acids and bases
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
What is ionisation
Breaking down of covalent molecule to form ions where water must be present
What is an acid
Substance that ionises in water to produce Hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water
Hydrogen causes acidity
Properties of acid
sour taste
Turns blue litmus paper red
React with alkalis, carbonates, and reactive metals
Dissolve in water to form solutions that conduct electricity
Why is dry hydrogen chloride not acidic
Hydrogen atom is still covalently bonded to chlorine atom
Hence no H+ ions present, no acidic properties
What is an alkali
Substance that dissolves in water to form hydroxide ions (OH-) where water must be present
Hydroxide ions case alkalinity
Properties of alkalis
bitter
Slippery and soapy
Turn red litmus paper blue
Reacts with acids
Dissolve in water to form solutions that conduct electricity
What is the pH scale
Measure of how acidic or alkaline a solution is
The lower the pH, the higher the the concentration of hydrogen atoms
Unreactive metals
Copper, silver, gold
Reaction of acid with reactive metals
Metal + acid —> salt + hydrogen (gas)
What happens to metals atoms and hydrogen ions during reaction
Metal lose electrons to form metal ions (specify)
Hydrogen ions gain electrons to form hydrogen atoms, atoms bond to form molecules (H2)
Ionic equation for acid and metal reaction
M + 2H+ —> M*+ + H2
How to test for hydrogen gas
Place lighted splint at the mouth of test tube
If hydrogen is present, lighted splint extinguishes with pop sound
Chemical equation for hydrogen test pop sound
2H2 + O2 —>2H2O (combustion)
General equation for acid + carbonate
Acid + carbonate —> salt + caarbon dioxide + water
Ionic equation for acid + carbonate reaction
