Microbial Diversity 2
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
Phylum Phaeophyta (Brown Algae)
harvested for algin
Phylum Rhodophyta (red algae)
harvested for agar and carrageenan
Phylum Chrysophyta (golden algae)
important in lakes
Flagellates (Mastigophora)
motile through the use of flagella
Giant Kelp

Sargassum

Licmophora

Saccharomyces
Positive - Bread, wine, beer
Negative - Food spoilage
Trichoderma
Positive - Cellulose used for juices and fabric
Negative - Cryphonectria parasitica (chestnut blight)
Sexual spores
fusion of two gametes (ascospores, basidiospores, zygospores)
Chlamydosphores
thick-walled spore-like
Flatworms
flat, no definite body cavity; digestive tract a blind pouch; simple excretory & nervous systems
Trematodes (flukes)
flattened , non-segmented worms with sucking mouthparts
Roundworms (nematodes)
round, a complete digestive tract, a protective surface cuticle, spines & hooks on mouth; excretory & nervous systems poorly developed
Intermediate Host
Harbors the developmental stage of the parasite
Diagnostic Stage
Stage in the parasitic life cycle that can be identified by examining patient specimens
Subcutaneous mycoses
fungal infections beneath the skin
Systematic mycoses
fungal infection deep within the body
Eukaryotes
Includes species of algae, fungi, protozoa, lichens, and slime molds.
Phytoplankton
Microscopic, free-floating, autotrophic organisms that function as producers in aquatic ecosystems
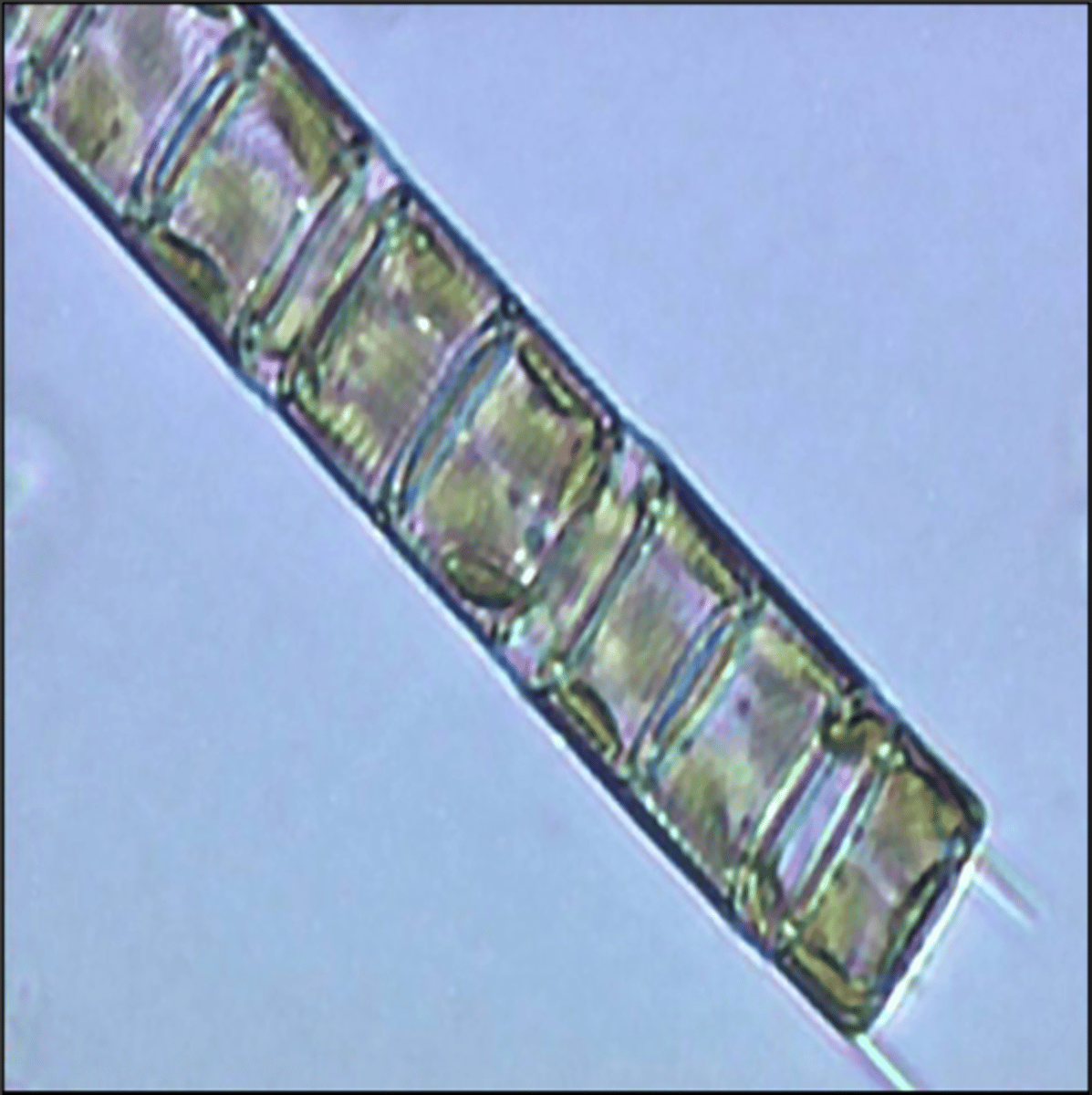
Phylum Bacillariophyta
Diatoms; attractive geometric shapes
Phylum Dinoflagellata
dinoflagellates; produce neurotoxins causing paralytic shellfish poisoning
Phylum Chlorophyta (green algae)
gave rise to plants; green algae
algin
used as a gelling agent in food and other industries.
