[ATI] Medications for Lower Respiratory Airflow Disorders
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
Bronchodilators + Anti-inflammatories (2)
Glucocorticoids: Beclomethasone, prednisone
Leukotriene modifiers: Montelukast & Zileuton
Pure Bronchodilators (5)
Beta2‑adrenergic agonists: Albuterol (B-2 Agonists)
Inhaled anticholinergics: Ipratropium (Muscarinic Antagonists)
Methylxanthines: Theophylline
Bronchodilator Side Effects (General) (4)
Tachycardia
Hypertension
Hypotension
Chest pain
Beta2-Adrenergic Agonists Use (3)
Manages chronic asthma (LABA)
Prevention of exercise-induced bronchospasm
Treats acute asthma (SABA)
Manages COPD
Beta2-Adrenergic Agonists Mechanism
Activate B2 receptor in lungs bronchodilate and vasodilator
Inhaled Anticholinergics Use (2)
Relief of bronchoconstriction in clients who have COPD
Decreases secretions in clients with COPD
Manages allergen-induced and exercise-induced bronchospasm
Methylxanthines Use
Manages chronic asthma in p/t that metabolize meds slowly
Manages COPD (not first line)
Glucocorticoid Use/Actions
Action: Prevents inflammation, suppresses airway mucus production, reduces airway mucosa edema
Long-term manages chronic asthma
Short-term manages post-attack acute asthma (oral)
Analogy: Fire extinguishers—they cool down the inflammation and prevent it from spreading, but overusing them can make the body a little too cool
Leukotriene Modifiers Use
Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of allergic rhinitis, CHRONIC asthma, and exercise-induced bronchospasm
Inhaled Anticholinergics Mechanism/Action
aka Muscarinic Antagonists
Inhibits the acetylcholine acting on muscarine receptors of the parasympathetic nervous system (causes bronchoconstriction)
Increases Bronchodilation
Methylxanthines Mechanism/Action
Inhibits phosphodiesterase (contracts bronchi smooth muscles)
Bronchodilation (relaxes smooth muscles of bronchi/oles)
Glucorticoid Mechanism/Action
Inhibits the release of leukotrienes, prostaglandins, and histamine (causes inflammation)
Suppresses inflammation
Inhibits action of WBCs (causes inflammation and protects immune system)
Suppresses immune system
Decreases edema in airways
Leukotriene Modifiers Mechanism/Action
Inhibits the action of Leukotrienes (causes allergic reactions: airway inflammation and mucus production)
Suppresses inflammation via receptor antagonists (Montelukast, Zafirlukast)
Suppresses inflammation via elimination (Zileuton)
Beta2-Adrenergic Agonists Adverse/Side Effects
Chest pain, palpitations
Nervousness, restlessness, tremors
Inhaled Anticholinergics Adverse/Side Effects
Dry mouth, irritation of the pharynx
Increased intraocular pressure
Urinary retention
Methylxanthines Adverse/Side Effects
(Stimulatory)
Restlessness, insomnia
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
Toxicity: Seizures
Dysrhythmias
GI distress, intestinal bleeding
Hyperreflexia
Hyperglycemia
Hypokalemia
Metabolic Disturbances
Tachycardia/Palpitations
Primary hypertension
Secondary hypotension (Tachycardia)
Methylxanthines Pharmacological Effects (image)
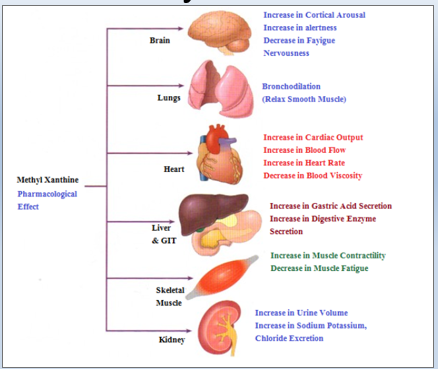
Glucocorticoid Adverse/Side Effects
Bone demineralization, muscle wasting
Hyperglycemia (blocks glucokinase receptors on pancreas: insulin resistance)
Peptic ulcer disease
Infection
Fluid and electrolyte imbalances
Headache
Inhaled: Oral candidiasis (rinse mouth)
Oral: Suppression of adrenal function
Nasal: Dry mucous membranes, epistaxis, sore throat
Oral Glucocorticoid Adverse/Side Effects
Suppression of adrenal function
Hyperglycemia (blocks glucokinase receptors on pancreas)
Inhaled Glucocorticoid Adverse/Side Effects
Oral candidiasis (rinse mouth)
Hoarseness
Osteoporosis
Bleeding
Nasal Glucocorticoid Adverse/Side Effects
Dry mucous membranes, epistaxis, sore throat
Leukotriene Modifiers Adverse/Side Effects
Liver damage (Zileuton/Zafirlukast)
Neuropsychiatric effects such as suicidal ideations
Potentiates warfarin and theophylline
Infection
Beta2-Adrenergic Agonists Interventions/Considerations/Administrations/Instructions
Monitor and report dizziness, heart palpitations, chest pain, and shortness of breath
Monitor and report tremors
Notify provider if tremors interfere with activities of daily living.