2H+ + CO3²- —> CO2 + H2O
Test for carbon dioxide
Bubble the gas into limewater
If carbon dioxide is present, white precipitate is formed in limewater
Equation for test for carbon dioxide (white precipitate is formed)
Ca(OH)2 (aq) + CO2 (g) —> Ca CO3 (s) + H2O (l)
What are bases
Any metal oxides that contain either oxide ion (O²-) or hydroxide ion (OH-)
What is neutralisation
When acid reacts with base to form salt and water
General equation for acid and alkali reaction
Acid + alkali —> salt + water
Ionic equation for acid and alkali reaction
H+ + OH- —> H2O (applies only on alkalis/ insoluble base and not insoluble bases)
Graphs for excess alkali added to acid
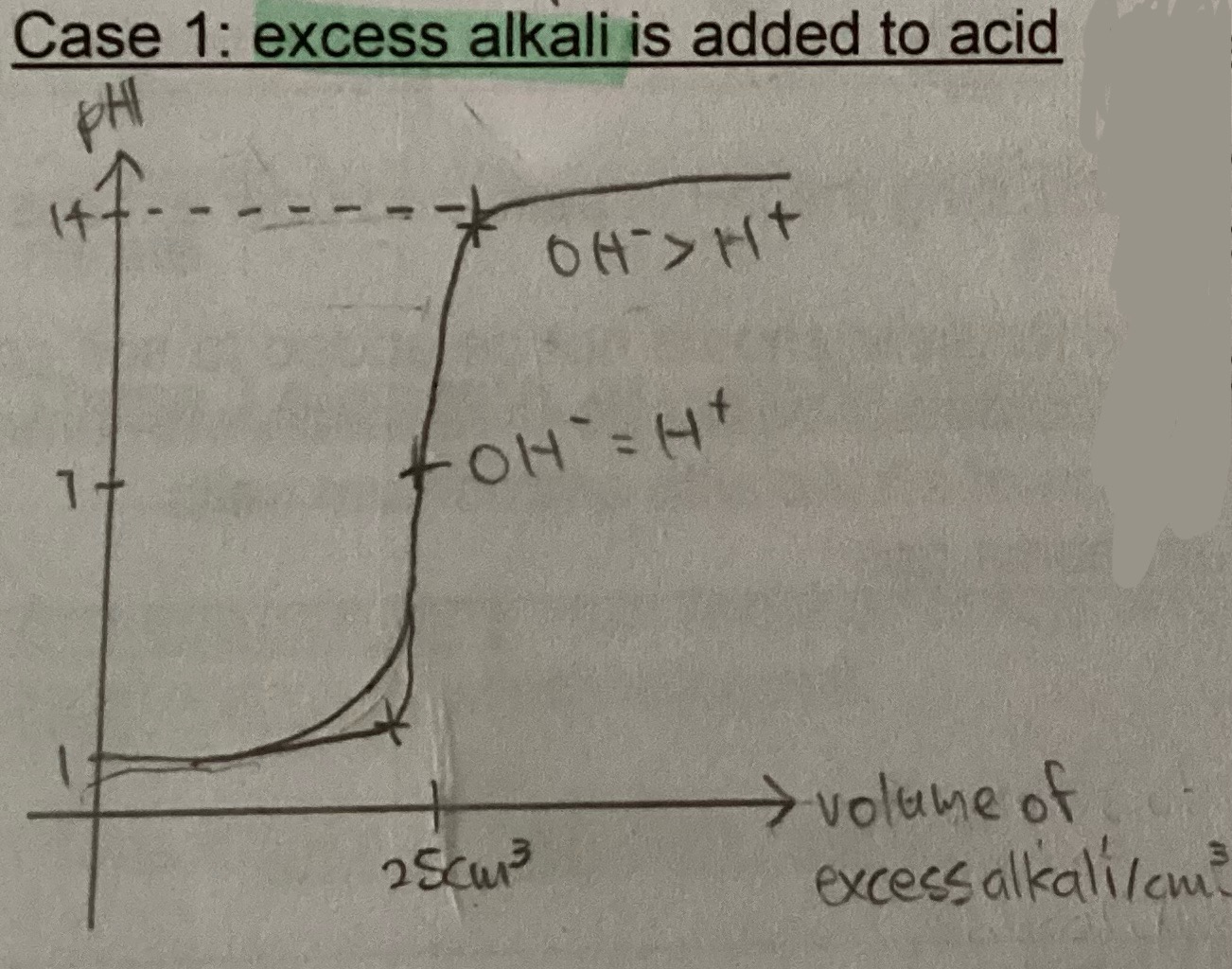
Graph for excess acid added to alkali
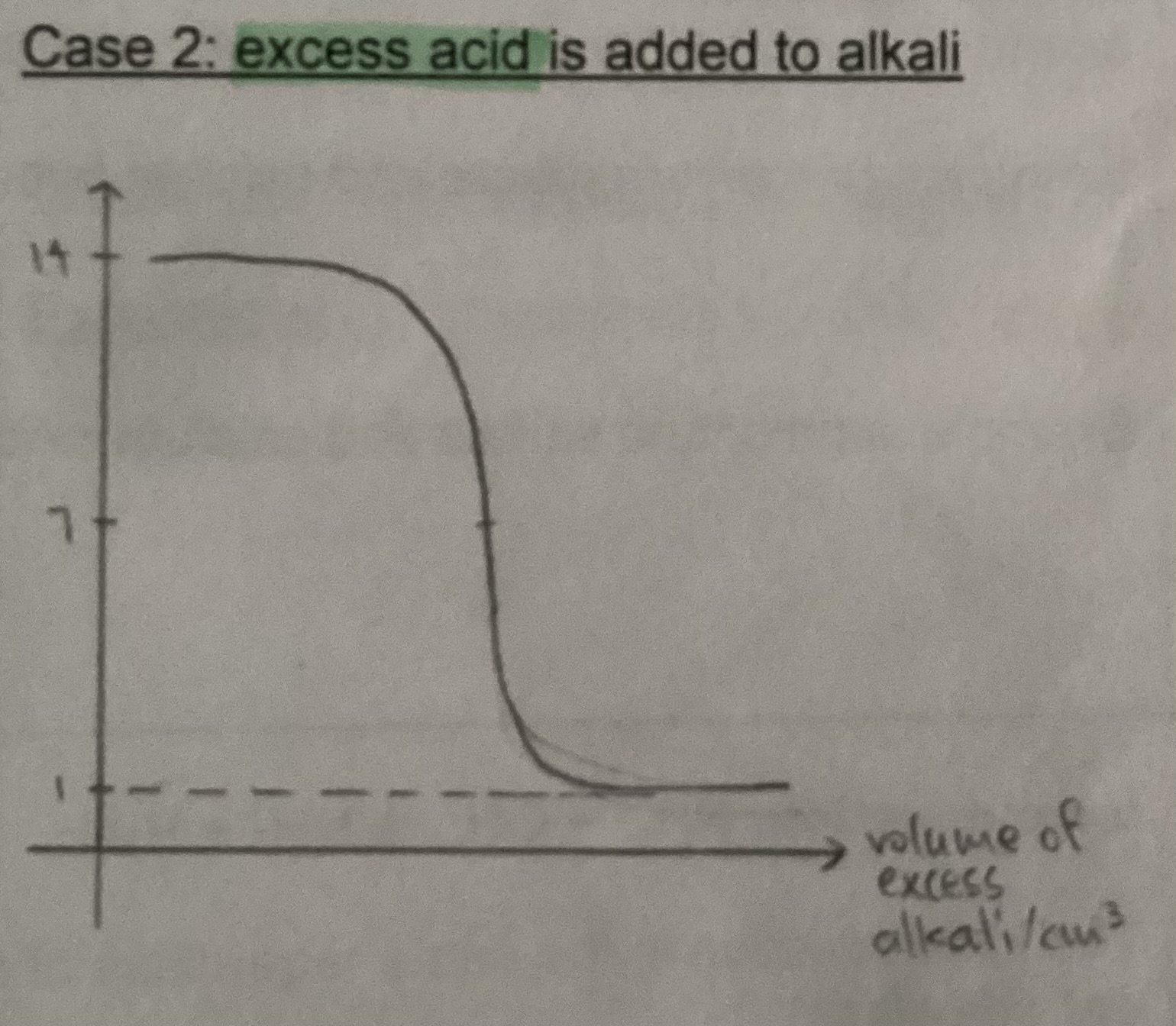
Graph for excess insoluble base added to acid
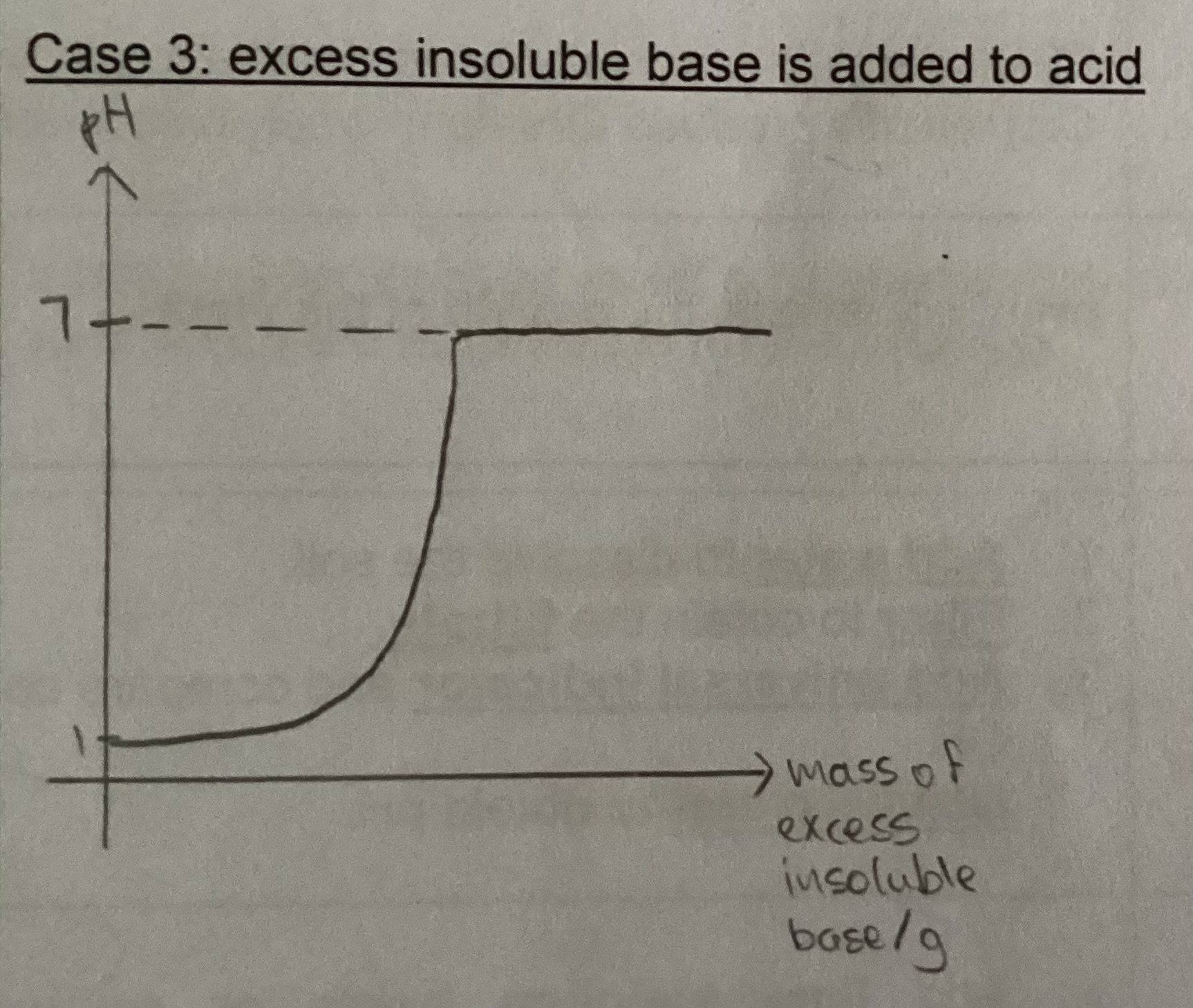
