Nuclear Physics
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
150 Terms
Isotopes (Definition)
Atoms of the same element which have different numbers of neutron
What element has the lowest number of isotopes?
Hydrogen
What are the three atoms/isotopes of hydrogen?
Hydrogen. Deuterium. Tritium
Proton and neutron counts of hydrogen
1 proton and 0 neutrons
Proton and neutron counts of deuterium
1 proton and 1 neutrons
Proton and neutron counts of tritium
1 proton and 2 neutrons
Draw a diagram of hydrogen
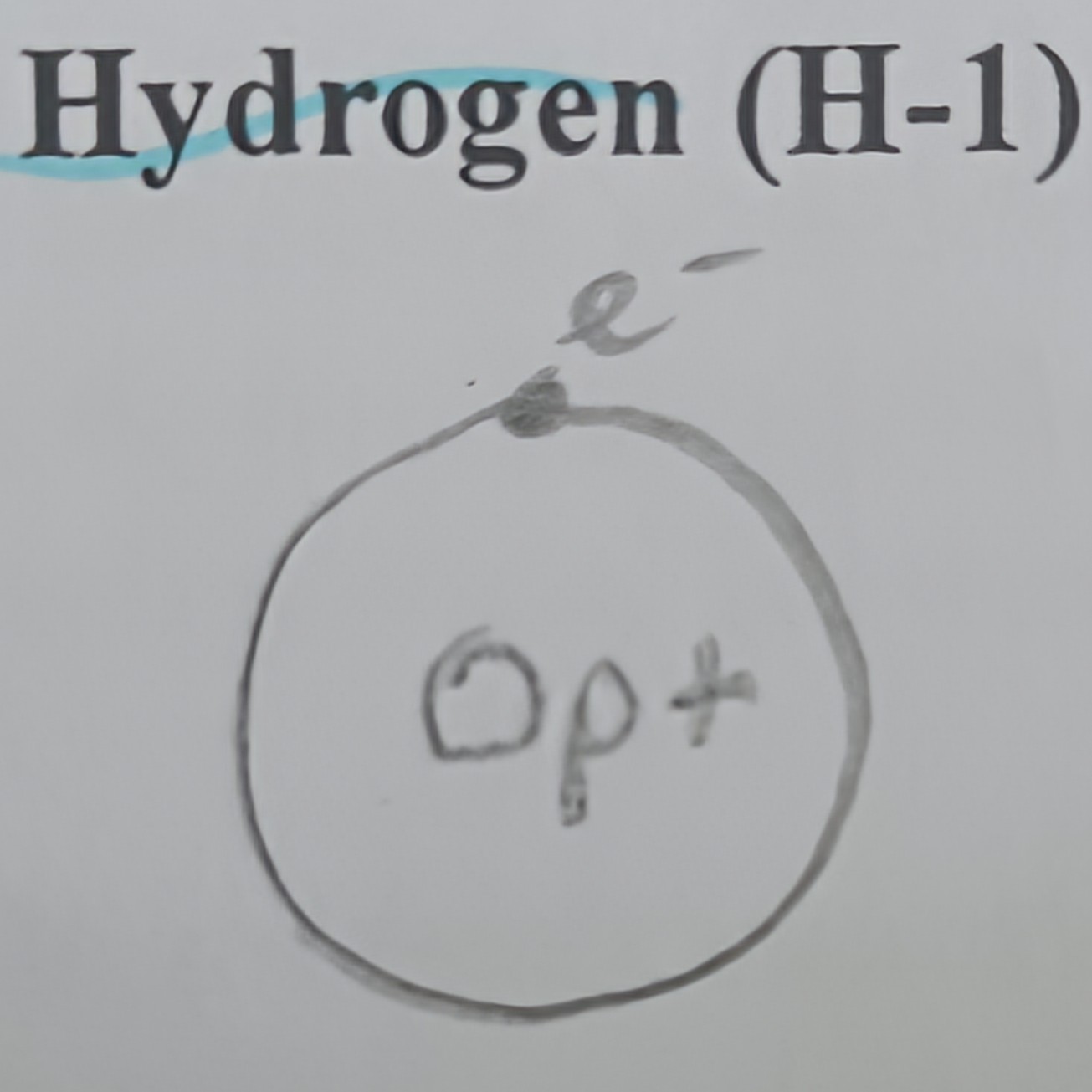
Draw a diagram of deuterium

Draw a diagram of tritium

Which hyrdogen isotope is radioactive?
