4 - PPC & opportunity cost
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
what does a Production Possiblity Curve/Frontier show
all combinations of products that can be produced using all available resources
every point on the curve means all FOPs are being used (productive efficiency)
what happens to production when resources are reallocated
opportunity cost
value of the alternative forgone
aka real cost
opportunity cost increases as you move along the PPC
why is a PPC a curve and not a straight line
certain workers/machinery are specialised in making one thing. They can’t be substituted perfectly
a point inside of the curve has __ opportunity cost
No
because resources are abundant
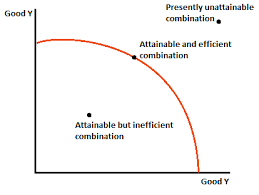
a point outside the curve is _________
unatainable
not possible to reach with current levels of FOPs
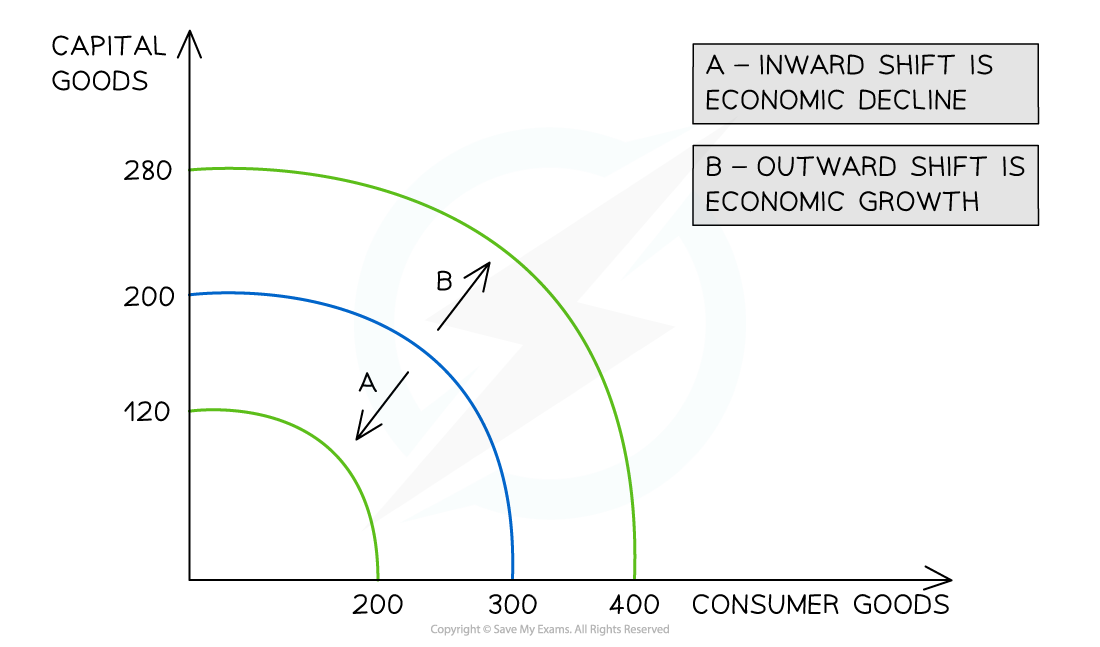
an outward/right shift represents ______
economic growth
increase in productive capacity
an outward/right shift is because of ______
increase in FOPs/supply of labour (e.g. immigrants)
improved training/skill development
development of new capital (e.g. robots)
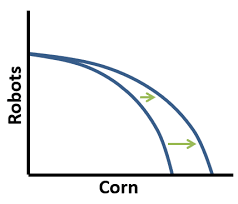
how does technology biased growth affect the PPC?
less resources needed, easier to make certain products
curve does not completely shift out, but stays rooted at 1 point while the rest of the curve shifts
free goods
good with 0 opportunity cost (you don’t have to sacrifice anything)
no substitutes (replacements)
no complements (nothing to pair with it)
e.g. rain, sunlight
economic goods
any good with an opportunity cost in consumption
have complements, scarcity, and substitutes