Animal Taxonomy, Phylogeny, and Species Concepts Overview
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What is the estimated number of named animal species?
More than 1.5 million species.
What percentage of all living animals do named species account for?
Less than 20%.
Who was the first to classify organisms?
Greek philosopher Aristotle.
Who designed the current scheme of classification?
Carolus Linnaeus.

What is the hierarchical system of classification developed by Linnaeus?
It includes 7 major groups: Kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species.
What is the formal system for naming and classifying species called?
Taxonomy.
What is systematics?
The broader science of comparative biology.
What is binomial nomenclature?
A system for naming species consisting of two words: the genus (capitalized) and the specific epithet (lowercase).
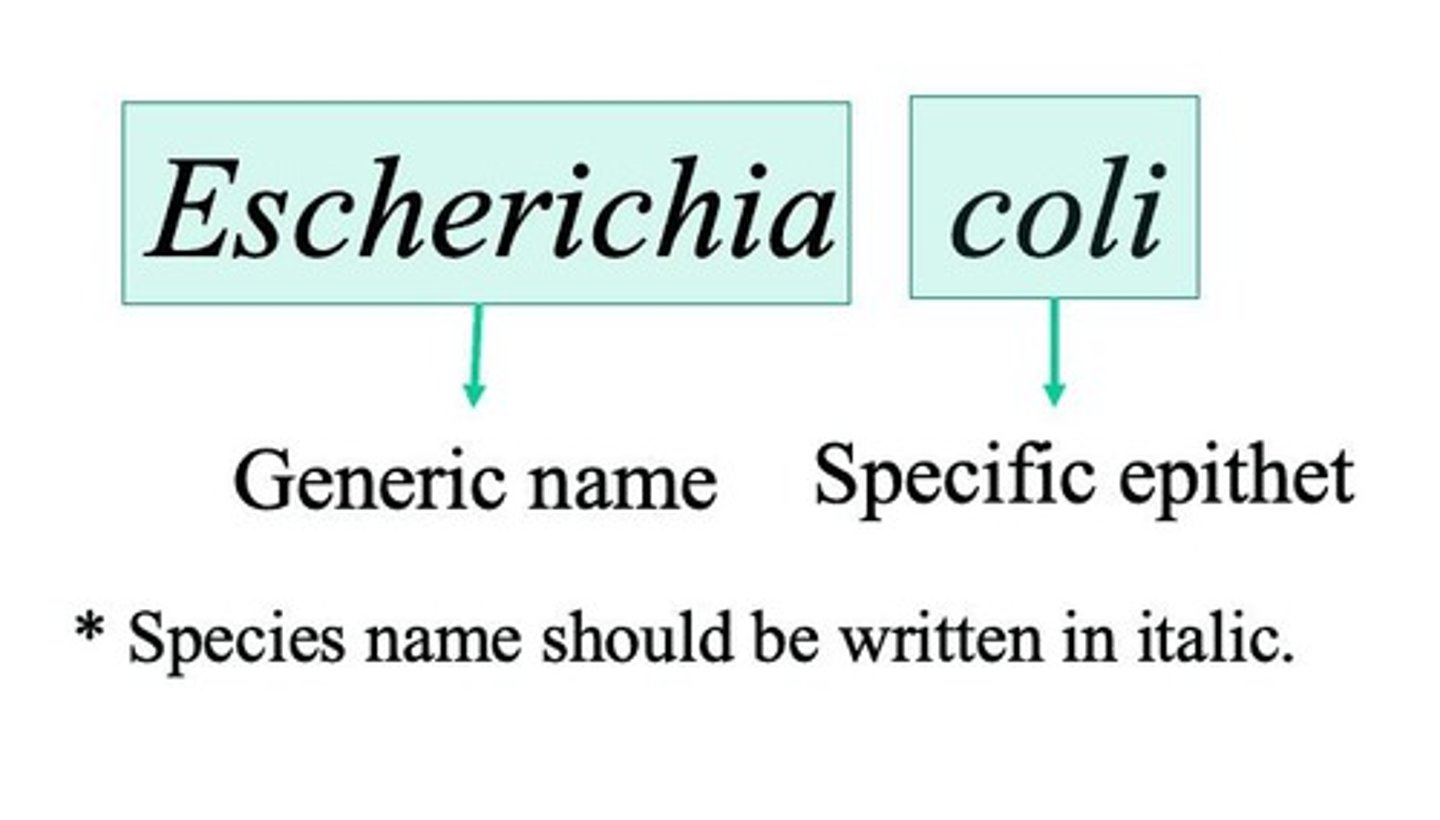
What is the significance of the species epithet?