Tritium
How are isotopes identical?
Chemically identical to one another
Mass defect (Definition)
The difference between the mass of the atom and the sum of the masses of its constituent parts
Binding energy (Definition)
The amount of energy that must be supplied to a nucleus to completely separate its nuclear particles. Binding energy is the energy equivalent of the mass defect
Binding energy per nucleon (Definition)
Binding energy divided by the number of nucleons (protons + neutrons)
Explain binding energy
When an atom other than Hydrogen is made a little bit of mass disappears. This missing mass is converted to binding energy to keep positively charged protons together in the nucleus
What formula is linked to binding energy?
E = mc²
Why do larger atoms have more binding energy?
Binding energy has to be spread over more nucleons
How to find how well stuck together different nuclei are?
Work out binding energy and divide it by the number of nucleons in the nucleus
Draw a graph of binding energy for a nucleon versus mass number
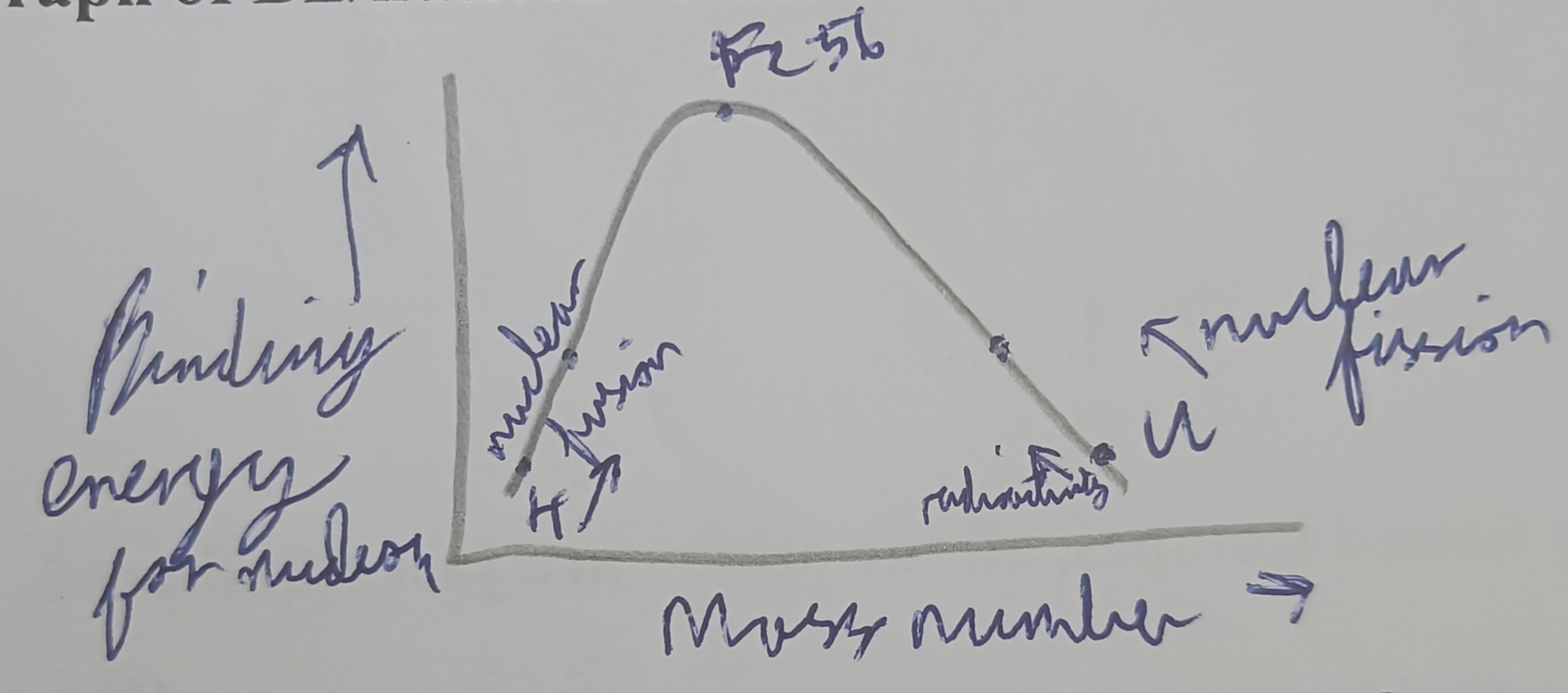
What is the most stable isotope?
