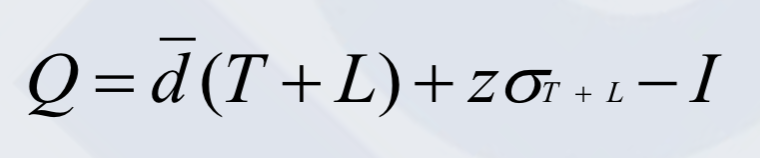EOQ and Fixed Time Period Models
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Inventory management
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Inventory control questions
When to order ?
How much to order ?
When to supply ?
How much to supply ?
Multi period Inventory Models
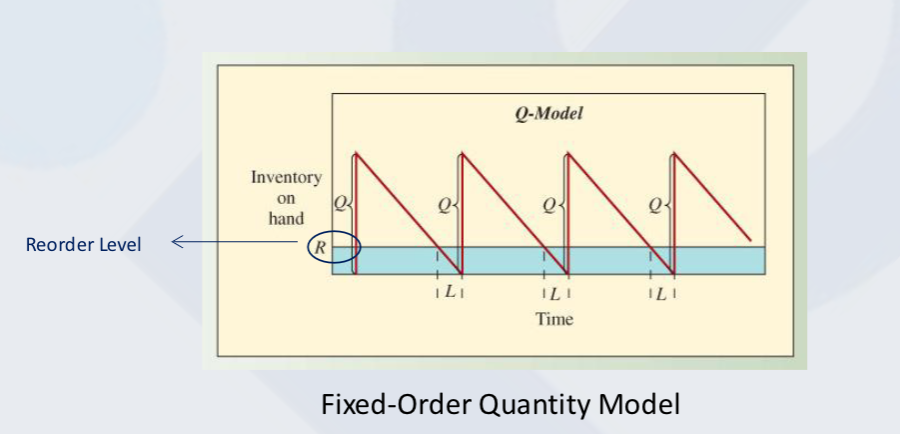
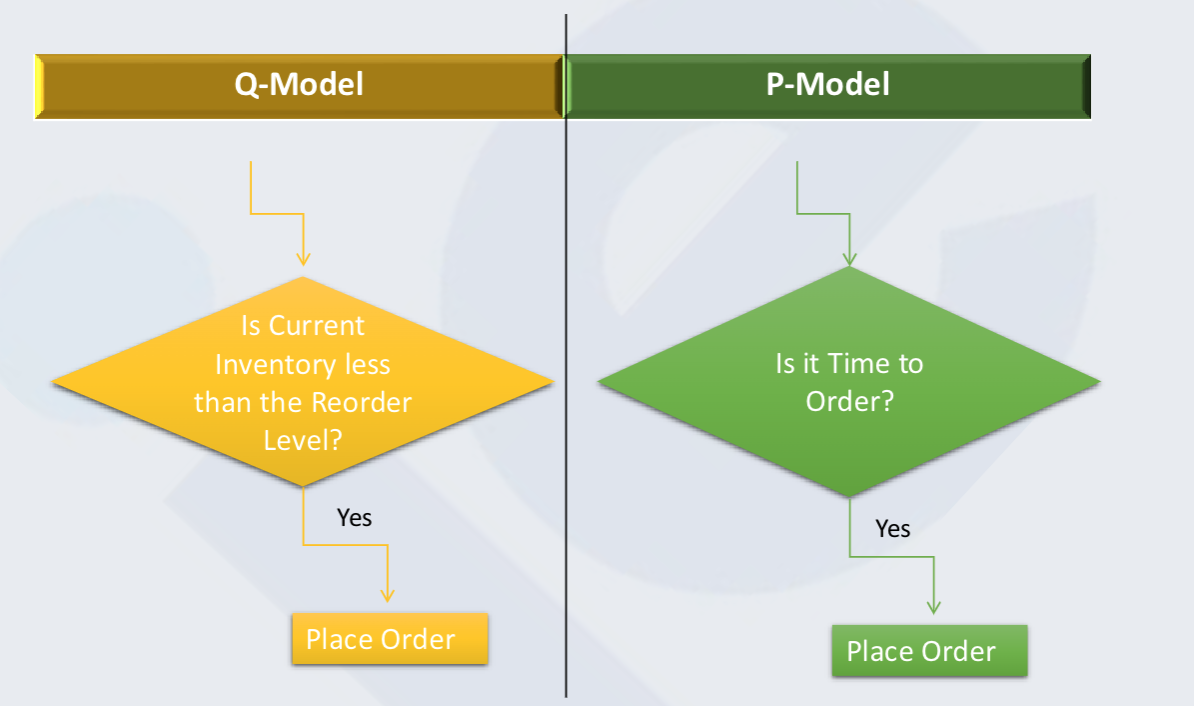
Fixed Order Quantity model (FOQ) - Q model
Place order when inventory reaches a specified level, called Reorder Level
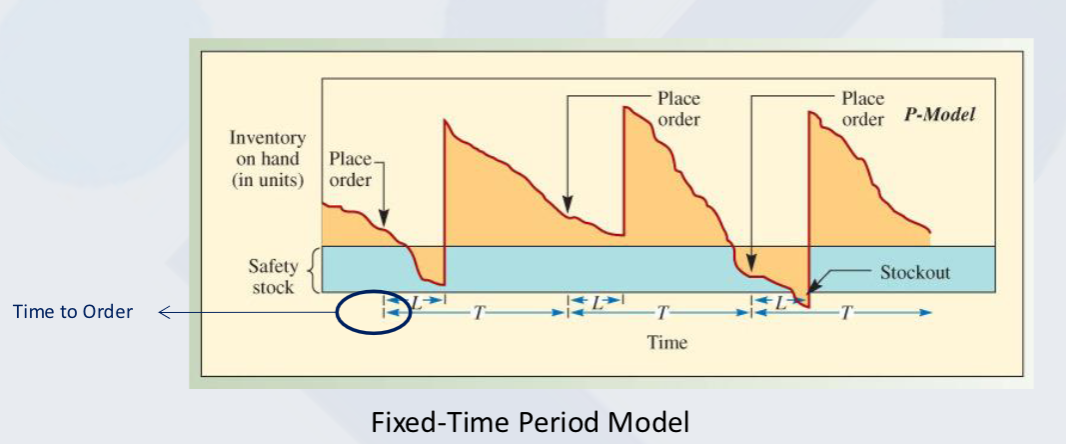