It is usually an adjective that must agree in gender with the species and is never used alone.
What is the biological species concept?
A species is a reproductive community of populations that occupies a specific niche in nature and is reproductively isolated from others.
What challenges does the biological species concept face?
It lacks an explicit temporal dimension and does not define species that reproduce asexually.
What is the phylogenetic species concept?
An irreducible grouping of organisms that is diagnosably distinct from other groupings and has a parental pattern of ancestry and descent.
What is homology?
Character similarity resulting from common ancestry.
What is homoplasy?
Non-homologous similarity that misrepresents common descent.
What is a synapomorphy?
A derived character state shared by two or more taxa that evolved in their common ancestor.
What is a clade?
An ancestral lineage and all descendant species.
What are the three types of phyletic groups?
Monophyletic, paraphyletic, and polyphyletic groups.
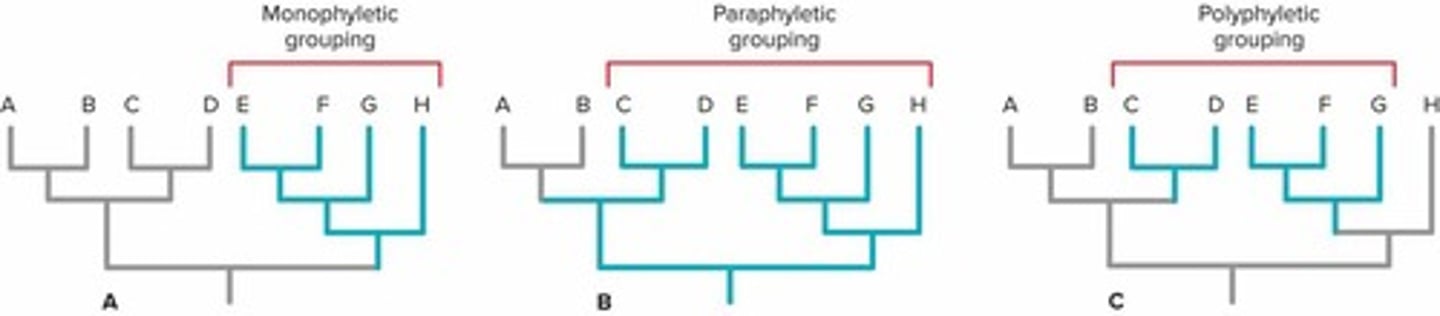
What is the difference between monophyletic and polyphyletic groups?
Monophyletic groups include a common ancestor and all its descendants, while polyphyletic groups do not include the common ancestor.
What is the taxon Bilateria?
It is split into two taxa: Deuterstomia and Protostomia.
What does Deuterstomia refer to?
Embryonic blastopore becomes the anus.
What does Protostomia refer to?
Embryonic blastopore becomes the mouth.
What is the major goal of systematics?
To infer an evolutionary tree or phylogeny that relates all extant and extinct species.
What are taxonomic characters?
Features used to study variation within and among species.
What is the significance of phylogenetic trees?
They depict and analyze evolutionary history as a branching tree.
What is the role of characters in phylogenetic analysis?
Characters are used to identify patterns of similarity among organisms.
What is an example of convergent evolution?
The spines of cacti and euphorbs.
What is a derived character?
A character that has evolved from an ancestral state.
What is the importance of character similarity in taxonomy?
It helps to infer evolutionary relationships and common ancestry.