Prototheca
rare parasitic, non-photosynthetic algae
cause protothecosis
Carrageenan
gelatinous material that can be a thickening agent
Amoebas (Sarcodina)
move through pseudopods
or false feet
Sporozoans (Apicomplexa)
non-motile, parasitic
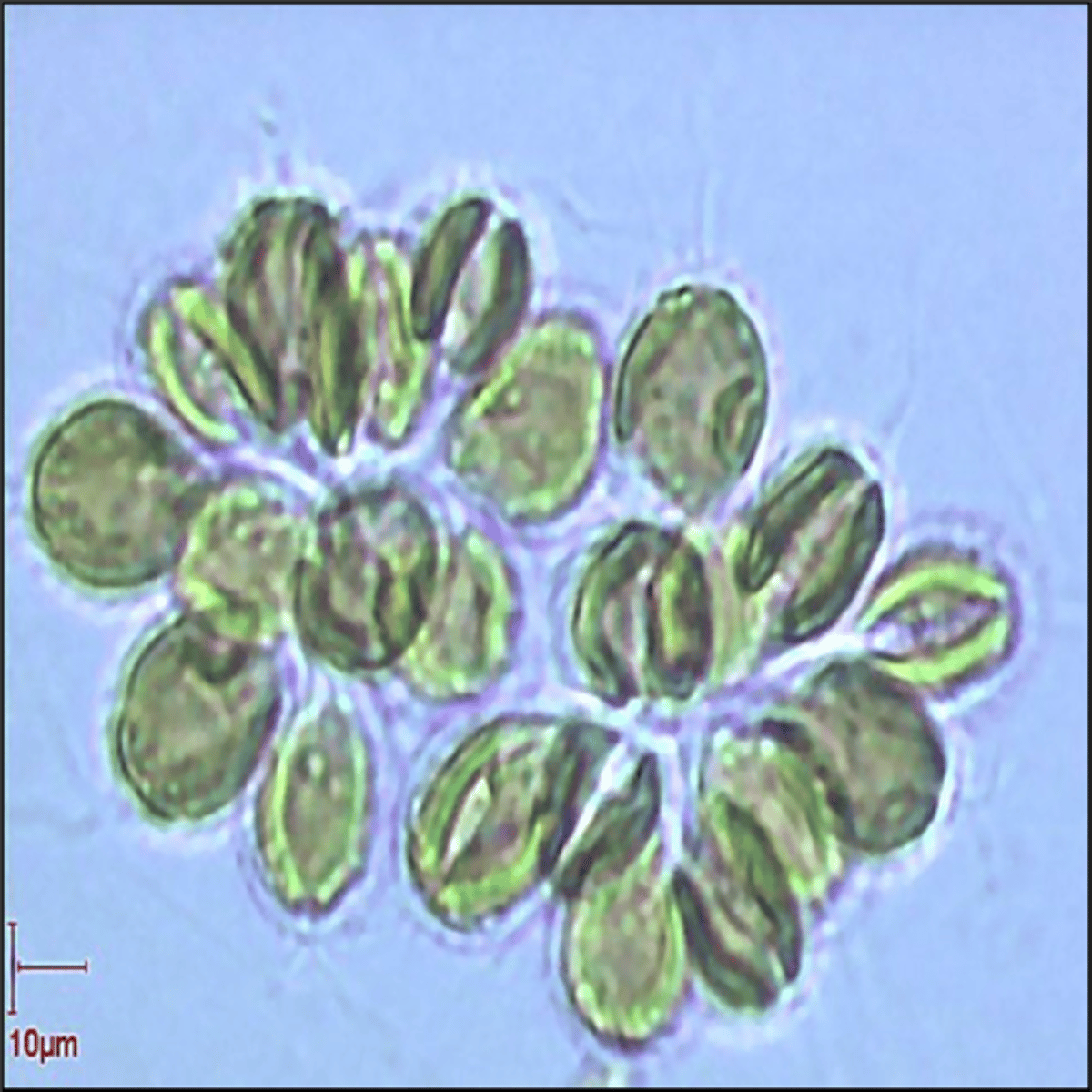
Microcladia

Porphyra

Gibsmithia

Synura
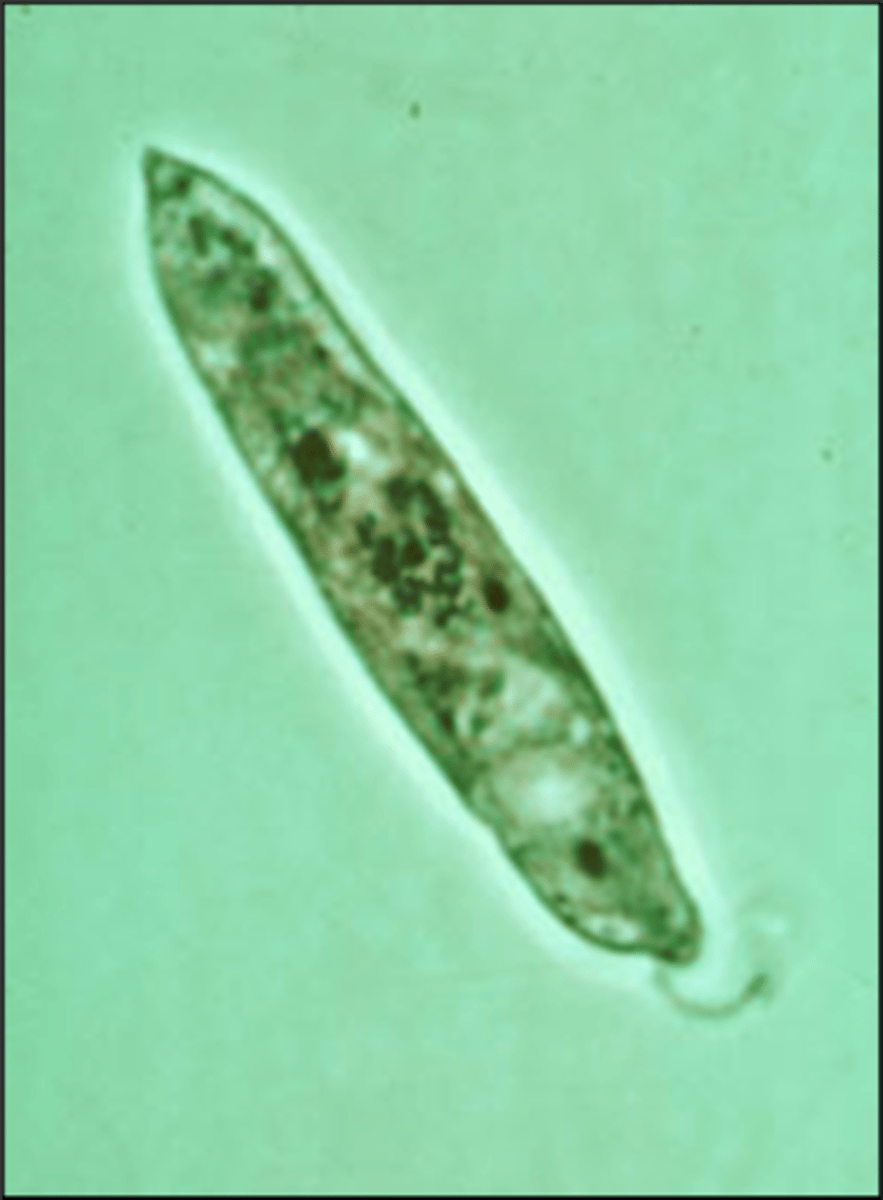
Euglena Acus

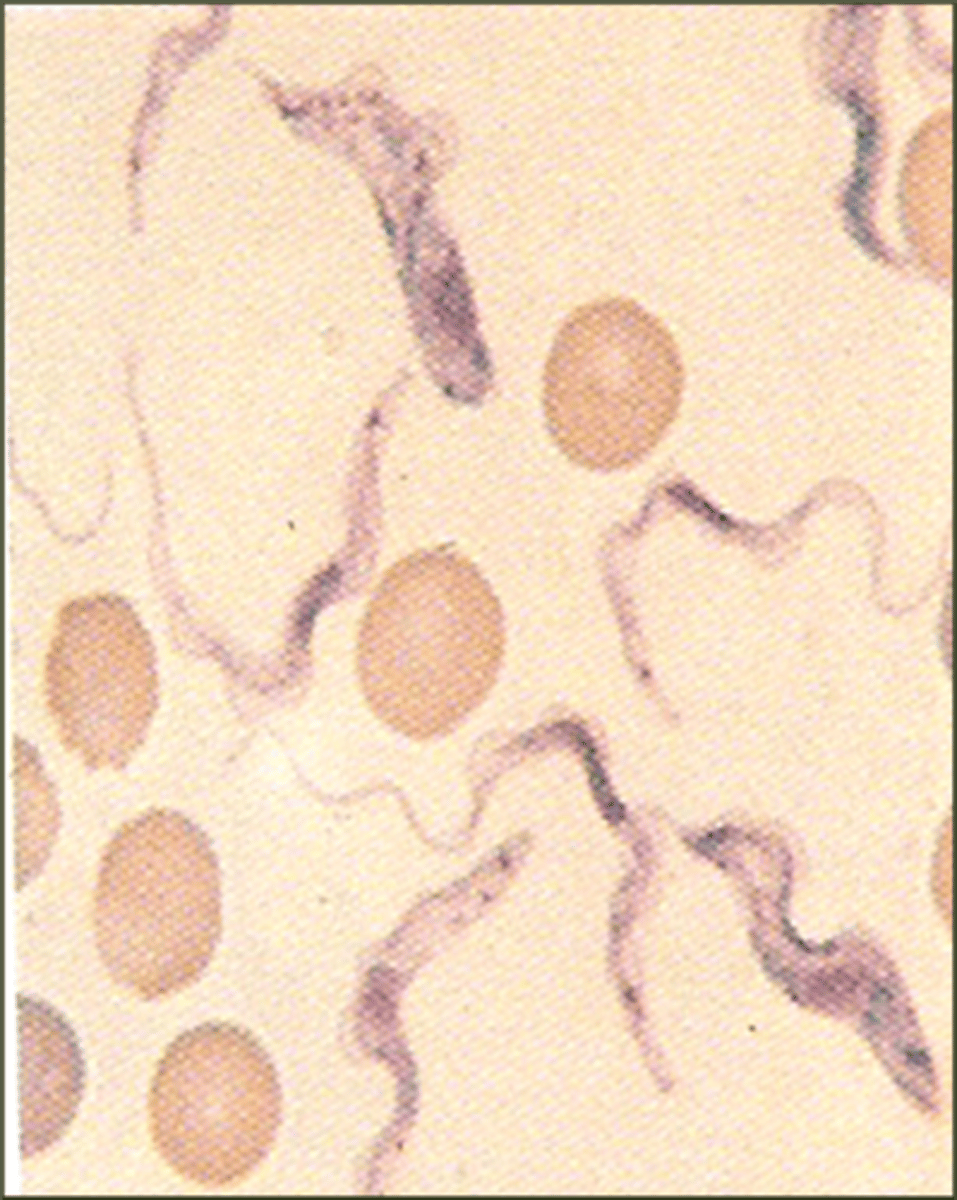
Trypanosoma
Euglena
Hyphae
long filamentous fungi or molds
Entamorphaga
Positive - Gypsy moth control
Conidia
asexual spores; not formed by fusion
Plasmogamy
Fusion of the cytoplasm of two cells; occurs in the sexual stage of a fungal life cycle.