Fixed Time Period Model (FTP) - P model
Place order at the end of a predetermined Time Period
Comparison of Q and P models
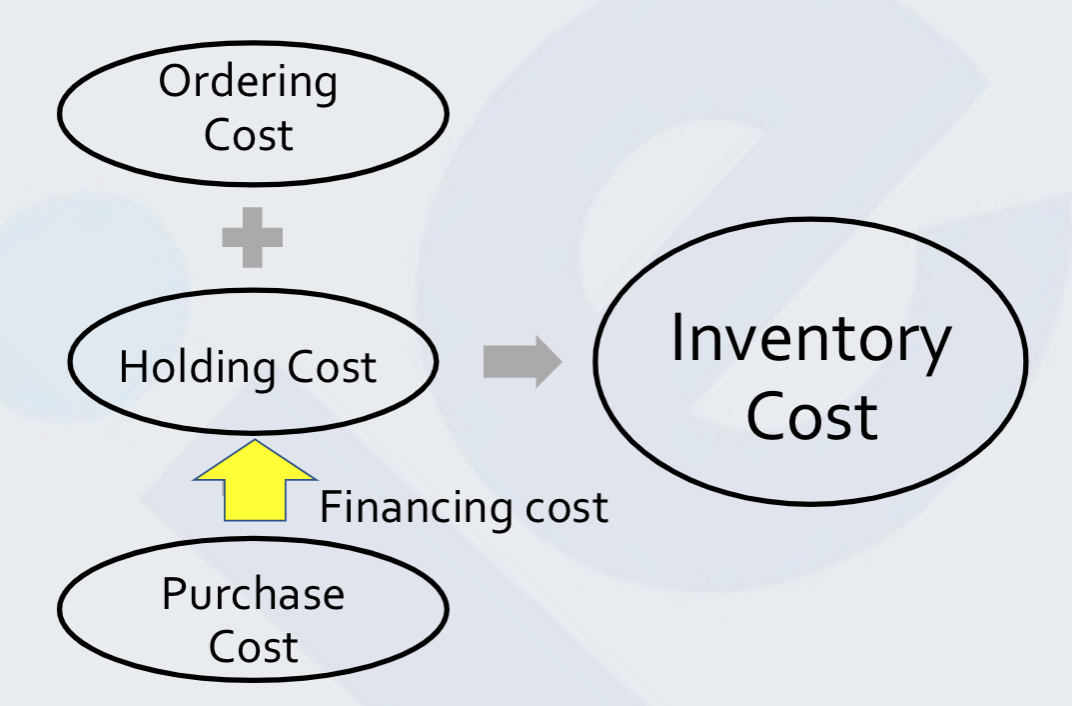
Inventory Cost
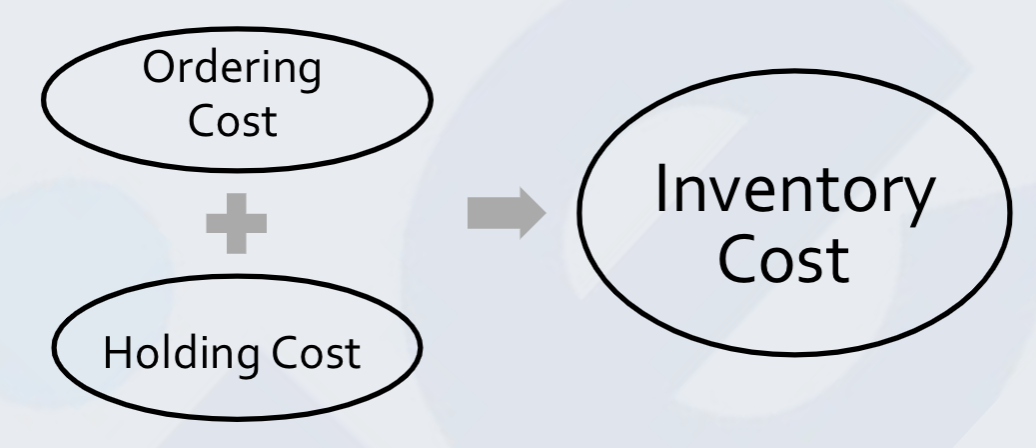
Inventory Cost
Fixed order or Quantity Model (EOQ)
• Purchasing cost is the cost of purchasing inventory. If we assume total
demand is met, then Amount purchased = ?
• Purchasing Cost = ?
• Amount purchased = Demand (D)
• Purchasing Cost = D C
• Holding cost = Purchasing cost Interest rate
Fixed-Order Quantity Model
(D) Annual Demand is 1000 units per year (S) Each Order costs € 10 to place.
(H) Annual Cost to carry inventory is € 2 per unit
(C) Cost per unit is € 12 Assume optimal order quantity is Q.
=> Holding Cost is the annual holding and storage cost per unit of average inventory.
• Average Inventory = ?
• Holding Cost = ?
• Holding Cost is the annual holding and storage cost per unit of average inventory.
• Average Inventory = Q/2
• Holding Cost = Q/2 H
• Ordering Cost is the annual cost incurred in placing orders.
• If annual demand is D and each Order placed is for quantity Q, then # of orders placed annually is = ?
• Order Cost = ?
