Science Final REVIEW with waves
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
129 Terms
solid
definite shape and definite volume. Particles closely packed
liquid
no definite shape but a definite volume
gas
no definite shape and no definite volume
melting
change from solid to liquid
freezing
change from liquid to solid
vaporization
when particles in a liquid gain enough energy to form a gas
evaporation
vaporization that takes place only on the surface of a liquid
boiling
vaporization that occurs when a liquid changes to a gas below its surface
condensation
when particles in a gas lose enough thermal energy to form a liquid
sublimation
a change directly from solid to the gas state without becoming liquid
pressure
the force applied to a unit area of surface
deposition
a change directly from a gas to the solid state without becoming a liquid.
endothermic
absorbing thermal energy
exothermic
releasing thermal energy
motion
the act of changing location from one place to another
reference point
A place or object used for comparison to determine if an object is in motion
meter
the basic unit of length
speed
distance travelled per unit time
average speed
Total distance divided by total time
velocity
speed in a given direction
slope
The steepness of a line on a graph; rise/run
acceleration
The rate at which velocity changes
Positive acceleration
increasing speed
Negative acceleration
decreasing speed
gravity
the force that pulls objects toward each other
air resistance
force that opposes the motion of objects that move through the air
Newton's First Law of Motion
An object at rest will remain at rest, and an object moving at a constant velocity will continue moving at a constant velocit, unless it is acted upon by an unbalanced force. Another name is Law of Inertia
Newtons' Second Law of Motion
Acceleration depends on the objects mass and on the netforce acting on the object
inertia
the tendency of an object to resist any change in its motion
Newton's Third Law of Motion
For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction
momentum
mass x velocity
fluid
a material that can easily flow
density
mass/volume

work
when an object moves in the same direction in which the force is exerted; force X distance

