Constituents of the atom, stable and unstable nuclei, decay.
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
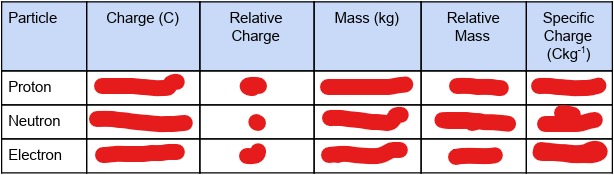
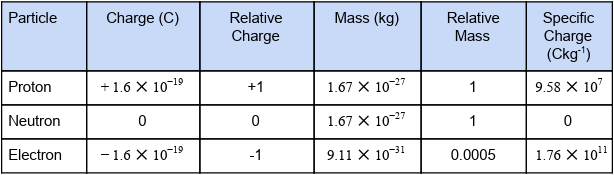
fill in the table
define specific charge
the mass to charge ratio of a particle
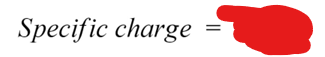
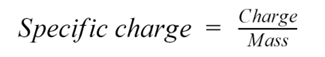
What is the ‘nucleon number’ of a particle?
the amount of protons and neutrons in the particle
define an isotope
an atom with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons
what does the Strong Nuclear Force do?
it keeps nuclei stable by counteracting the electrostatic force of repulsion between protons in the nucleus.
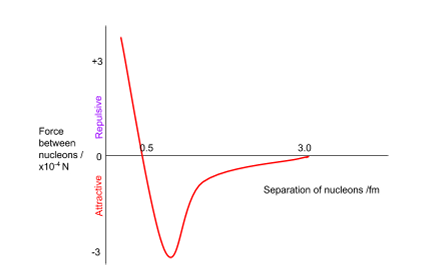
to what length is the strong nuclear force attractive or repulsive?
attractive until 3 fm but repulsive before 0.5 fm.
what does the graph of attraction due to strong nuclear force look like?
define an unstable nuclei.
nuclei which have too many of either protons, neutrons or both.
why does this make a nucleus unstable?
the unstable amounts of nucleons causes the SNF to not be enough to keep them stable.
what do unstable nuclei do to become stable?
decay.

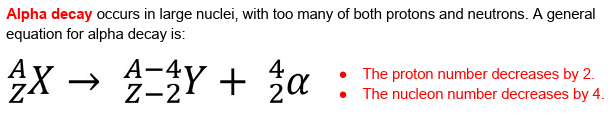

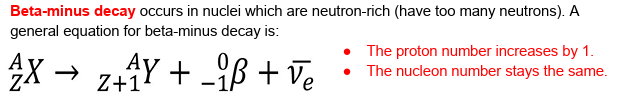
why were neutrinos theorised to be in Beta decay?
as the interaction didn’t conserve energy, so there had to be something missing.