BIO 110 Final Exam Review: Taxonomy, Cell Biology, Genetics, and Evolution
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
What are Domains?
The highest taxonomic rank in the biological classification system, which includes three main categories: Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya.
Levels of Linnaean Classification
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
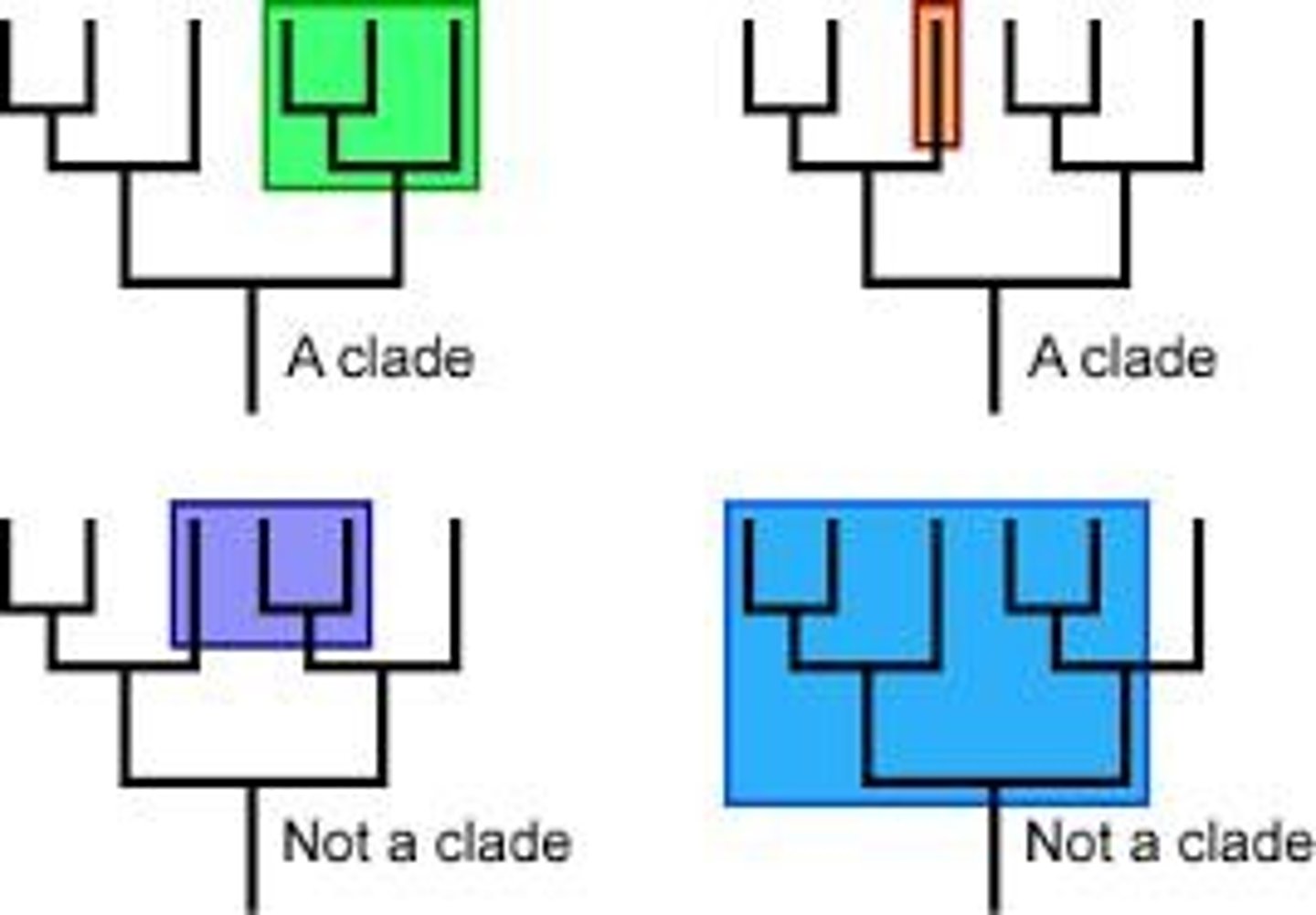
What is a clade?
A group of organisms that includes an ancestor and all its descendants, representing a branch on the tree of life.
