ARH 252 Exam 1
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
1
New cards
Paleolithic
Old Stone Age lasting from 50000 BC to 9000 BC; when primitive stone tools were used; nomadic lifestyle
2
New cards
Neolithic
New Stone Age lasting from 8000 BC to 2300 BC depending on the area; when ground or polished stone tools were used; agricultural revolution when civilizations began to develop
3
New cards
Mural Painting (Cave Paintings)
oldest is the Wild Pig dating back to 45000 BC
4
New cards
Sculpture in the Round
3-D sculptures that were not part of a cave or rock formation
5
New cards
Megaliths (Megalithic)
large stones used to create a structure or monument (stonehenge)
6
New cards
Agricultural Revolution
plants and animals were domesticated and nomadic groups began to stay in one place
7
New cards
Corbel Vault
a vault formed by piling stone blocks in horizontal courses, cantilevered inward until the two walls meet in an arch
8
New cards
Post-and-Lintel Construction
a system of construction in which two vertical posts support a horizontal lintel
9
New cards
Henge
Stonehenge in Salisbury Plain, England, ca. 2550-1600 BC
10
New cards
Twisted Perspective
when a profile of an animal or human is shown while another portion of the same object is shown frontally
11
New cards
Composite Creature
a figure with an animal head on a human body
12
New cards
Mesopotamia/Fertile Crescent
an area that gave rise to some of the worlds first civilization; the fertile soil found near rivers allowed for farming and trade routes
13
New cards
Sumer
3500-2332 BC; an handful of independent city-states
14
New cards
Ziggurat
pyramidal stepped temple
15
New cards
Cuneiform
Sumer’s language that started as pictographs; considered the oldest written language
16
New cards
Lamassu
an Assyrian deity in the from of a winged, human-headed bull or lion; 720-705 BC
17
New cards
High Relief/ Low Relief
carved deep into the material/carved shallow into the material
18
New cards
Relief Sculpture
projects from a 2-D background (connected to what it was carved out of)
19
New cards
Hierarchy of Scale
whoever is the largest is the most important
20
New cards
Register
a horizontal level in a work that consists of several levels arranged above each other
21
New cards
Votive Statues
used in rituals to appease the gods
22
New cards
Ishtar Gate
one of the gateways into Babylon, Iraq, ca. 575 BC
23
New cards
Stele of Hammurabi
the laws of King Hammurabi of Babylon
24
New cards
Persepolis
Gate of All Nations or Gate of Xerxes at Persepolis, separated people based on their social status
25
New cards
Hollow-Cast Bronze Method (Lost Wax)
an ancient method used to make sculptures that were transportable and not too heavy
26
New cards
Predynastic and Early Dynastic Period
3500-2575 BC
27
New cards
Old Kingdom; New Kingdom
2575-2134 BC;1550-1070 BC
28
New cards
Amarna Period; First Millennium BCE
1000-30 BC
29
New cards
Column
column fluting
30
New cards
The sun god Ra (Ben-Ben)
a falcon headed god that ancient Egyptians worshipped; Ben-Ben is a pyramid associated with Ra who was also often depicted as a pyramid
31
New cards
Great Pyramids of Giza
great pyramids were built as burial sites for Egypt’s Pharaohs
32
New cards
Funerary Statue
held Ka (soul/spirit)
33
New cards
Canon of Proportions
a set of ideal, mathematical relationships in art
34
New cards
Hatshepsut
first female pharaoh
35
New cards
Akhenaton and Nefertiti
Akhenaton abandoned the worship of the Egyptian gods in Favor of Aton; Nefertiti was his chief wife and she took over after his death before his son was old enough to lead
36
New cards
Tutankhamen
the only pharaoh’s tomb we have found fully intact
37
New cards
Ptolemaic dynasty
Ptolemy (one of Alexander the Great’s generals) takes over Egypt after his death and him and his descendants rule until 30 BC when the Romans take over
38
New cards
Mastaba
ancient Egyptian tomb with sloping sides and a flat roof
39
New cards
Imhotep
first recorded artist, and creator of the Great Pyramids
40
New cards
Engaged Columns
a column that is built into a wall, serving as decoration
41
New cards
Mortuary Temple and Complex
where a pharaoh would be buried and monuments to their success would be placed
42
New cards
Sphinx
with the pyramid of Khafre, possibly associated with the Egyptian god Ra; there was a cult of the sphinx, but it was a secret society leaving little information behind
43
New cards
Rock-Cut Tomb
a tomb cut into an existing, naturally occurring rock formation
44
New cards
Ka
the life force or spirit of a person
45
New cards
Pylon Temple
a monumental tower/gate of an Egyptian temple
46
New cards
Hypostyle Hall
interior space where the roof rests on pillars or columns
47
New cards
Clerestory
a top row of windows or openings that let in light and air right where the roof is
48
New cards
Obelisk
tall rectangles topped with a pyramid, typically in pairs in front of temples; many are now in Rome
49
New cards
Book of the Dead
an ancient Egyptian book made to help the dead on their journey to the afterlife
50
New cards
Weighing of the Heart Ceremony
if the heart of the deceased weighed more than a feather then they would go with Amit (hell) if it weighed less then they got to go to the goof place
51
New cards
Akkad
2332-2150 BC; first Mesopotamian rulers to call themselves Kings
52
New cards
Babylonia; Neo-Sumerian
2150-1600 BC
53
New cards
Assyria; Neo-Babylonian
900-539 BC; Assyria conquered the majority of Mesopotamia and was heavily military based
54
New cards
Persia
559-330 BC
55
New cards
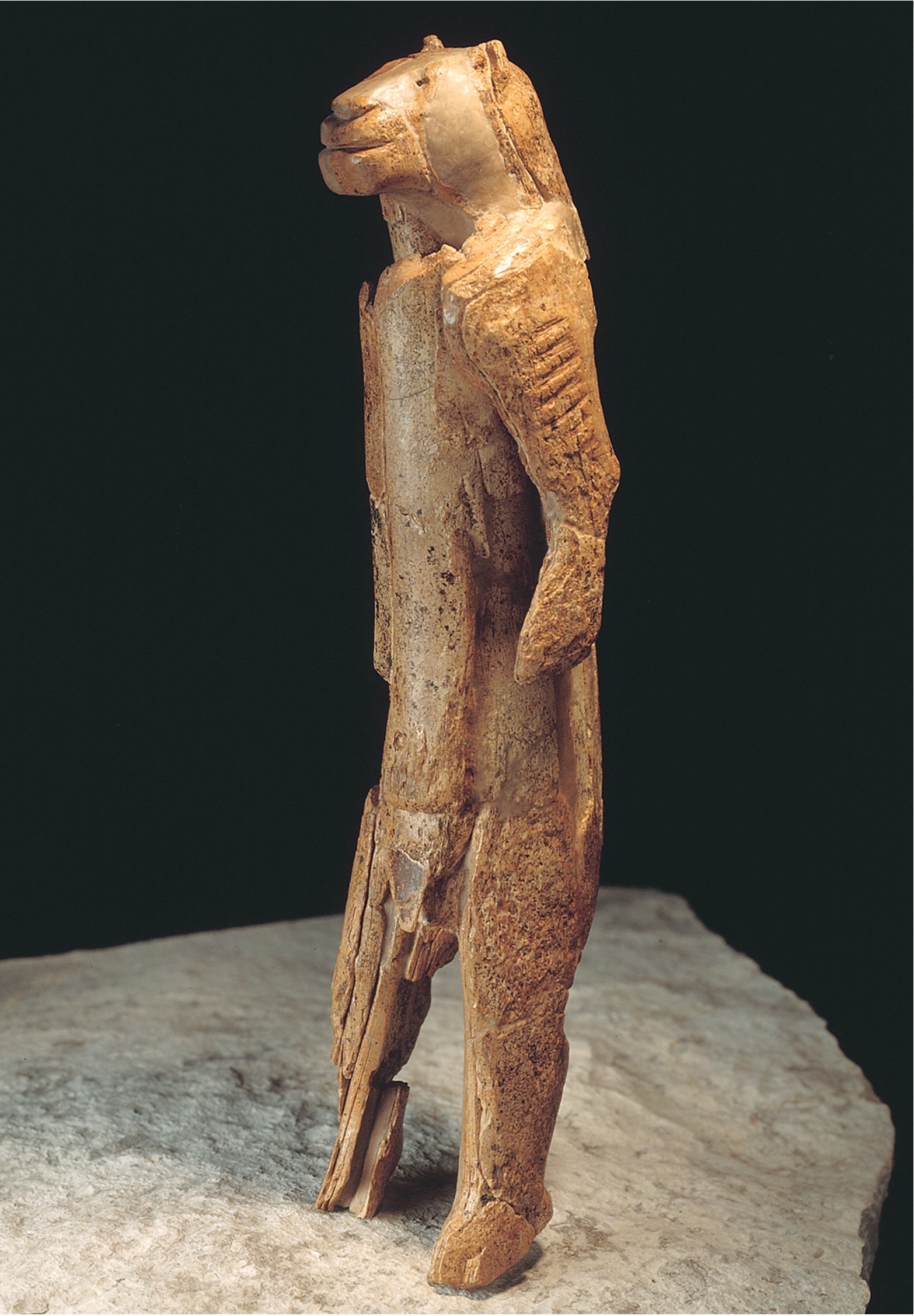

