Lecture 11: Tumors & Gallbladder
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Three general categories of cholestasis
↑ serum concentrations of Conjugated bilirubin, Bile Acids/salts, Cholesterol
Pre-Hepatic: ↑ Unconjugated
Hepatic: ↑ Mixed
Post-Hepatic: ↑ Conjugated
Conjugated → Dark urine
Causes:
Mechanical obstruction of bile ducts: of EXTRAHEPATIC DUCTS or smaller INTRAHEPATIC DUCTS
Hepatocellular/metabolic: conjugated bilirubin, bile acids still made, but excretion by liver cells into the bile canaliculi is impaired
Acholuric jaundice
Jaundice due to unconjugated Bilirubin
Extrahepatic Obstructive (large ducts)
Adults : Gallstones in common bile duct (Choledocholithiasis), tumors (head of pancreas adenocarcinoma, cholangiocarcinoma), Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (UC), iatrogenic bile duct strictures
Kids: Biliary Atresia, CF, Choledochal cysts (bile stasis → recurrent infections → inflammatory strictures)
Intrahepatic Obstructive (small ducts)
Adults: Hepatitis, Alcoholic cirrhosis, autoimmune (Primary Biliary Cholangitis)
Kids: Rare Alagille Syndrome (paucity of intrahepatic bile ducts)
No benefit from surgery
Hepatocellular (non-obstructive/metabolic)
Drugs (anabolic steroids, chlorpromazine); often due to inhibition of Bile Salt or Conjugated Bilirubin Export Pumps
↑ Conjugated Bili and/or ↑ Bile Acids
Sepsis, Transplant rejection
Genetic: Dubin-Johnson, Rotor syndromes
Do not benefit from surgery
Hepatocellular + Intrahepatic Obstructive
Grouped clinically as “Intrahepatic Cholestasis”
Common clinical manifestations of Cholestasis
Jaundice from ↑conjugated Bilirubin
Pruritus from ↑ Bile salts
Skin Xanthomas from ↑ Cholesterol
Clinical Complications of Cholestasis
Intestinal malabsorption of fats: Due to lack of Bile acids
Chronic cholestasis → deficiency of fat-soluble vitamins (A,D,E,K)
Secondary/Obstructive Biliary Cirrhosis: Bile acids hepatotoxic “detergents” & injure or kill hepatocytes
Chronic uncorrected obstruction incites fibrosis of the portal tracts
Ascending Cholangitis: large duct partial/intermittent obstructions ↑ risk of ascending bacterial infection
Fever, chills, abdominal pain, jaundice; often leads to Sepsis/Shock
Ascending Cholangitis
Subtotal or intermittent large duct obstruction predisposes to secondary bacterial infection
Agents: Coliforms; enterococci common
Fever & chills, RUQ abdominal pain, & Jaundice; suppurative cholangitis, septic shock
Cholestasis plus ductular reaction; stromal neutrophils; neutrophils infiltrate bile duct epithelium & lumens
Strictures (scarring) of large ducts that may lead to Secondary Sclerosing Cholangitis or Secondary Biliary Cirrhosis
Labs in Cholestasis
Hyperbilirubinemia: ↑ Conjugated Bilirubin
GGT: ↑ in biliary obstruction (more than AST & ALT)
Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP): ↑ 3-5 X in extrahepatic & usually < 3 X, for intrahepatic cholestasis
Hypercholemia: ↑ serum Bile Acids