Fe - 56
How do light nuclei become more stable?
Become more heavier via nuclear fusion
Examples of light nuclei
Hydrogen. Helium
How do heavy nuclei become more stable?
Become lighter by spitting out abit of themselves (radiation) or fission
Examples of heavy nuclei
Uranium. Plutonium
Does fusion or fission release more energy? Why?
Fusion releases more energy than fusion as the slope of the graph for fusion is steeper than fission.
Is fusion or fission more radioactive?
Fission is more radioactive than fusion
Why is Fe-56 the most stable?
Highest binding energy per nucleon and is therefore the best stuck together/stable nucleus
What does alpha radiation consist of?
Fast moving Helium nuclei
Ionisation and penetrating power of alpha radiation
Most ionising radiation but has the least penetrating power
What is alpha radiation deflected by?
Deflected by electric or magnetic fields
What do alpha particles deflect/attract?
Anything that's charged
What does beta radiation consist of?
Fast moving electrons
Ionisation and penetrating power of beta radiation
Medium ionising power and medium penetrating power
What is beta radiation deflected by?
Deflected by electric or magnetic fields
What must you never shield beta radiation with?
Lead
Why mustn't you shield beta particles with lead?
Produce x-rays as electrons strike a dense metal
Transmutation (Definition)
Where one element is changed to another
What happens in the nucleus of an atom undergoing beta radiation?
A neutron is changed to a proton and a beta particle. Beta particle is shot off
What does gamma radiation consist of?
Very high energy electromagnetic waves which travels at the speed of light
Ionisation and penetrating power of gamma radiation
Least ionising ability but highest penetrating power
Can gamma radiation get deflected by electric and magnetic field?
No
Why can't gamma radiation get deflected by electric and magnetic field?
It has no charge
Explain how gamma radiation affects the nucleus of an atom
Neutrons and protons arrange themselves so that they are more tightly arranged. This leaves some extra nuclear glue/ binding energy which is released as gamma radiation
When are gamma rays emitted?