General equation for alkali reaction with ammonium salt
Ammonium salt + alkali —> salt + water + ammonia
Ionic equation for alkali react with ammonium salt
NH4+ + OH- —> NH3 + H2O
How to determine pH of soil
Add water to dissolve soil
Filter to obtain filtrate
Add universal indicator and compare colour against chart ? Use pH meter
How to reduce excess acidity in soil
add lime ( calcium oxide or calcium hydroxide or calcium carbonate) to the soil to react with the excess H+ present in the soil
This increases pH of soil
Type of fertiliser plant need
Fertiliser containing nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), potassium (K)
Common fertilisers: ammonium sulfate, potassium phosphate, ammonium nitrate
Why can’t add ammonium compounds to freshly limed soil
Ammonium ions from fertiliser reacts with hydroxide ions in soil to form ammonia gas which escapes, there is loss of nitrogen nutrient
Ionic equation for ammonium salt react with alkali
NH4+ + OH- —> NH3 + H2O
Test for ammonia gas
Place moist red litmus paper at the mouth of test tube If hydrogen
If ammonia gas is present, moist red litmus paper turn blue
Why must red litmus paper be moist for ammonia gas test
So that ammonia can dissolve to produce OH- ions which is responsible for the alkalinity
What are some soluble and insoluble bases (metals)
All group 1 oxides/ hydroxides and Ca(OH)2 , Ba(OH)2
All other metal oxides are insoluble
What are some acidic non metal oxides
CO2, NO2, SO2
What are some neutral non metal oxides (do not react with acids and bases)
NO, CO, H2O
What are some amphoteric oxides (react with both acids and bases)
ZnO, Al2O3, PbO (ZAP)
Test for oxygen
Place glowing splint into test rube
If oxygen is present glowing splint relights
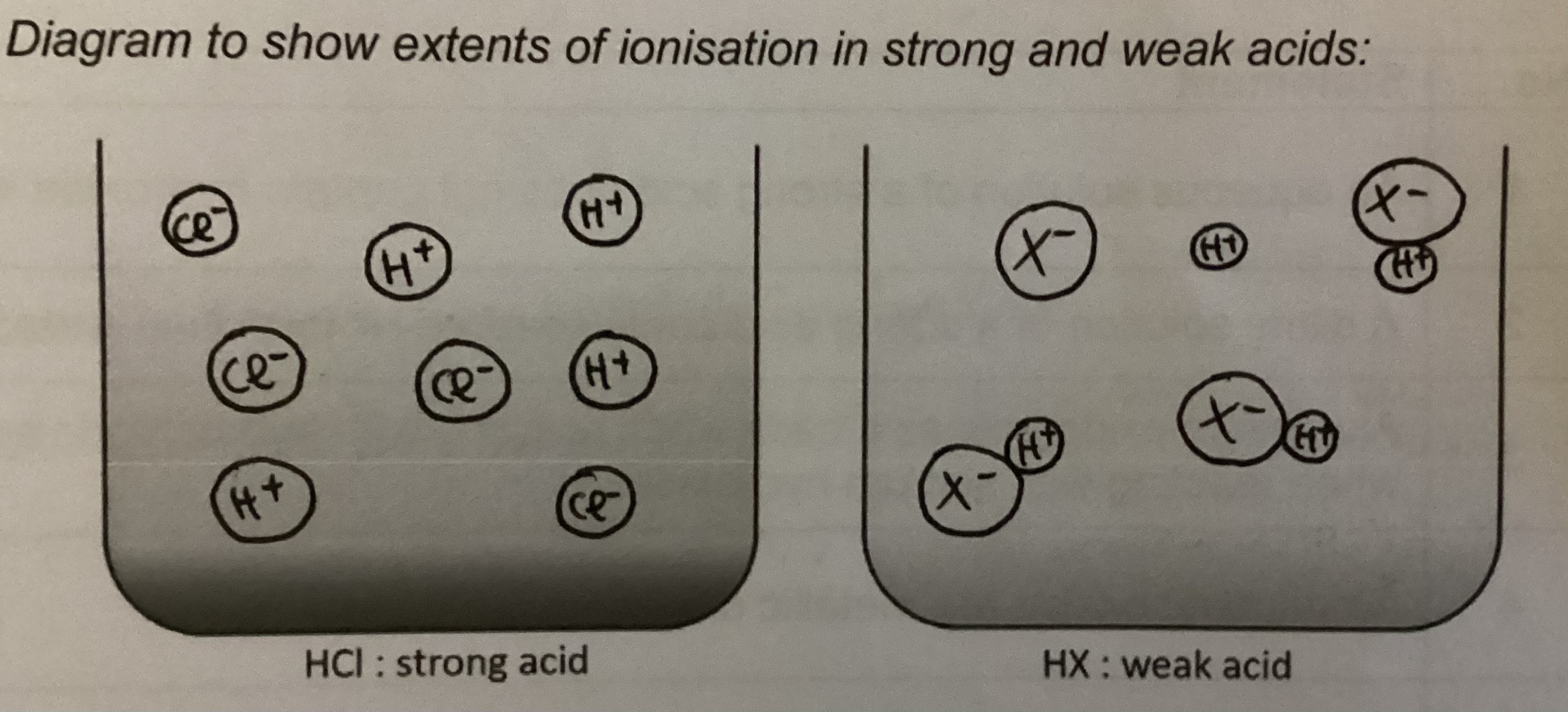
