Bot-Lec (Sem-1) - Chapter 2: Continuity through Evolution
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Jean Baptiste de Lamarck
first evolutionist to believe that organisms change over time as a result of some natural phenomenon rather than divine intervention; thought organisms could pass traits acquired during their lifetimes to their offsprings

Nicolaus Copernicus
Polish astronomer who proposed a heliocentric model of the universe

Charles Robert Darwin
proposed the theory of evolution based on his observations while voyaging aboard the HMS Beagle

HMS Beagle
the ship Charles Darwin sailed on
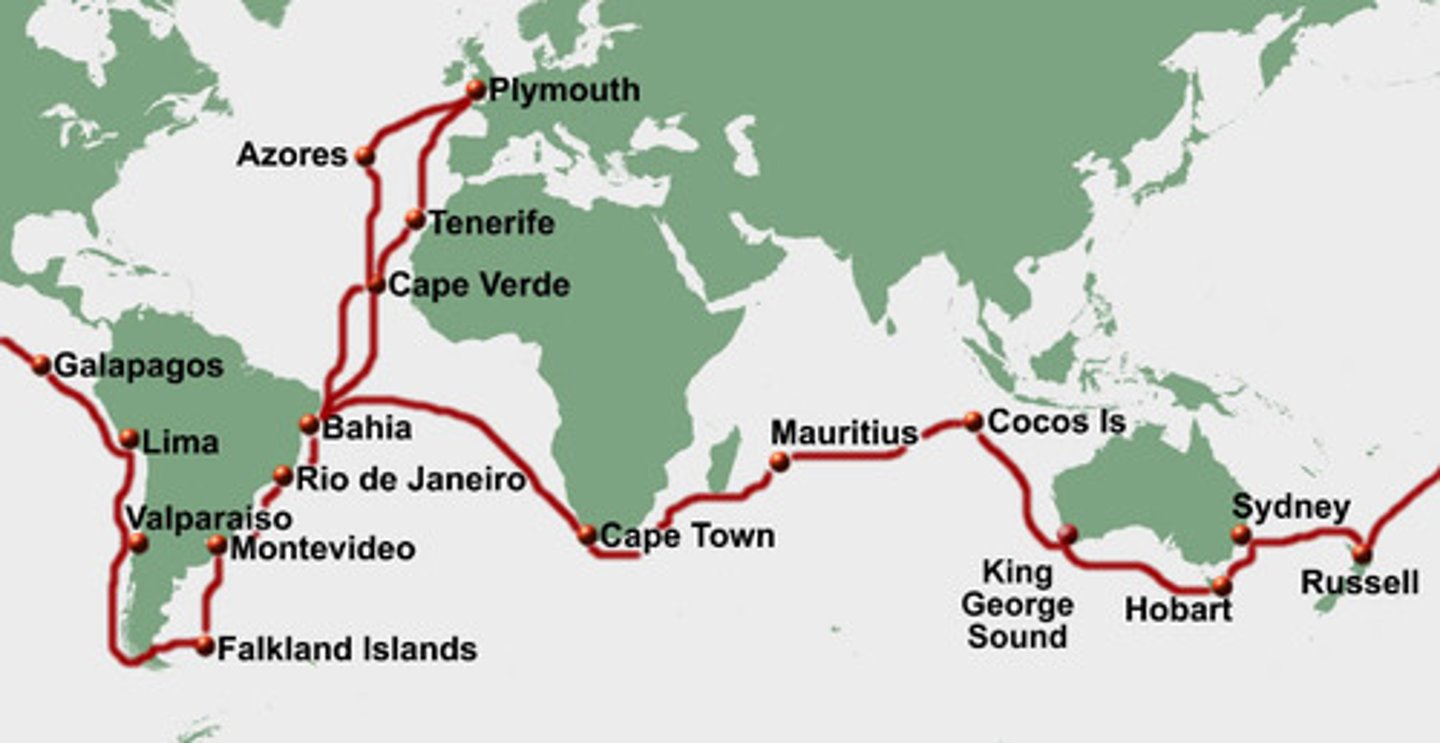
Galapagos Islands
chain of islands in Ecuador where Darwin developed his theory of natural selection by studying the unique life there

