T Cells: TCR and Thymic Differentiation (Exam 2)
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Both TCRs and BCRs are ______ specific and ______ distributed.
antigen, clonally
Both TCRs and BCRs are generated via ______ gene rearrangement.
V(D)J
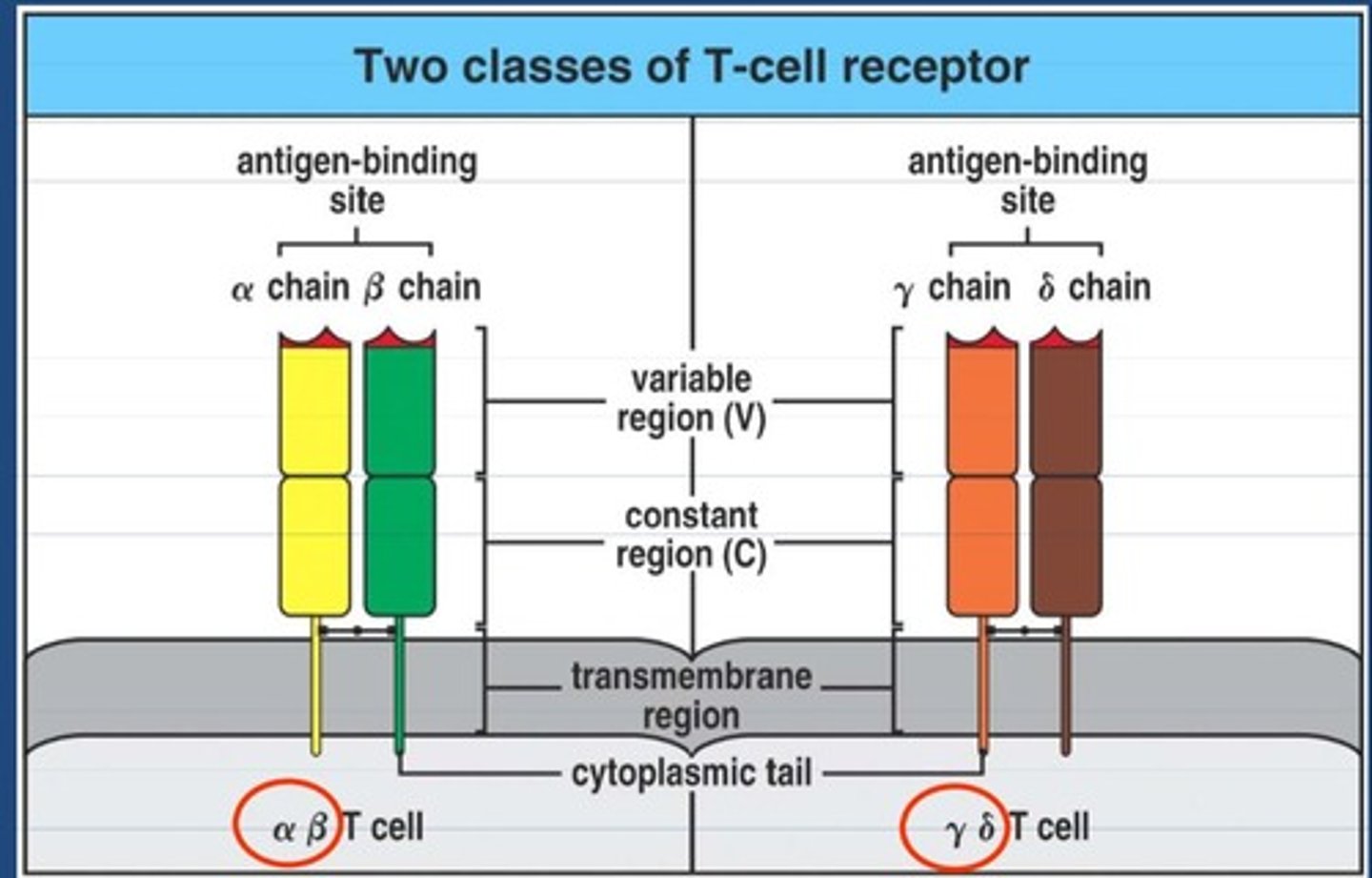
TCRs can be either ______ or ______.
αβ (more common), ɣ𝛿 (few)
TCR subunits
One alpha, one beta (or one gamma, one delta)
TCRs have ______ chain(s) and ______ antigen binding site(s).
2, 1
TCRs predominantly recognize ______ antigens.
protein/peptide
The protein/peptide that TCRs recognize must be bound to ______.
MHC
TCRs can only interact with other ______.
cells
TCRs ______(are/are not) secreted on activation.
are not
Does TCR structure change upon response to antigen?
No
BCRs have ______ chain(s).
4
BCRs can recognize ...