\
**Human with feline head**, from **Hohlenstein-Stadel, Germany**, ca. 40,000–28,000 BCE. Mammoth ivory, **(Paleolithic)**
56
New cards

**Nude woman** (*Venus of Willendorf*), from **Willendorf, Austria**, ca. 28,000–25,000 BCE. Limestone, **(Paleolithic)**
57
New cards
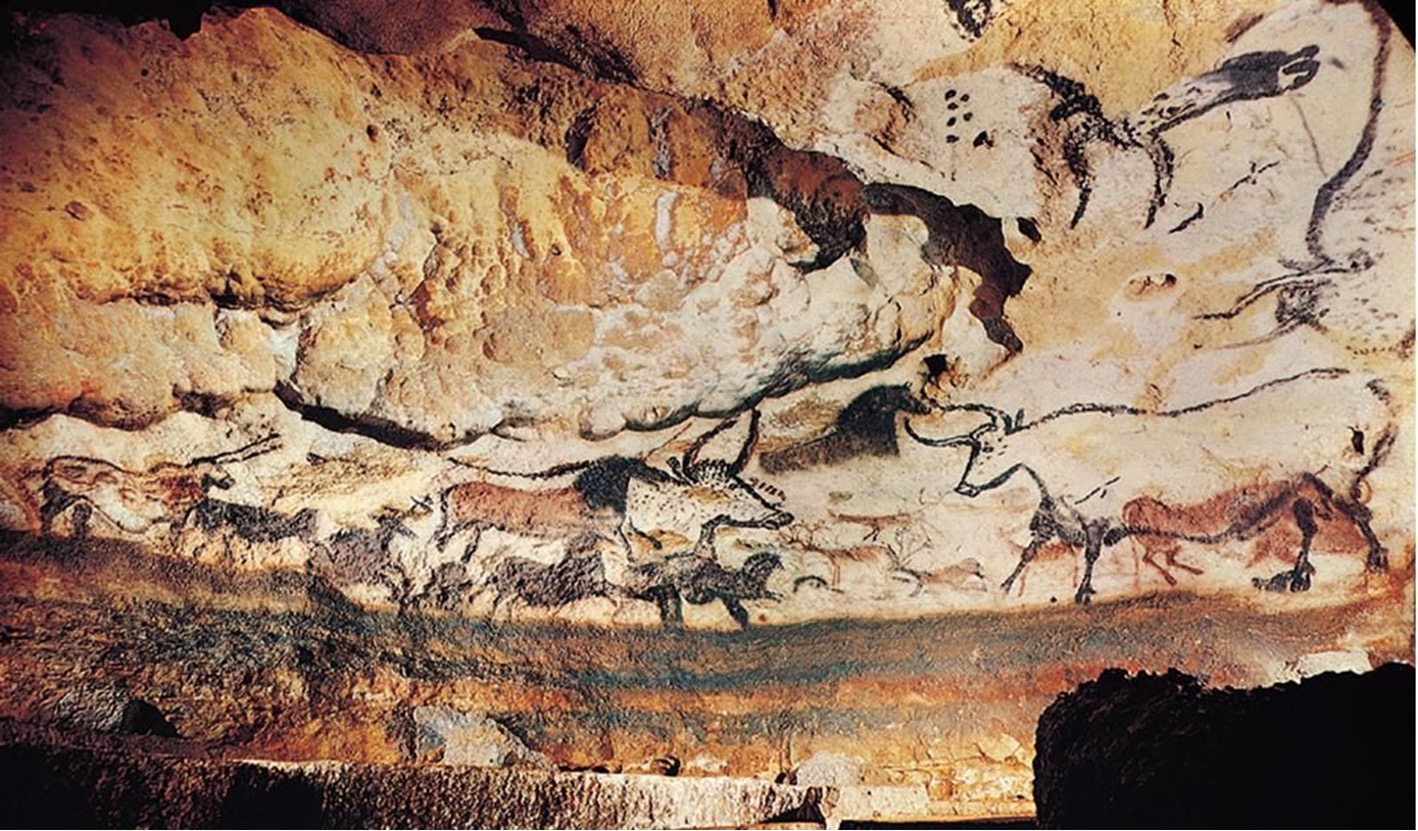

**The Hall of the Bulls** in the cave at **Lascaux, France**, c. 16,000-14,000 BCE. **(Paleolithic)**
58
New cards
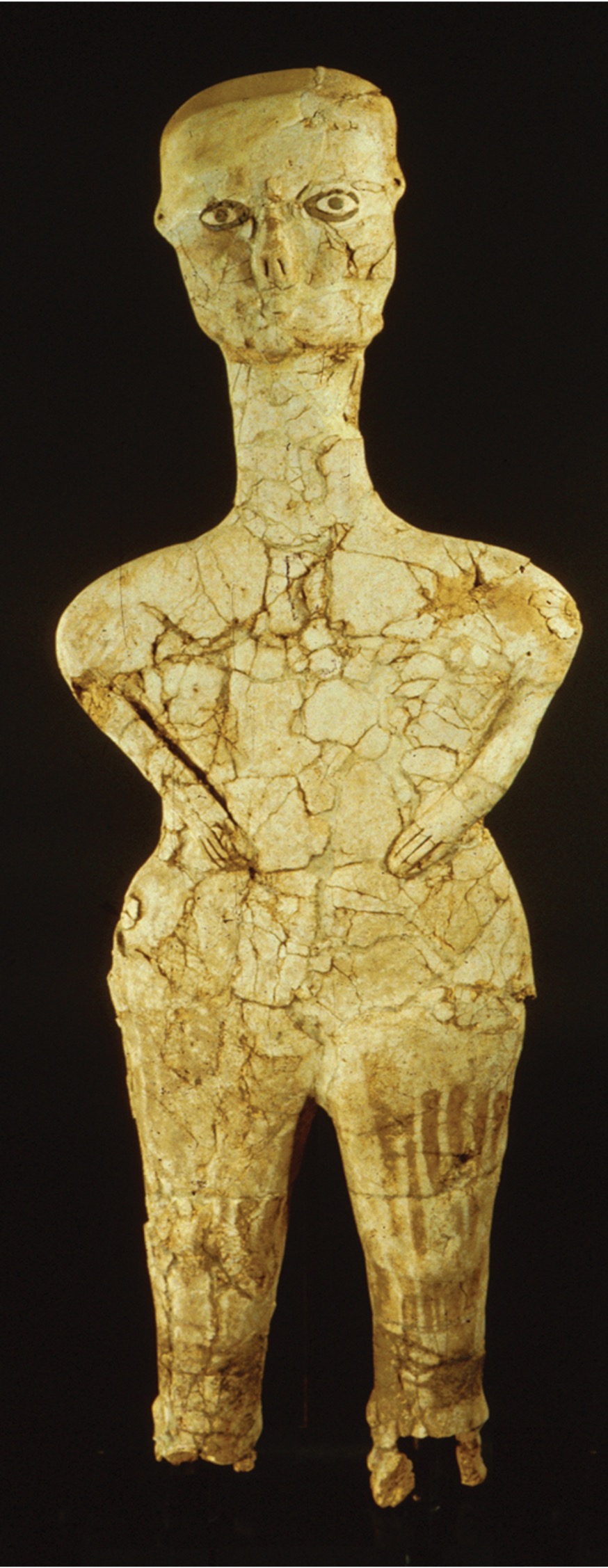
**Human figure**, from **Ain Ghazal, Jordan**, ca. 6750–6250 BCE. Plaster, painted and inlaid with bitumen, **(Neolithic)**
59
New cards
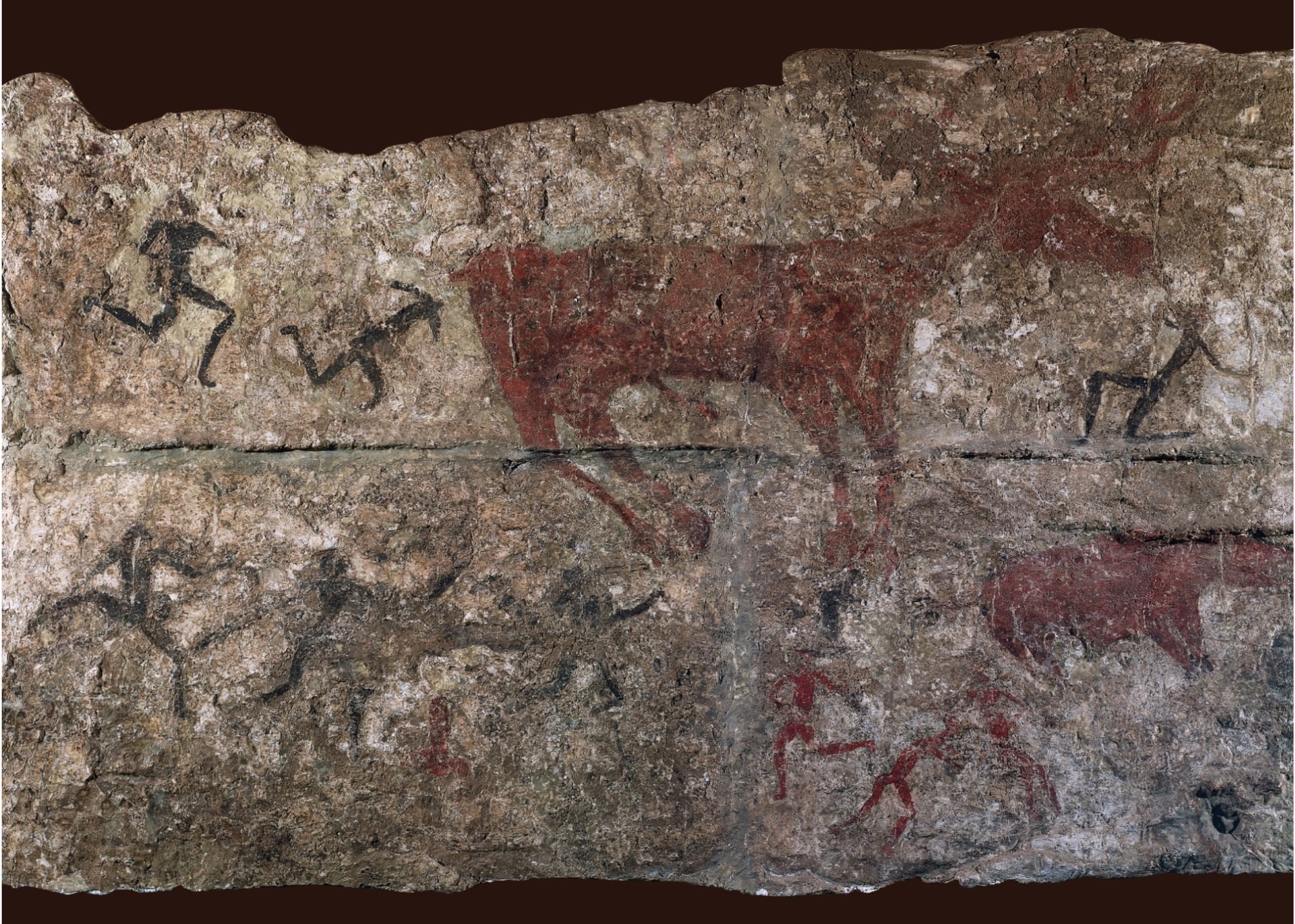