Ecuador
country which the Galapagos Islands belong to

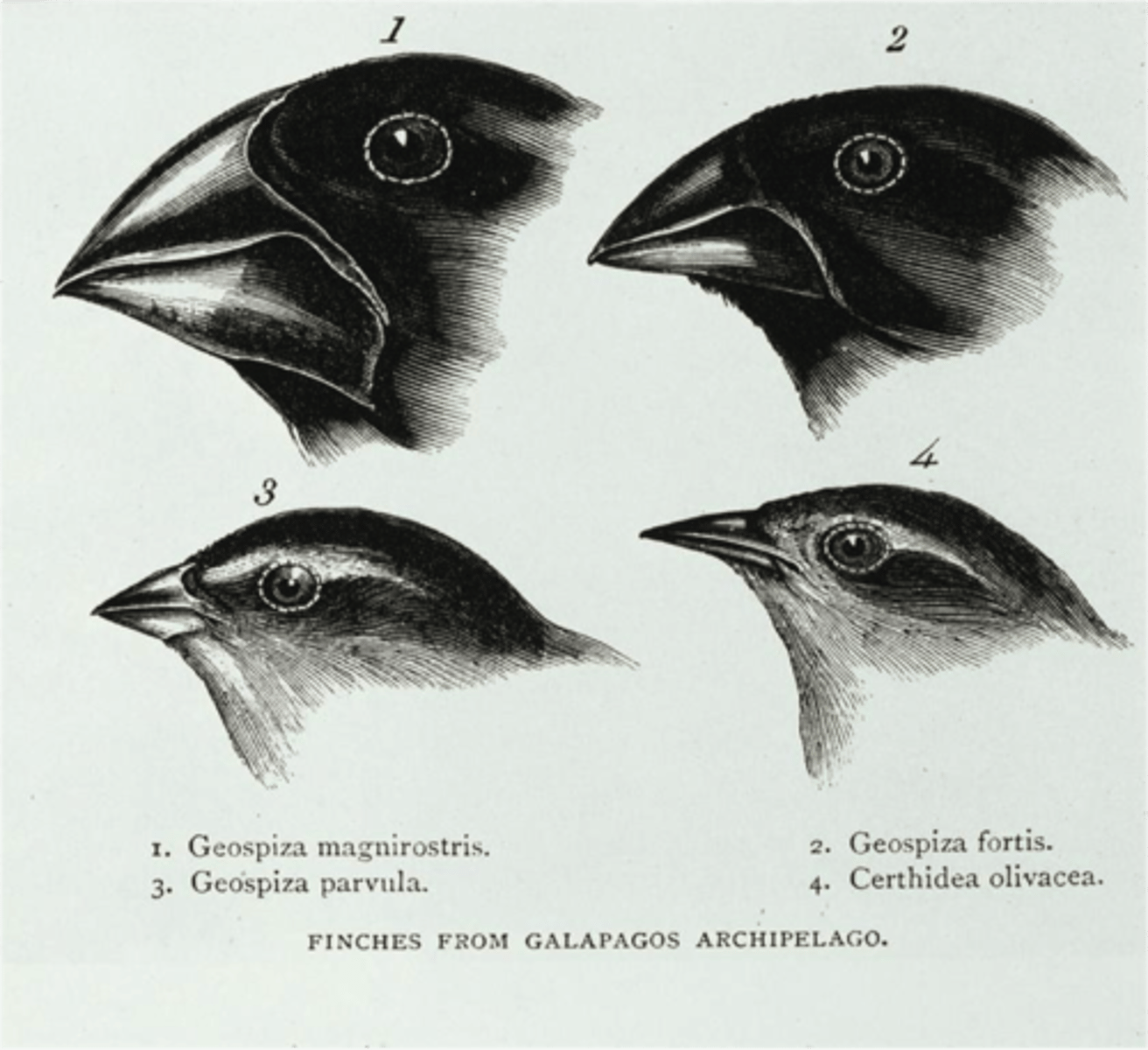
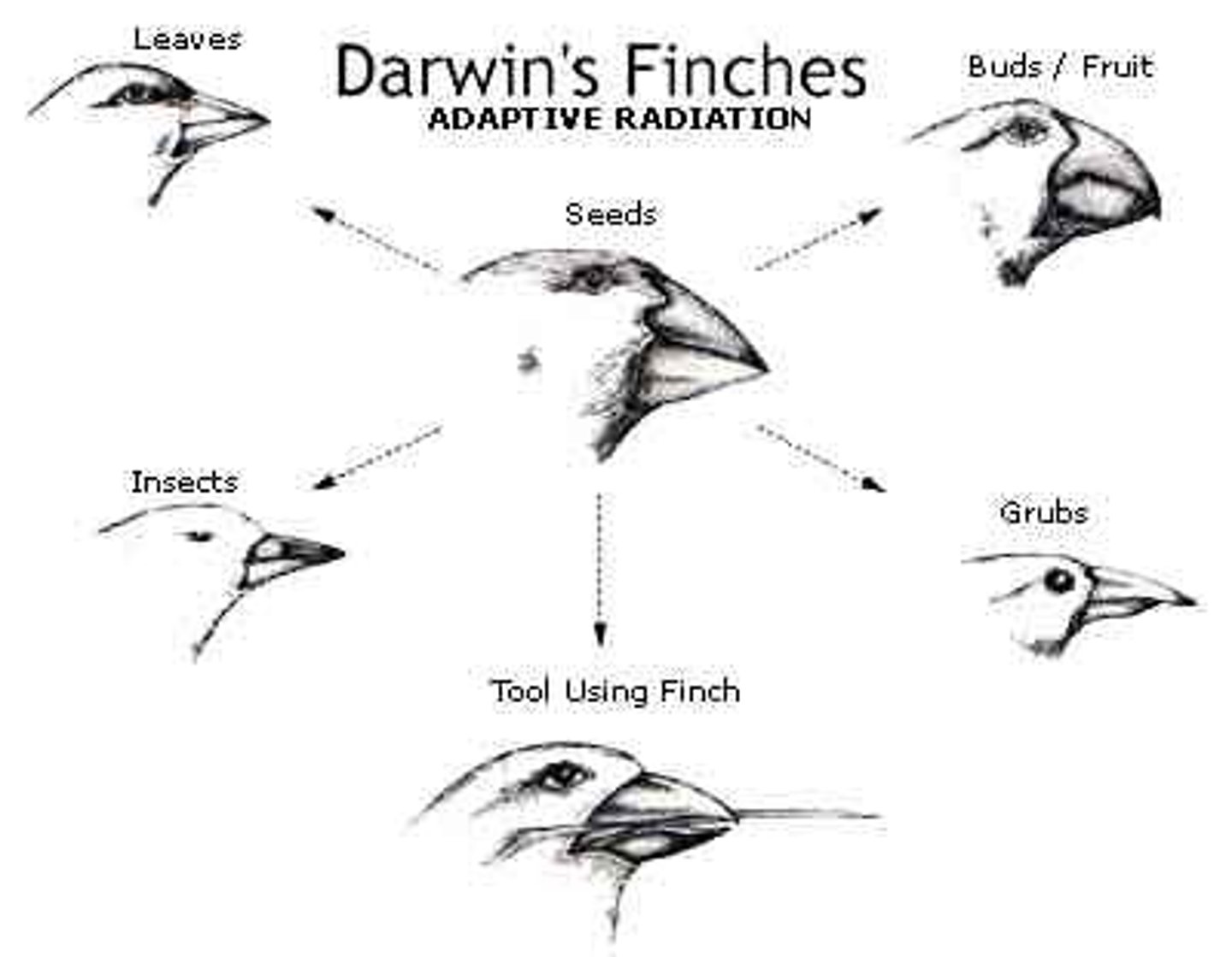
Galapagos finches
during drought, directional selection favored birds with large beaks
Opuntia echios
giant prickly pear trees found in Galapagos Islands