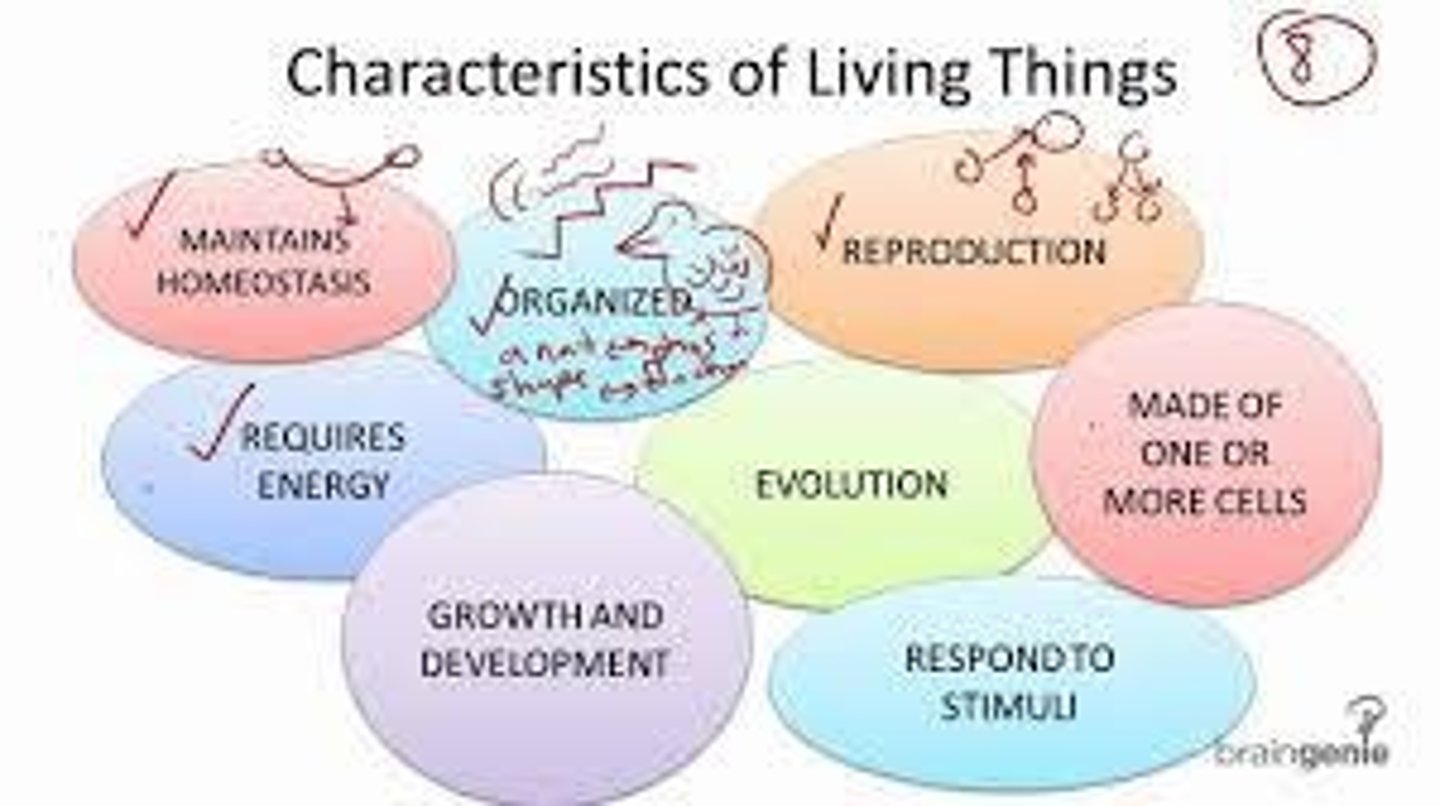
Characteristics of life
1. All organisms are made of one or more cells. 2. They undergo metabolism. 3. They grow and develop. 4. They respond to stimuli. 5. They reproduce. 6. They adapt to their environment.
How does the cell theory relate to the characteristics of life?
Cell theory states that all living organisms are composed of cells, which is a fundamental characteristic of life, emphasizing that cells are the basic unit of life.
Define and put in hierarchical order: Biosphere, Tissue, Population, Community, Organ, Individual, Ecosystem
1. Biosphere: the global sum of all ecosystems. 2. Ecosystem: a community of living organisms and their environment. 3. Community: a group of interacting organisms. 4. Population: a group of individuals of the same species. 5. Individual: a single organism. 6. Organ: a part of an organism that performs a specific function. 7. Tissue: a group of cells that work together.
Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Prokaryotic cells are generally smaller, lack a nucleus, and have circular DNA, while eukaryotic cells are larger, have a nucleus, and possess linear DNA. Both have cytoplasm, a plasma membrane, ribosomes, and may have a cell wall.
What is an autotroph?
An organism that produces its own food from inorganic substances, typically through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis.
What is a heterotroph?
An organism that cannot produce its own food and instead obtains nutrients by consuming other organisms.