What is a strong acid/ alkali
Substance that ionises fully in water to produce hydrogen/ hydroxide ions when dissolved in water
Eg HCl, HNO3, H2SO4/ NaOH, KOH
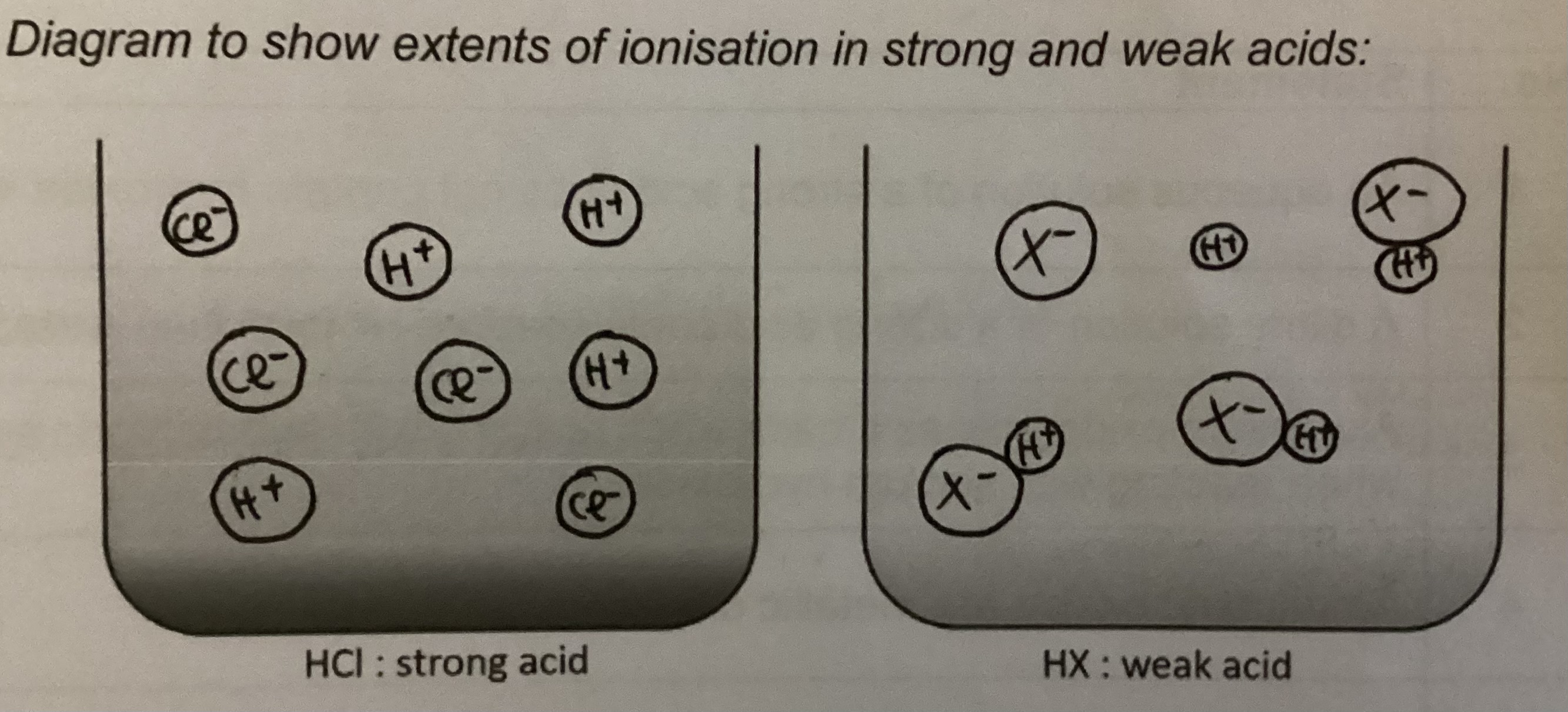
What is a weak acid/ alkali
Substance which ionises partially to produce hydrogen/ hydroxide ions when dissolved in water
Eg ethanoic acid/ aqueous ammonia
Simple test to distinguish between strong and weak acids
Strong acid
universal indicator greeen Ui turns red
pH meter 1-2
Electrical conductivity higher current (more mobile ions)
Weak acids
Green UI turns yellow/ orange
pH meter 4- 6
Electrical conductivity lower current ( less mobile ions)
Experiments to distinguish between strong and weak acids
add reactive metal or metal carbonate to equal volumes to strong and weak acids of equal concentration
Measure volume of gas produced in a fixed time
Strong acid produce larger volume of gas than weak acid in the same time
