[BIOLOGY] The Cell Part 2
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/63
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
1
New cards
1. Passive Transport
2. Active Transport
Cell Transport Mechanisms
2
New cards
#### Simple Diffusion and Osmosis
Types of Passive Transport
3
New cards
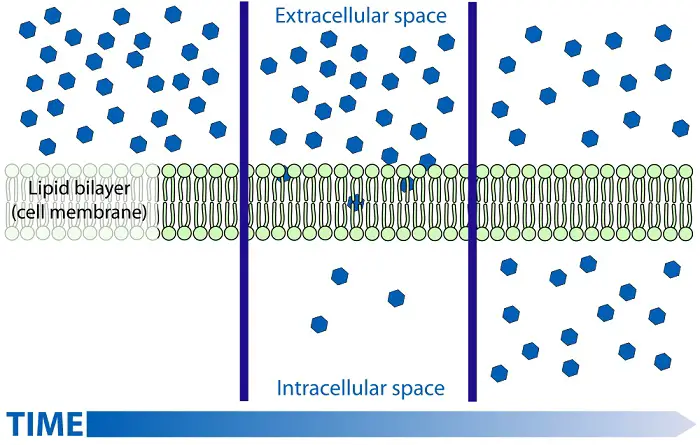
Simple Diffusion
the tendency of particles to spread out into available spaces. Randomly moving molecules will diffuse through air and water–or into and out of the cell. This spread can be visualized when trying to make drinks from powdered formulas or when adding dye to the water.
4
New cards
Simple Diffusion
5
New cards
concentration gradient
is the term for the difference in concentration between spaces
6
New cards
Osmosis
a special type of diffusion wherein water or other solvents diffuse through a semi-permeable membrane.
7
New cards
tonicity
refers to the ability of the surrounding solution to cause cells to lose or gain water.
8
New cards
**isotonic solution**
concentration of solutes is relatively equal to those of the outside environment, the cell is able to maintain its shape. This is why intravenous fluids administered to patients must be isotonic to the blood to prevent complications.
9
New cards
**hypotonic solution**
the solute concentration of the environment is lower than that of the cell (more water outside), resulting in water entering the cell, which then leads to lysis or burst.
10
New cards
hypertonic solution
water concentration in the cell is higher than in the outside environment
11
New cards
crenation
describe the formation of uneven notched corners on cells caused by osmosis water loss
12
New cards
osmoregulation
the process of maintaining salt and water balance (osmotic balance) across membranes within the body.
13
New cards
**turgor pressure**
the hydrostatic pressure in excess of ambient atmospheric pressure which can build up in living, walled cells.
14
New cards
plasmolysis
defined as the process of contraction or shrinkage of the protoplasm of a plant cell and is caused due to the loss of water in the cell.
15
New cards
#### **Facilitated Diffusion**
the diffusion of solutes through transport proteins in the plasma membrane
16
New cards
#### **Facilitated Diffusion**
One transport protein provides a **channel** for specific molecules or ions to pass through the membrane. Another type, called **carrier proteins**, binds its passenger, which causes the protein to change shape, releasing the transported molecule on the other side.
17
New cards
aquaporins
protein channels that allows very rapid diffusion of water into and out of the cell.
18
New cards
active transport
requires cells to expend energy for substances to be moved against a concentration gradient
19
New cards
Protein pumps
are often used to push solutes against a concentration gradient. The process uses energy in the form of ATP to allow transport proteins to change shape in such a way that it is able to transfer substances on the side opposite the concentration gradient.
20
New cards
exocytosis
a process wherein bulky materials such as proteins or polysaccharides must be exported out of the cell. The Golgi apparatus facilitates this movement in cells by creating transport vesicles that move to the edge of the cell, fusing with the plasma membrane and releasing its contents.
21
New cards
**endocytosis**
a process where large molecules or droplets of fluid are taken into the cell.
22
New cards
1. **Phagocytosis**
2. Receptor-mediated endocytosis
3. Pinocytosis
3 types of **endocytosis**
23
New cards
Phagocytosis
occurs when a cell engulfs a particle by wrapping around it with extensions called pseudopodia and packaging it as vacuoles. The vacuole must then fuse with a lysosome to digest the contents of the vacuole.
24
New cards
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
allows cells to acquire specific substances. These are proteins for specific molecules, and once they bind with a specific compound, they begin engulfing those substances.
25
New cards
**Pinocytosis**
allows the cell to engulf small particles of fluids.
26
New cards
binary fission
Single-celled organisms usually reproduce by dividing in half, termed **_______**, resulting in offspring that are genetic replicas of the parent cells.
27
New cards
Sexual reproduction
requires the fusion of gametes, cells specialized for reproduction, i.e., egg and sperm cells
28
New cards
**chromatin**
refers to a mixture of DNA and proteins that form the chromosomes found in the cells of humans and other higher organisms.
29
New cards
sister chromatids
joined copies of the original chromosome held together by proteins
30
New cards
centromere
a constricted region of a chromosome and plays a key role in helping the cell divide up its DNA during division (mitosis and meiosis)
31
New cards
cell cycle
an ordered sequence of events that run from the moment a cell is formed until it divides into two cells.
32
New cards
Cell division
is the basis of reproduction for every organism
33
New cards
**interphase (growing stage) and mitotic phase (actual cell division)**
Two main stages of cell cycle
34
New cards
1. G1 Phase or the first gap
2. S phase or synthesis of DNA
3. G2 phase or the second gap
three subphases of interphase
35
New cards
S phase
subphase of interphase where chromosomes are duplicated and DNA is copied
36
New cards
G2 Phase
subphase of interphase where the cell completes preparation for cell division.