**Deer hunt,** detail of a wall painting from Level III, **Çatal Höyük, Turkey,** ca. 5750 BCE. **(Neolithic)**
60
New cards
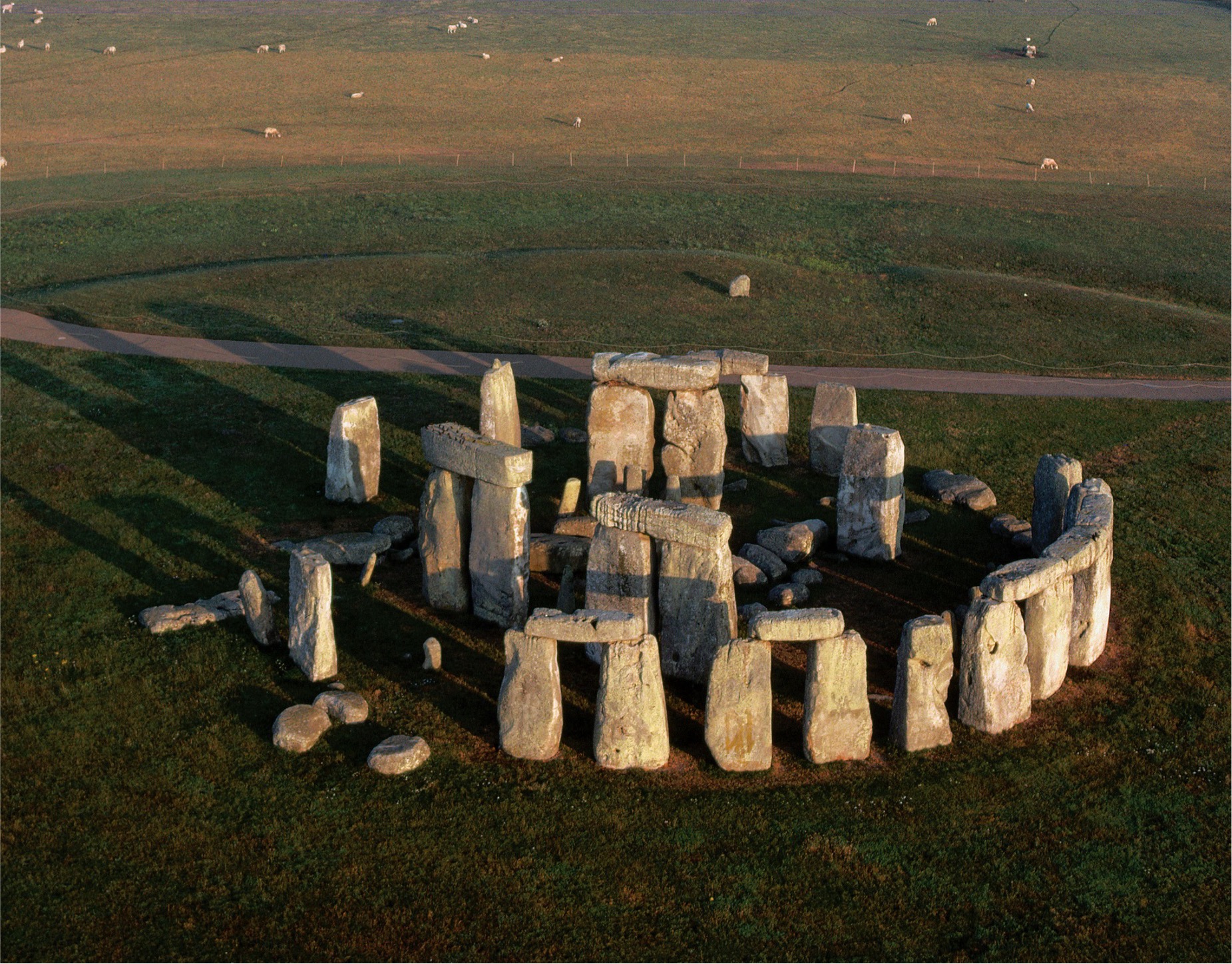

**Stonehenge**, **Salisbury Plain, England**, ca. 2550–1600 BCE. **(Neolithic)**
61
New cards
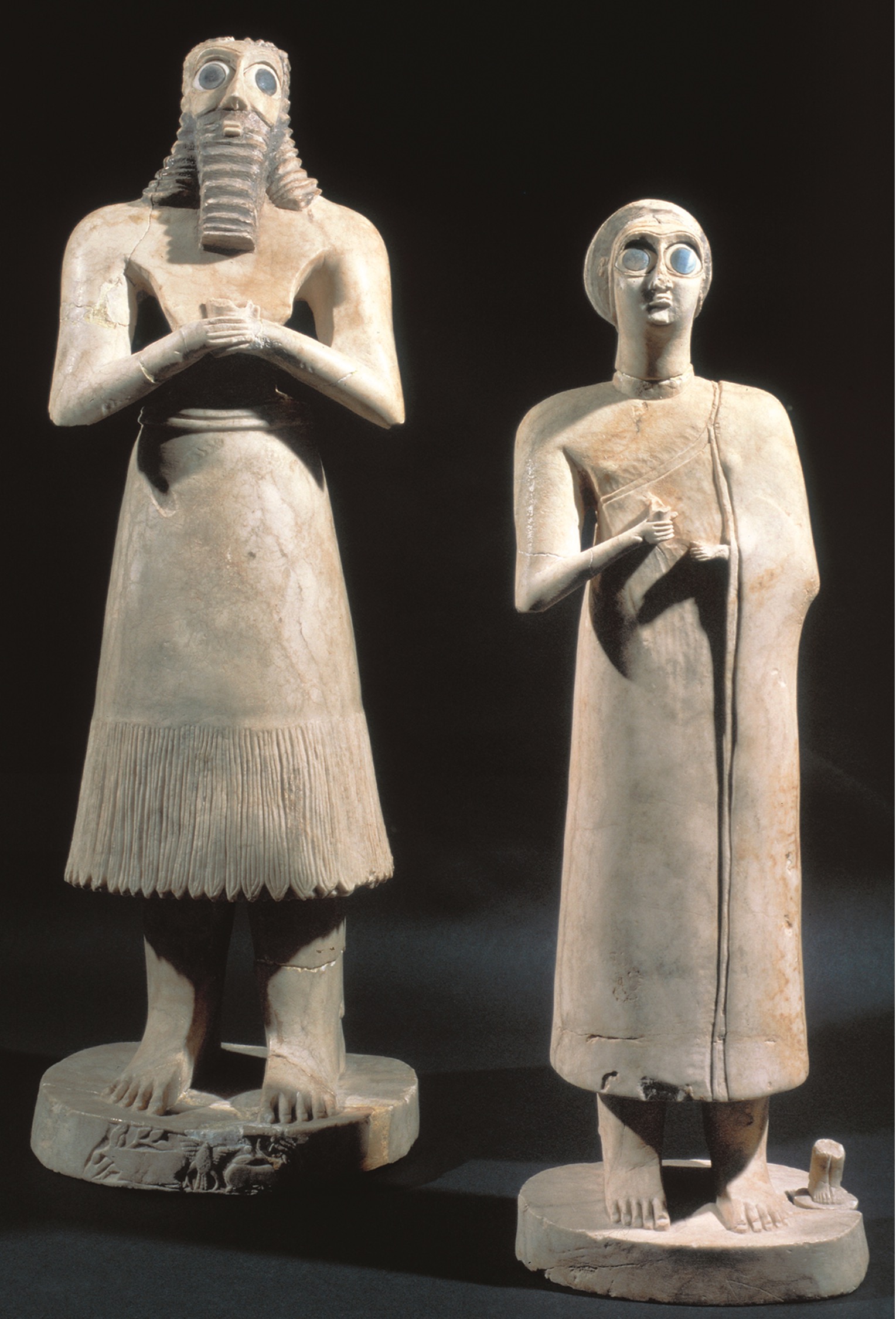

