final bio test part 2
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
6.7 menstrual cycle
menstural cycle
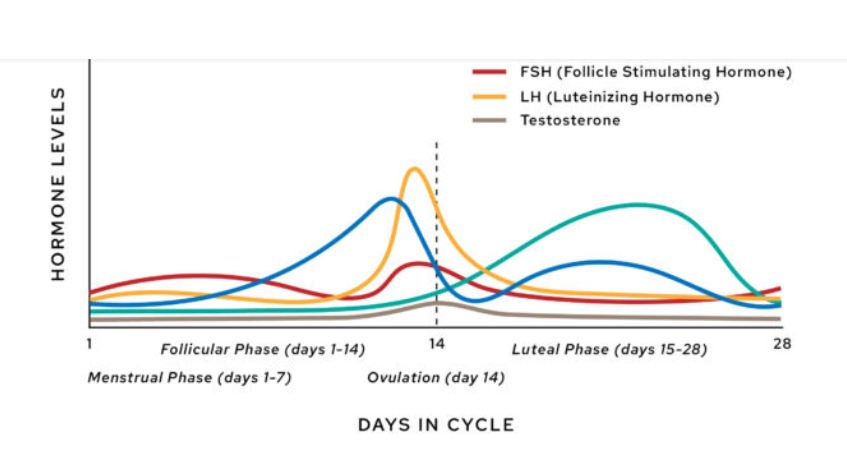
ovarian hormones
estrogen and progesterone
pituitary hormones
LH (luteinizing hormone) and FSH (follicle stimulating hormone)
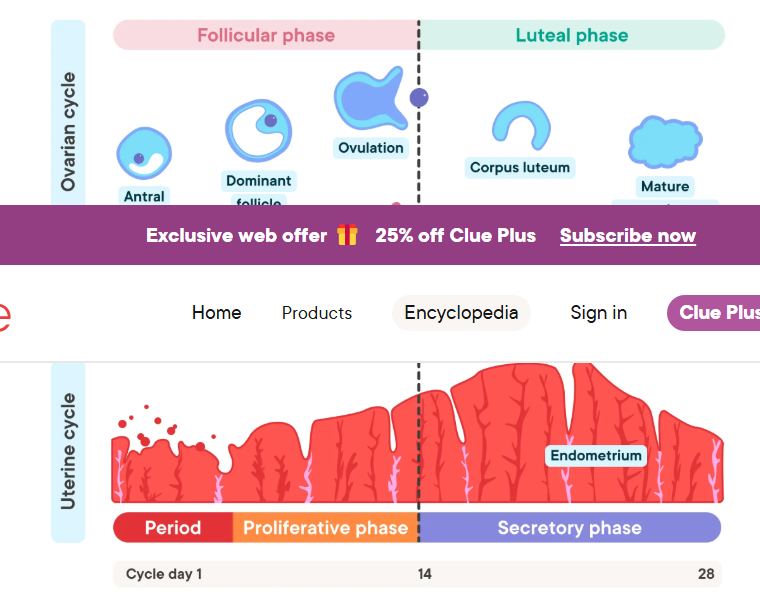
Follicular phase
day one of the cycle is the onset of the follicular phase
the endometrium (inner lining) starts to thicken
follicles start to grow on the ovaries
follicular phase pt.2
FSH signals an increase in ovarian estrogen (positive feedback)
this estrogen thickens the endometrium again
FSH also signals a group of follicles to develop (each follicle an egg is stimulated to grow)
Phase 1
the follicles release even more estrogen. this increase in estrogen stimulates the release of from the pituary gland
LH also builds the follecular walll
LH and estrogen have what kind of relationship?
Positive feedback as a large follicular wall means more estrogen is released
ovulation
when LH spikes, the most developed follicle grows enough to rupture, releasing its ovum into the oviduct (fallopian tube)
marks the end of the follicular phase
Very high estrogen levels inhibit……
LH and FSH to allow the frogression to phase 2
this is negative feeback
Phase 2: Luteal
endometrium continues to thicken
the ruptured follicle becomes a corpus luteum which releases estrogen and progesterone
progesterone maintains the endometrium
estrogen and progesterone
continue to inhibit LH and FSH until the next cycle begins (negative feedback)
if fertilization does not occur
the corpus luteum breaks down
progesterone and estrogen drop, causing the endometrium to break down
the endometrium is shed during mentation
menstruation marks the end of the cycle and beginning of the next follicular phase
progression of hormones
6.8 reproduction
In an unchanging environment what type of reproduction is likely to occur?
asexual reproduction
sexual reproduction
increases the variation required to adapt to a changing environment
human reproduction
humans are sexually dimorphic
hormones control the development of sex specific characteristics
10 weeks into pregnancy Gonadotropin releasing hormones are released by the fetus
Gonadotropin hormones
allow for sex specific characteristics
when present maternal hormones encourage female typical development
testosterone form the fetal testis encouraging male-typical development
6 months after birth, gonadotropin…….
stops being produced
and children develop in similar ways until puberty
during puberty
GnRH is released again by the hypothalamus
GnRH flows directly to the pituary gland which release LH and FSH and these change the gonands
(testies and ovarys)
LH and FSH
bring on the menstrual cycle in females, increases estradiol and progesterone causing sex specific changes
increase growth of the testies and secreation of testosterone in males causing changes
human egg (ovum)
Human sperm (Spermatozoa)
Spermatogenesis
starts in the outer part of the seminiferous tubules and progresses inward toward the lumen
seminiferous tubules
surrounded by a basement membrane
there is a layer of diploid germinal epithelial cells beneath this membrane
these are called spermatogonia (they go through mitosis)
spermatogonia
stems cells that divide repeatedly by mitosis to replace themselves
may also divide my meiosis to produce sperm
Sertoli cells
nurse cells
supply enerfy for differentialtion