Inhale before inhaling glucocorticoids
Avoid caffeine/stimulants
Report chest pain and heart palpitations.
Notify provider if tremors interfere with activities of daily living.
SABA for acute asthma
LABA for chronic asthma (maintenance)
Inhaled Anticholinergic Interventions/Considerations/Administrations/Instructions
Provide water and hard candy to client (frequently)
Schedule routine testing for glaucoma.
Monitor urinary elimination patterns, especially in older adults (report changes)
Delay use of other inhalants for 5 minutes
Do not use as an emergency rescue medication
NOT FOR ACUTE ASTHMA (RESCUE) - COPD ONLY
Rinse the mouth after use to reduce unpleasant taste
Do not swallow
Inhalation via HandiHaler device (dry-powder capsule in haler)
Methylxanthines Interventions/Considerations/Administrations/Instructions
Monitor plasma medication levels
Discontinue if toxic levels found
Give activated charcoal to decrease absorption.
Prepare to initiate anticonvulsant therapy and seizure precautions.
Monitor heart rate and rhythm.
Give antidysrhythmics to restore heart rate and rhythm.
Chew chewables thoroughly
Do not crush or chew sustained-release/enteric-coat
Strict schedule between doses
Do not double if dose missed
Reduce or eliminate caffeine intake
Glucocorticoid Interventions
Provide/prescribe a spacer.
Monitor potassium levels
Initiate antifungal therapy as needed.
Observe for suppression of adrenal function.
Monitor plasma medication levels.
Recommend alternate-day dosing.
Monitor for signs of bone demineralization, muscle wasting.
Recommend the lowest possible effective dose and alternate-day dosing.
Monitor blood glucose levels, especially for clients who have diabetes mellitus.
Recommend adjustment of dosages of insulin/hypoglycemic medications accordingly.
Observe for gastrointestinal bleeding (bloody vomitus; black, tarry stools).
Implement gastric protective measures.
Give drug with food or meals.
Recommend analgesic substitute if NSAID is prescribed.
Observe for signs of infection that may not include fever or inflammation (sore throat, fatigue, tachycardia, and discharge from a wound).
Recommend initiation of appropriate antimicrobial therapy.
Monitor for weight gain or edema (hypernatremia).
Monitor for generalized weakness (hypokalemia).
Recommend initiation of appropriate fluid and electrolyte replacement therapy.
Provide client with water and hard candy or throat lozenges to suck on.
Provide humidified air for epistaxis and sore throat.
Administer non-NSAID analgesic such as acetaminophen
Glucocorticoid Interventions (Inhaled)
Use on a regular schedule rather than PRN.
Do not use these drugs for an acute attack.
When using concurrently with a beta2 adrenergic agonist inhaler, use the beta2 agonist first to dilate the airway before using the glucocorticoid.
Glucocorticoid Interventions (Oral)
Use twice daily for 5 to 10 days.
For long-term use (10 days or more), take once daily using alternate-day dosing.
Taper the dose slowly when symptoms are controlled to establish the lowest possible oral dose.
Take supplemental doses as needed in times of stress (illness, surgery).
Glucocorticoid Interventions (Nasal)
WEAN: Use a metered-dose device
Use the full dose initially and taper to the lowest effective dose. Expect the full therapeutic effect to take 2 to 3 weeks.
Use a nasal decongestant (sympathomimetic) first if the nares are completely blocked.