**Statuettes of two worshipers**, from the Square Temple at **Eshnunna, Iraq**, ca. 2700 BCE. Gypsum inlaid with shell and black limestone, **(Sumerian)**
62
New cards
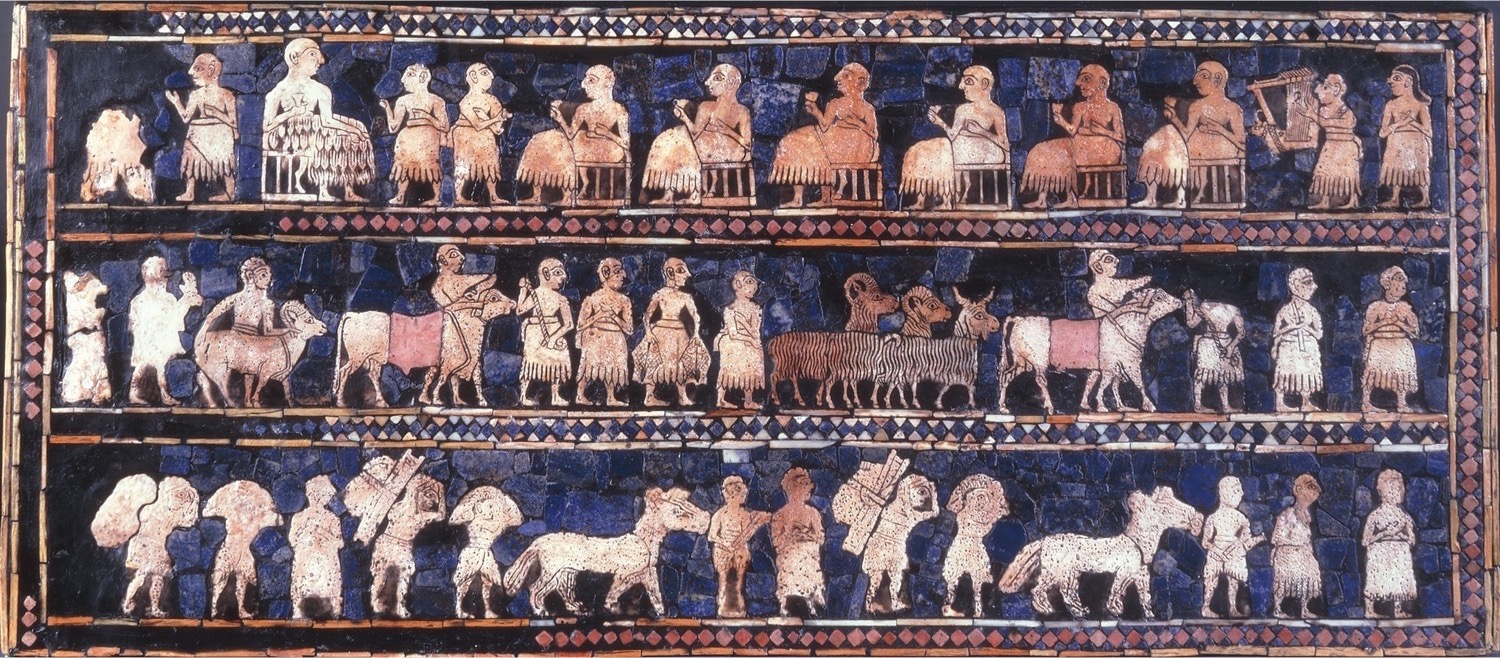

**Peace side of the** ***Standard of Ur***, Royal Cemetery, **Ur, Iraq,** ca. 2600 BCE. Wood inlaid with shell, lapis lazuli, and red limestone set into bitumen, 7’ 7/8” x 1’ 6 1/2”. **(Sumerian)**
63
New cards

**Victory stele of Naram-Sin**, from **Susa, Iran**, 2254–2218 BCE. Pink sandstone, 6’ 7” high. Louvre, Paris. **(Akkadian)**
64
New cards
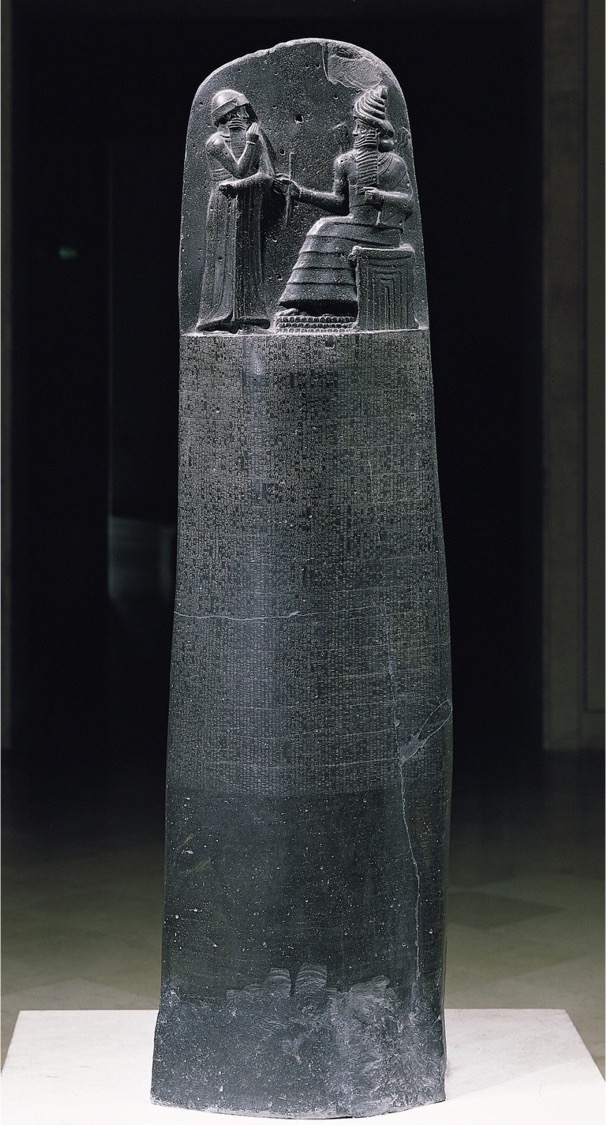