example of autotroph
plants, algae, bacteria
example of heterotroph
humans and animals
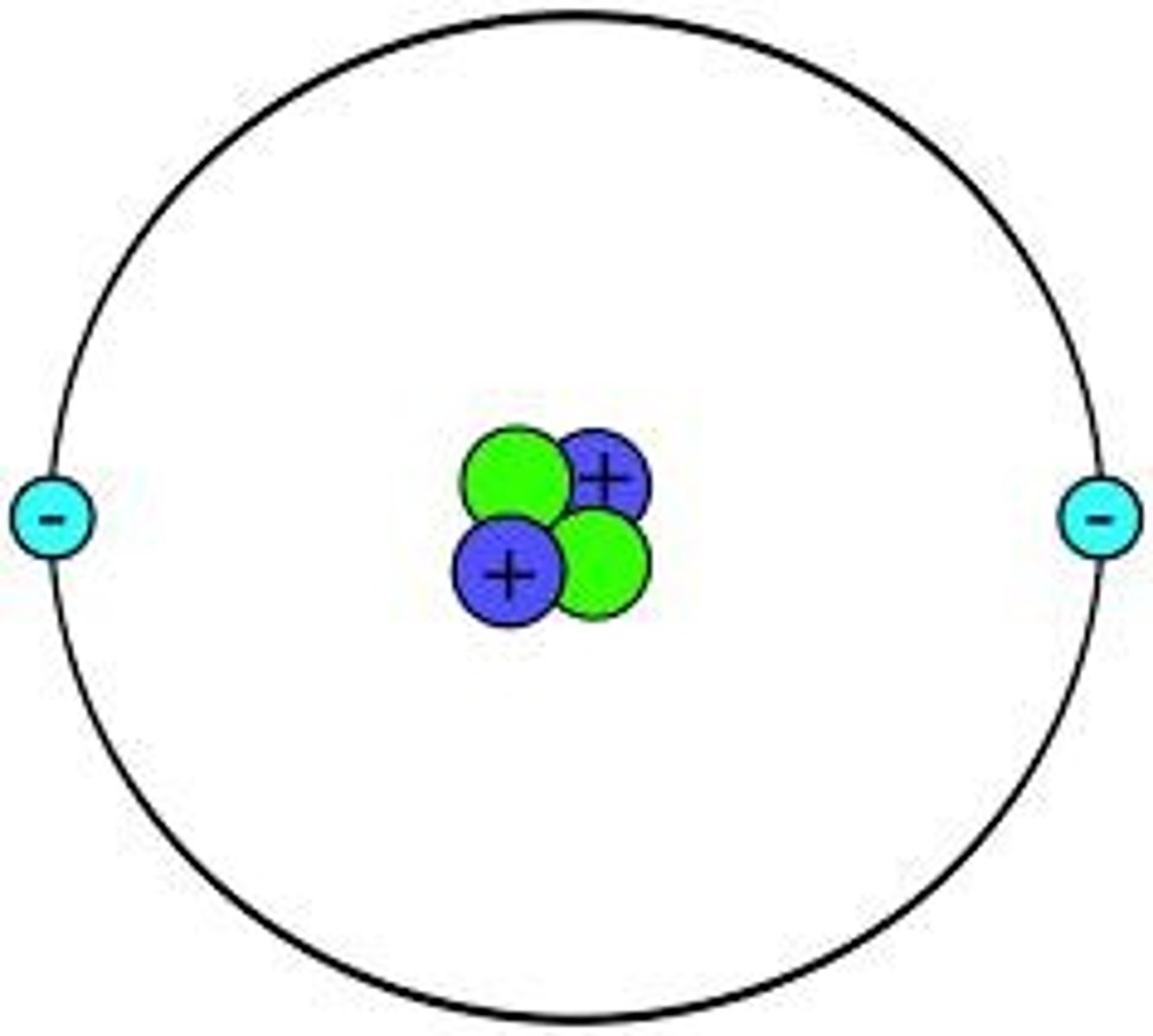
What part of the atom gives it its identity?
The number of protons in the nucleus of the atom determines the type of element.
hydrogen bond
weak attraction between a hydrogen atom and another atom
covalant bond
a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms
ionic bond
Formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another
What is a buffer?
A solution that resists changes in pH when an acid or base is added, helping to maintain a stable pH in biological systems.