Emitted from a nucleus which has already emitted an alpha or beta particle. It results from an internal rearrangement of the nucleons. Nucleus structure remains the same but loses energy and becomes more stable
Atomic number (Definition/ calculation)
Number of protons (and usually number of electrons
Mass number (Definition/calculation)
Number of protons + Number of neutrons
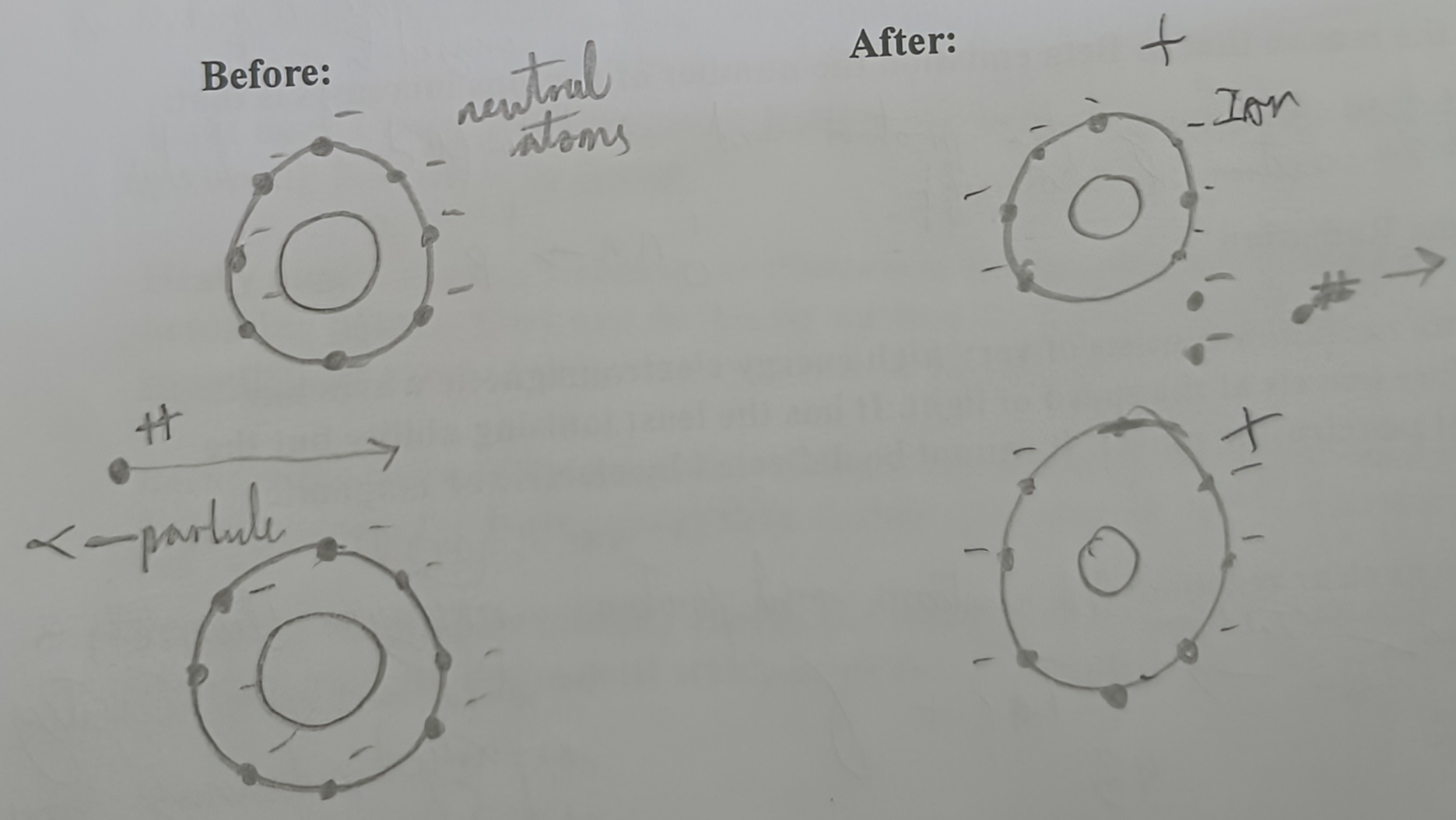
How do alpha particles cause harm?
Once it enters a substance it rips electrons from neutral atoms creating ions. This causes harm.
What happens to the negative electrons left after the alpha particle rips other electrons?