**Stele with law code of Hammurabi**, from **Susa, Iran**, ca. 1780 BCE. Basalt, 7’ 4” high. Louvre, Paris. **(Babylon)**
65
New cards
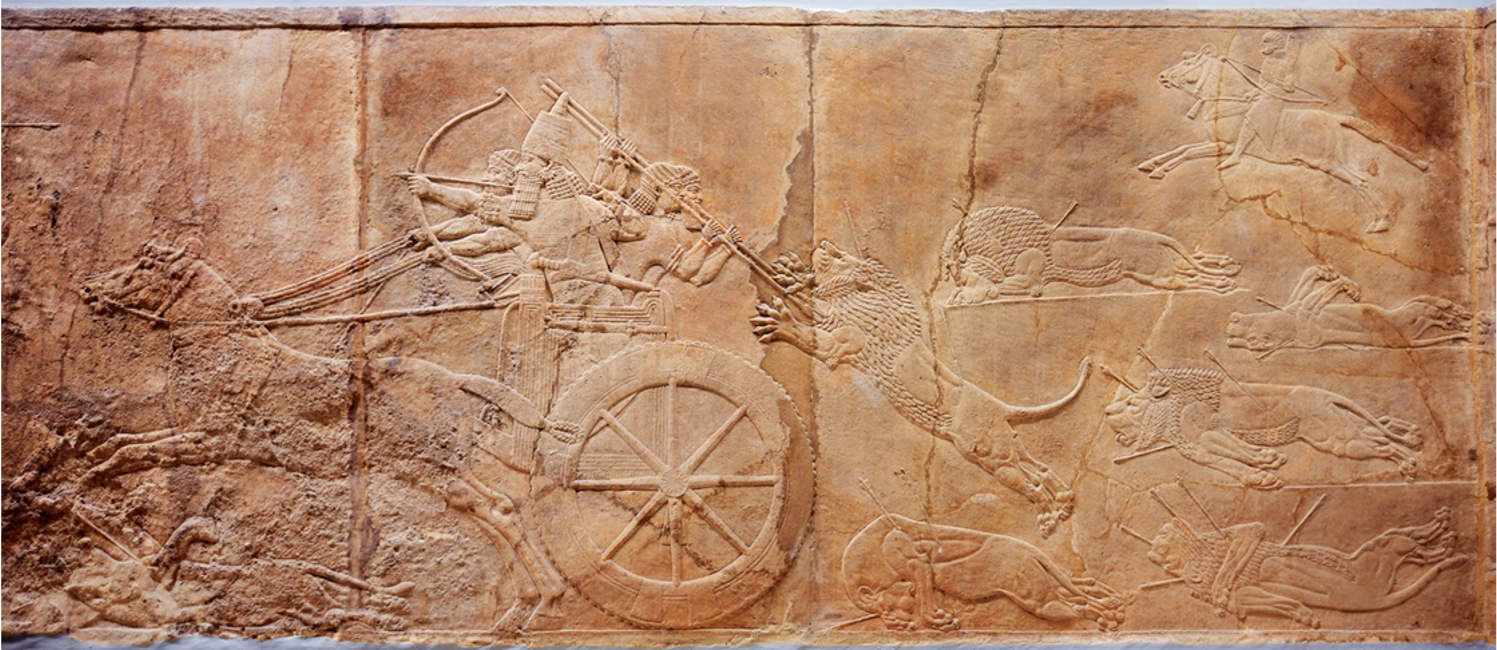

**Ashurbanipal hunting lions**, relief from the north palace of Ashurbanipal, **Nineveh, Iraq**, ca. 645–635 bce. Gypsum, 5' 4" high. British Museum, London. **(Assyrian)**
66
New cards
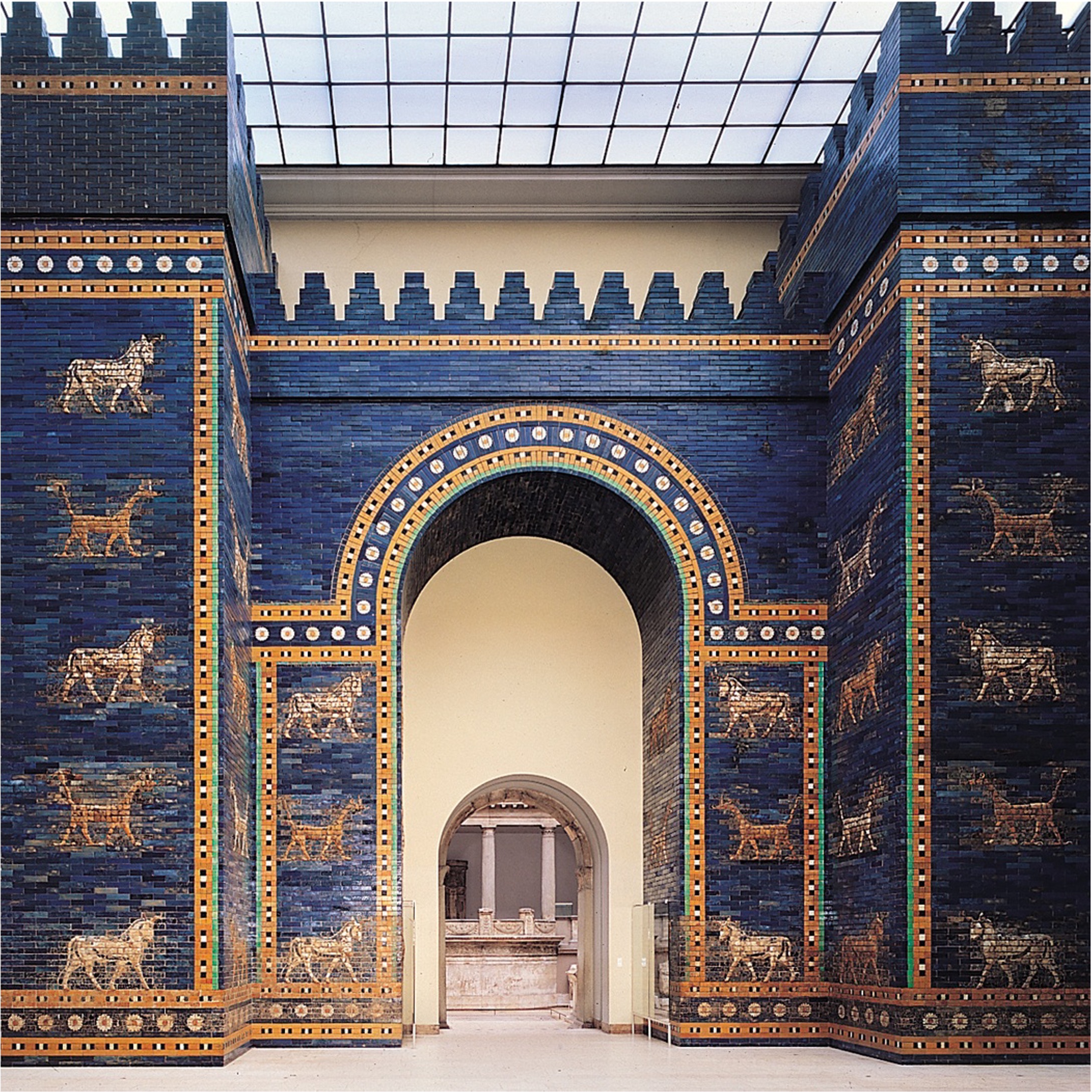

