Biology - B1
5.0(3)
Card Sorting
1/15
Earn XP
Last updated 7:45 PM on 6/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
1
New cards
what are the two different types of cells?
eukaryotic - has a nucleus (animal and plant)
prokaryotic - without a nucleus (bacteria)
prokaryotic - without a nucleus (bacteria)
2
New cards
what are the function of organelles?- nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondria, ribosomes, cell membrane, cell wall
nucleus - hold genetic information
cytoplasm - where chemical reactions take place
mitochondria - where aerobic respiration takes place
ribosomes - protein synthesis
cell membrane - allows substances in + out of the cell
cell wall - gives structure
cytoplasm - where chemical reactions take place
mitochondria - where aerobic respiration takes place
ribosomes - protein synthesis
cell membrane - allows substances in + out of the cell
cell wall - gives structure
3
New cards
microscopes and their uses
light: for living things, less resolution, cheaper, in colour
electron: not for living things (vacuum), better resolution, used by unis/government, higher magnification
electron: not for living things (vacuum), better resolution, used by unis/government, higher magnification
4
New cards
REQUIRED PRACTICAL - microscopes
1. take specimen and place on slide
2. stain specimen
3. place a cover slip on
4. start on lowest magnification then focus
5. repeat on higher magnification
5
New cards
what are the specialised animal cells?
sperm: flagellum for swimming, acrosome containing enzymes, mitochondria for energy to travel to the cells, half the genetic info
muscle cells: many mitochondria to respirate + release energy for movement
nerve cells: heavily insulated, long to speed up electric impulse
muscle cells: many mitochondria to respirate + release energy for movement
nerve cells: heavily insulated, long to speed up electric impulse
6
New cards
what are the specialised plant cells?
xylem - dead cells form a tube that transports water from the roots (one way transportation)
phloem - transport glucose (both directions)
root hair cells - large surface area for active transport of ions, lots of mitochondria for energy to transport
phloem - transport glucose (both directions)
root hair cells - large surface area for active transport of ions, lots of mitochondria for energy to transport
7
New cards
what is cell differentiation?
animal cells - differentiate in the early stages ONLY
plant cells - differentiate throughout life
plant cells - differentiate throughout life
8
New cards
REQUIRED PRACTICAL - growing micro-organisms
1. petri dish + culture are sterilised
2. spread onto agar plate with inoculating loop (passed through flame)
3. sellotape and store upside down
4. in schools - stored at 25C not body temp
once grown, chemicals can be placed on to see what kills them - zones of inhibition around chemical
larger zone of inhibition = chem works better
9
New cards
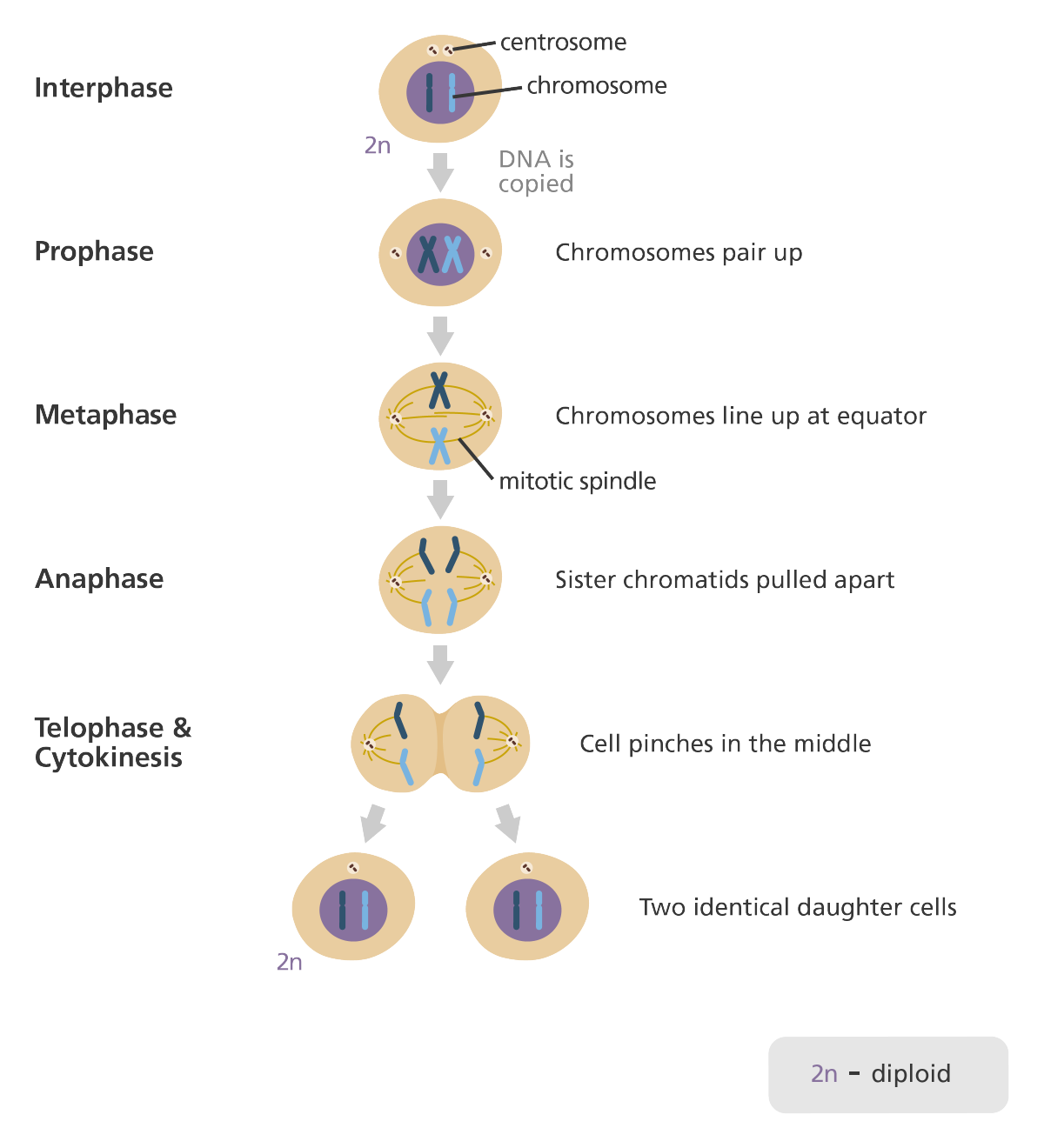