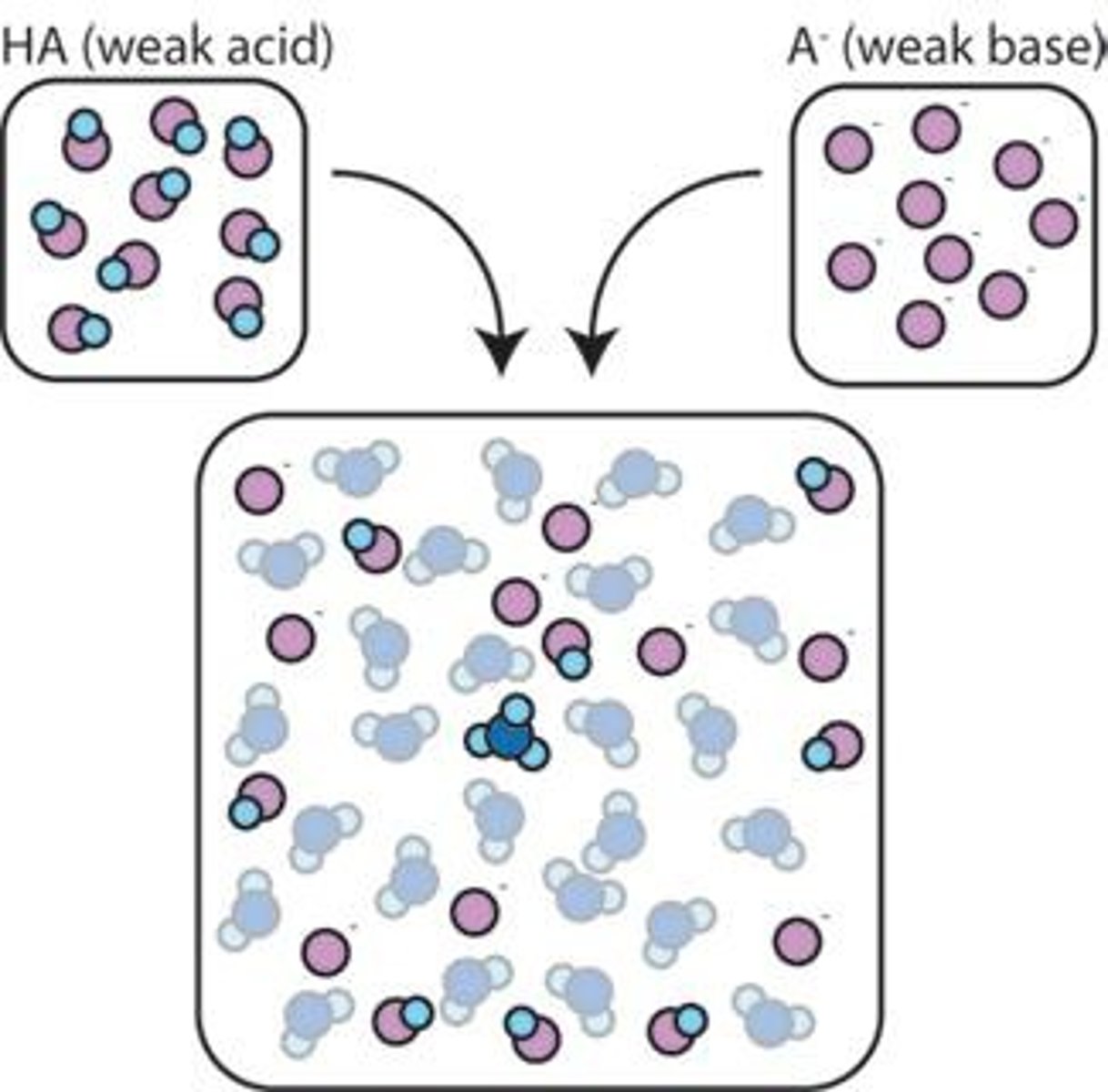
What are acids?
proton donors
What are bases?
proton acceptors
What are the macromolecules?
1. Carbohydrates: made of sugars, provide energy. 2. Proteins: made of amino acids, perform various functions. 3. Lipids: made of fatty acids, store energy and make up cell membranes. 4. Nucleic acids: made of nucleotides, store and transmit genetic information.
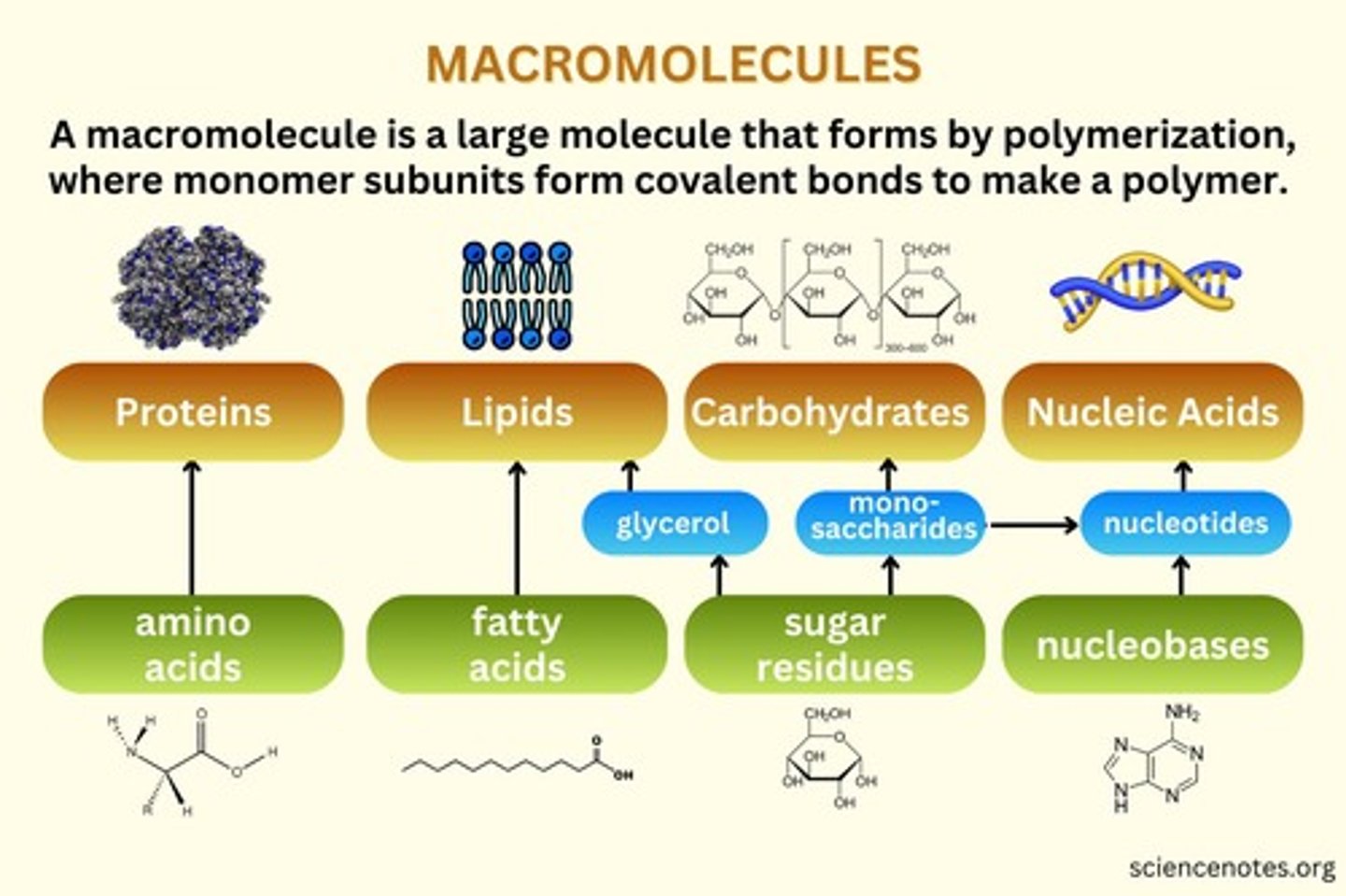
dehydration synthesis
A chemical reaction in which two molecules covalently bond to each other with the removal of a water molecule.