Hyperlipidemia: ↑ Total serum Cholesterol
5’-Nucleotidase: ↑ in parallel with ALP (used like GGT to confirm liver origin of ALP)
Microscopic morphology of Cholestasis
in all causes:
Centrilobular cytoplasmic Bile pigmentation of Hepatocytes & Kupffer cells
dilated bile canaliculi with retained bile (Canalicular bile plugs)
if large extrahepatic duct obstruction also see:
Ductular Reaction: portal tract bile ductular proliferation, edema & neutrophilic inflammation
Ductular bile lakes
Cholate stasis: periportal hepatocyte feathery degeneration due to Bile Acid toxicity
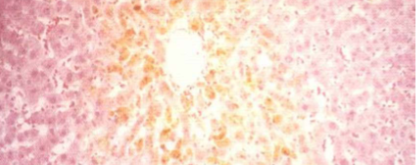
Cholestasis (Zone 3, Centrilobular)
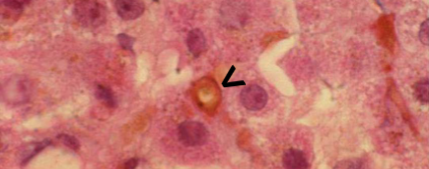
Cholestasis
Canalicular bile plugs
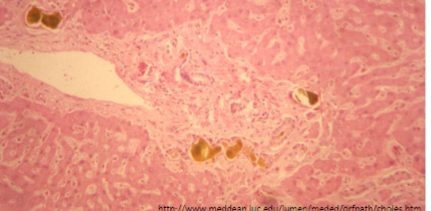
Large Extrahepatic Duct Cholestasis
Portal tract Ductular reaction with bile lakes
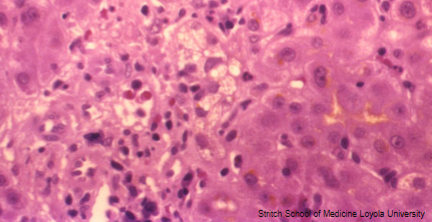
Large Extrahepatic Duct Cholestasis
Cholate stasis of periportal hepatocytes
Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
End stage Primary Biliary Cholangitis
Small duct obstruction
Autoimmune; Anti-mitochondrial Ab
Fibrosis/Cirrhosis with "Florid Duct Lesions" (Granulomas & mostly non-suppurative inflammation, destruction of ductular epithelium with focal pseudo stratification & papillary infoldings)
End-stage liver disease (ESLD) due to chronic large or small bile duct obstruction
In fibrotic stage, attempts at repair, result in ductular proliferation
Secondary Biliary Cirrhosis
Large duct obstruction
Mechanical obstruction, Fibrosis/Cirrhosis with "Ductular Reaction" (Portal tract bile ductular proliferation, edema & neutrophilic inflammation with bile lakes, reflecting external blockage)
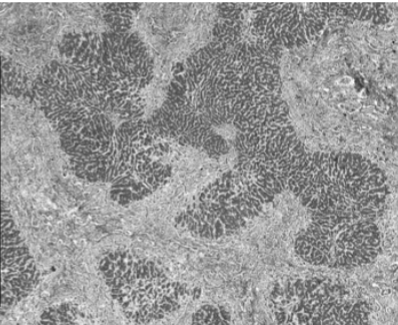
Jigsaw Puzzle pattern of fibrosis (elongated micro nodules)
Biliary Cirrhosis (Primary or Secondary)
Neonatal Cholestasis
Jaundice in the first 24 hours or after 2 weeks should trigger a work-up for Neonatal Cholestasis (↑ Conjugated Bili)
Two types:
Obstructive
Nonobstructive/Intrahepatic affecting secretion of conjugated bilirubin
Obstructive Neonatal Cholestasis
Extrahepatic Biliary Atresia most commonly develops in first 3 months after birth by progressive obstruction of normally formed extrahepatic bile ducts → intrahepatic tree
If identified before progression proximally into the intrahepatic ducts or development of ascending cholangitis → amenable to surgical correction
Biliary Atresia is most common cause of death from liver disease in early childhood
Inflammation & strictures of Common Hepatic or Common Bile ducts
Present with ↑ Direct Bili in 6-12 range; uncorrected will develop Cirrhosis within 3-6 months; death within 2 years
Rx: If limited to extrahepatic ducts → Surgery (Hepatoportojejunostomy/Kasai Procedure)
50% progress to intrahepatic tree involvement & require Liver Transplantation to survive
Nonobstructive/Intrahepatic affecting secretion of conjugated bilirubin Neonatal Cholestasis