Carbohydrate, DNA, lipid, protein
BCRs can recognize ______ antigen.
free
BCRs can deal with any antigen in ______.
body fluids
BCRs ______ (are/are not) secreted upon activation.
are
BCRs can undergo ______ and ______, while TCRs cannot.
somatic hypermutation, class switch recombinase
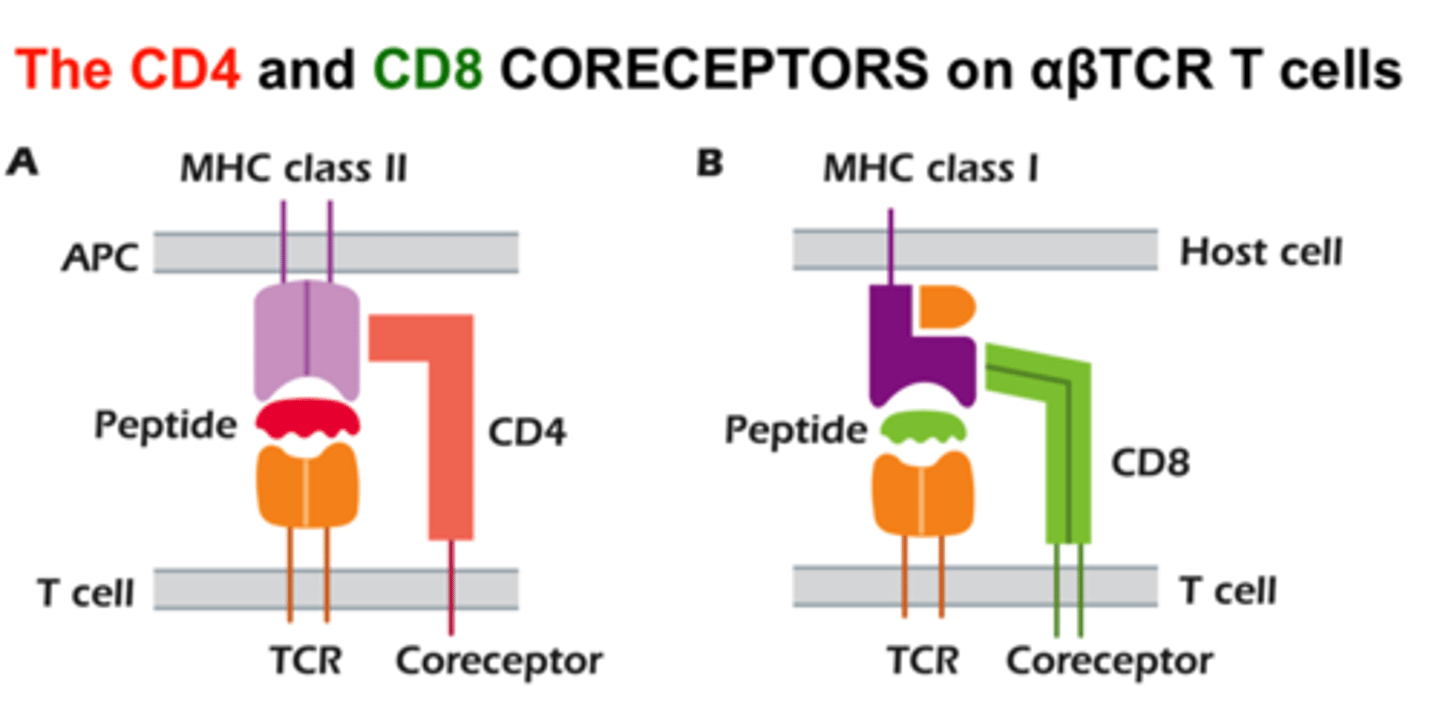
______ co-receptor is found exclusively on the surface of T cells.
CD3
CD3 functions in ______.
signal transduction
What are the other T cell co-receptors?
CD4 or CD8
CD4 and CD8 only bind ______.
MHCII, MHCI (repsectively)
CD4/8 function as ______ molecules and are essential in ______.
adhesion, signal transduction
______ (virus) can bind to CD4.
HIV-1
TCR and co-receptors
ɣ𝛿 T cells are found at ______ and in ______.
mucosal epithelia, circulation (small numbers)
ɣ𝛿 T cells respond ______.
rapidly
ɣ𝛿 T cells secrete ______.
cytokines
ɣ𝛿 T cells do not bind to ______.
MHC
ɣ𝛿 T cells are ______-like T cells.
innate
ɣ𝛿 T cells also possess ______ on the surface.
CD3
What rearrangement comes first in TCR recombination? (beta/delta or alpha/gamma)
beta and delta (these act as the heavy chains)
Once one of the "heavy" TCR chains is chosen, its corresponding ______ chain will be chosen.
"light" (alpha or gamma)
If beta is chosen first, ______ cannot be chosen second (allelic exclusion).
gamma
If delta is chosen first, ______ cannot be chosen second (allelic exclusion).
alpha
TCR diversity is generated by ...
- V(D)J gene rearrangements
- Random combination of chains
- Improper joining during recombination
TCR diversity does not occur through ______.
somatic hypermutation
The ______ is the primary site for T cell differentiation.
thymus
T cell differentiation ______ after puberty.
declines
What two things occur in the thymus in regard to TCR formation?
Positive and negative selection
Prior to positive selection, T cells are ______.
double positive (CD4+/CD8+)
Once the CD4+/CD8+ T cell receptor interacts with MHC, ______ occurs.
positive selection
This interaction determines the ______ that the T cell will commit to.
lineage (CD4 or CD8)
If no CD4+/CD8+:MHC interaction occurs, the T cell will ______.
die (most cells)
Positive selection selects for the T cells that can recognize ______.
self (MHC restricted)
Positive selection occurs in the ______.
thymic cortex
Prior to negative selection, T cells are ______.
single positive (CD4+ OR CD8+)
When these CD4+ or CD8+ T cells interact with their corresponding MHC, the ______ of the interaction is assessed.
affinity
If there is a high affinity, T cells will undergo negative selection and ______.
die
If there is low/intermediate affinity interaction, the cells will ______.
survive
Negative selection produces T cells that are ______ of self.
tolerant
Negative selection occurs in the ______.
thymic medulla
Mature T cells enter ______ to respond to MHC:antigen.
peripheral lymphoid organs
TCR structures