Lecture 2: Basic Principles
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What LD50 stand for?
Lethal Dose/Concentration that kills 50% of a test population
What does MTD stand for?
Minimum Toxic Dose
What does MLD/MLC stand for?
Minimum Lethal Dose/Concentration
Out of LD50, MTD, MLD which value is likely of most clinical use and why?
MTD to determine what values will cause toxicity
MLD is not clinically relevant because patient will probably already be dead
Does exposure equal intoxication, why?
NO, exposure does NOT equal intoxication because of Toxicokinetics
What is Toxicokinetics? (3 steps)
Toxin must be absorbed
Toxin must reach its site of action at a high enough concentration
Toxin must remain at site for a sufficient amount of time to cause a toxic effect
Because of Toxicokinetics, what is the main treatment of intoxication?
Decontamination to get the toxin out before it causes damage
What are the 4 basic events in Toxicokinetics? (in order)
Absorption
Distribution
Metabolism
Excretion
Describe Toxicokinetics: Absorption
How does its get into the body?
Orally/Ingestion
Dermal exposure
Injection
Inhalation
How can we minimize absorption?
Give examples
Decontamination!
Dermal: give a bath
Oral: emesis
Describe Toxicokinetics: Distribution
Where does it go in the body?
Fat or Water Soluble
Protein binding
pH of tissues and compartments
Describe Toxicokinetics: Metabolism
What happens to it when it gets there?
Biotransformation
Metabolites are more readily excreted because converted to a more water-soluble product
Where does Metabolism often occur?
Liver
Describe Toxicokinetics: Excretion
How does it get out of the body?
What are some primary routes of excretion?
Urinary
Biliary/Fecal
Milk, Sweat, Saliva
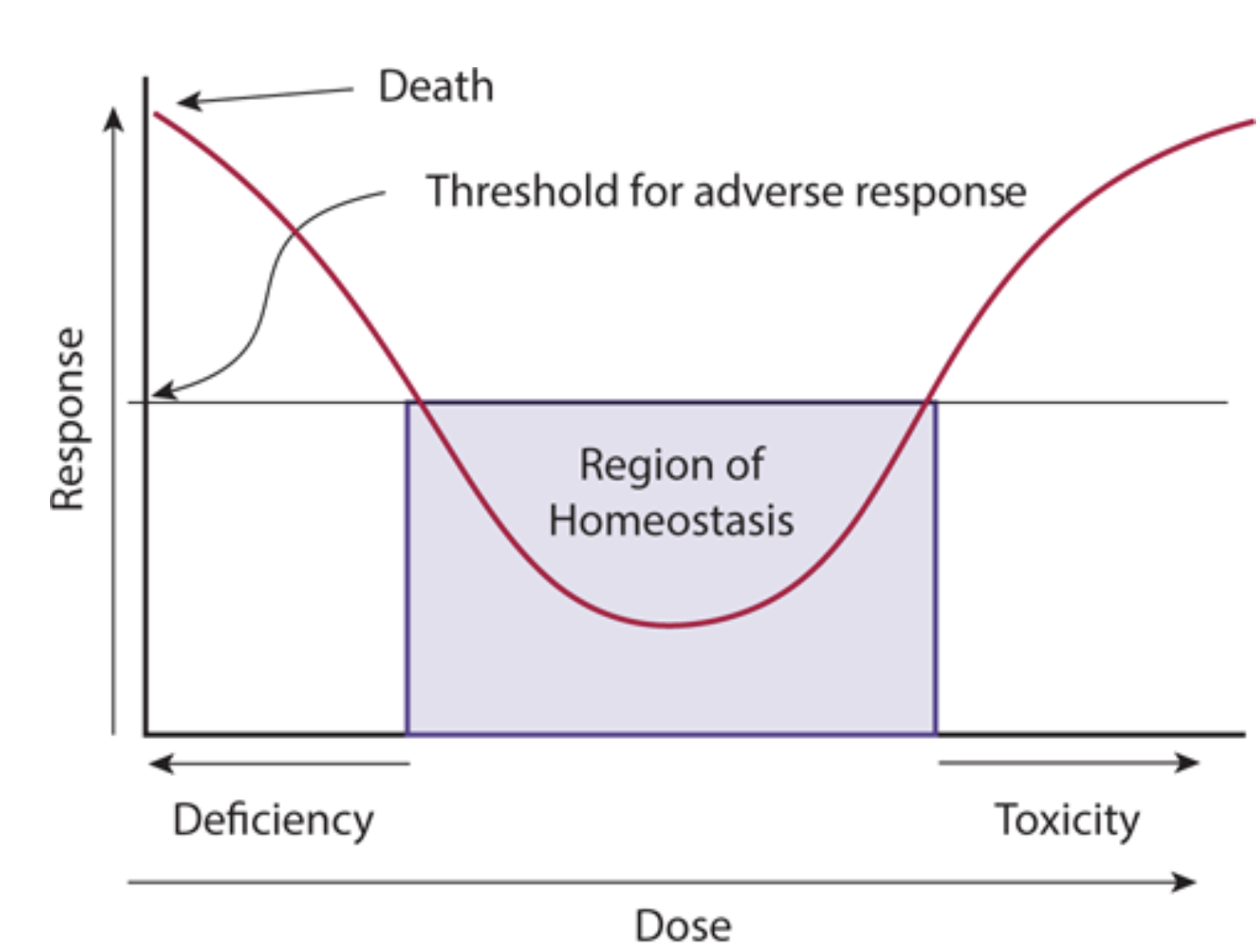
What is an exception to the “typical” dose-response curve? Why?