Hydrolisis
the breaking of a bond molecule using water
Describe each level of protein structure.
1. Primary: sequence of amino acids. 2. Secondary: folding into alpha helices or beta sheets. 3. Tertiary: overall 3D shape. 4. Quaternary: arrangement of multiple polypeptide chains.
What is the endomembrane system?
A system of membranes in eukaryotic cells that includes the nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and vesicles, involved in the synthesis, modification, and transport of proteins and lipids.
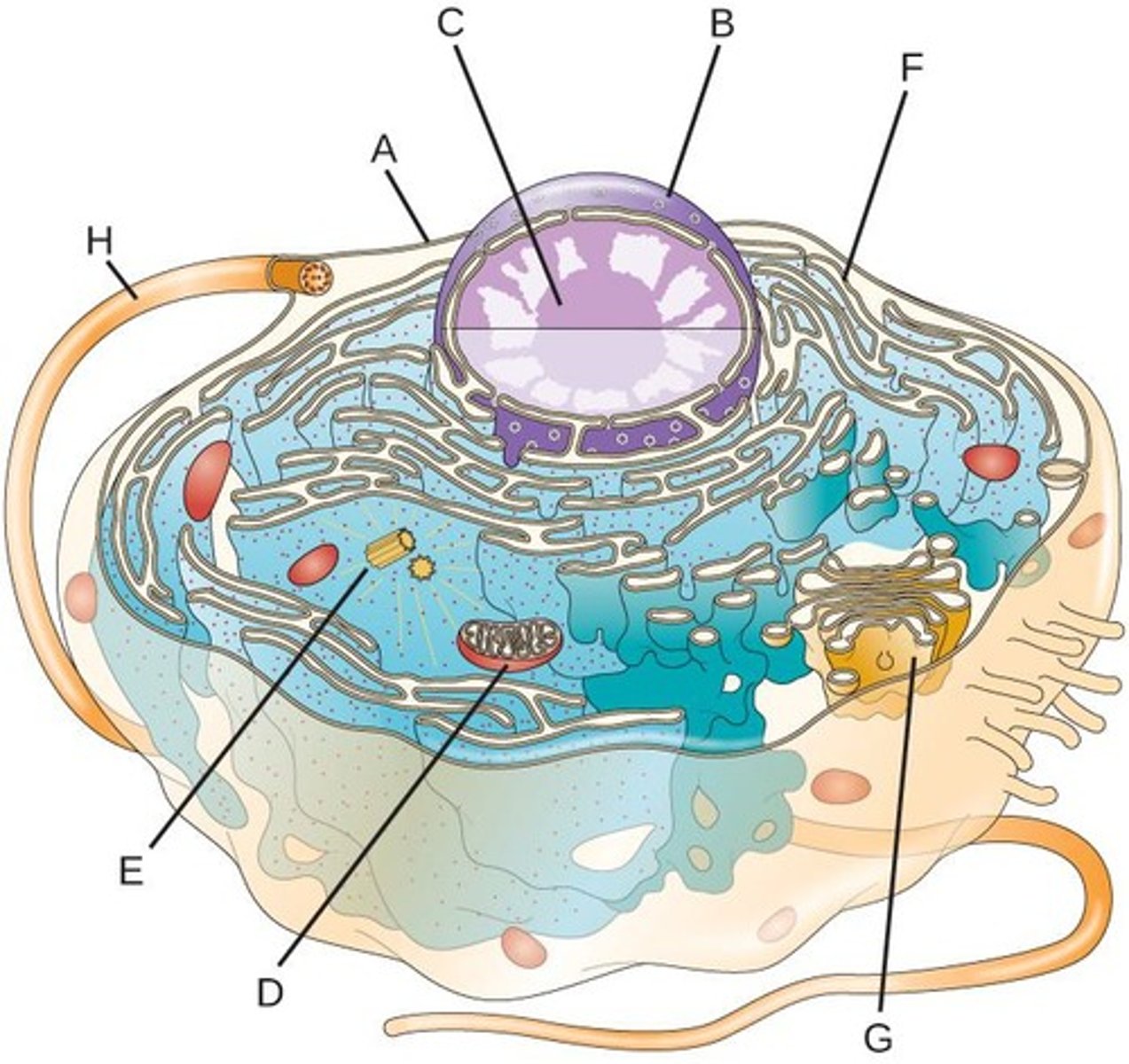
Endoplasmic Reticulum
A cell structure that forms a maze of passageways in which proteins and other materials are carried from one part of the cell to another.
