G23- Management of a patient with acute liver failure
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Define acute liver failure
Acute deterioration in liver function in patient (most often) without underlying chronic liver disease
2-3x elevation of transaminases (marker of liver damage)
fulminant hepatic failure = acute hepatic necrosis= fulminant hepatic necrosis= fulminant hepatitis
Define acute on chronic liver failure
acute deterioration in liver function and extrahepatic organ failures in patients with chronic liver disease with high mortality rate
Define decompensation of cirrhosis
an advanced stage of liver disease where the liver can no longer function properly due to severe scarring, leading to life-threatening complications
What is fulminant liver failure
potentially reversible condition- consequence of severe liver injury
with an onset of encephalopathy within 8 weeks of appearance of the first symptoms and in the absence of pre existing liver disease
What is the treatment of acute liver failure
only transplant
What are teh symptoms of decompensation of liver cirrhosis
ascites
hepatic encephalopathy
renal impairment
GI bleeding
What is the classification of acute liver failure
Based on time between onset of symptoms and development of hepatic encephalopathy
hyperacute- HE within 7 days
acute- 8-28 days
subacute- 5-12 weeks
Define hyperacute liver failure
increased transaminase levels/ severe coagulopathy/ increase in bilirubin which usually precedes clinical encephalopathy
better prognosis with higher incidence of cerebral oedema
acetaminophen toxicity, ischaemic hepatopathy
Define subacute/ subfulminant
milder increase in serum transaminases/ deep jaundice/ mild to moderate coagulopathy + splenomegaly, ascites, shrinking in liver volume
worse prognosis with lower incidence of cerebral oedema, renal failure and portal HT are more frequent
Wilson’s ddisease
What is the etiological factors of ALF
metabolic
Wilsons
Drugs
tylenol, prescription meds, ecstasy, amanita
Viral
HAV, HBV/HDV, Non A E
vascular
Budd Chiari, ischaemia
pregnancy
HELLP, fatty liver
HELLP-syndrome: haemolysis, elevated liver enzymes and low platelet count
autoimmune
infiltrative
lymphoma, melanoma, TB
What are the main hepatotoxic drugs
paracetamol, NSAIDs
amoxicillin- clavulanate, antibiotics
antituberculotics
statins
ketoconazole
antiepileptics
What is the pathomechanism of acute liver failure
injurous agent causes hepatocyte damage directly, or by forming free radicals
→ coagulation activation, cytokine release, DAMP release from hepatocytes
→ systemic inflammation, possible infections
→ organ failures
What are the complications of ALF
CNC disturbances
hepatic encephalopathy, cerebral oedema, seizures
infections
coagulopathy and bleeding
renal failure/ hemodynamic collapse
metabolic derangement
What are the diagnostic steps in ALF
history
clinical signs
PE- liver and spleen
lab- blood + urine
abdominal US/ CT/ MRI
fibroscan, upper GI endoscopy, echocardiography
biopsy
What are important during history taking in ALF
alcohol consumption
family ihstory of liver disease
occupation
sexual contact
muschroom consumption with unknown origin
transfusion
tattoo, piercing
travelling history
meal, food
medication, herbs
What are the symptoms of ALF
jaundice
mental confusion, difficulty concentration, disorientation
RUQ pain
nausea, vomiting
pruritus
fatigue, malaise
melena/ hematemeses
ascites
ankle oedema
muscle tremors
What are the physical findings in ALF
icterus- sclera, mucosa, skin
neurological signs
flepping tremour, consciousness
