOT true about true tapeworms?
they are dioecious
they can self-fertilize within one proglottid
they have 5 hooklets on their immature hexacanth
they can cross-fertilize between two different proglottids
they have laterally located male and female reproductive organs in each strobilus
they are dioecious
Which of the following is a canine and feline fluke that is acquired by eating infected mice, snakes or frogs and has a unique half flat, half spherical shape?
Nanophyetus salmincola
Paragonimus kellicoti
Heterobilharzia americana
Schistosoma species
Alaria species
Alaria species
What is the intermediate host of Hymenolepis nana?
there isn’t one
Tapeworms and pseudotapeworms absorb nutrients from the host through their:
tegument
Based on what we’ve learned about the life cycle of Dipylidium caninum, explain why treatment for this parasite must also include treatment for the intermediate host and why this is necessary to completely clear the infection.
Dogs and cats become infected with Dipylidium caninum by ingesting the intermediate host, the flea. Dipylidium caninum is zoonotic and can also infect humans; humans also get infected by ingesting infected fleas. Children are more likely to ingest the intermediate host and become infected. Good flea control minimizes the chances of reinfection of this parasite.
Treat flea infestation as well because they will continue to get reinfected with Dipylidium over and over.
The second intermediate host of Paragonimum kellicotti is the:
crayfish
Most flukes are hermaphroditic with the exception of _______________.
Schistosoma species
Both flukes and tapeworms are members of which Phylum?
Platyhelmenthes
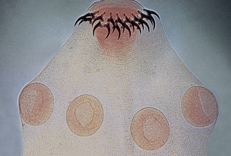
The true Cestode has a scolex (head) that is a holdfast organelle. The suction cup looking apparati are called:
acetabula
The site of adult schistosomes like Heterobilarzia Americana in the definitive host is the:
small blood vessels
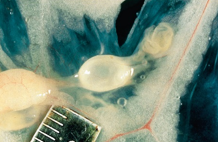
This tapeworm pea-sized bladder worm larval stage is found in the greater omentum or abdominal organs of the rabbit. The definitive host is the dog. What is the tapeworm called?
Taenia pisiformis
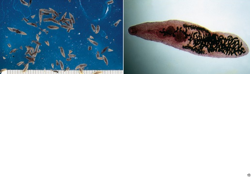
The lancet fluke uses the snail and ant as intermediate hosts and can cause behavior changes in both, particularly tetanus in the ant so its mouth parts stay attached to grass blades and are more likely to be eaten by the definitive host. What trematode is this?
Dicrocoelium dendriticum
What is the intermediate host of Taenia ovis?
sheep
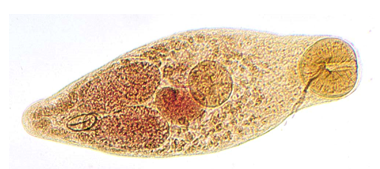
This is the smallest fluke at less than 1 mm in length that is also known as the “salmon-poisoning fluke” of dogs in the Pacific Northwest.
Nanophyetus salmincola
Most trematode eggs are too heavy to be seen a fecal float and are more commonly diagnosed by:
fecal sedimentation
Which of the following parasites forms a unique strobilocercus on day 42 in the intermediate rodent liver?
Taenia taeniaformis
This parasite produces a unique coenurus as an immature form that contains many scolices.
Multiceps
Which of the following is true about Fasciola magna?
the definitive host does not shed eggs in feces
the incidental hosts are dead ends because they do not shed eggs
the intermediate host is the grain mite
the definitive host suffers from chronic cough and lethargy
the intermediate host can be diagnosed by a blood smear looking for extracellular parasites
the incidental hosts are dead ends because they do not shed eggs
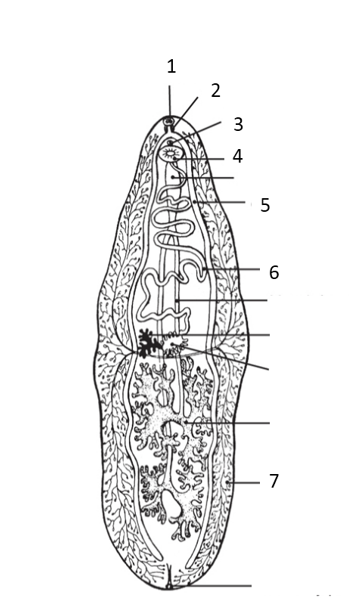
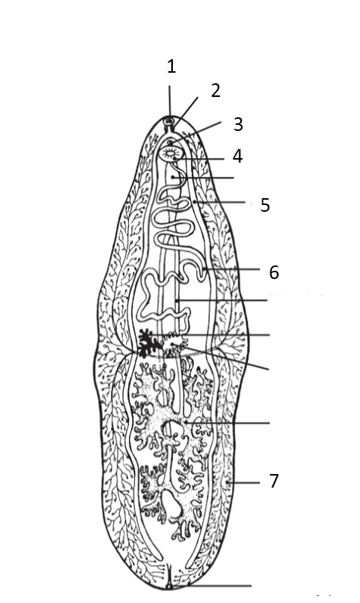
Label your answers 1-8. Fluke morphology. Refer to the following figure to answer the questions below.
What structure is labeled in 1?
What number represents the “bifurcating cecum”?
What number represents the pharynx?
What structure is labeled in 6?
What is the function of 3?
What structure is labeled in 7?
What number represents the ventral sucker?
Explain how flukes release waste if they do not have an anus.
oral sucker
esophagus
genital pore
ventral sucker
cecum
reproductive tract
vitellarium
They regurgitate their meals and release it into the host as fluke puke