Give examples
Essential Nutrients
Nutrients have a region of homeostasis
Too little or too much nutrients = problem
Ex.
Vitamins A, D, E can cause problems because they are fat soluble vitamins
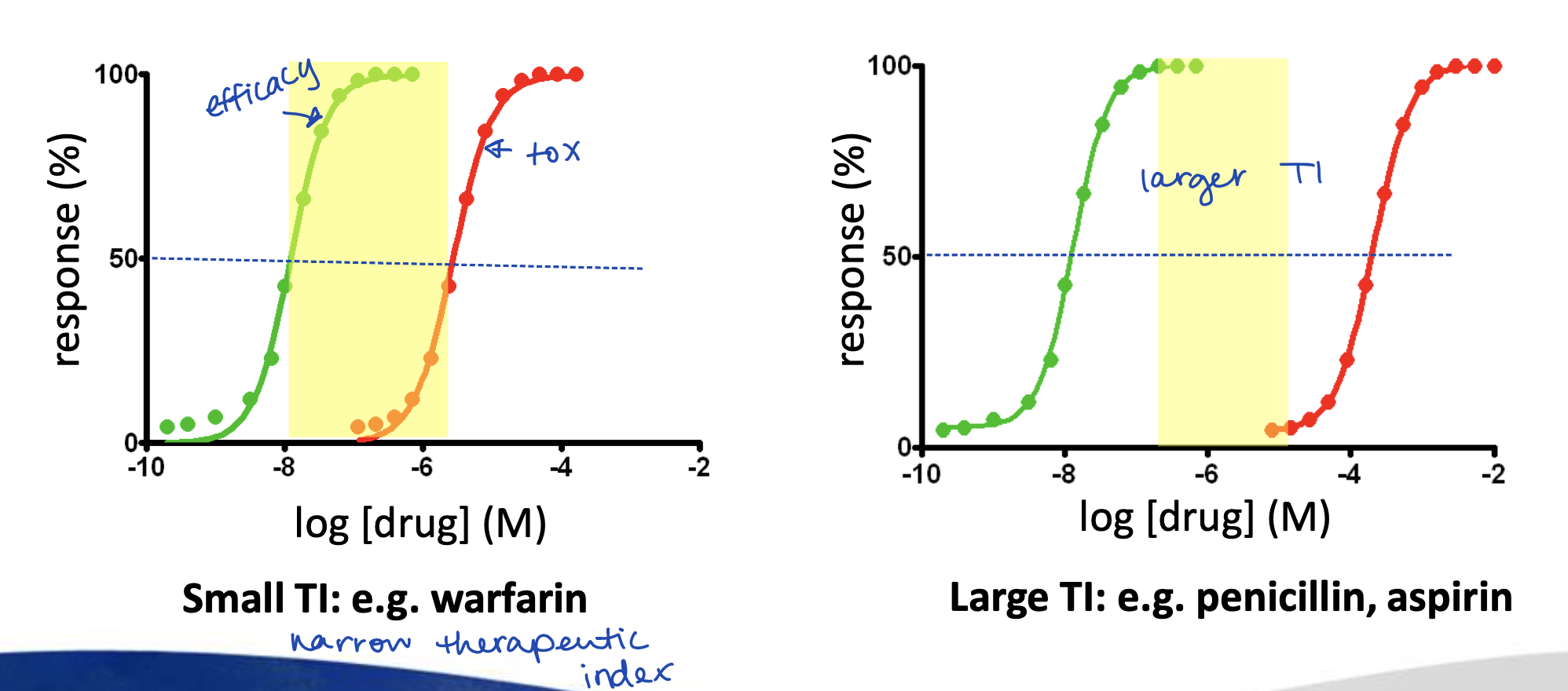
What is Therapeutic Index?
The ratio of the drug dose that causes an unwanted (toxic) effect to producing a wanted (therapeutic) effect
TI = LD50/ED50
What are 5 factors that influence toxicity?
Characteristics of the animal exposed
Route of exposure
Frequency of exposure
Characteristics of the toxicant
Environmental conditions
What is the biggest thing to consider for characteristics of the animal exposed?
Species
What are 7 Characteristics of the animal exposed to consider?
Species
Genetic differences
Age
Sex/Reproductive Status
Concurrent disease
Concurrent exposure to other drugs or chemicals
Nutritional status
What are 6 Characteristics of the Toxicant to consider?
Formulation
Valence state of metals
Charge of the molecule will tell if its toxic
Ionization
Decomposition
Impurities
Stain/Subspecies
What are 3 things to consider for the Frequency of Exposure?
One time exposure
Repeated exposures
Cumulative effects
What are 6 things to consider for Environmental Conditions?
Drought
Time of Year
Growth Stage
Temperature
Photo Period
Winds
What is considered a WRONG question? What should be asked instead?
WRONG: Is this toxic?
At what dosage?
In what species?
Under what conditions?
When are dose calculations used?
In cases involving a KNOWN exposure to a specific toxicant
Why calculate a dose of exposure?
To determine if the dose is high enough to pose a risk of intoxication or death
Of the dose of exposure is below MTD, don’t need to treat
Why should you NOT just treat any exposure?
The risk of treatment may outweigh the risk of intoxication
ex. bleach consumption = NO emesis because they will cause more damage
If the animal ingested a possible toxicant, what is one most important thing to get from owners?
the LABEL