**Ishtar Gate, Babylon, Iraq**, ca. 575 BCE. (**Neo-Babylonian)**
67
New cards
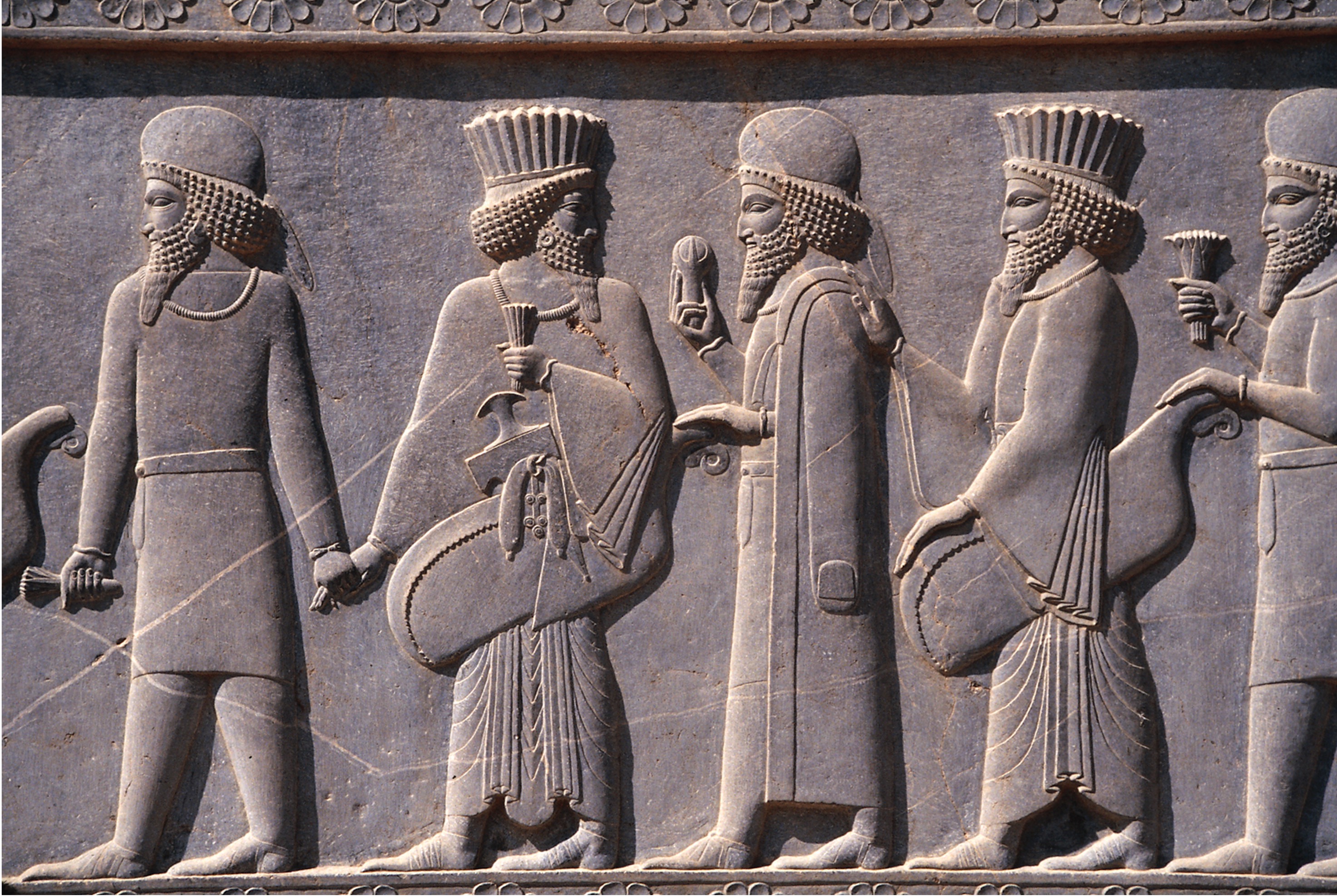

**Persians and Medes, Processional frieze** on the terrace of the apadana, **Persepolis, Iran**, ca. 521–465 BCE. Limestone, (**Persian**)
68
New cards
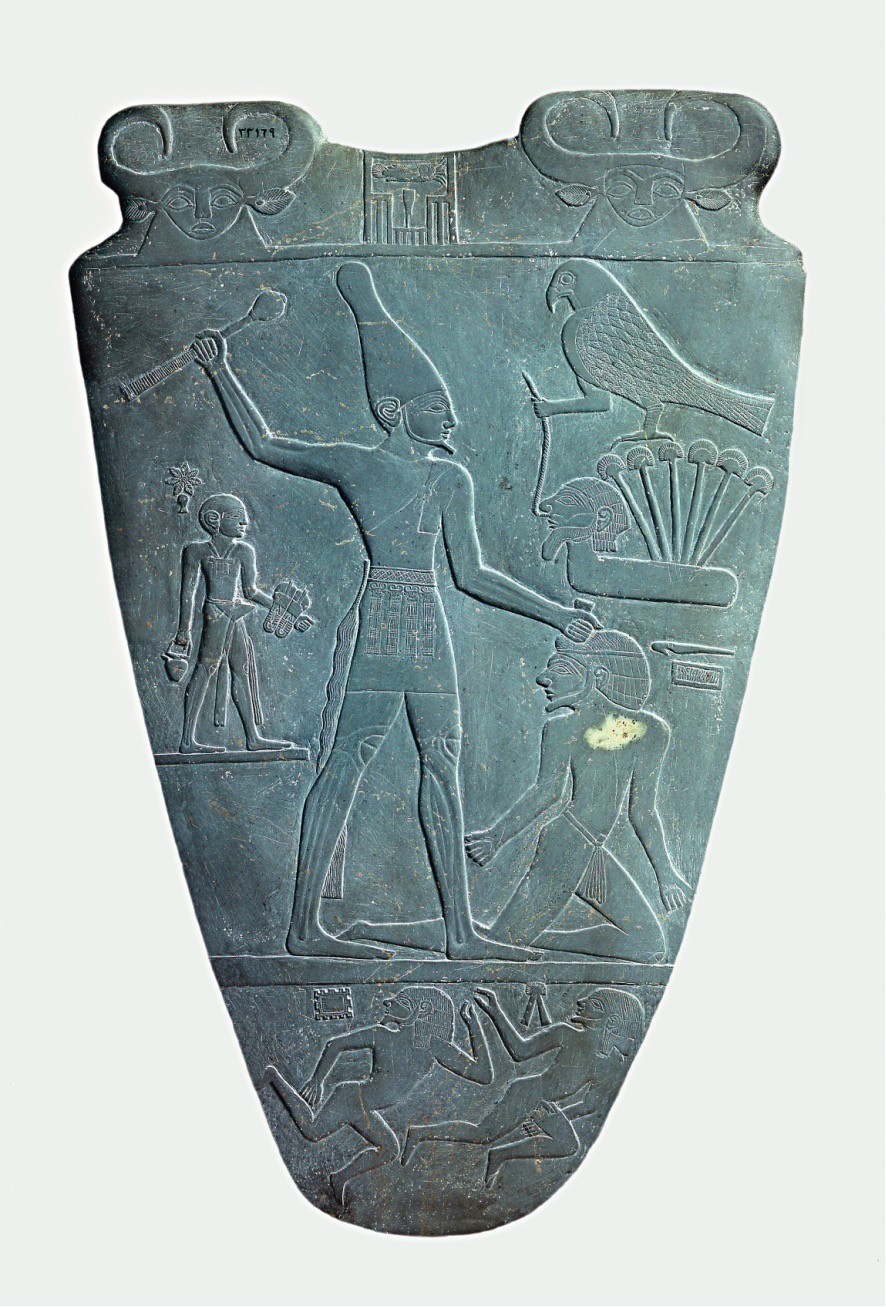

**Palette of King Narmer*****,*** **from Hierakonpolis, Egypt,** ca. 3000–2920 BCE. Slate, (**Predynastic)**
69
New cards
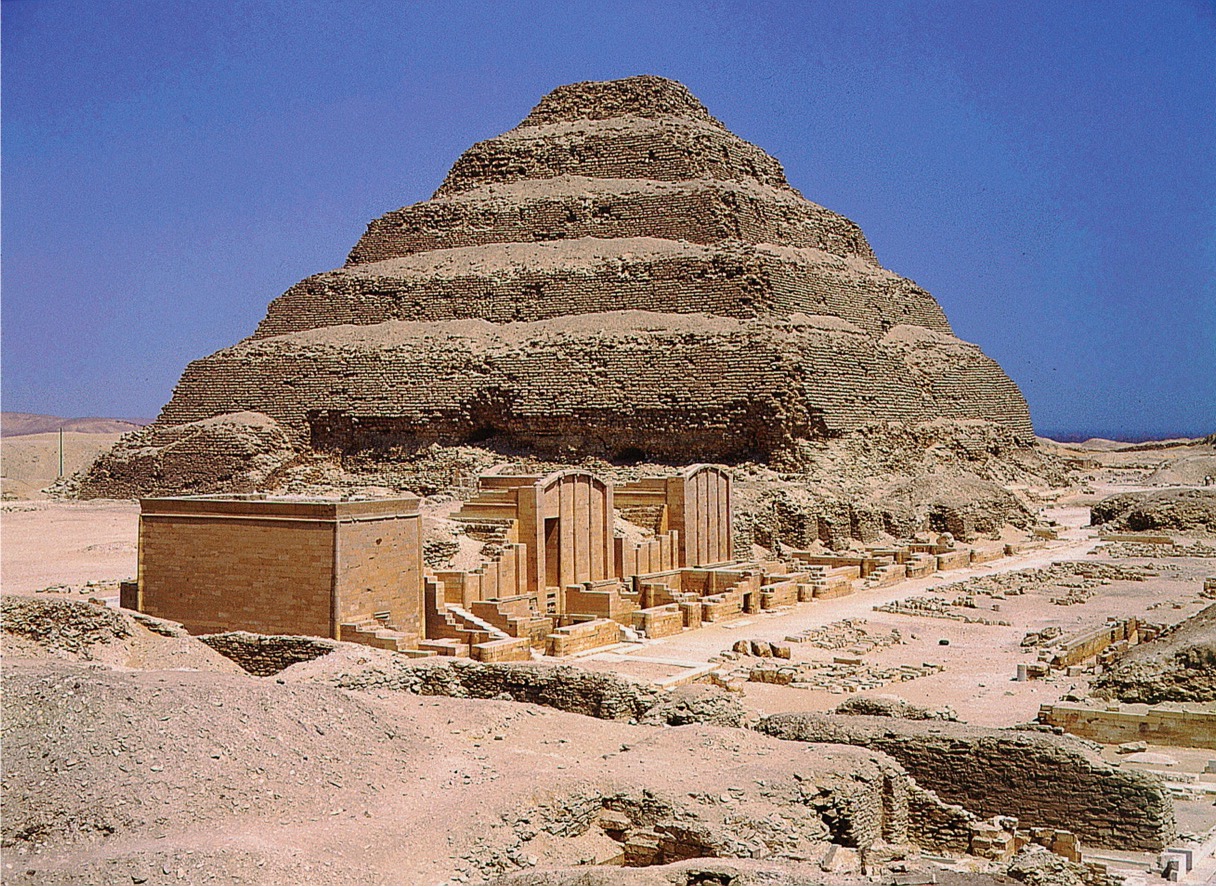