• Each Order placed is for quantity Q, then # of orders placed annually is = D/Q
• Order Cost = D/Q S
Q model, Assume order quantity is Q
The simplest EOQ model assumes:
Constant and uniform Demand
Constant Cost per unit
Constant Holding Cost
Constant Ordering Cost
Constant Lead time (time between placing order and receiving goods - All demand is satisfied
EOQ model
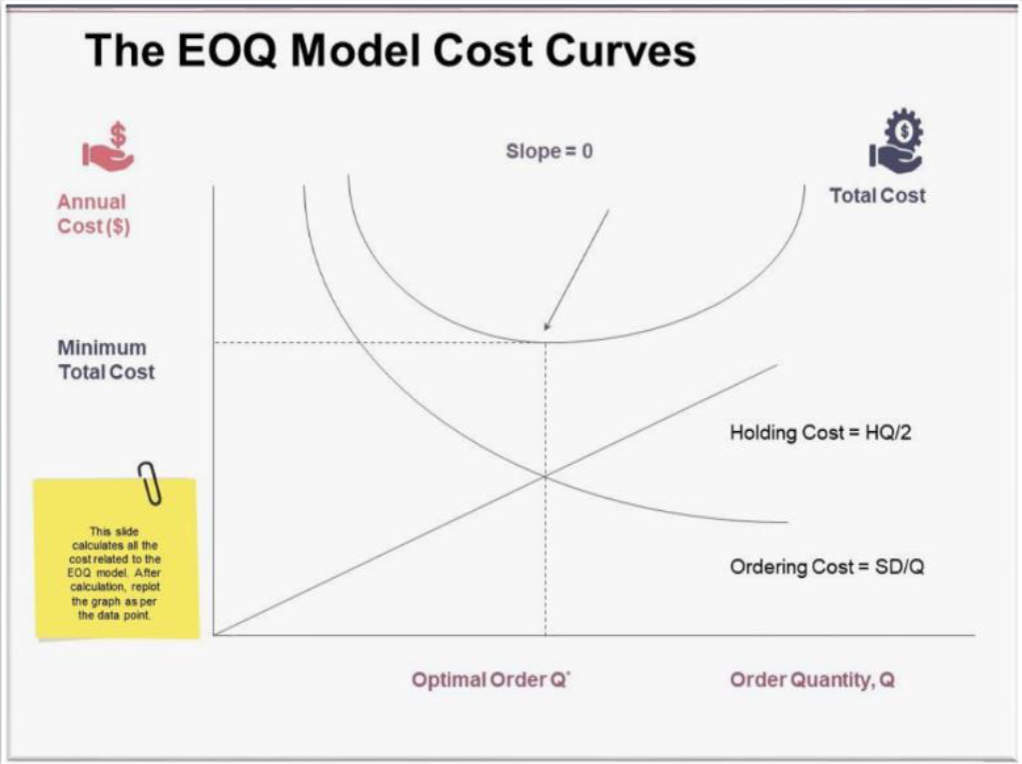
Optimal order quantity
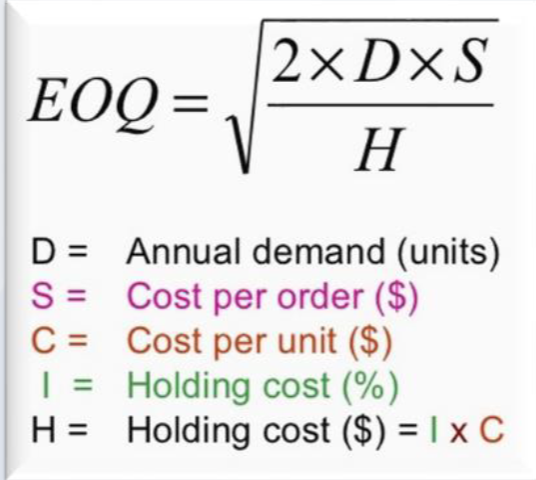
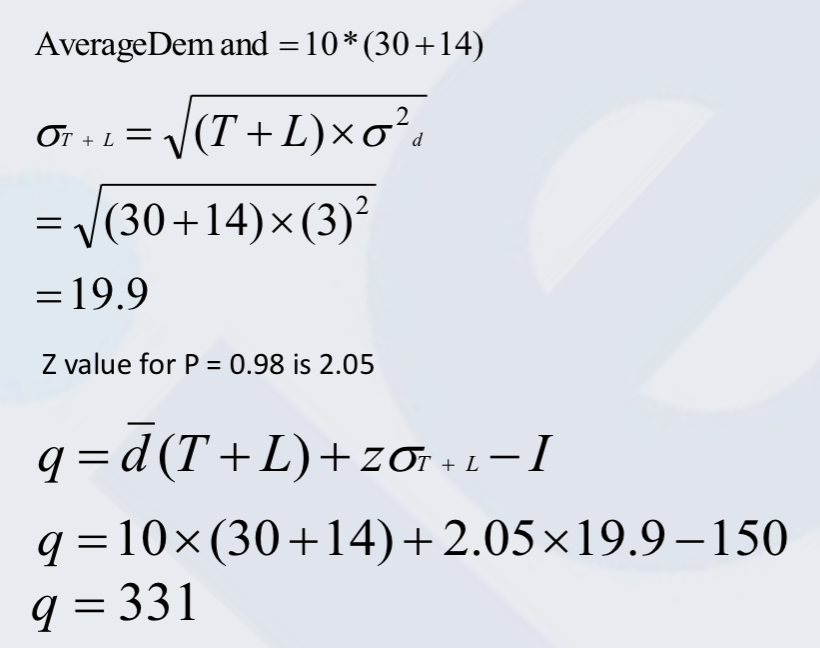
Reorder point calculation

Comparison of Q and p models
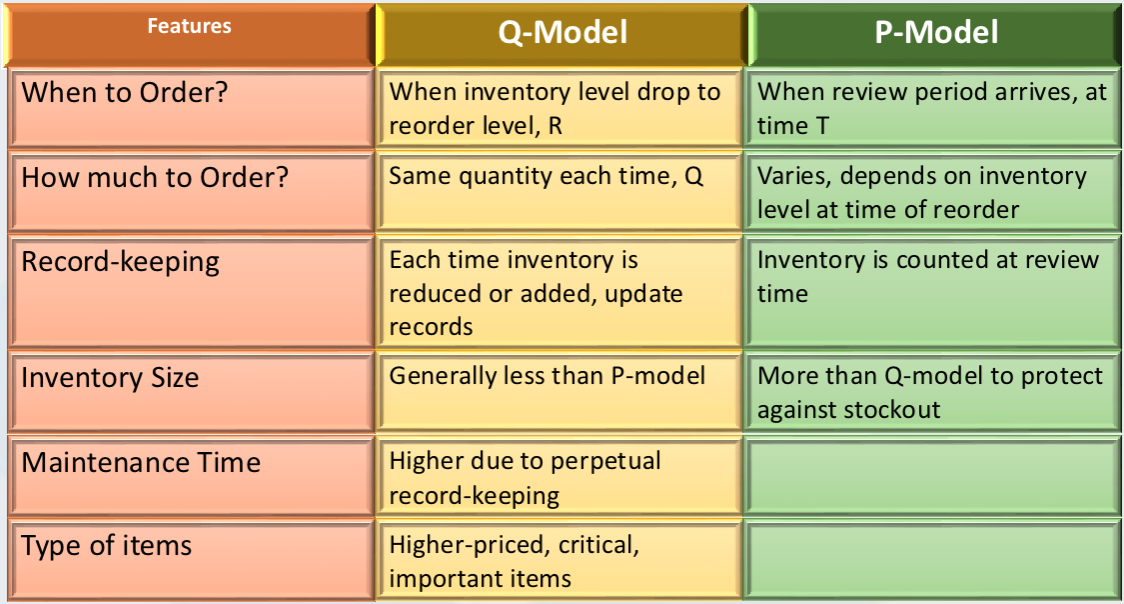
Fixed Time Inventory Model