Aim away from septum
Glucocorticoid Instructions
Use a spacer (on most glucocorticoid metered-dose inhalers) to deposit less medication in the oropharynx.
Rinse the mouth and/or gargle after using the glucocorticoid inhaler to prevent candidiasis.
Explain the schedule of alternate-day therapy.
Taper the dose before discontinuing it. NEVER stop abruptly.
Take the medication on alternate days.
Perform weight-bearing exercise daily.
Consume adequate calcium and vitamin D.
Avoid taking NSAIDs.
Take the medication with food or meals.
Use a humidifier during sleep.
Increase fluid intake.
Suck on hard candy or lozenges.
Take over-the-counter, non-NSAID analgesics as needed.
Report any of the following conditions immediately:
Polyphagia, polydipsia, and polyuria
Indigestion or bloody vomitus as well as black, tarry stools
Manifestations of infection, such as a sore throat, that may not be accompanied by fever or inflammation
Painful mucous membranes with white patches
Weight gain or edema
Weakness
Leukotriene Modifiers Interventions/Considerations/Administrations/Instructions
Periodic LFT (risk of liver damage)
Report abdominal tenderness, nausea, or anorexia.
Observe/report behavioral changes (such as such as agitation, insomnia, anxiety, or irritability)
Mix oral granules with applesauce, carrots, rice, or ice cream or place directly on the tongue.
Take 2 hours before exercise to prevent exercise-induced bronchospasm (EIB)
Do not repeat dose for 24 hours
Take on an empty stomach once daily (Montekulast)
Beta2-Adrenergic Agonists Contraindications
Allergy to albuterol or levalbuterol
Inhaled Anticholinergic Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to ipratropium, atropine, belladonna alkaloids, or bromide
Methylxanthines Contraindications
Impaired metabolism
Tobacco or marijuana use (boosts metabolism)
Caffeine (boosts metabolism)
Glucocorticoid Contraindications
Recent live virus immunization
Systemic fungal infection
Oral candidiasis
Leukotriene Modifiers Contraindications
Liver dysfunction (zileuton and zafirlukast), not montelukast
Acute asthma exacerbations
Status asthmaticus
Beta2-Adrenergic Agonists Safety Alerts
Note various inhalation devices and measurements
Clients must notify of chest pain, heart palpations, or increased pulse rate
History of CV, HTN, or taking digitalis-type meds
Inhaled Anticholinergic Safety Alerts
NOT FOR ACUTE ASTHMA (RESCUE) - COPD ONLY
Methylxanthines Safety Alerts
Use antidysrhythmic if life-threatening cardiac dysrhythmias occur
Use anticonvulsant therapy and seizure precautions if a seizure occurs
Metabolic rates are affected by age, medications, and disease, as well as smoking either tobacco or marijuana
Monitor plasma levels to prevent toxicity
Taking the OTC med cimetidine for indigestion or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) increases the risk for toxicity.
Glucocorticoid Safety Alerts
Oral
Gastric-protective measures to prevent gastric ulcers
Avoid in oral candidiasis, systemic fungal infection or live virus immunization (lowers immune system)
Avoid NSAIDs (use acetaminophen)
Take with snack or meal
Immediately report black, tarry stools and blood vomit
Immediately report infection signs (lowers immune system)
Sore throat (fever not guranteed)
Inflammation, fatigue, tachycardia, drainage
White patches on mucous membranes (oral candidiasis)
Leukotriene Modifiers Safety Alerts
Periodic LFT (risk of liver damage)
Report abdominal tenderness, nausea, or anorexia.
Observe/report behavioral changes (such as such as agitation, insomnia, anxiety, or irritability)
Clients should alert provide if taking Zileuton or Zafirlukast
Increases anticoagulant effects of warfarin (bleeding, hemorrhage)
Hepatotoxic
Beta2-Adrenergic Agonists Precautions
Diabetes mellitus
Hyperthyroidism
Cardiovascular disease
Hypertension
Angina pectoris
Tachydysrhythmias
Tachycardia due to digitalis toxicity
Anticholinergic Precautions
Glaucoma
Prostatic hypertrophy
Bladder neck obstruction
Methylxanthines Precautions
Heart disease
Liver dysfunction (linked to injury, Hep C, elevated ALT)
Acute pulmonary edema
Glucocorticoid Precautions
Peptic ulcer disease
Diabetes mellitus
Hypertension
Renal dysfunction
Use of NSAIDs
Leukotriene Modifiers Precautions
Severe asthma
Beta2-Adrenergic Agonists Interactions
Blockers reduce the effectiveness
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) and tricyclic antidepressants increase the risk of hypertension, tachycardia, and angina.