Attract the positive alpha particles and slows them down until they stop
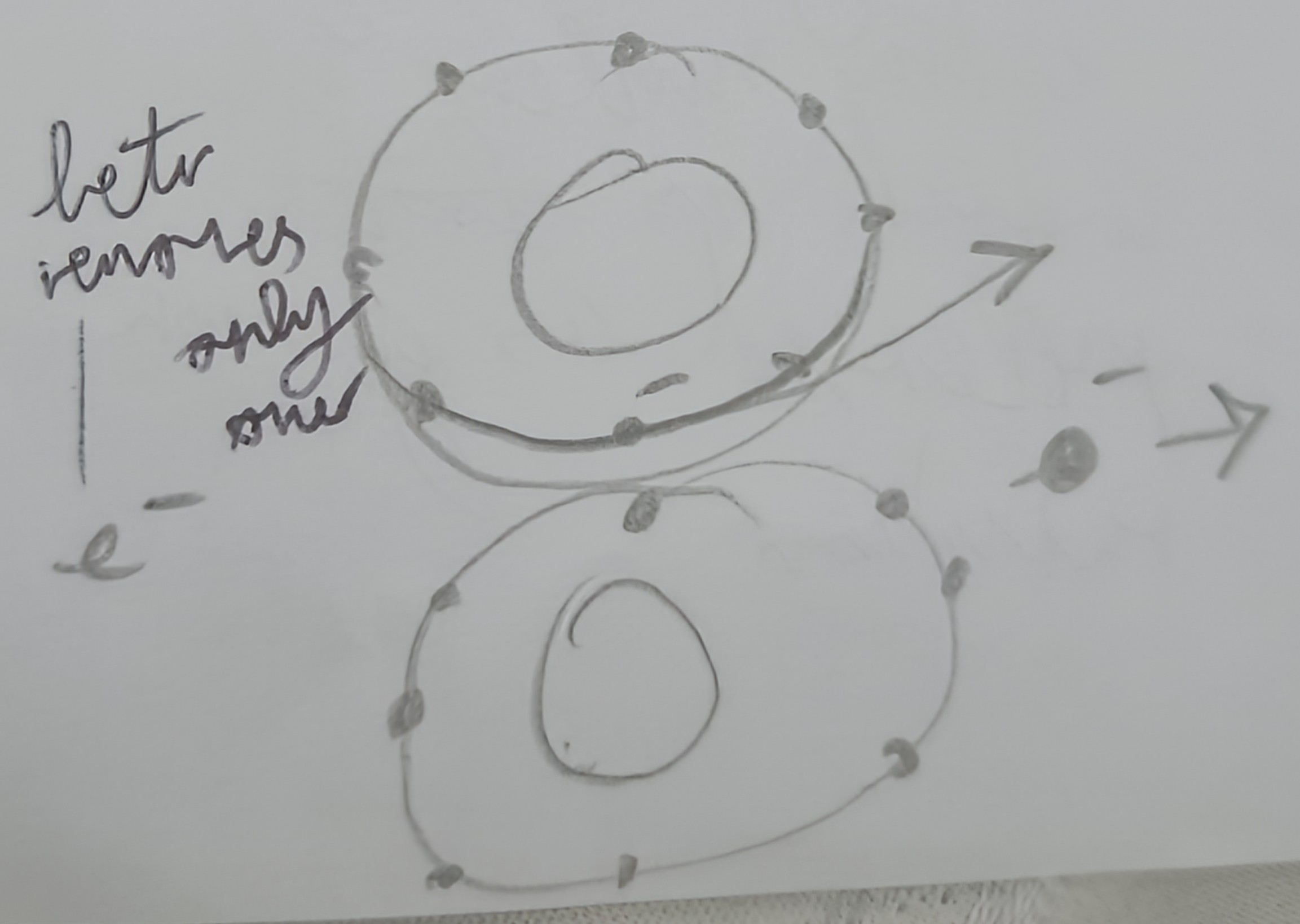
How do beta particles cause harm?
They cause less ionisation but penetrate further. They repel electrons out of shells.
What causes beta particles to be really dangerous?
High concentration is what causes beta particles to be dangerous
Why do gamma rays have the least ionisation?
