SAT Formulas
1/20
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Slope of a Line
m = (y2-y1)/(x2-x1)
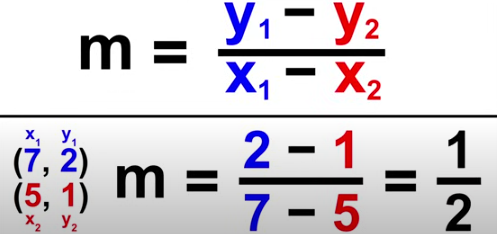
Slope-Intercept Form
y = mx+b
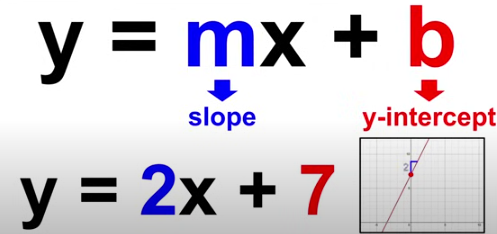
Point-Slope Form
y-y1 = m(x-x1)
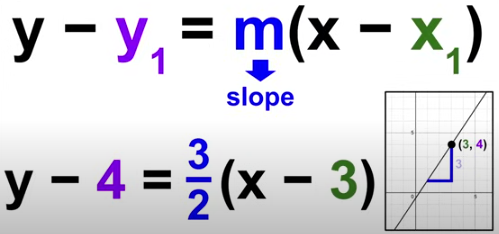
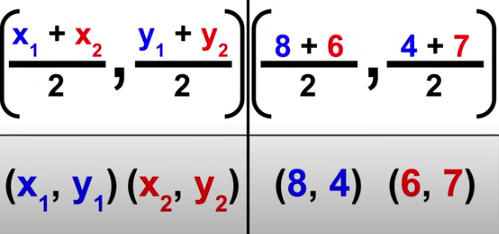
Midpoint Formula
midpoint = (((x1+x2)/2), ((y1+y2)/2))
Distance Formula
distance = sqrt((x2-x1)²+(y2-y1)²)

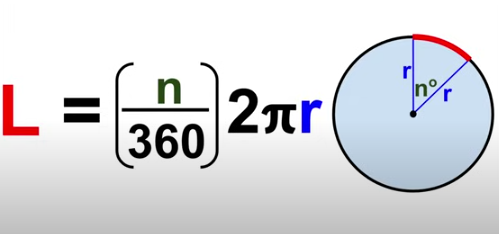
Length of an Arc
length = (n/360)2pir
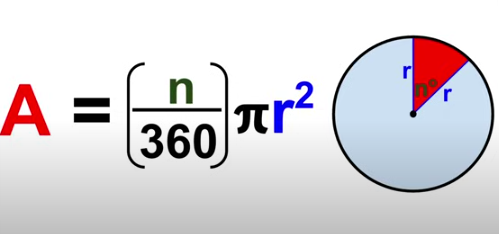
Area of a Sector
area = (n/360)pir²
Quadratic Formula
x = (-b±sqrt(b²-4ac))/2a
y = ax²+bx+c
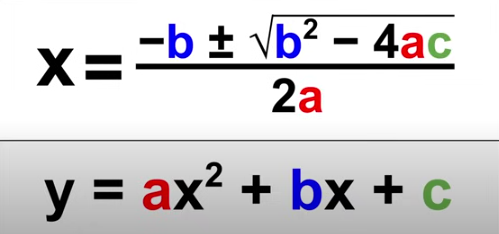
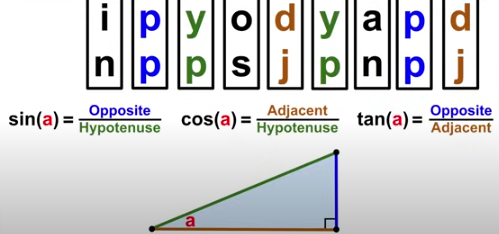
SOHCAHTOA
Sin = Opposite/Hypotenuse, Cosine = Adjacent/Hypotenuse, Tangent = Opposite/Adjacent
Probability
# of favorable outcomes/total number of outcomes

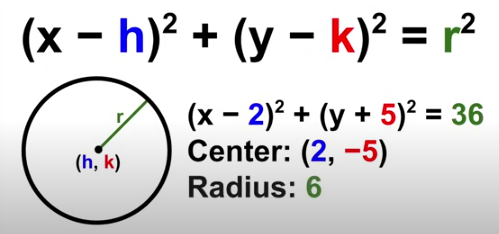
Circle Equation
(x-h)²+(y-k)²=r²
h = x coordinate of the middle of the circle
k = y coordinate of the middle of the circle
