Embryogenesis and Pituitary Gland
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Embryogenesis
Post-fertilization development
Differentiaiton of single cell zygote
Production of three distinct germ layers
Germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm
Ectoderm
skin, hair, nails, sweat glands
nervous system: hypothalamus, both lobes of pituitary
oral and nasal cavity
repro tract:
Mesoderm
muscle
blood vessel
reproductive system: gonads (male and female), uterus, cervix, part of vagina, epididymis, ductus deferens, accessory sex glands
urinary and skeletal system
Endoderm
digestive system (including liver and pancreas)
respiratory system
most glands
Adenohypophysis
anterior lobe
Neurohypophysis
posterior lobe
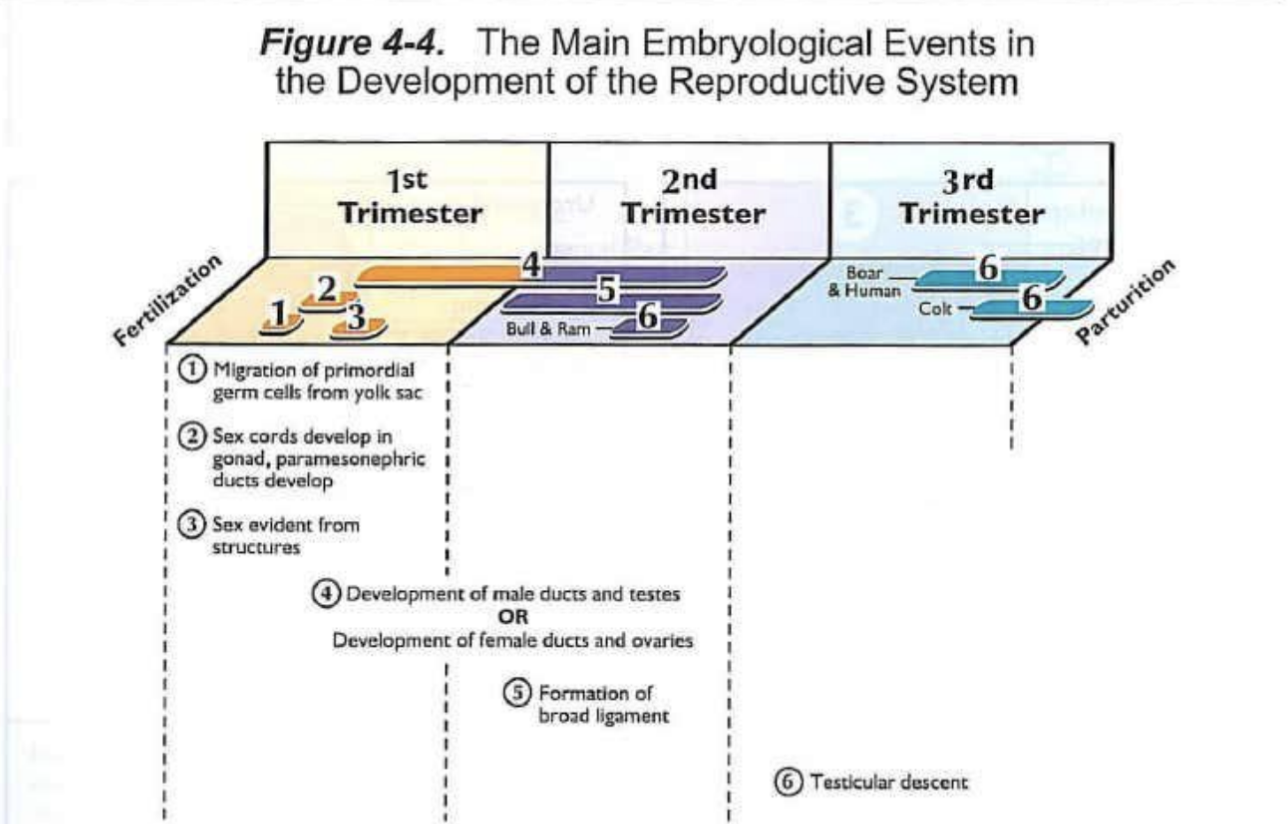
The reproductive system develops in close proximity to and at the same time as the renal system