what is cell division?
1. every body cell needs same number of chromosomes so cell duplicates all of the organelles before division
2. the chromosomes are pulled to the edge of the cell and the nucleus divides
3. cytoplasm and cell membrane divides
10
New cards
stem cells + their uses (humans)
undifferentiated cells - can turn into any cell
found in embryos (any cell) and bone marrow (blood cell)
stem cells can treat diabetes + paralysis
therapeutic cloning = embryo produces with the patients genes so tissue is not rejected
issues: risk of viral transfer and ethical reasons
found in embryos (any cell) and bone marrow (blood cell)
stem cells can treat diabetes + paralysis
therapeutic cloning = embryo produces with the patients genes so tissue is not rejected
issues: risk of viral transfer and ethical reasons
11
New cards
stem cells (plant)
found in the meristem tissue
can turn into any cells throughout life
make clones quickly, species can be protected, crop plants with disease can be cloned
can turn into any cells throughout life
make clones quickly, species can be protected, crop plants with disease can be cloned
12
New cards
what is diffusion?
diffusion is the movement of gas + liquid from a high to low concentration
PASSIVE - no energy required
rate of diffusion is increased by:
* high concentration
* temperature increase
* larger surface area
PASSIVE - no energy required
rate of diffusion is increased by:
* high concentration
* temperature increase
* larger surface area
13
New cards
how is diffusion helped?
in large animals diffusion is increased by:
* areas of large surface area (lungs or small intestine)
* thin membrane to allow shorter pathway
* good blood supply
* being ventilated (gaseous exchange)
\
other organisms have gills, roots + leaves which improve diffusion
* areas of large surface area (lungs or small intestine)
* thin membrane to allow shorter pathway
* good blood supply
* being ventilated (gaseous exchange)
\
other organisms have gills, roots + leaves which improve diffusion
14
New cards
what is osmosis?
osmosis is the movement of water molecules from a high to low concentration
PASSIVE - no energy required
has to go through a semi-permeable membrane
sugars + salts CANNOT pass through membrane, ONLY WATER
PASSIVE - no energy required
has to go through a semi-permeable membrane
sugars + salts CANNOT pass through membrane, ONLY WATER
15
New cards
what is active transport?
movement of molecules from low to high concentration
ACTIVE - requires energy from respiration so cells (such as root hair cells) have many mitochondria
ACTIVE - requires energy from respiration so cells (such as root hair cells) have many mitochondria
16
New cards
REQUIRED PRACTICAL - concentrations + at
1. fill 5 test tubes with different concentrations of solution
2. weigh the 5 pieces of potatoes (or any veg)
3. places pieces into the different solutions
4. leave for a set amount of time
5. take potato out, blot with paper and reweigh