joule
a unit of work equal to one newton-meter
power
the rate at which work is done; work/time
simple machine
device that allows you to do work in a way that is easier or more effective
input force
the force you exert on a machine
output force
the force exerted on an object by a machine
input work
input force x input distance
output work
output force x output distance
mechanical advantage
the number of times the force exerted on a machine is multiplied by the machine; output force/input force
efficiency
the ratio of the output to the input of any system; output work/input work X 100%
inclined plane
a sloping surface, such as a ramp, that reduces the amount of force required to do work
wedge
a double inclined plane that moves
screw
inclined plane wrapped around a cylinder
lever
a rigid bar pivoted about a fulcrum
fulcrum
the fixed point around which a lever pivots
wheel and axle
simple machine made from two circular objects of different diameters that are attached and rotate together
pulley
a simple machine consisting of a grooved wheel that holds a rope or a cable
compound machine
a device that combines two or more simple machines
force
a push or pull
newton
unit of force
net force
the combination of all forces acting on an object
unbalanced forces
the forces acting on an object that causes a change in velocity; making the object speed up, slow down, or change direction
balanced forces
equal forces acting on an object in oppisite directions
friction
the force that one surface exerts on another when the two rub against each other
static friction
friction that acts on objects that are not moving
sliding friction
friction that occurs when one solid surface slides over another
rolling friction
friction that occurs when an object rolls over a surface
fluid friction
friction that occurs as an object moves through a fluid
weight
the force of gravity on a person or object at the surface of a planet
free fall
the motion of a falling object when the only force acting on it is gravity
subtraction
two forces pushing AGAINST each other
addition
two forces pushing WITH each other
solution
well-mixed mixture that contains a solvent and at least one solute
suspension
a mixture in which particles can be seen and easily separated by settling or filtration
atom
Smallest particle of an element
molecule
More than one atom bonded together
element
Contains only one type of atom
compound
A substance made up of atoms of two or more different elements joined by chemical bonds
proton
a positively charged particle located in an atom's nucleus
neutron
a neutral particle located in an atom's nucleus
electron
a negatively charged particle located outside an atom's nucleus about 2000 times smaller than either a proton or neutron
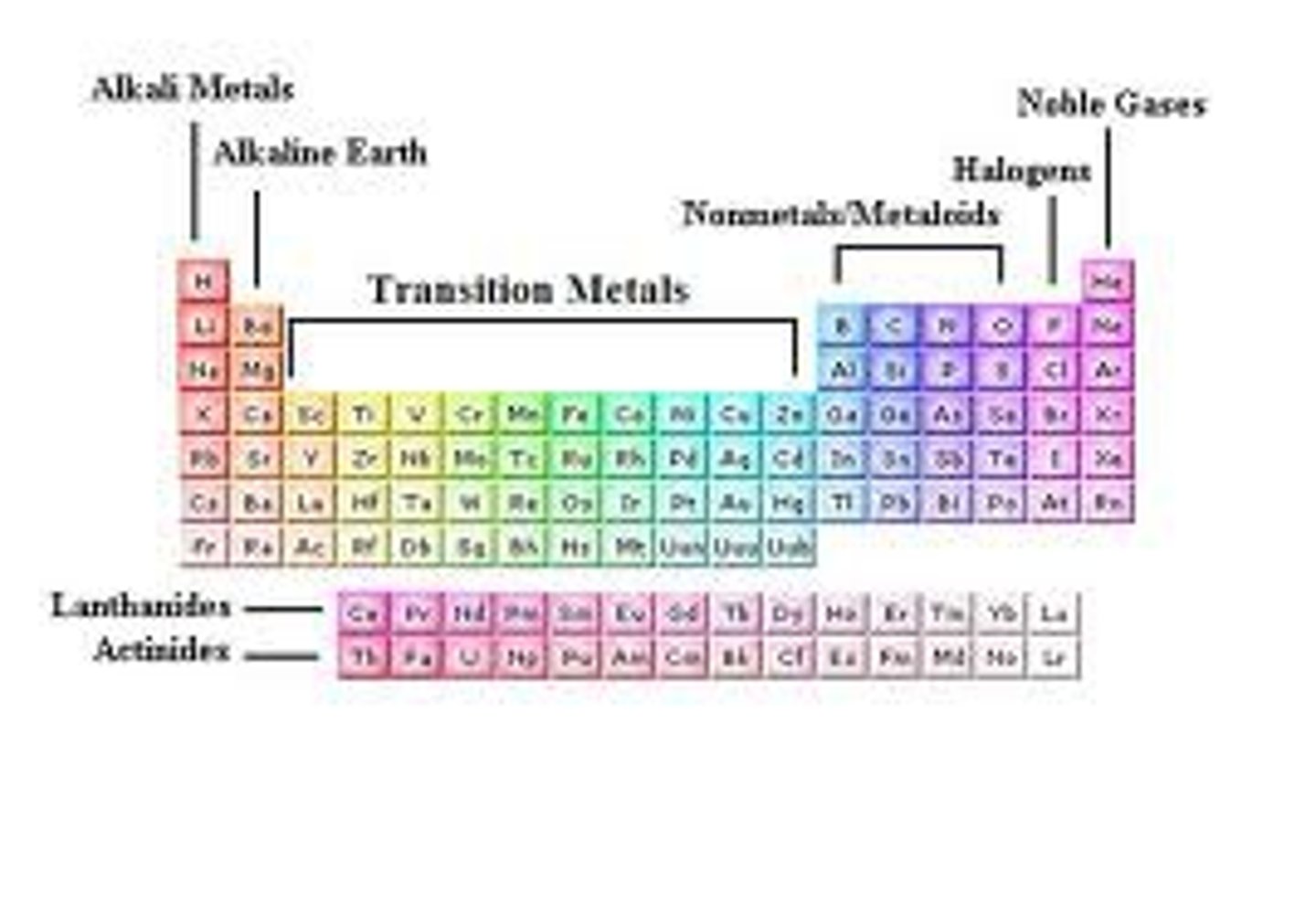
periodic table
a table of the elements, arranged by atomic number, that shows the patterns in their properties
water displacement
Process for finding the volume of an irregular solid
grams
unit for measuring mass
milliliters (mL)
unit for measuring volume of a liquid
solvent
substance that does the dissolving. For example, the water when sugar dissolves in water.
heterogeneous mixture
a type of mixture in which the parts of the mixture are noticeably different from one another
homogeneous mixture
a mixture that is the same throughout
physical change
A type of change that involves the physical properties of a substance. No new substance is created.
chemical change
Process by which substances are changed into different substances with different properties
physical
chocolate melting, salt dissolving in water and painting a wall are all examples of __________________ changes
chemical
paper burning, bubbles forming when vinegar is added, and milk going sour are all examples of __________ changes
inferring
explaining or interpreting the things you observe
predicting
making a forecast of what will happen in the future based on past experience or evidence
hypothesis
possible explanation for a set of observations or possible answer to a scientific question
manipulated (independent) variable
factor in an experiment that a scientist purposely changes; also known as independent variable
responding (dependent) variable
factor in an experiment that a scientist wants to observe, which may change in response to the manipulated variable; also known as a dependent variable
thermal energy
energy of particle motion (makes things warm)
mechanical energy
energy an object has because of its motion or position

chemical energy
Energy stored in chemical bonds
electrical energy
Energy caused by the movement of electrons.
nuclear energy
The potential energy stored in the nucleus of an atom

kinetic energy
Energy of motion

potential energy
energy that is stored

Sound energy
the energy produced when sound waves move outward from a vibrating object or sound source

light energy
a form of energy that travels in waves, visible with the eye

noble gases
What do we call the group all the way to the right, on the periodic table? (see image)