Hypoglycemic (antidiabetic) drugs require increased dosing because of hyperglycemic effects.
Inhaled Anticholinergic Interactions
Beta2-adrenergic agonists enhance bronchodilation
Methylxanthines Interactions
Cimetidine, some fluoroquinolones, and caffeine increase the risk of toxicity.
Phenobarbital, phenytoin, and nicotine increase metabolism of theophylline.
Glucocorticoid Interactions
Potassium-depleting diuretics, such as furosemide increase risk of hypokalemia.
NSAIDs increase the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding.
Effects of insulin and oral hypoglycemics are decreased.
Leukotriene Modifiers Interactions
Concurrent use with phenobarbital, rifampin, and phenytoin may necessitate higher dosages.
Potentiates warfarin and theophylline
Short Acting Beta2-Adrenergic Agonists (SABA) Medications (Inhaled) (6)
Albuterol (Proventil HFA / Ventolin HFA)
Ephedrine
Epinephrine (like Sympathomimetics)
Levalbuterol
Metaproterenol
Terbutaline (Generic only)
Long Acting Beta2-Adrenergic Agonists (LABA) Medications (Oral)
Formoterol (Foradil Aerolizer)
Salmeterol (Severent)
Aformoterol
Idacaterol
Short Acting Muscarinic Antagonists (SAMA) Inhaled Anticholinergics Medications
Ipratropium
Long Acting Muscarinic Antagonists (LAMA) Inhaled Anticholinergics Medications
Umeclidinium
Tiotropium
Aclidinium
Revefenacin
Methylxanthines Medications
Theophylline
Aminophylline (generic only) (IV)
Glucocorticoid Medications (nasal)
Fluticasone
Budesonide
Glucocorticoid Medications (4)
Beclomethasone dipropionate (inhalant)
Prednisone (oral)
Fluticasone (intranasal or inhaled)
Budesonide (nasally or inhaled , also for allergic rhinitis)
Methylprednisone (IV)
Glucocorticoid Medications (oral)
Prednisone
Glucocorticoid Medications (inhaled)
Budesonide
Beclomethasone dipropionate
Fluticasone
Beclomethasone dipropionate (inhalant)
Classification: Glucocorticoids
Therapeutic use: Used for long-term management of chronic asthma and short-term management of post-exacerbation manifestations.
Prednisone (oral)
Classification: Glucocorticoids
Therapeutic use: Used for long-term management of chronic asthma and short-term management of post-exacerbation manifestations.
Fluticasone (intranasal or inhaled)
Classification: Glucocorticoids
Therapeutic use: Used for long-term management of chronic asthma and short-term management of post-exacerbation manifestations.
Budesonide (nasally or inhaled - allergic rhinitis)
Classification: Glucocorticoids
Therapeutic use: Used for long-term management of chronic asthma and short-term management of post-exacerbation manifestations.
Albuterol
Classification: Short-Acting Beta2-Adrenergic Agonists (SABA)
Therapeutic use: Manages asthma, prevents exercise-induced bronchospams, treats ongoing asthma exacerbations.
Ipratropium
Classification: Short-Acting Anticholinergic (SAMA)
Therapeutic use: Relieves bronchoconstriction and decreases secretions in clients who have COPD.
Tiotropium
Classification: Long-Acting Anticholinergic (LAMA)
Therapeutic use: Relieves bronchoconstriction and decreases secretions in clients who have COPD.
SAMA
Short-Acting Muscarinic Antagonist
Theophylline
Classification: Methylxanthines
Therapeutic use: Manages chronic asthma.
Montelukast
Classification: Leukotriene Modifiers (Antagonist)
Therapeutic use: Treats rhinitis, asthma, and exercise-induced bronchospasm.
Zileutron
Classification: Leukotriene Modifiers (Eliminates)
Therapeutic use: Treats rhinitis, asthma, and exercise-induced bronchospasm.
(Hepatotoxic & Amplifies Warfarin)
Zafirkukast
Classification: Leukotriene Modifiers (Antagonist)
Therapeutic use: Treats rhinitis, asthma, and exercise-induced bronchospasm.