Karyogamy
Fusion of the nuclei of two cells; occurs in the sexual stage of a fungal life cycle
Budding
yeasts divide asymmetrically
Candida albicans
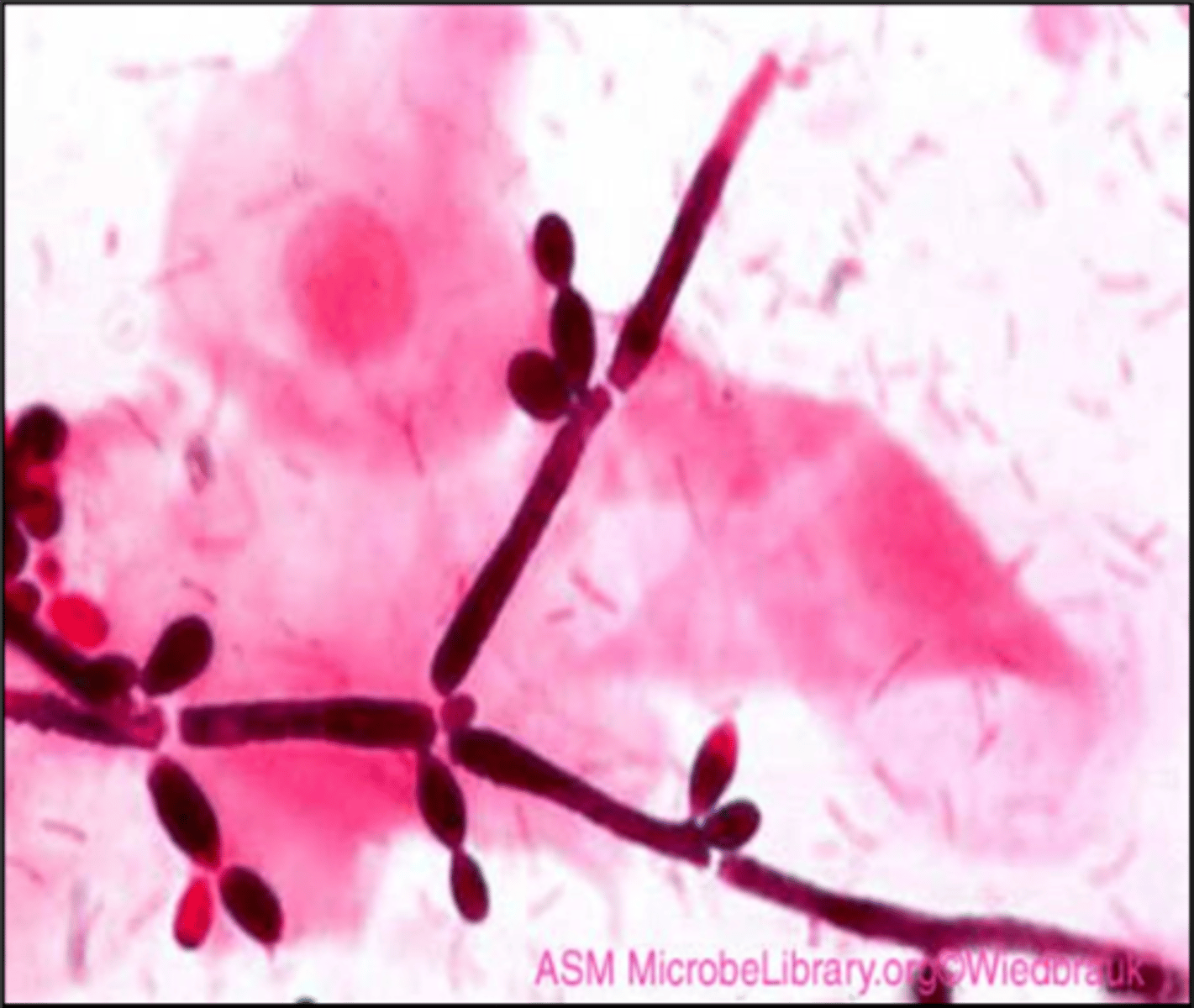
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
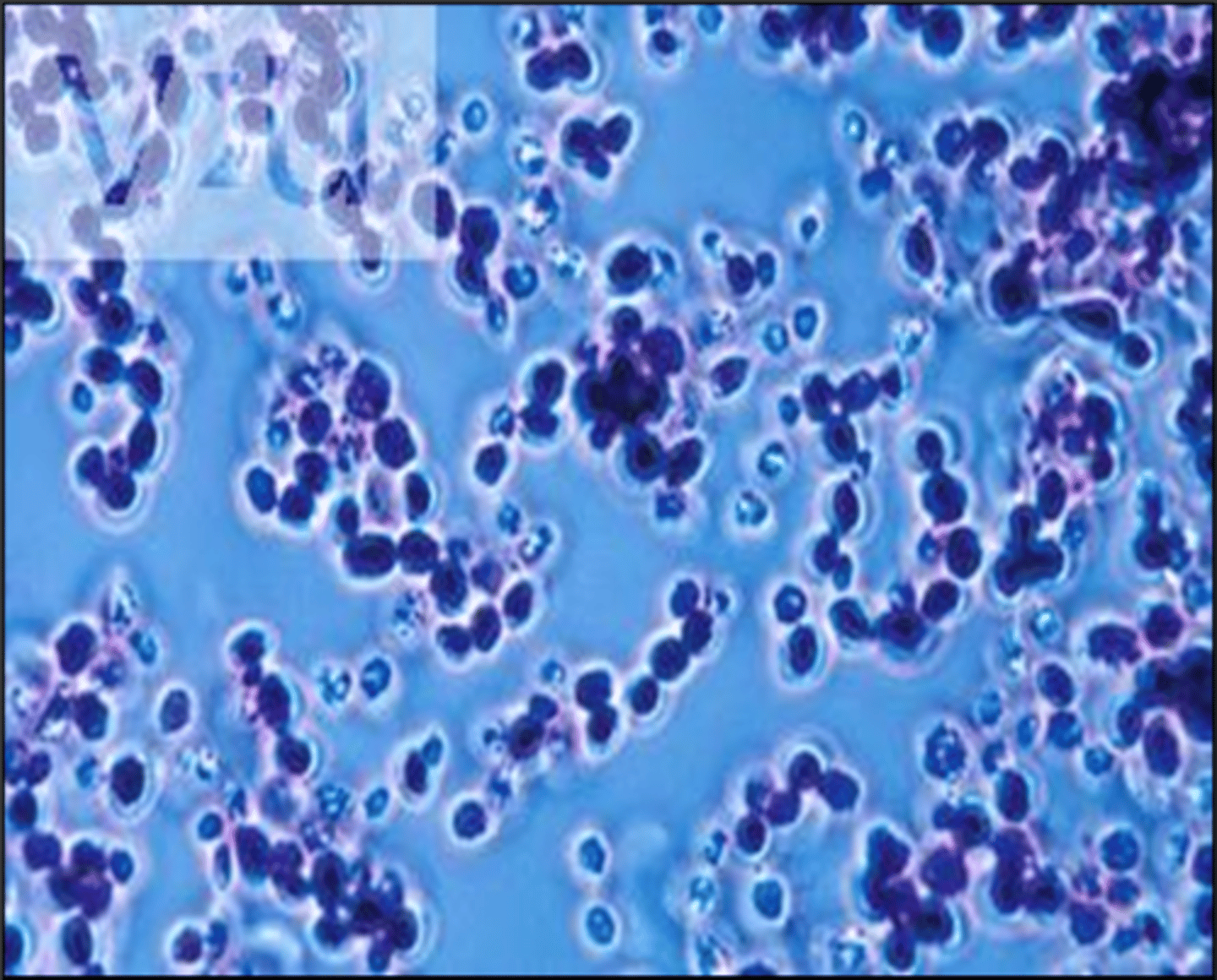
Plasmodial slime molds
-Multinucleated large cells
-Cytoplasm separates into stalked sporangia
-Nuclei undergo meiosis and form uninucleated haploid spores
Cestodes
tapeworms
Definitive Host
Harbors the sexually reproducing parasite
Infective Stage
The stage of the life cycle at which the parasite is capable of entering and continuing development within the host.
Inhalation Anthrax
This is the most severe and deadly form of anthrax
It occurs when the spores are inhaled, typically through contaminated air or soil, and can cause severe respiratory symptoms
Cutaneous Anthrax
It occurs when the bacterium enters the body through a cut or abrasion on the skin, typically on the hands, arms, or face.
common form of anthrax
Gastrointestinal Anthrax
This form of anthrax is rare and occurs when contaminated meat is ingested.
Pseudomurein
a substance similar to peptidoglycan that is found in the cell wall of archaea
