Biology- the eyeball
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Receptor
A specialised cell that receives stimuli from the external & internal environment
Protective structures in place externally
Bony socket + adipose tissue
Eyebrows
Eyelids + eyelashes - reflex closure when exposed to bright light or moving object
spreads tears+ oily secretion over cornea
Stops objects touching conjunctiva
Lachrymal glands- tears wash away dust, moisten conjunctive, lysosome enzymes prevent microbial infections
Glands of Meiboom- oil secretion mixes with tears = hydrates the eye
Define a sense organ
a concentration of a certain receptors, together with other tissues for support and effective function.
Three outer most layers of the eye
outer sclera - continues into the cornea, opaque, tough
Middle choroid - vascular and nutritive: it contains pigments and blood vessels provide retina with nutrients and oxygen. - it also continues into the ciliary body, suspensory ligaments and iris
Retina - contains photoreceptors ( rods and cones)
Another name for 3D vision
binocular vision
Define pupillary mechanism
the physcological response that varies the size of the pupillary
Define accommodation
the adjustment of the curvature of the lens for vision at distances closer than 6m
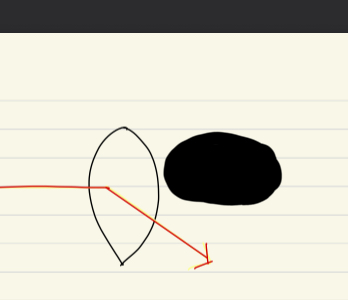
What shape is this lens? what does it do to light
biconvex, refracts light
What does biconcave mean?
the light is refracted at an angle, this is not the shape of our Len’s
State two functions of the vitreous humour in the posterior chamber.
Helps maintain the shape of the eye
Plays a role in refraction of light
Prevents desiccation of structures in the eye
Describe the visual defect when the curvature of the cornea is uneven
Astigmatism
Explain how someone’s eyesight is effected if they develop cataracts
the lens will become opaque
No/ less light will enter the eye
Causing no sight
Describe the process of accommodation that takes place when an object is less than 6m away
the ciliary muscles contract
The suspensory muscles slacken
The tension on the lens decreases
Causing lens to become more convex
Light rays are refracted more
Therefore light focuses on the retina
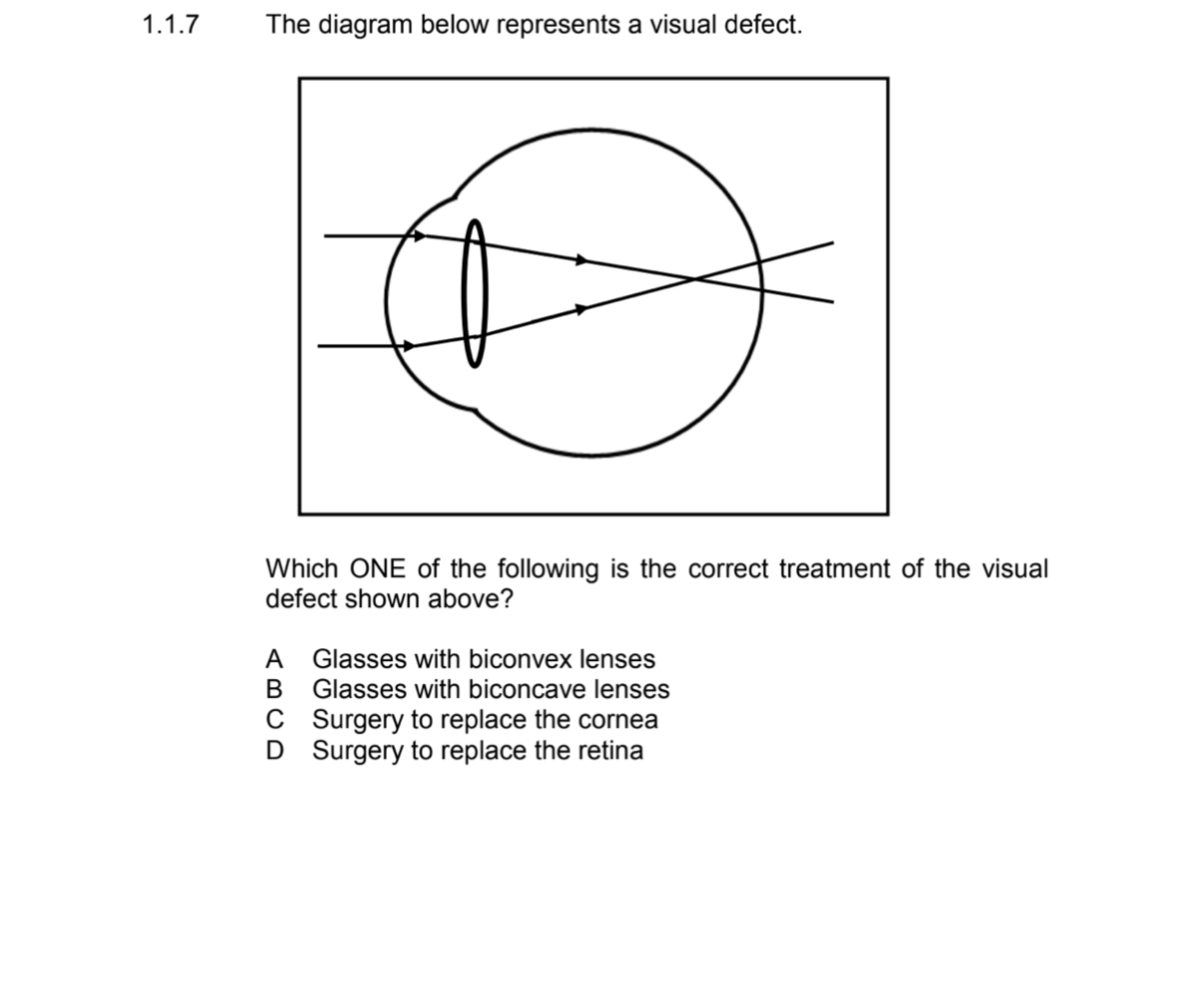
answer
B
Name the type of lens for people with Myopia
biconcave lenses will help to diverge the light
To ensure it focuses on the retina
Explain one way that the lens is structurally suited for accomodation
it is elastic
It can change its shape to focus on light rays on the retina
Describe astigmatism
Light is refracted unevenly due to uneven cornea
Forms a blurred image
Two pathways of light at two different focal points in the retina