**Imhotep, Stepped Pyramid of Djoser, Saqqara, Egypt**, Third Dynasty, ca. 2630–2611 BCE. **(Early Dynasties)**
70
New cards
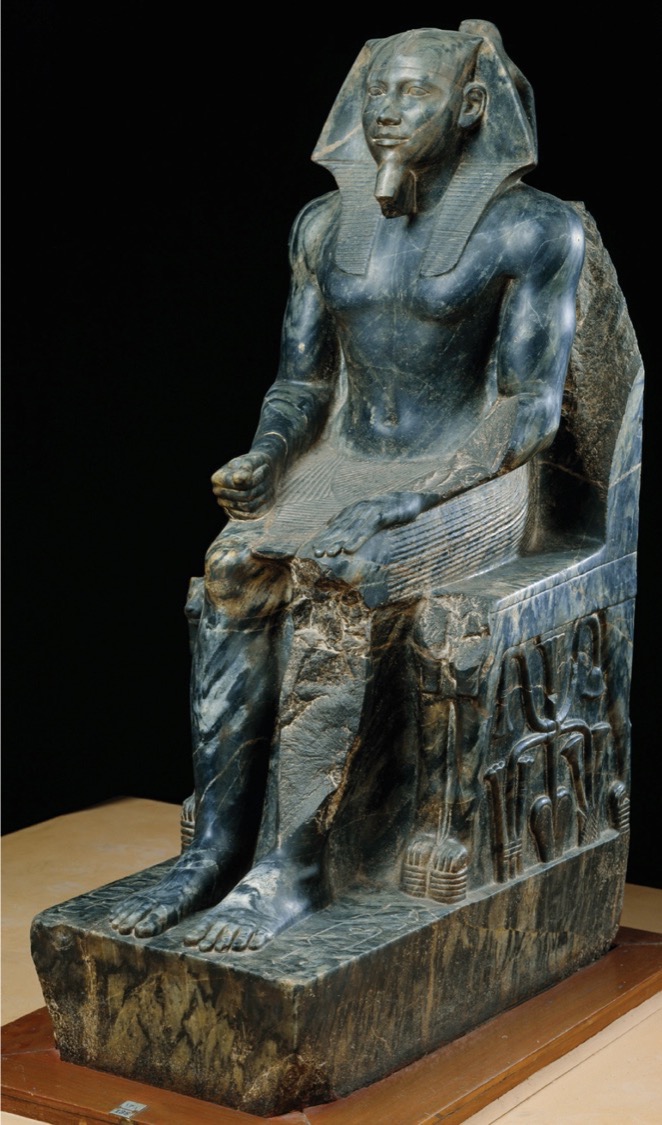

**Khafre enthroned**, from **Gizeh, Egypt**, Fourth Dynasty, ca. 2520–2494 BCE. Diorite, 5’ 6” high. Egyptian Museum, Cairo. **(Old Kingdom)**
71
New cards
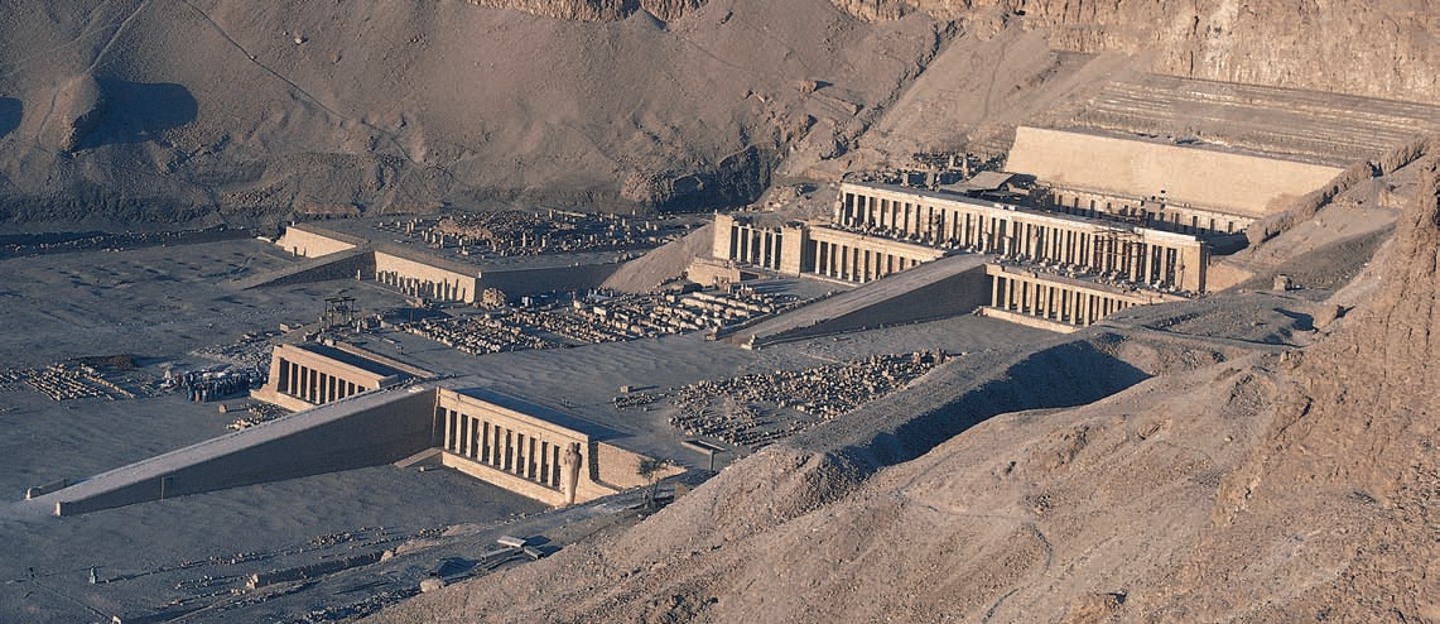

**Mortuary temple of Hatshepsut**, **Deir el-Bahri**, **Egypt**, 18th Dynasty, ca. 1473–1458 BCE. **(New Kingdom)**
72
New cards
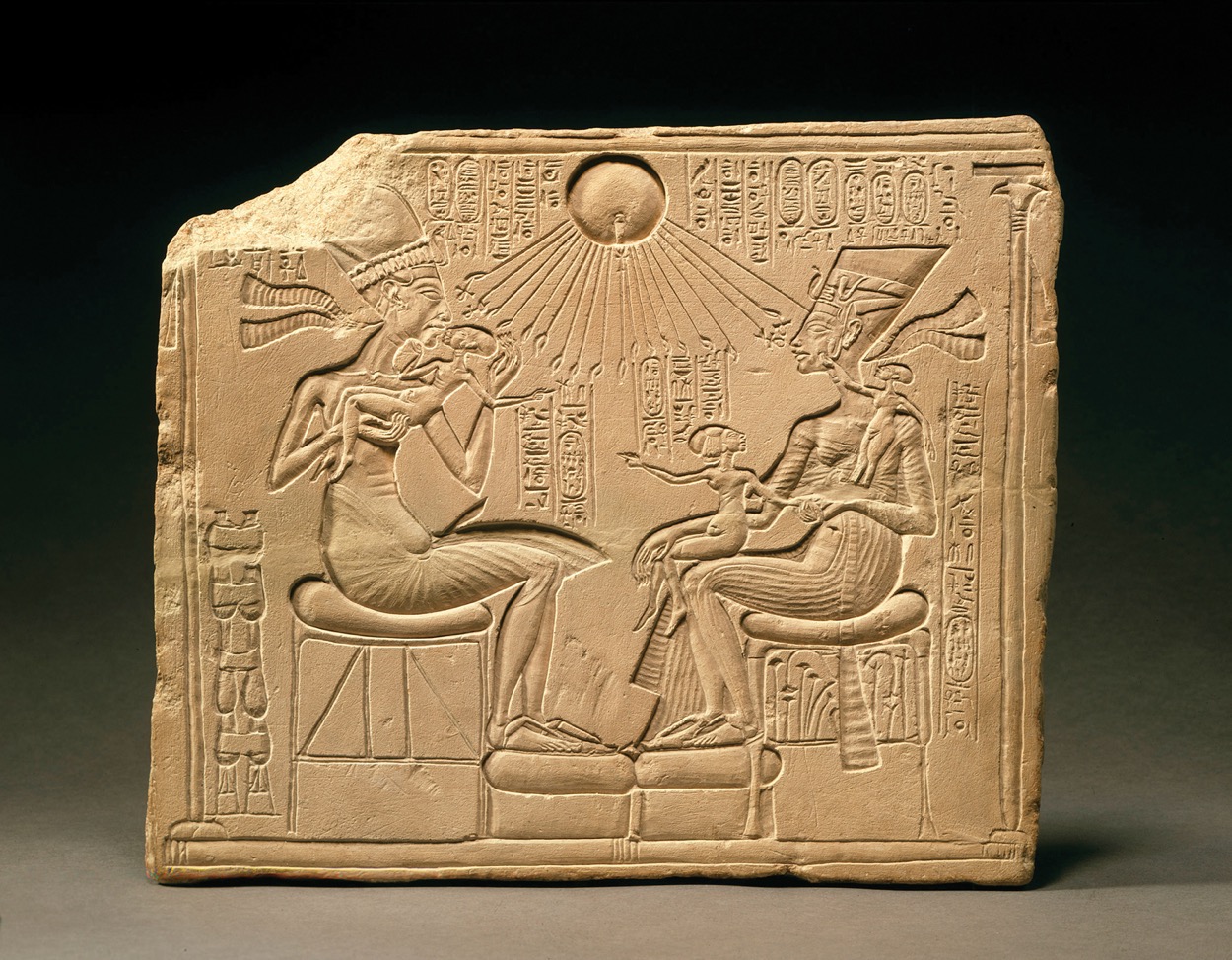