What to consider when collecting gases
Solubility of gas on water
Density of gas compared to air (to compare density of air, compare Mr of the gas with Mr of air which is about 30)
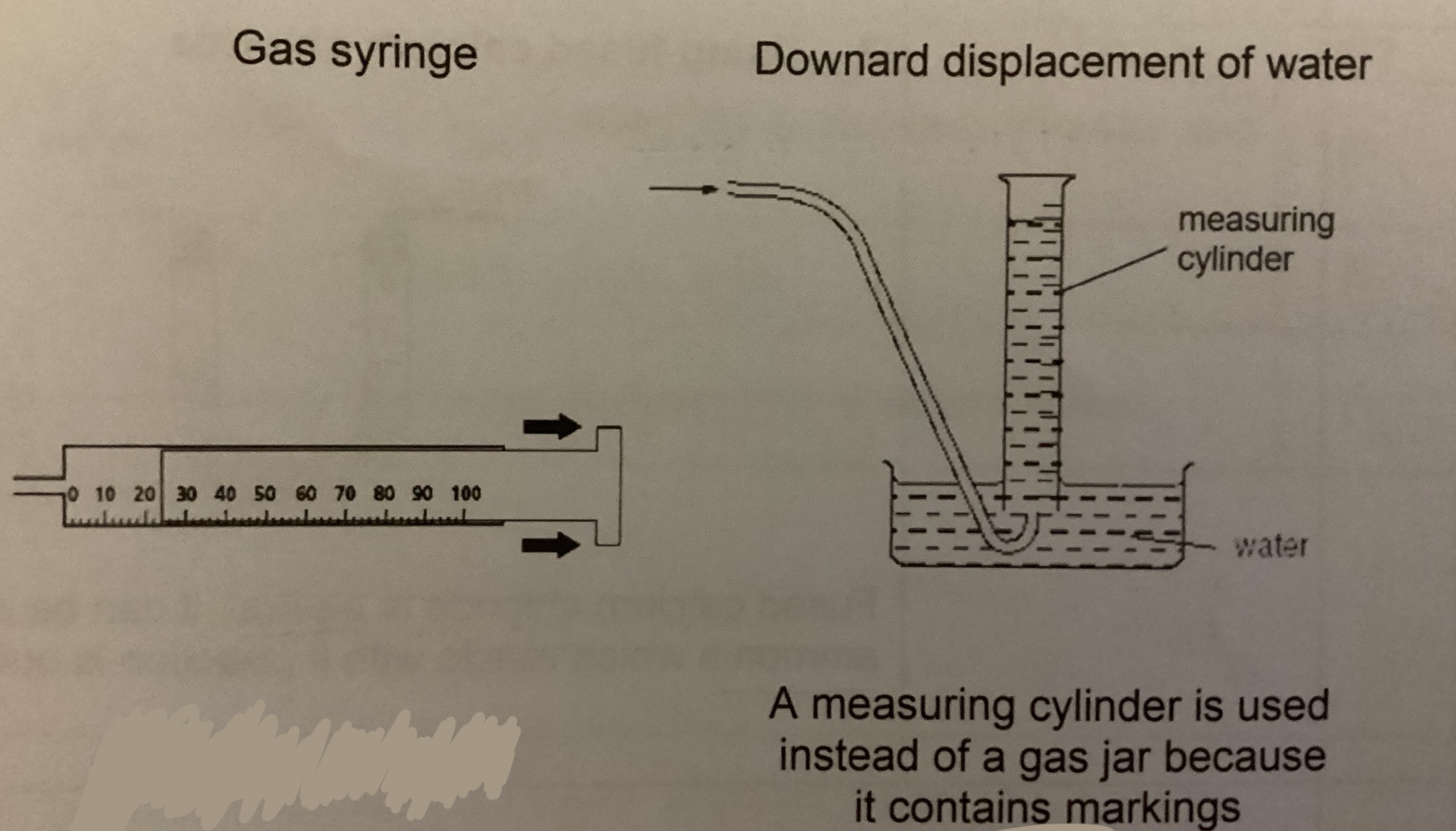
How to collect gas slightly insoluble/ insoluble in water
Downward displacement of water method
How to collect gas less dense than air
Upward delivery method
How to collect gas more dense than air
Downward delivery method
How to measure volume of gas collected
How to dry acidic gases
concentrated sulfuric acid
Fused calcium chloride
How to dry alkali gas
calcium oxide
Fused calcium chloride
What is relative molecular mass (Mr)
Tells us how heavy/ light a substance is
What is relative atomic mass (Ar)
Refers to mass of single atom (Ar can be found in periodic table bottom number)
How to calculate Mr
Add up all the Ar of each atom present