They are uncharged
Effect of gamma ray's low ionisation
Makes them difficult to detect
Numbers of gamma rays
Large number
How do gamma particles cause harm?
Removes electrons from the substance hit by hitting at electron to remove it
Draw a diagram of an alpha particle hitting an atom (Before and After)
Draw a diagram of a beta particle hitting an atom (Before and After)
Draw Half life Vs Radioactivity
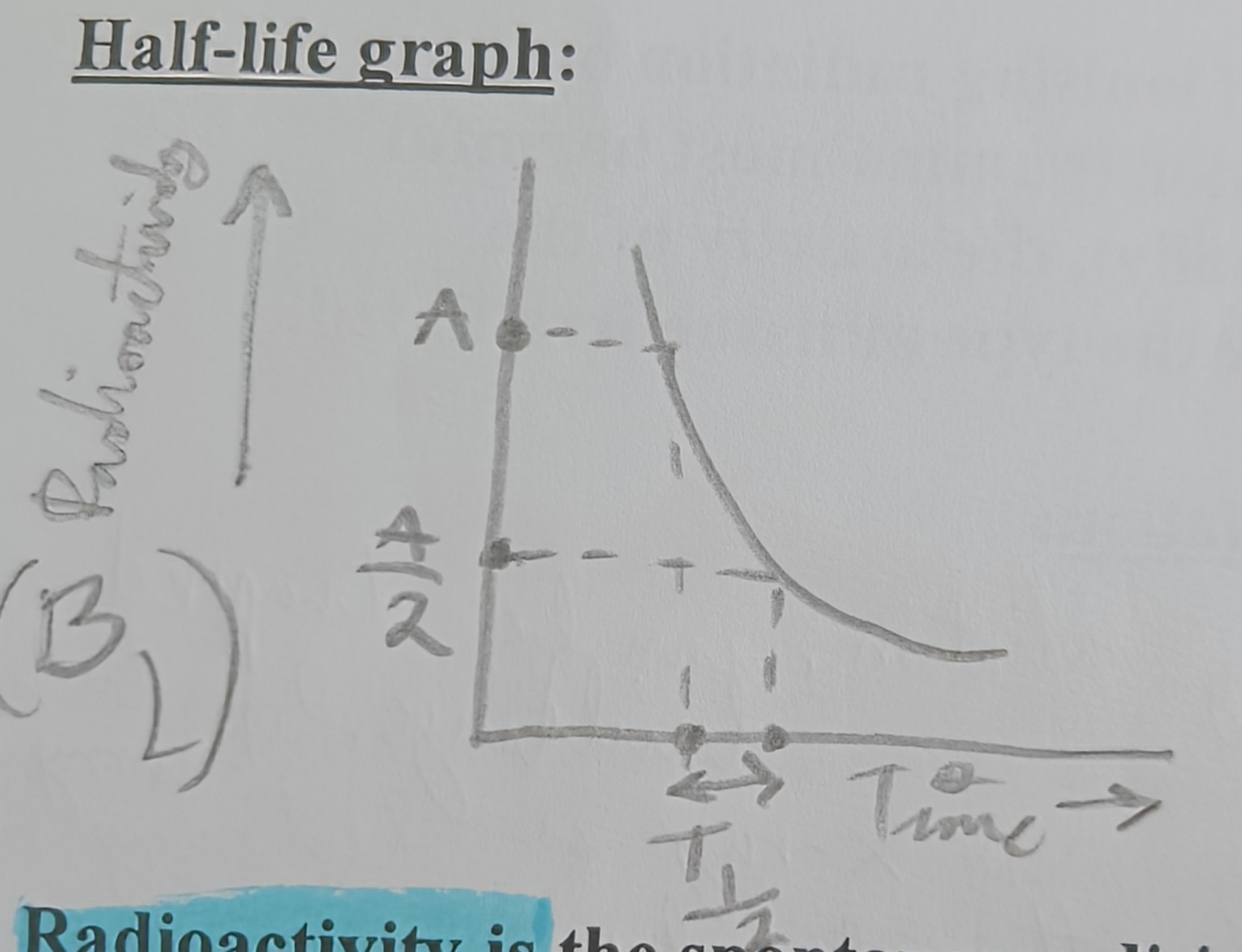
Radioactivity (Definition)
The spontaneous disintegration of unstable nuclei with the emission of one or more types of radiation. It is unaffected by physical or chemical processes/changes
Who discovered by radioactivity?