Infections, CF, α-1 Antitrypsin deficiency, some cases of Dubin-Johnson, Alagille Syndrome (portal tract bile duct paucity due to NOTCH mutations), Idiopathic
Non-obstructive cholestasis often shows Neonatal Hepatitis with inflammation, intracanalicular cholestasis & Giant or syncytial cells
Preeclampsia
Toxemia of pregnancy
Hypertension + Proteinuria (+/- edema) or + evidence of other organ involvement (low platelets, renal insufficiency, liver involvement, pulmonary edema, or Cerebral/visual symptoms) developing after 20 weeks gestation
Hepatic Aminotransferases >x2
Very high BP
↓ Platelets
Pulmonary edema
Renal insufficiency
HELLP syndrome
Hemolysis, Elevated Liver enzymes, Low Platelets
preceded by preeclampsia & is life threatening to mother & baby
Typically develops at 28-36 weeks of gestation, but 2nd trimester (27 weeks or less) or postpartum onset is also common (up to 7 days postpartum)
abdominal pain/tenderness in the mid-epigastrium or RUQ, nausea, vomiting, malaise
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC), placental abruption, acute renal failure, pulmonary edema, & subcapsular or intraparenchymal liver hematoma
Preeclampsia → HELLP → DIC
Anemia, Thrombocytopenia (<100,000)
Peripheral smear – Schistocytes (Microangiopathic hemolysis)
Liver function tests – ↑ AST & ALT → 2x reference
elevated LDH (≥600 U/L) from hemolysis
Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy
Onset, in late 2nd or early 3rd trimester, of generalized itching, often beginning in palms & soles
Hypercholemia (↑ serum Bile Acids) may be X 3 – 100 normal
Mild ↑ in Transaminases, ALP & Conjugated Bilirubin
Generally benign, but ↑ incidence of fetal distress, prematurity & stillbirth
Stillbirth mostly preventable by induced delivery at 37 weeks
Resolves postpartum
Acute Fatty Liver of Pregnancy
Mild subclinical hepatic dysfunction (↑ ALT, ↑ AST only) or rapid progression to acute liver failure & death
Present in 3rd Trimester with N&V, RUQ/epigastric pain, or symptoms of Liver failure (bleeding, jaundice, encephalopathy)
Risk factors: Fetal long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl CoA dehydrogenase (LCHAD) deficiency, Preeclampsia or HELLP syndrome, multiple gestation; low BMI
Dx: Clinically by exclusion; CT may suggest fatty liver
Liver biopsy showing MICROVESICULAR STEATOSIS
Focal Nodular Hyperplasia
result from local alterations of blood flow
usually single nodule with central scar & fibrous septae with ductular reaction resembling focal cirrhosis
fibrotic septae with narrowed vessels; triads present
Most common in adult women
nodule/s in a noncirrhotic liver
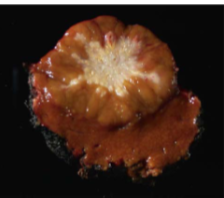
Focal Nodular Hyperplasia
Central scar
Hepatic Adenoma
Solitary
women aged 20–45
RUQ or epigastric pain produced by enlargement or hemorrhage; may rupture through liver capsule & bleed, requiring emergency surgery
Risk of spontaneous rupture proportional to size (> 5 CM high risk).