Golgi apparatus
A system of membranes that modifies and packages proteins for export by the cell
cell wall
A rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms.
plasma membrane
A selectively-permeable phospholipid bilayer forming the boundary of the cells
Nucleus
Control center of the cell
Nucleolus
Found inside the nucleus and produces ribosomes
Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell, organelle that is the site of ATP (energy) production
Where are ribosomes found?
free-floating in the cytosol, or bound to the rough ER or the nuclear envelope
homologous chromosomes
Chromosomes that have the same sequence of genes and the same structure
sister chromatids
Identical copies of a chromosome; full sets of these are created during the S subphase of interphase.
When are chromatids formed?
as the DNA makes a copy of itself before cell division
Diploid
(genetics) an organism or cell having two sets of chromosomes or twice the haploid number
Haploid
An organism or cell having only one complete set of chromosomes.
Mitosis
part of eukaryotic cell division during which the cell nucleus divides
Purpose of mitosis
divides cells that are too large, replaces damaged/dying cells, allows for growth
Stages of mitosis in order
interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokinesis
What happens at the stages of mitosis
- chromosomes in parent cell are long and uncoiled. each chromosome replicates to form two identical chromatids.
- each chromosome now consists of 2 chromatids. chromosomes have coiled up
- chromosome line up along equator of cell. Spindle fibres attach to each pair of chromatids at centromere
- spindle fibres pull chromatids apart, go to opposite poles of cell. once separated chromatids are now called chromosomes
- nuclear membrane reforms around each set of chromosomes. cytoplasm starts to divide
- two identical daughter cells are formed each with the same number of chromosomes as the original parent cell
Hypertonic
Having a higher concentration of solute than another solution.
Hypotonic
Having a lower concentration of solute than another solution
Isotonic
Having the same solute concentration as another solution.
Difussion
movement from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
facillitated diffusion
when transport proteins make room for larger substances to pass through cell membrane
passive transport
the movement of substances across a cell membrane without the use of energy by the cell
active transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration difference
Contransport
a single ATP-powered pump that transports a specific solute can indirectly drive the active transport of several other solutes in a mechanism
What molecules can pass through a membrane
small, non polar, hydrophobic molecules
Enzymes
Proteins that speed up chemical reactions
What do enzymes bind to
substrate (reactant)
optimum temperature
The temperature at which an enzyme is most active
competitive inhibition
substance that resembles the normal substrate competes with the substrate for the active site
non-competitive inhibitor
a molecule that binds to an enzyme at a location outside the active site and inhibits the enzyme's function.
feedback inhibition
A metabolic pathway is switched off by the inhibitory binding of its end product to an enzyme that acts early in the pathway.
What is osmosis?
The diffusion of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration.