Henry Becquerel
Half-life (Definition)
Of an element is the time taken for half of the nuclei in any given sample to decay
Half-life (Activity Definition)
Of an element is the time taken for half for the activity of any given sample to decrease to half of its original value
Decay constant (Definition)
The proportion of the number of atoms that decay per second
Decay constant unit
s⁻¹
Law of radioactive decay (Activity formula)
A = dN / dt or A = -λN
Law of radioactive decay (Activity formula/calculation)
A = λN
What is A (Law of radioactive decay)?
Activity
What is activity/radioactivity activity measured in?
Bq
What is N (Law of radioactive decay)?
Number of nuclei in sample
What is λ (Law of radioactive decay)?
Decay constant
1 Becquerel = … disintegration per second
1
Half life formula
T1/2 = Ln2 / λ
What is T1/2? (half-life formula)
Half-life
What is λ? (half-life formula)
Decay constant
Einstein's mass-equivalence equation
E = mc²
What is E? (Einstein's mass-equivalence equation)
Energy
What is m? (Einstein's mass-equivalence equation)
Mass
What is c? (Einstein's mass-equivalence equation)
Speed of light
Name 4 health hazards of ionising radiation
Radiation burns. Genetic mutations. Cancer. Death
Environmental radiation (Definition)
The effect of ionisation radiation on humans depends on the type of radiation (gamma most harmful externally alpha most harmful internally). The activity of the source in Bq. The time of exposure. The type of tissue irradiated.
Sources of background (ionising) radiation
Granite/Radon. Medical & Dental X-Rays. Airline Flights
Explain Granite/Radon (Background radiation)
Found from rocks releasing radiation. Can be trapped under buildings. Pipes built under to carry it out and to air
Explain Airline Flights (Background radiation)
Long haul flights by more x-rays as higher up means less air density means getting hit by more x-rays from space at a higher risk of cancer
Precautions when handling radioactive sources (3)
Should never be handled directly. Should not eat or drink in their vicinity. Should be stored in a shielded secure place
Uses of ionising radiation (10)
Curing cancer. Medical tracers. Smoke alarms. Dating organic material. Dating rocks. Heart pacemakers. Measuring thickness of materials/structural defects.Industrial/agricultural tracers. Food preservation. Sterilizing surgical equip
What chemical is used to cure cancer?
Cobalt-60
Curing cancer use (Explain)
Has a short half-light and is chemotherapy when injected into the body
What chemical is used for medical tracers?
Iodine-131
Medical tracers use (Explain)
Used to check if thyroid is functioning. If there's radiation everywhere it means thyroid isn't working
What chemical is used for smoke alarms?
Americium-241
When do smoke detectors expire?
Expiry due to half-life
What chemical is used for dating organic material?
Carbon-14
What chemical is used for heart pacemakers?
Plutonium-238
What is Plutonium-238 used for in artificial pacemakers?