**Akhenaton, Nefertiti, and three daughters**, **Amarna, Egypt,** 18th Dynasty, ca. 1353–1335 BCE. Limestone, 1’ 1/4” high. **(Amarna Period)**
73
New cards
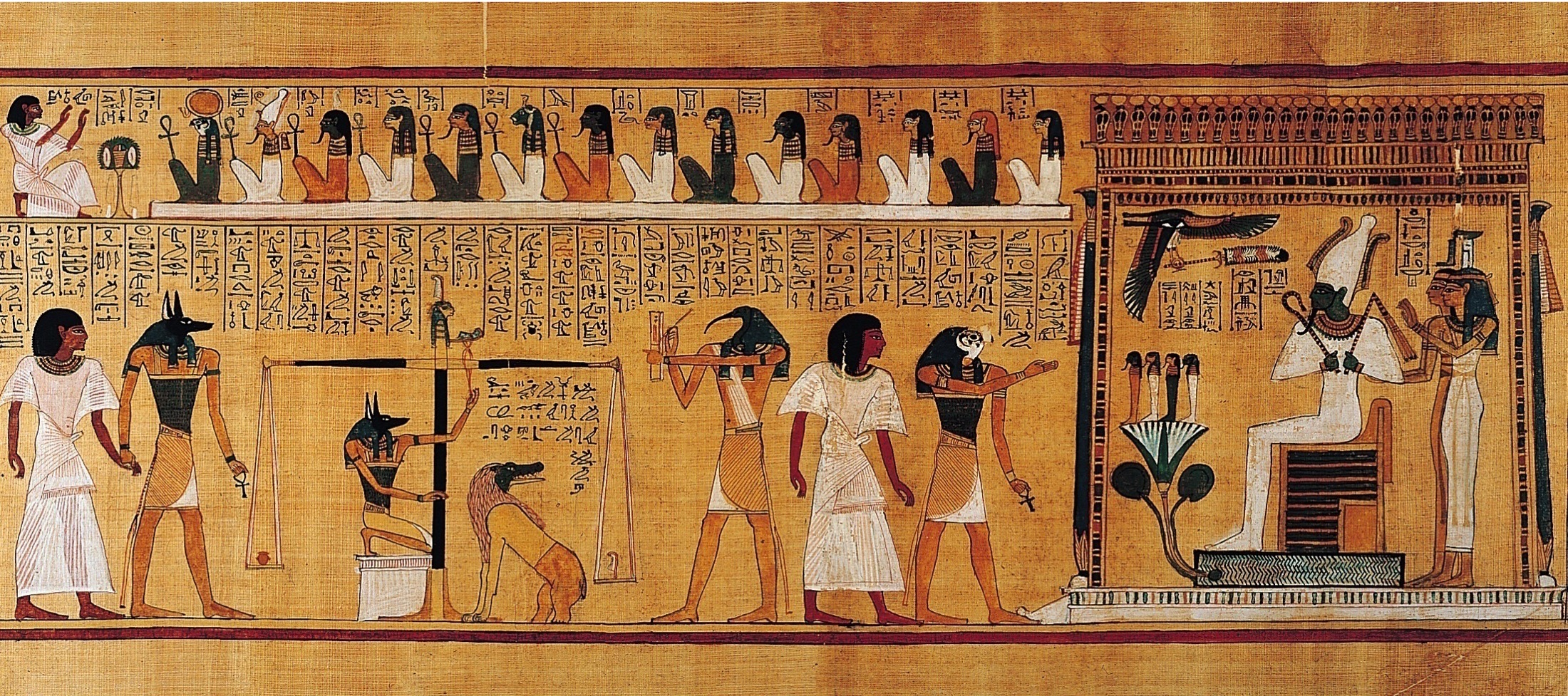

**Last judgment of Hu-Nefer**, **Thebes, Egypt,** 19th Dynasty, ca. 1290–1280 BCE. Painted papyrus scroll, (**New Kingdom)**
74
New cards
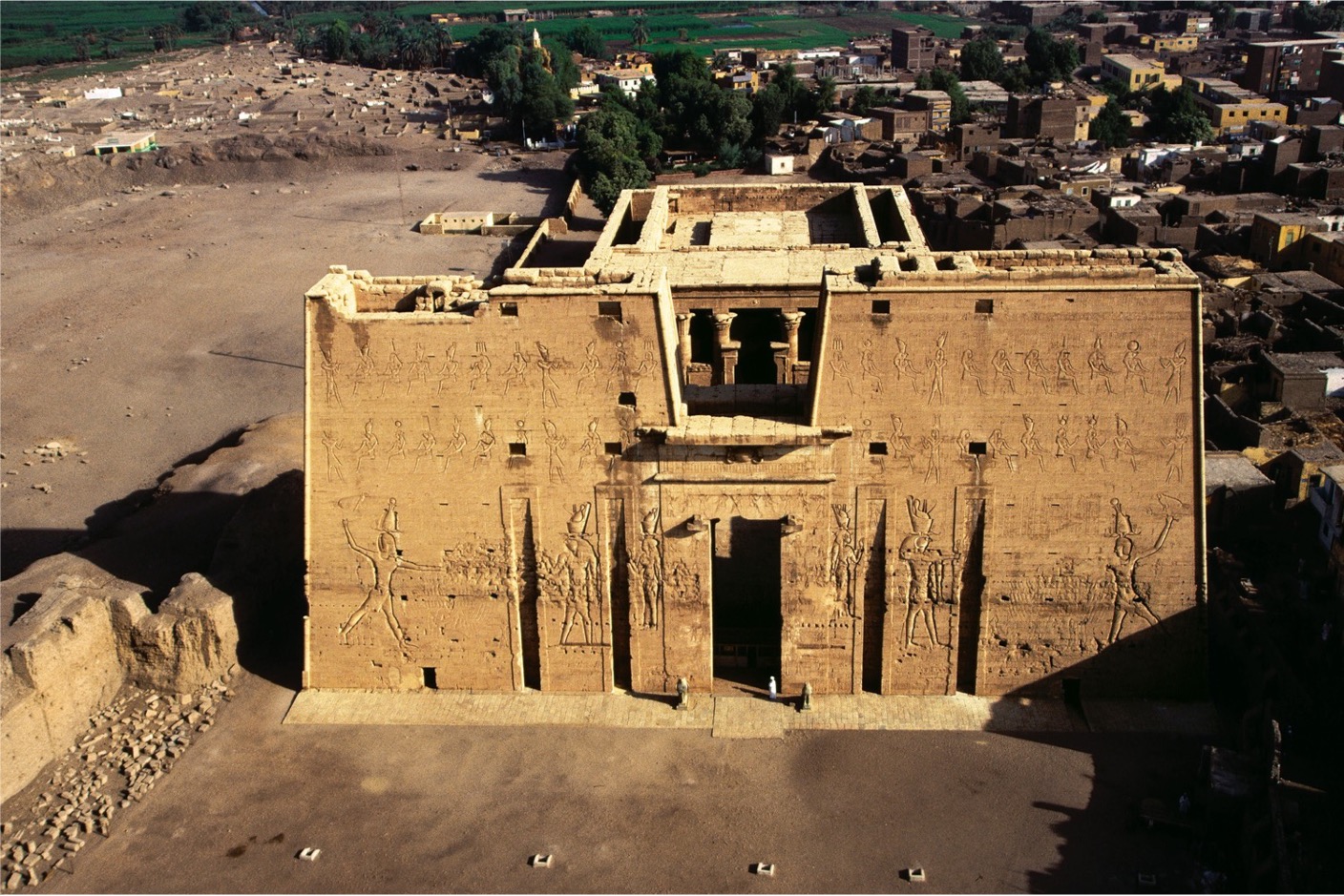

**Temple of Horus, Edfu, Egypt**, ca. 237 – 47 BCE. **1st Millennium BCE**