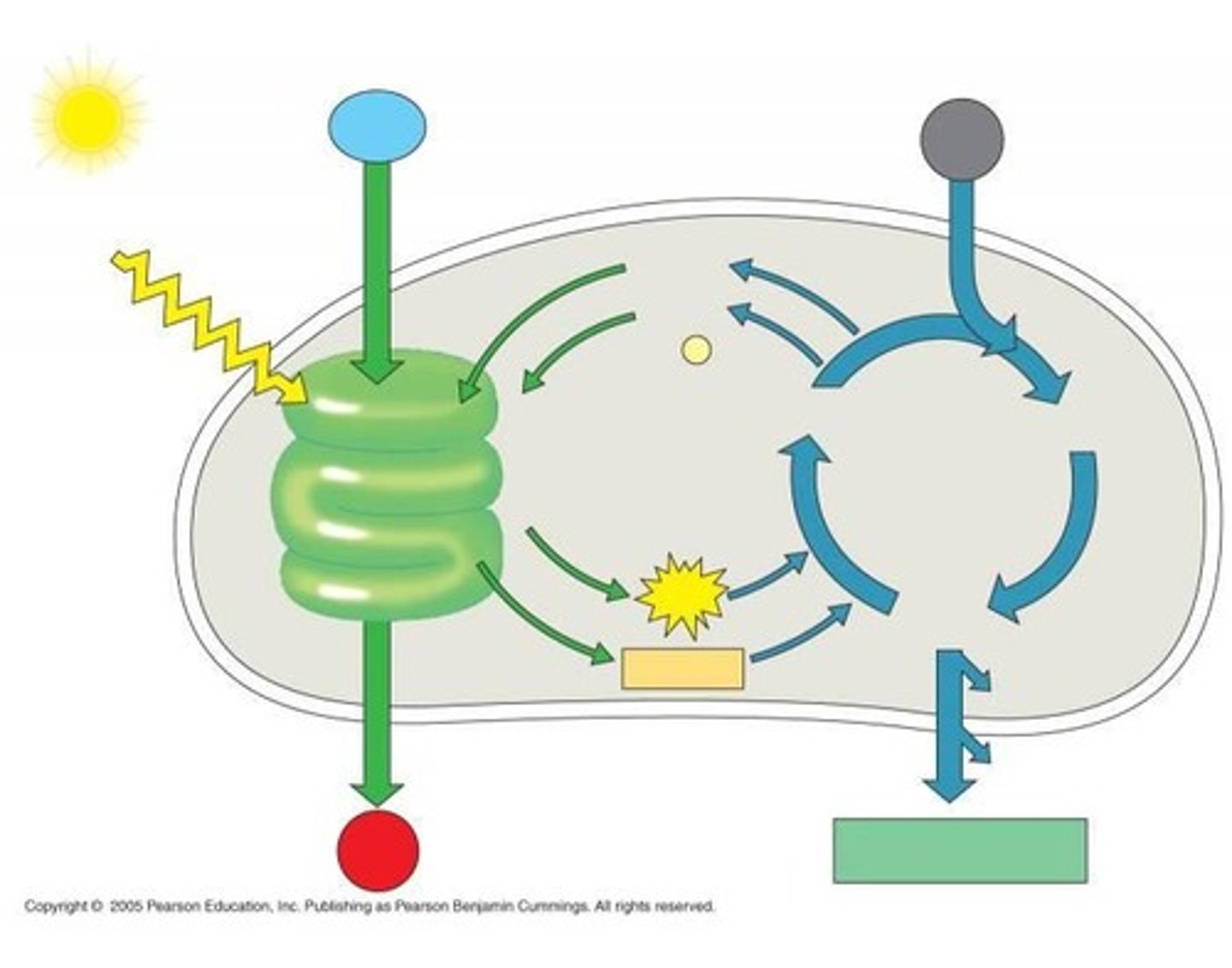
What is cellular respiration?
The process by which cells convert glucose and oxygen into energy (ATP), carbon dioxide, and water, occurring primarily in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells.
Role of NADH and FADH2
electron energy carriers
Role of O2 in Cellular Respiration
O2 is the final electron acceptor at the end of cellular respiration
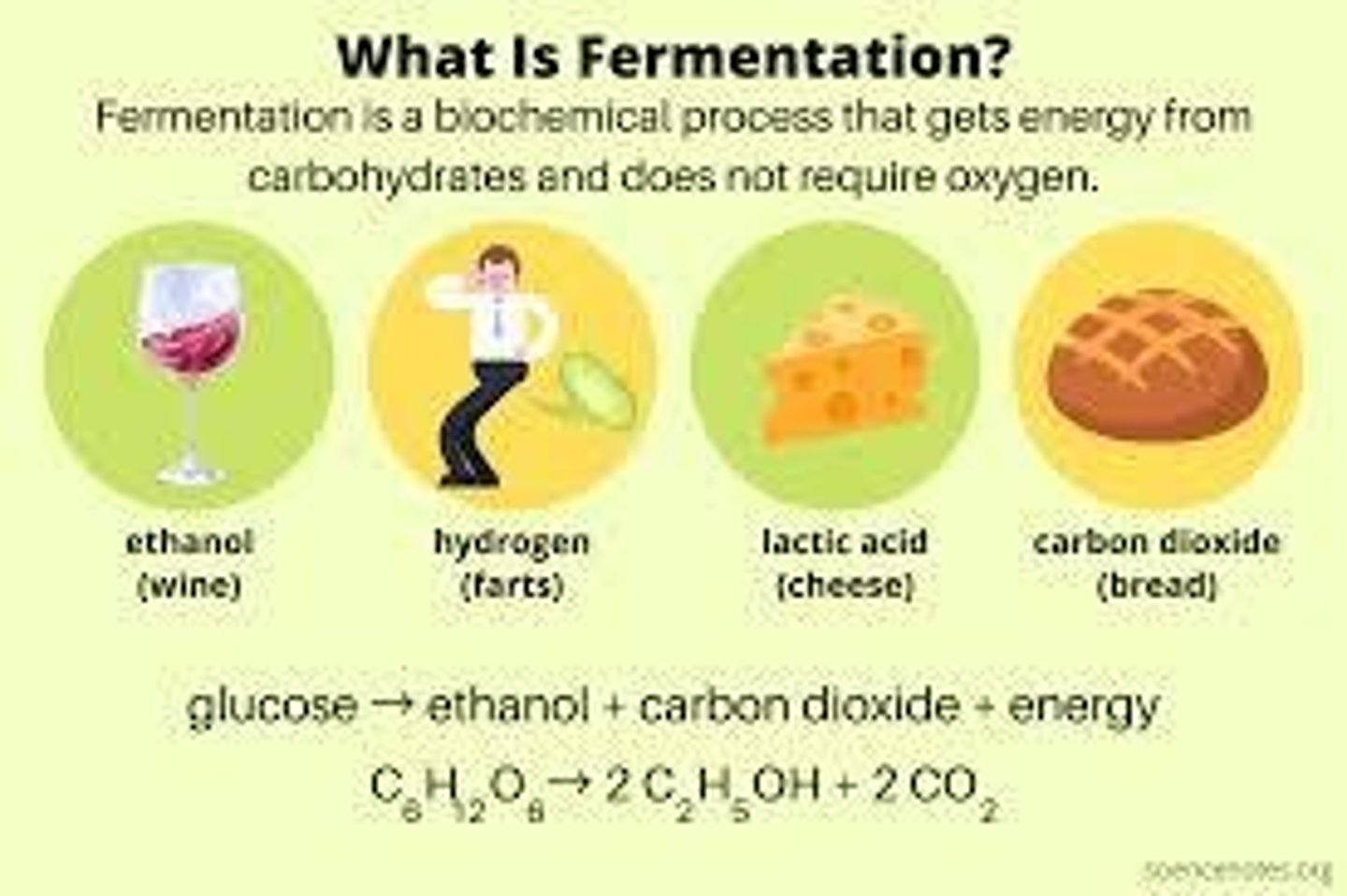
What is fermentation?