37
New cards
**karyokinesis** or mitosis and **cytokinesis**.
2 overlapping stages of mitotic phase
38
New cards
karyokinesis
in this mitotic phase, the nucleus and its contents (emphasis on the duplicated chromosomes) divide and are distributed into the nuclei of the two daughter cells.
39
New cards
Cytokinesis
this phase begins before the end of mitosis and causes the cell’s cytoplasm to divide into two. The combination of these two produces genetically identical daughter cells, and each daughter cell may then proceed through G1 and repeat the cycle.
40
New cards
1. Prophase
2. Metaphase
3. Anaphase
4. Telophase
stages of mitosis
41
New cards
prometaphase
stage that occurs between prophase and metaphase
42
New cards
prophase
Changes occur in both the nucleus and cytoplasm. In the nucleus, the chromatin forms chromosomes and begins to duplicate into sister chromatids. In the cytoplasm, microtubules grow from centrosomes forming mitotic spindles that begin to move away from each other.
43
New cards
Prometaphase
The nuclear envelope dissolves. Microtubules extend into the nuclear region and reach the chromosomes. Each sister chromatid contains sites called kinetochores where some of the spindles attach. The spindles move chromosomes toward the center of the cell.
44
New cards
**kinetochores**
large protein assemblies that connect chromosomes to microtubules of the mitotic and meiotic spindles in order to distribute the replicated genome from a mother cell to its daughters.
45
New cards
Metaphase
The mitotic spindle is fully formed, with its poles at opposite ends of the cell. The chromosomes line up on an imaginary plate in the middle of the cell called the metaphase plate, with the centromeres lined up on the plate. For each chromosome, the kinetochores of the sister chromatids are attached to opposite spindles from each pole.
46
New cards
Anaphase
The centromeres come apart, separating the sister chromatids towards opposite poles of the cell. As this happens, the spindle microtubules attached to the chromatids shorten while those unattached lengthen. This moves the poles further apart so that by the end of this stage, there are equal collections of chromosomes on the two poles.
47
New cards
Telophase
The cell continues to elongate. Daughter nuclei appear, and the nuclear envelope begins to form around the chromosomes. In terms of process, this is like the reverse of what occurred in the prophase. By the end of this stage, the chromatin uncoils, and the mitotic spindle disappears.
48
New cards
cleavage furrow
a shallow groove on the cell’s surface. This site has a microfilament ring that ultimately contracts and pinches the cell into two.
49
New cards
cell plate
grows outward, accumulating more cell wall material as vesicles fuse with it until it fuses with the plasma membrane and the cell plate joins the parental cell wall.
50
New cards
**locus**
The physical site or location of a specific gene on a chromosome.
51
New cards
sex chromosomes
x and y chromosomes
52
New cards
autosomes
chromosomes other than x and y
53
New cards
diploid number
The total number of chromosomes in an organism
54
New cards
Meiosis
he cell division that produces haploid gametes in diploid organisms
55
New cards
Haploid
the presence of a single set of chromosomes in an organism's cells.
56
New cards
diploid
the presence of two complete sets of chromosomes in an organism's cells, with each parent contributing a chromosome to each pair. Humans are diploid, and most of the body's cells contain 23 chromosomes pairs.
57
New cards
1. Prophase I
2. Metaphase I
3. Anaphase I
4. Telophase I
stages of Meiosis I
58
New cards
tetrad
four chromatids aligned gene by gene.
59
New cards
Prophase I
* Homologous chromosomes, composed of two sister chromatids, come together in pairs forming a **tetrad**, four chromatids aligned gene by gene.
* **Crossing over**, one of the most important events in meiosis occurs, that is chromatids exchange segments with one chromatid of the other homologous pair. This rearranges genetic information.
* As prophase I continue, the chromosome coil, the nuclear envelope dissolves, and the tetrad is captured by the spindle microtubules and moves them to the center of the cell.
* **Crossing over**, one of the most important events in meiosis occurs, that is chromatids exchange segments with one chromatid of the other homologous pair. This rearranges genetic information.
* As prophase I continue, the chromosome coil, the nuclear envelope dissolves, and the tetrad is captured by the spindle microtubules and moves them to the center of the cell.
60
New cards
Metaphase I
* The tetrads are aligned on the metaphase plate. The spindles are attached to the kinetochores at the centromeres. In each tetrad, the homologous chromosomes are held together at the sites where crossing over took place.
* For each tetrad, the spindle from opposite poles of the cell attaches to one of the homologous pairs. This arrangement directs each tetrad to move toward opposite poles of the cell.
* For each tetrad, the spindle from opposite poles of the cell attaches to one of the homologous pairs. This arrangement directs each tetrad to move toward opposite poles of the cell.
61
New cards
Anaphase I
* This stage is marked by the migration of chromosomes toward the poles of the cell.
* In contrast to mitosis, the sister chromatids remain attached, and only the tetrads which contain sites of cross-over split up.
* In contrast to mitosis, the sister chromatids remain attached, and only the tetrads which contain sites of cross-over split up.
62
New cards
Telophase I
* The chromosomes arrive at the poles, resulting in each pole having a haploid set of chromosomes.
* After cytokinesis, two haploid daughter cells are formed.
* After cytokinesis, two haploid daughter cells are formed.
63
New cards
Meiosis II
can be summarized as sister chromatids separating and are essentially the same as mitosis.
64
New cards
tumor cells
Cells in the human body, if left unchecked, may proliferate into an abnormal mass, forming _____