AP Macro Unit 3, Topic's; 3.1 & 3.2
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
SRAS
short-run aggregate supply
LRAS
Long run aggregate supply
AD
aggregate demand
aggregate
total
real gdp= _______ = ________ = _________
real gdp= aggregate output=aggregate spending=aggregate omcp,e
aggregate output
the economy's total production of goods and services for a given time period
aggregate spending
the total spending on domestically produced final goods and services in the economy (C, I , G, Xn)
aggregate income
wages + rent + income + profit
what does the horizontal axis measure on an AD/AS model?
it measures changes in aggregate output, that tells us what's happening in aggregate spending and income, and the unemployment rate
what is the aggregate price level a measure of
inflation, it is based on the gdp deflator, not an inflation rate
Aggregate Demand
the demand for all goods and services purchased in product markets
what does a downward slopping AD curve represet
the inverse relationship between aggregate price level and the quantity of aggregate output demanded
When the aggregate price level falls, the quantity of aggregate output demanded _______
rises
When aggregate price levels rise, the quantity of aggregate output demanded _______
falls
an increase in the price levels causes ____________________
movement up and to the left of an AD curve
a change in quantity demanded is....
a movement along a given demand curve and is only causes in a change in price
real wealth effect
a change in the price level causes the purchasing power of a given amount of wealth to change
when the price level rises, the purchasing power of a given amount of wealth __________
decreases
interest rate effect
occurs when a change in the price level leads to a change in interest rates and, therefore, in the quantity of aggregate demand
interest rate
the price of money is that interest rate
exchange rate effect
a lower price level causes the real exchange rate to depreciate, which stimulates spending on net exports
what are the determinates of consumption
wealth, income, income tax, expectations
when consumers have more wealth consumption __________
increases
when income taxes decrease consumption __________
increases
When consumers expect the economic conditions to prove consumption ________
increases
there is a __________ relationship between AD and tax
inverse
________ relationship spending between gov. spending and AD
positive
exports and ad have a ________ relationship
positive
imports and ad have a ________ relationship
inverse
autonomous
independent
expenditure
the spending of something
autonomous spending
the spending, which is independent of income
Disposable Income (DI)
gross income- income tax
what can you do with disposable income
you can either save or consume
multiplier effect
an inital change in spending will see of a spending chain that is magnifiied in the economy
Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC)
the fraction of extra income that households consume rather than save, exp: if MPC=0.8 and income rises to $100, C rises $80
what is the equation for mpc
change in consumption/change in income
what is the marginal propensity to save (MPS)
how much people save rather than consume when there is a change in come, also always expressed as a fraction
what is the equation for MPS
change in savings/change in income
is it always true that "mpc+mps=1"
yes
what are the equations for the spending multiplier
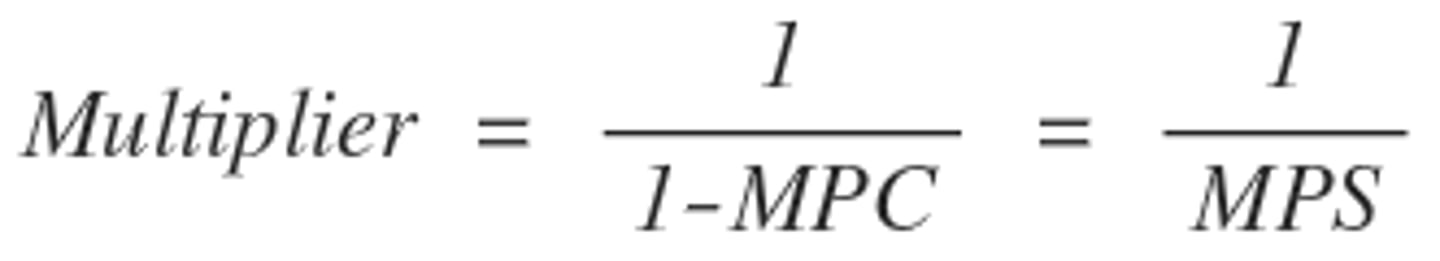
what is the equation for the total change in GDP
multiplier x initial change in spending
as output falls, unemployment __________
rises
if the price level increases inflation, then real gdp demanded _______
falls
if the price level decreases (delfation), then real gdp demanded _______
increase
what doesn't shift the AD curve
changes in price shifts only QD, changes in price level causes a slide against the curve
an increase in spending shifts AD ______
right
a decrease in spending shifts AD _____
left
shifters of aggregate demand: change in consumer spending
increase/decrease of disposable income, consumer expectations (if ppl fear a recession they will spend less), taxes (decrease in income taxes causes people to spend more)
shifters of aggregate demand: changes in investment spending
real interest rate (price of borrowing money), expectations, productivity and tech, business taxes
shifters of aggregate demand: changes in gov spending
gov expenditures (decrease in detense? spending) (increase in public work programs)
shifters of aggregate demand: changes in net exports
exchange rates (if the us dollar appreciates relative to the euro), national income compares to abroad
AD=.....
AD=GDP=C+i+G+Xn