RUQ tenderness, hepatomegaly, skin bleedings
petechia, purpura, echymosis, suffusion
ascites
hernias
What are the containdications of liver transplant
alcohol consumption and alcohol caused chronic liver disease
recent malignancy
severe cardiovascular problems
What are the laboratory markers in ALF
- hepatic: AST, ALT, GOT
- cholestatic: GGT, ALP
- total blood count, LDH, coagulation
- bilirubin, ammonia, albumin, glucose
- arterial blood gas
- urine toxicology screen
- viral serology
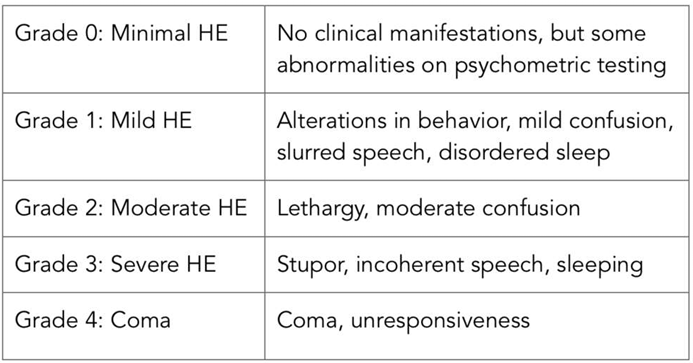
What are the gradings for hepatic encephalopathy
What are the diagnostic criteria of ALF
1. prolongation of INR >1.5
2. any degree of hepatic encephalopathy
3. no prior evidence of liver disease
4. <26 weeks disease course
What can you see on US
hepatomegaly
inhomogeneity
check blood supply- differentiate from Budd CHiari
What are the indications for a liver biopsy
no exact etiology based on lab and imaging tests but
specific treatment or conduct can be decided ( AH, DILI, viral infection, mushroom, Wilsons, malignancy)
to distinguish ALF from chronic liver disease
Transjugular apprach is prefered
What is the differential diagnosis of ALF
acute decompensation of cirrhosis
acute on chronic liver failure
alcoholic hepatitis with underlying cirrhosis
eclampsia/ preeclampsia
What are the teratment modalities of ALF
specific- treat underlying cause
supporttive- independently from underlying etiology
decide whether they need ICU or center with active liver transplantation
What are the specific therapies
Autoimmun hepatitis
glucocorticoids-with careful consideration-infection risk!
Acute hepatitis B
antiviral treatment (NA: entecavir, tenofovir)
Amanita phalloides
gastric aspiration, lavage, activated charcoal, silibinin, penicillin G, Nacetylcystein
Pregnancy-related liver disease
pregnancy interruption
Budd-Chiari syndrome
transjugular intrahepatic shunt placement, surgical decompression, thrombolysis
Acetaminophen intoxication
N-acetylcystein
What is the supportive treatment
haemomdynamic stabilisation
fluid, vasopressors, NE, terlipressin, inotropic drugs
ventilatory support
AKI
renal replacement therapy
uraemia, fluid overload, hyperkalemia, acidosis, sodium imbalance, hyperammonemia
infections
bacteria- pneumonia, UTI, BSI, multiresistant
fungal
routine sampling for cultures, CXR, diagnostic paracentesis
broad spectrum antibiotics
hepatic encephalopathy
lactulose, rifaximin
severe protein restriction must be avoided
nutritional
metabolic abnormalities
acidosis, hypokalaemia, hyponatreaemia, hypophosphatemia, hypoglycemia
coagulation
decreased amount
thromboelastography- evaluates coagulation phenotype
give necessary haemoderivatives
intracranial HT
invasive monitoring- intraparenchymal microtransucers
non invasive- transcranial doppler
serum sodium must be monitored, mannitol
extreacorporal support
MARS- molecular absorbent recirculation system- albumin dialysis
What are bad prognostic factors for liver transplantation
>50
requirement of life support
BMI >30
serum creatinin >2mg/dl
other- reduced organ size, donor age >60, incompatible ABO group, donor liver steatosis
What are the kings college criterias for paracetamol induced ALF
arterial pH <7.3 after fluid resusucitation, >24 h since ingestion
or
lactate > 3 mmol/l
or
the 3 following criteria:
HE grade>3
serum creatinine >300 umol/l
INR>6.5
What is the Kings college criteria for non paracetamol induced ALF
INR>6,5
or-3 out of the 5 following criteria:
aetiology: „indeterminate”, drug induced
age <10 years or >40 years
icterus HE interval >7 days
bilirubin >300 umol/l
INR>3.5