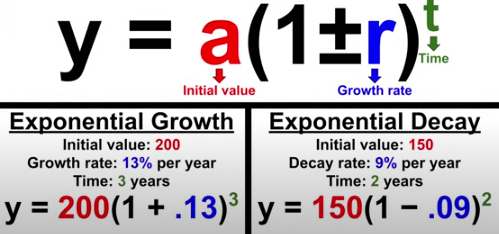
Exponential Growth
y = a(1+r)^t
a = initial value
r = rate
t = time
Vertex of a Parabola
x = -b/2a
“banana” in the quadratic formula
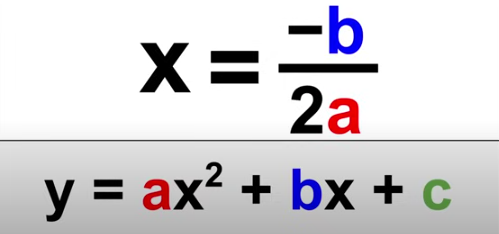
Vertex Form
a(x-h)²+k
vertex = (h, k)
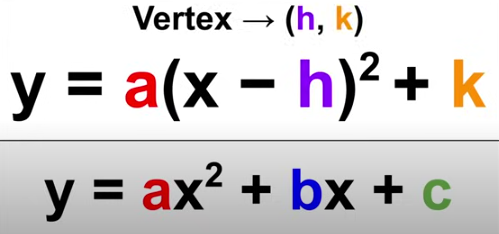
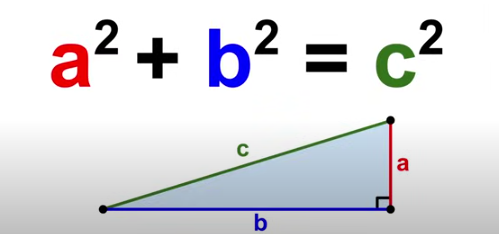
Pythagorean Theorem
a²+b² = c²
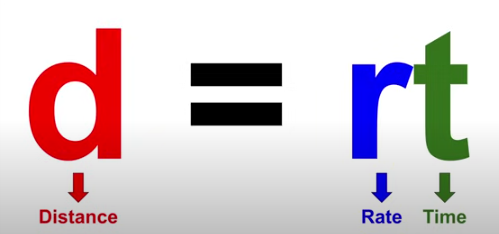
Distance = Rate x Time
d = rt
Sine & Cosine
sin(x) = cos(90-x)
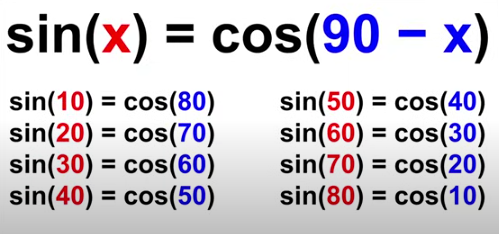
Discriminant
b²-4ac
b²-4ac < 0 | no real solutions
b²-4ac = 0 | 1 real solution
b²-4ac > 0 | 2 real solutions
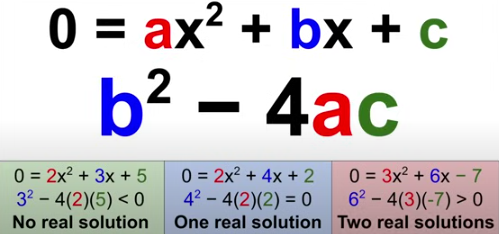
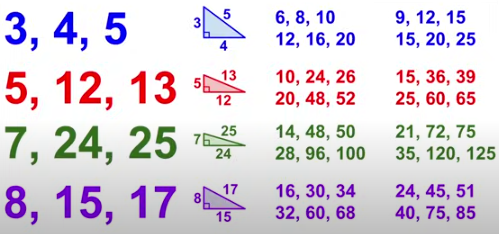
Pythagorean Triples
3, 4, 5
5, 12, 13
7, 24, 25
8, 15, 17
can be multiples of any of these too
Perpendicular Slope
opposite reciprocal
neg → pos or pos → neg, then swap numerator/denominator
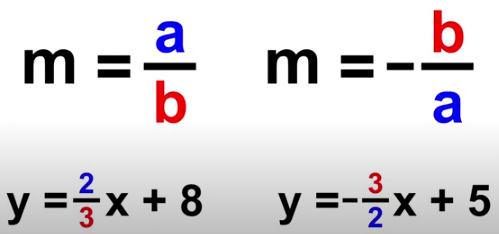
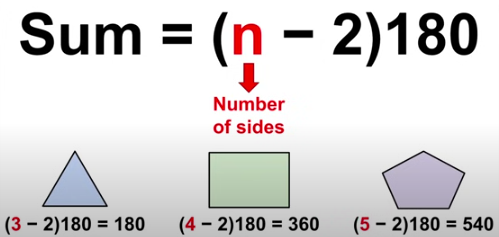
Sum of Angles
sum = (n-2)180
n = number of sides