(Hepatotoxic & Amplifies Warfarin)
Monitor Liver (3)
Zafirkukast (Leukotriene Modifiers) - Toxic
Zileutron (Leukotriene Modifiers) - Toxic
Theophylline (Methylxanthines) - Injury
Potentiates Anticoagulant Effect of Warfarin (2)
Zafirkukast (Leukotriene Modifiers)
Zileutron (Leukotriene Modifiers)
Monitor Heart (2)
Theophylline (Methylxanthines) - Precaution (Arrythmias, myocardial infarction)
Albuterol, Formoterol, Salmeterol, Terbutaline (Beta2-Adrenergic Agonists) - Safety Alert (chest pain, heart palpations, increased pulse rate)
Avoid caffeine (2)
SABA Albuterol, LABA Formoterol/Salmeterol/Terbutaline (Beta2-Adrenergic Agonists)
Theophylline (Methylxanthines) - Contraindication (increases toxicity risk)
MANAGES COPD (3)
SAMA Ipratropium, LAMA Tiotropium (Inhaled Anticholinergics)
Benzonatate (Nonopioid Antitussives)
Theophylline (Oral Methylxanthines)
DO NOT USE FOR ACUTE ASTHMA (EMERGENCY) (3)
SAMA Ipratropium, LAMA Tiotropium (Inhaled Anticholinergics)
Montekulast, Zafirkulast, Zileuton (Leukotriene Modifiers)
(Inhaled Glucocorticoids)
Nosebleed (Epistaxis) (1)
Budesonide, Beclomethasone dipropionate, Fluticasone (Inhaled Glucocorticoids)
Suppression of adrenal fx (1)
Prednisone (Oral Glucocorticoids)
LONG-TERM (Chronic) Asthma Management (4)
Theophylline (Methylxanthines)
(Glucocorticoids)
Formoterol/Salmeterol/Terbutalin (LABA Beta2-Adrenergic Agonists)
Montekulast, Zafirkulast, Zileuton (Leukotriene Modifiers) - Adjunctive
ACUTE Asthma Management (Emergency)
Albuterol (SABA Beta2-Adrenergic Agonists) (wheezing)
Delay other inhalants for 5 mins
SAMA Ipratropium, LAMA Tiotropium (Inhaled Anticholinergics)
Manages exercised-induced bronchospasms (EIB) (3)
SABA Albuterol, LABA Formoterol/Salmeterol/Terbutaline (Beta2-Adrenergic Agonists)
SAMA Ipratropium, LAMA Tiotropium (Inhaled Anticholinergics)
Montekulast, Zafirkulast, Zileuton (Leukotriene Modifiers) - Adjunctive
Post-Attack Acute Asthma Management (1)
Prednisone (Oral Glucocorticoids)
Hyperglycemia (1)
(Glucocorticoids)
Taper doses (1)
Fluticasone/Budesonide, Prednisone (Nasal/Oral Glucocorticoids)
Bone demineralization (use Vit. D + Calcium) (1)
(Glucocorticoids)
Avoid if urinary retention (1)
SAMA Ipratropium, LAMA Tiotropium (Inhaled Anticholinergics)
Seizures
Theophylline (Methylxanthines)
Diabetes (2)
SABA Albuterol, LABA Formoterol/Salmeterol/Terbutaline (Beta2-Adrenergic Agonists)
(Glucocorticoids)
Hypertension (2)
(Beta2-Adrenergic Agonists)
(Glucocorticoids)
Avoid NSAIDs (GI bleed)
(Glucocorticoids)
ALWAYS TAKEN WITH/AFTER LABAs
(Glucocorticoids)
Take with food
(Glucocorticoids)
Engage weight-bearing exercise (reduces osteoporosis side effect)
(Glucocorticoids)
Candidiasis risk
Prednisone, Budesonide/Beclomethasone dipropionate/ Fluticasone (Oral/Inhaled Glucocorticoids)
Monitor potassium w/ potassium-wasting diuretics
(Glucocorticoids)
Infection Risk (2)
Prednisone, Budesonide/Beclomethasone dipropionate/ Fluticasone (Oral/Inhaled Glucocorticoids)
(Leukotriene Modifiers)
Take on empty stomach
(Leukotriene Modifiers)