An anaerobic process that allows cells to produce energy without oxygen, typically resulting in the production of lactic acid or ethanol and a small amount of ATP.
What is photosynthesis?
The process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose, using carbon dioxide and water, and releasing oxygen.
What is meiosis?
A type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, producing four genetically diverse gametes, essential for sexual reproduction.
stages of meiosis in order
Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, Telophase I, Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II, Telophase II
What causes genetic variation?
independent assortment, crossing over, random fertilization
Prophase 1 (crossing over)
Chromosomes become visible; nuclear envelope breaks down; crossing-over occurs.
Metaphase 1
Paired homologous chromosomes line up across the center of the cell
Anaphase 1
Homologous chromosomes separate
Telophase 1
2 daughter cells are formed, each daughter cell contains only one chromosome of the homologous pair.
Prophase 2
A new spindle forms around the chromosomes
Metaphase 2
Chromosomes line up in the middle
Anaphase 2
sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles
Telophase 2
A nuclear membrane forms around the chromosomes in each of the 4 new cells.
Differences between DNA and RNA
RNA is one strand of nucleotide as opposed to two strands. RNA contains ribose and DNA contains deoxyribose. RNA has uracil instead of thymine.
Replication
process of copying DNA prior to cell division
Translation
Process by which mRNA is decoded and a protein is produced
Transcription
(genetics) the organic process whereby the DNA sequence in a gene is copied into mRNA
Types of RNA and their functions
mRNA - Messenger RNA: Encodes amino acid sequence of a polypeptide.
tRNA - Transfer RNA: Brings amino acids to ribosomes during translation.
rRNA - Ribosomal RNA: With ribosomal proteins, makes up the ribosomes, the organelles that translate the mRNA.
Types of mutations
silent, missense, nonsense, frameshift
silent mutation
A mutation that changes a single nucleotide, but does not change the amino acid created.
nonsense mutation
A mutation that changes an amino acid codon to one of the three stop codons, resulting in a shorter and usually nonfunctional protein.
missense mutation
A base-pair substitution that results in a codon that codes for a different amino acid.
frameshift mutation
mutation that shifts the "reading" frame of the genetic message by inserting or deleting a nucleotide
base substitution mutation
simple substitution of one base for another
Differences between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells
1. Prokaryotic Cells are small, simple cells with no nucleus and no organelles.
2. Eukaryotic Cells are large, complex cells that have a nucleus and organelles
What is evolution?
The change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations, driven by processes such as natural selection, mutation, and genetic drift.
What is the difference between macroevolution and microevolution?
Macroevolution refers to large-scale evolutionary changes that occur over long periods, leading to the emergence of new species, while microevolution involves small-scale changes within a population.
convergent evolution
Process by which unrelated organisms independently evolve similarities when adapting to similar environments
divergent evolution
when two or more species sharing a common ancestor become more different over time
Fossils
Preserved remains of once-living organisms
comparative anatomy
The comparison of body structures and how they vary among species
Biogeography
Study of past and present distribution of organisms
DNA sequences
How bases are lined up in a strand of DNA, codes for genetic information
What does survival of the fittest mean?
A phrase that describes the process of natural selection, where individuals that are better adapted to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce.
Why is genetic variation necessary?
Genetic variation is essential for a population's ability to adapt to changing environments and for the process of natural selection to occur.
What is an adaptation?
A trait that enhances an organism's ability to survive and reproduce in its environment.
What is selection?
The process by which certain traits become more or less common in a population due to the effects of those traits on the survival and reproduction of individuals.
Impact of Overproduction
produced more goods than demand, prices dropped