SRY gene
Controls the pathway towards either male or female development, specifically on the
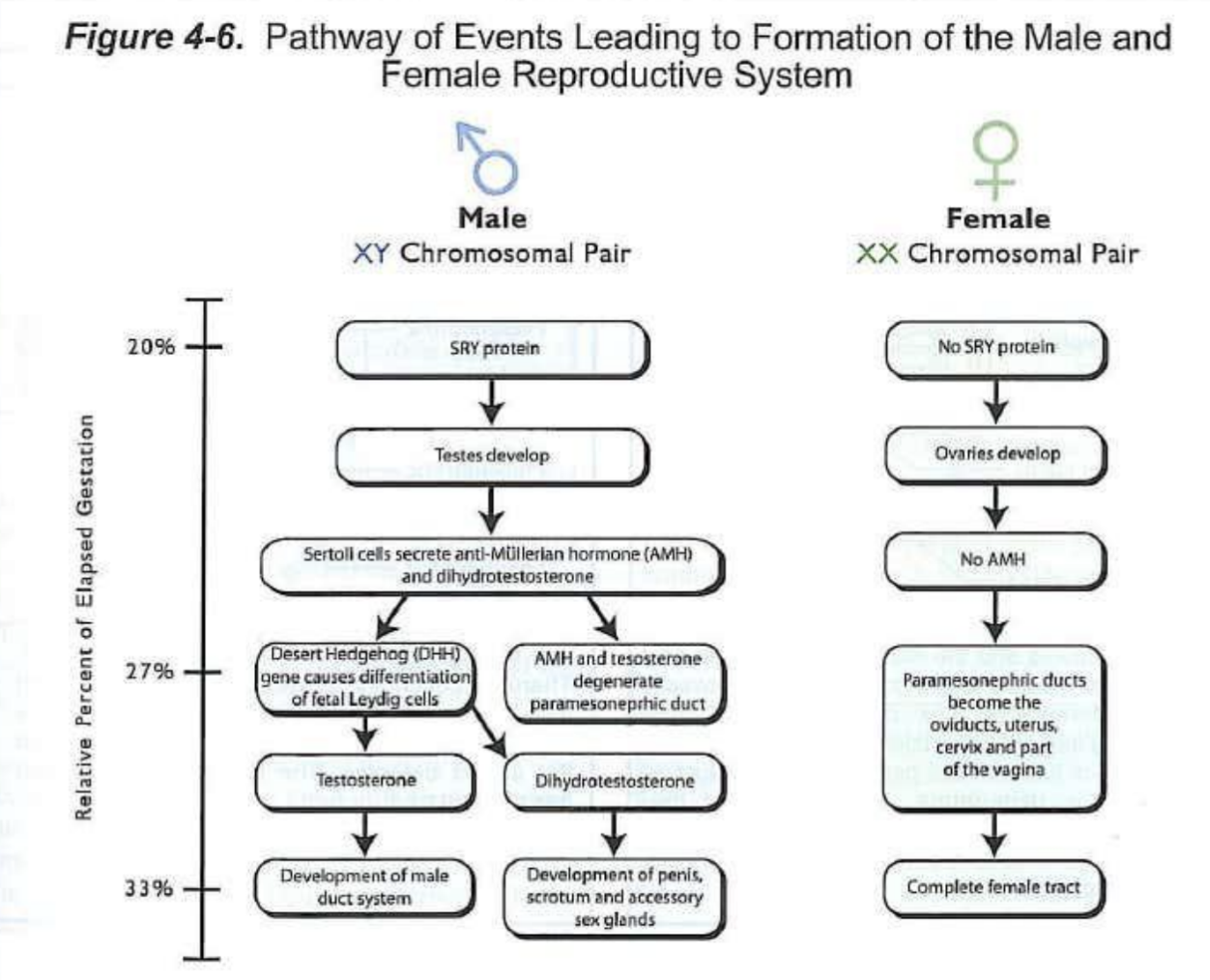
Y chromosome
Part of the male tract is derived from the mesonephros
mesonephric tubules —> efferent ducts
mesonephric ducts —> epididdymis and ductus deferens
The descent of testicles has three phases. They are:
growth and elongation of the fetal body away from the testes (transabdominal)
rapid growth of the extra abdominal gubernaculum (transabdominal)
shrinkage of the gubernaculum within the scrotum (inguinal-scrotal)
Two common testicular descent abnormalities are:
cryptorchidism
inguinal herniation
The uterus and vagina result from a fusion of the paramesonephric ducts.
A freemartin is a heifer born twin to a bull. The heifer calf is sterile, but the bull calf is fertile.