Power artificial pacemakers
Explain measuring thickness of materials/ structural defects
If thickness is even then constant amount of radiation will pass through. If some areas have a greater/lesser thickness then more or less radiation will pass through
Explain industrial tracers
Radioactive metal engines run and oil is checked for radiation to check for friction. The more friction makes it less fuel efficient
Explain food preservation
Radiation beamed to kill bacteria and fungi before shipping e.g. strawberries
Explain the sterilisation of surgical equipment
Equipment placed in bag and radiation beamed to kill microorganisms
Name a detector of ionising radiation
Geiger-Müller tube
Draw a Geiger-Müller tube
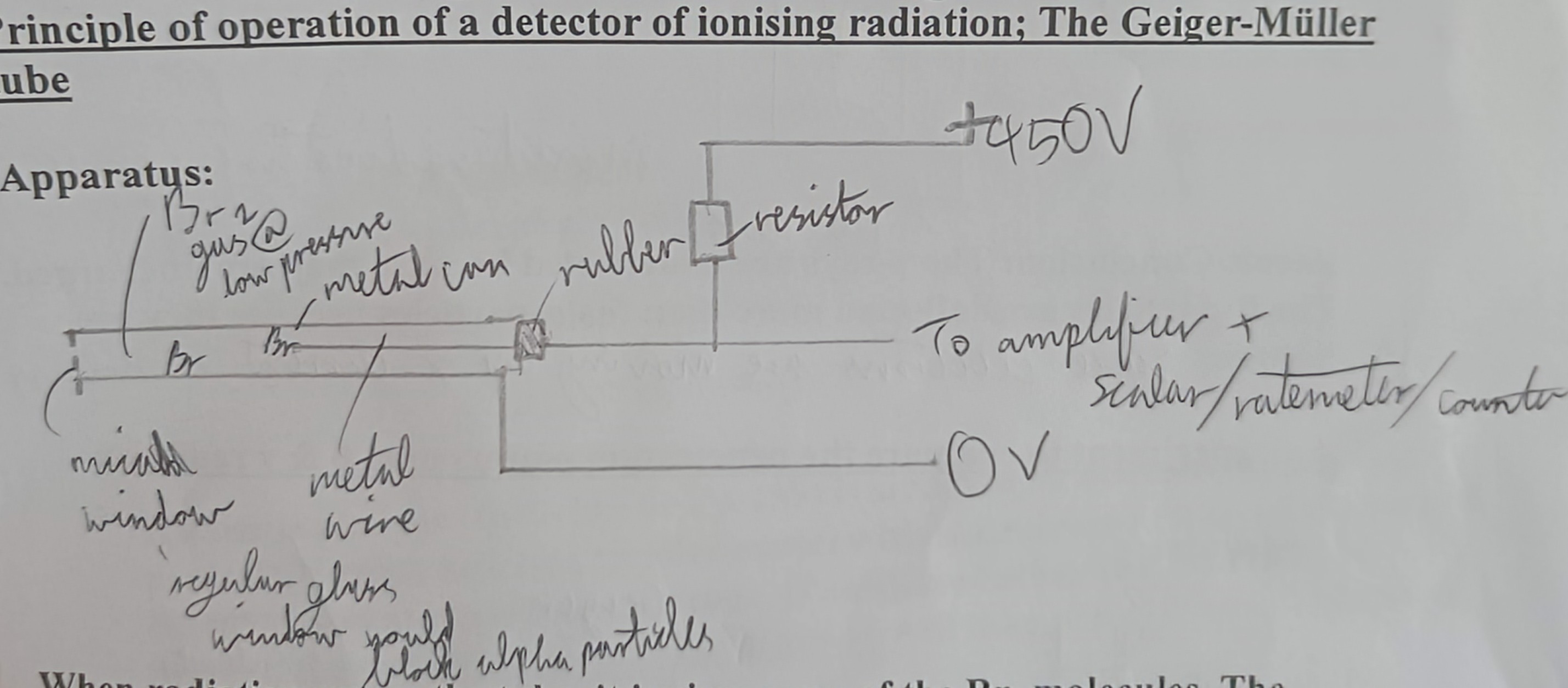
Explain a Geiger-Müller
When radiation enters the tube it ionises some of the Br2 molecules. The positive ions are attracted to the case and the negative ions are attracted towards the wire. Gas amplification occurs. When this charge reaches electrodes it passes arounf the external circuit as a pulse of current. This produces a potential difference across the series resistor and is used to operate a counting device.