Biology - Unit 9: Human Gas Exchange
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
what are features of gas exchange surfaces in humans
large surface area to allow faster diffusion of gases across the surface
thin walls to ensure diffusion distances remain short
good ventilation with air so that diffusion gradients can be maintained
good blood supply to maintain a high concentration gradient so diffusion occurs faster
what is the percentage of gases in atmospheric air?
oxygen = 21%
carbon dioxide = 0.04%
nitrogen = 78%
other gases = 0.96%
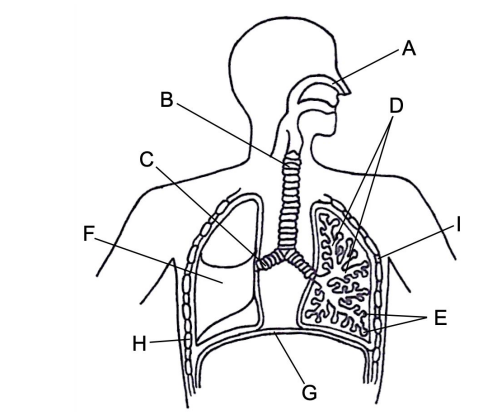
state the characteristics of, and describe the role of, the exchange surface of the alveoli in gas exchange
they (and the capillaries around them) have thin, single layers of cells to minimise diffusion distance
ventilation maintains high levels of oxygen and low levels of carbon dioxide in the alveolar air space
a good blood supply ensures a constant supply of blood high in carbon dioxide and low in oxygen
a layer of moisture on the surface of the alveoli helps diffusion as gases need to dissolve before taking part in metabolic reactions
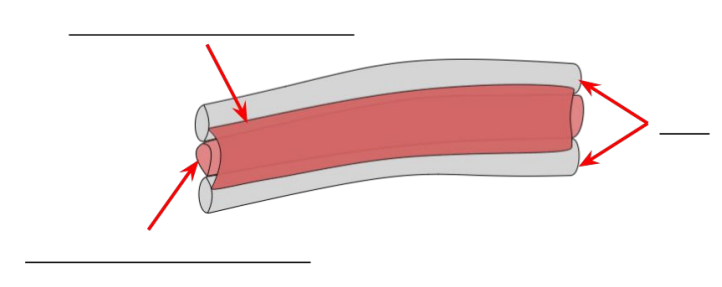
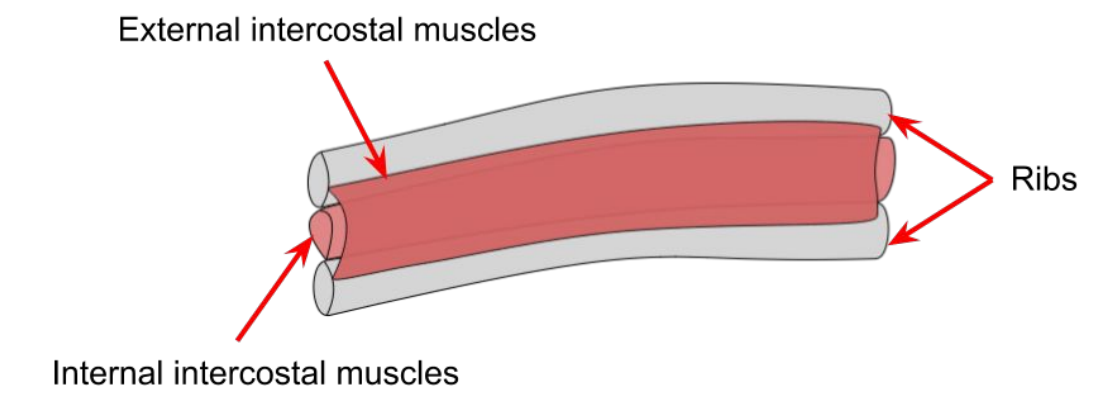
explain the role of the ribs, the internal and external intercostal muscles and the diaphragm in breathing in.
external intercostal muscles contract while internal intercostal muscles relax
ribcage moves up and out
diaphragm contracts and flattens
volume of thorax increases
pressure inside thorax decreases
air is drawn in
explain the role of the ribs, the internal and external intercostal muscles and the diaphragm in breathing out.
external intercostal muscles relax while internal intercostal muscles contract
ribcage moves down and in
diaphragm relaxes and becomes dome-shaped
volume of thorax decreases
pressure inside thorax increases
air is forced out
explain the role of goblet cells, ciliated cells and mucus in protecting the gas exchange system from pathogens and particles
the passages down to the lungs are lined with ciliated epithelial cells
cilia comes from the latin for eyelash, so unsurprisingly these cells have tiny hairs on the end of them that beat and push mucus up the passages towards the nose and throat where it can be removed
the mucus is made by special mucus-producing cells called goblet cells because they are shaped like a goblet or cup
the mucus traps particles, pathogens like bacteria or viruses, and dust and prevents them from getting into the lungs and damaging the cells there
how can we investigate the differences in inspired & expired air
set up 2 boiling tubes with limewater and rubber tubings connected to the mouth
when we breathe in, air is drawn through boiling tube A
when we breathe out, air is blown into boiling tube B
limewater is clear but becomes cloudy when carbon dioxide is bubbled through it
limewater in boiling tube A will remain clear but limewater in boiling tube B will become cloudy
this shows us that the percentage of carbon dioxide in exhaled air is higher than inhaled air
how can we investigate the effect of physical activity on breathing?
count the number of breaths taken during one minute at rest
measure how much the expands during each breath, using a measuring tape. find the average chest expansion over 5 breaths
exercise for a fixed amount of time
immediately after exercise, count the number of breaths taken in one minute
also measure the average chest expansion over 5 breaths
why does exercise increase the rate and depth of breathing?
exercise causes the body cells to respire faster, to release more energy
more carbon dioxide is produced so there’s an increased carbon dioxide concentration in the blood
this is detected by the brain, which signals the body to increase the rate and depth of breathing
this in turn, allows gas exchange to happen more rapidly. therefore, carbon dioxide is removed faster from the body and also there’s an increased intake of oxygen which is supplied to respiring cells faster.
what’s the difference in concentration of oxygen in inspired and expired air?
inspired air - 21%
expired air - 16%
what’s the difference in concentration of carbon dioxide in inspired and expired air?
inspired air - 0.04%
expired air - 4%
what’s the difference in concentration of water vapour in inspired and expired air?
inspired air - lower
expired air - higher
what’s the difference in concentration of nitrogen in inspired and expired air?
inspired air - 78%
expired air - 78%
why is the percentage of oxygen lower in expired air?
oxygen is removed from the blood by respiring cells so blood returning to the lungs has a lower oxygen concentration than the air in the alveoli which means oxygen diffuses into the blood in the lungs
why is the percentage of carbon dioxide higher in expired air?
carbon dioxide is produced by respiration and diffuses into blood from respiring cells; the blood transports the carbon dioxide to the lungs where it diffuses into the alveoli as it is in a higher concentration in the blood than in the air in the alveoli
why is the percentage of water vapour higher in expired air?
water evaporates from the moist lining of the alveoli into the expired air as a result of the warmth of the body
why is the percentage of nitrogen the same in expired air?
nitrogen gas is very stable and so cannot be used by the body, for this reason, its concentration does not change in inspired or expired air.