Strongly associated with ORAL CONTRACEPTIVES (risk 30-40 x) or use of anabolic steroids
β-catenin mutations are considered to have a high risk of malignant transformation into Hepatocellular carcinoma
“Inflammatory” variant associated with NAFLD affecting both men & women; ↑ risk for malignant transformation
Hepatocytes with little atypia & mitotic activity
No portal tracts or central veins
No fibrosis
↑ blood levels of Alpha Fetoprotein (AFP)
Hepatocellular Carcinoma
malignant transformation of hepatocytes
Most important risk factors: HBV, HCV, Aflatoxins and Alcohol
Secondary risk factors: metabolic diseases
β-catenin activation (mutations that prevent degradation)
Precursor lesions: Dysplastic nodules
Fibrolamellar variant of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Arises in normal livers of young adults
No association with Cirrhosis, Alcoholism or Hepatitis B/C infection
Does not produce AFP
Strongly associated with fusion gene activating Protein Kinase A
Less aggressive, but fatal if unresectable
Cholangiocarcinoma
Adenocarcinoma arising from the bile ductal epithelial cells of the biliary tree inside the liver
Klatskin Tumors: Cholangiocarcinoma that is perihilar at junction of right & left hepatic ducts with proximal common hepatic duct
Cholangiocarcinoma Risk Factors
Chronic parasitic infestation with LIVER FLUKES
Chronic inflammation of large bile ducts (PSC, stones,)
risk factors of HCC
congenital malformations of biliary tree (Choledochal Cysts, including intrahepatic only Caroli Disease), Congenital Hepatic Fibrosis (assoc. with Renal cystic diseases)
risk factors for cholesterol gallstones
Ethnic/genetic: Navajo, Pima, Hopi
Demographic: living in the West (US, Europe)
Gender: Females 2x males; oral contraceptives; pregnancy
Estrogen:
↑ liver HMG-CoA reductase activity thus ↑ cholesterol synthesis
inhibits hepatocyte Bile Salt Export Pump into the canaliculi (less bile acids)
Age: prevalence increases with age; usually affects middle age & older
Obesity, Hyperlipidemia, Rapid weight loss (post Bariatric surgery)
risk factors for Pigmented (bilirubin) stones
Hemolytic anemias: sickle cell anemia, thalassemia, malaria
Bacterial & parasitic infections ( predispose to bouts of Pyogenic Cholangitis) of biliary tree
Severe ileal dysfunction or bypass- Crohn disease
↑ spillage of bile acids into the colon carrying solubilized unconjugated bilirubin promote its absorption → ↑ re-excretion into the bile & stone formation
Complications of Gallstones
Cholecystitis - gallstones are usually involved
Choledocholithiasis - stones in biliary tree
Acute Cholecystitis
2° to obstruction of neck or cystic duct with a gallstone
Few are Acalculous; occurs in severely ill patients (Ischemia)
RUQ pain that lasts > 6 hours (< 6h = biliary colic)
Anorexia, N&V, mild fever
Murphy’s sign
CBC may see MILD leukocytosis
Best & most sensitive: Ultrasonography shows Cholelithiasis, Ultrasound Murphy’s Sign, wall thickening (> 3 mm), & pericholecystic fluid
if Dx still unclear: HIDA Scan (IV radioactive tracer → secreted into bile ducts by bile ductal cells → image biliary tree)
AST, ALT normal or mildly elevated
ALP & Bilirubin to r/o common duct obstruction
Amylase/Lipase to r/o pancreatitis
Pregnancy test if female
U/A to r/o pyelonephritis
Carcinoma of Gallbladder
Most common malignancy of extrahepatic biliary tract
Adenocarcinomas
Most important risk factor is Gallstones (more common in women, Native Americans)
Symptoms same as Cholelithiasis; most discovered incidentally at cholecystectomy & have already invaded the liver, cystic duct and spread to the liver hilar nodes.
Common driver mutations are in the EGF receptor Her-2/neu or downstream RAS pathway with loss of TP5
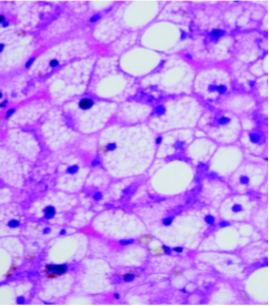
Acute Fatty Liver of Pregnancy
Microvesicular Steatosis
Metastasis to liver from
COLON, LUNG, BREAST, PANCREAS