Superficial mycoses
fungal infections of the skin or hair shaft
outermost layer of the skin
Cutaneous mycoses
fungal infections of the skin, hair or nails
living layers of the skin
Opportunistic mycoses
fungi harmless in normal habitat but pathogenic in a compromised host
Algae
Plantlike protists
can be found in moist environments
unicellular to multicellular
reproduce both ways
stigma, pellicle, and flagella
Volvox
a genus of green algae
forms colonies arranged in spherical shape
has flagella
Phycology
study of algae
Pellicle
thickened cell membrane
substitute for cell wall in protozoans
stigma
light-sensing organelle
diatoms
tiny, usually unicellular algae
members of phytoplankton
Dinoflagellates (Plankton)
responsible for red tides
can cause paralytic shellfish poisoning
flagellated
organisms with whip-like structures used for movements
phycotoxins
secretions are poisonous to humans, fish and other animals
Oomycota (water molds)
Decomposers and forms cottony masses on dead algae and animals
Zoospores
spores of oomycota, have two flagella
Protozoa
More animal like than plant like
found in soil and water
Schizogony
asexual reproduction by multiple fission
Contractile Vacuole
pump water out of cell
Cytostome (Primitive Mouth)
used by some flagellates and ciliates to ingest food
Trophozoite Stage
motile, feeding, dividing stage of protozoa
Cyst Stage
nonmotile, dormant, survival stage
Parasitic Protozoan Human Diseases
Malaria, giardiasis, African sleeping sickness, and amebic dysentery
Ciliates (Ciliophora)
motile through the use of cilia
most complex protozoa
Aulacoseira
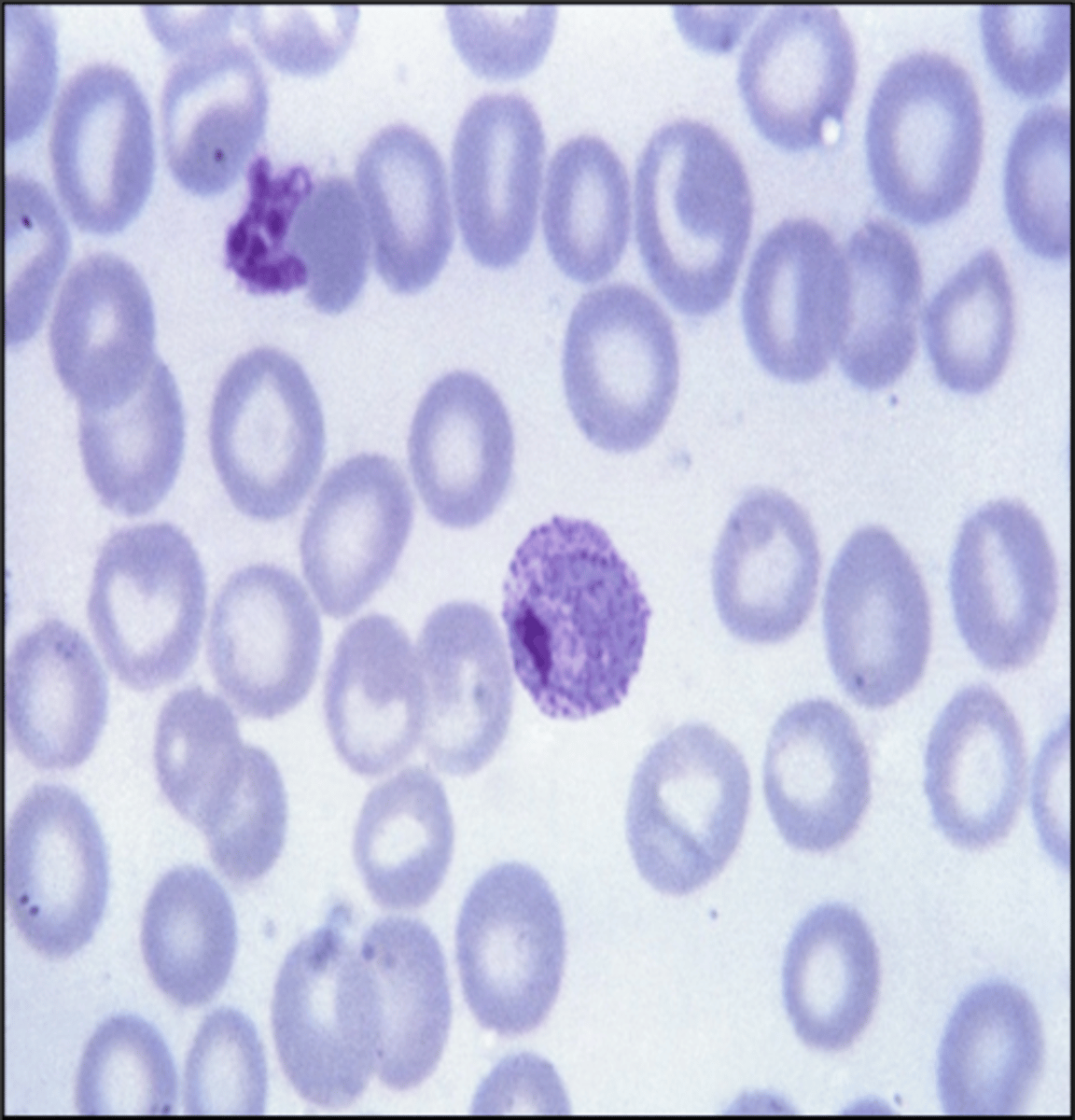
Plasmodium vivax
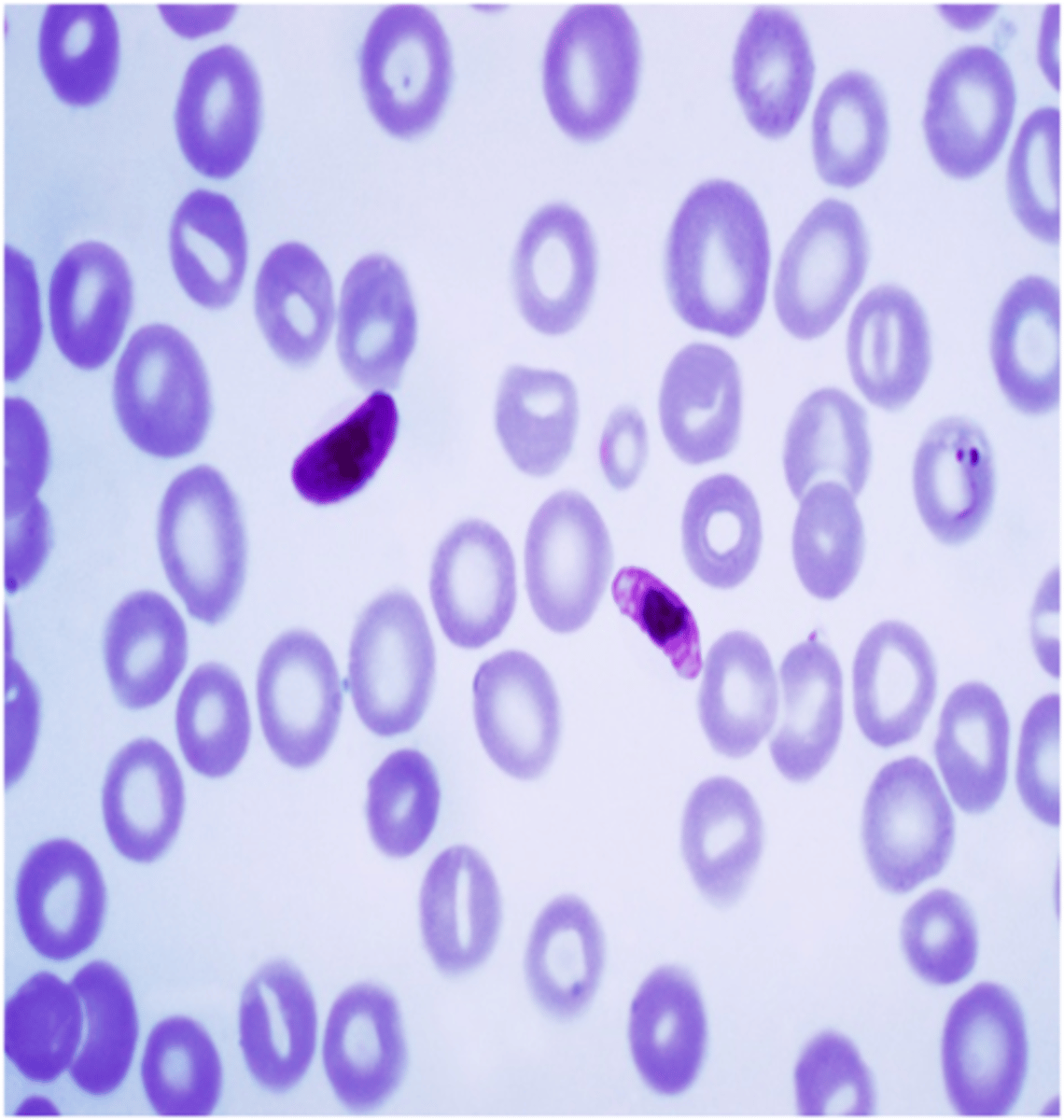
Plasmodium falciparum
Fungi
Most are decomposers, and chemoheterotrophic
Some are Saprophytic, others Parasitic
majority are unicellular or colonial, a few have cellular specialization
No chlorophyll
Cell wall contain chitin
Yeast
Round ovoid shape, asexual reproduction
Unicellular fungi
Pseudohypha
chain of yeasts formed when buds remain attached in a row
Dimorphic
occurring or existing in two different forms depending on growth conditions
Taxomyces
Positive - Taxol production (chemotherapy drug)
Negative - Ceratocystis ulm (Dutch elm disease)
Decomposers
Organisms that break down the dead remains of other organisms
Saprophyte
absorbs nutrients from dead and decaying organic matter
Chitin
Fungal cell walls are composed primarily of
Thallus
body of a mold or fleshy fungus; consists of long filaments of cells joined together
Septate Hyphae
hyphae with cross walls
Coenocytic Hyphae
no septa, long, continuous cells, multinucleated cytoplasm
Mycosis
Fungal infection
Conidiophore
a hypha that bears conidia
Fission
yeasts divide symmetrically
Molds
Fungi seen in water & food
Lichens
Mutualistic combination of an alga (or cyanobacterium) & fungus - Symbiotic
Slime Molds
-Found in soil, rotting logs
-Have both fungal and protozoal chars. & interesting life cycles
-Start out in life as independent amoebae
Cellular Slime molds
-Resemble amoebas, ingest bacteria by phagocytosis
-Cells aggregate into stalked fruiting body.
-Some cells become spores
Parasitic Helminths
-Multicellular animals, organs for reproduction, digestion, movement, protection
-Parasitize host tissues
-Have mouthparts for attachment to or digestion of host tissues
-Most have well-developed sex organs that produce eggs and sperm
-Fertilized eggs go through larval period in or out of host body