Brachycereus nesioticus
lava cactus found in Galapagos Islands

Conolophus subcristatus
Galapagos land iguana

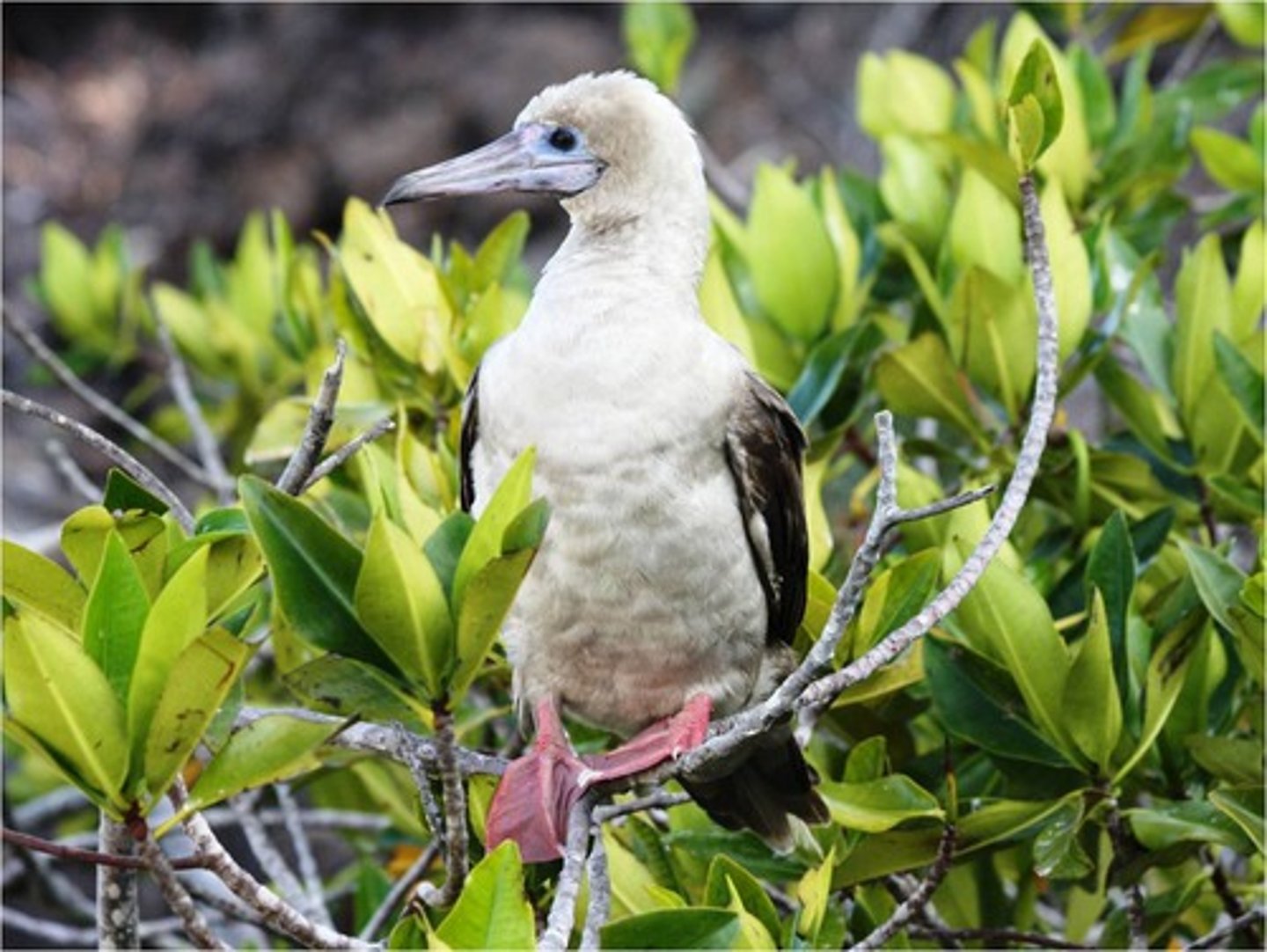
Sula sula
red-footed booby

evolution
accumulation of inherited changes within populations over time
physical evolution
physical changes and adaptations of organisms over time; ex: sea grass (plant, not algae) have air pockets for buoyancy
behavioral evolution
development of behavioral traits; ex: tropism in sunflowers, the venus flytrap, and the makahiya
tropism
a growth response of a plant toward or away from a stimulus
physiological evolution
variation of the structure of plants at a cellular and molecular level over time; ex: poison
adaptation
an evolutionary modification that improves an organism's chances of survival and reproductive success

natural selection
mechanism of evolution in which individuals with inherited characteristics well suited to the environment leave more offspring than do individuals that are less suited to the environment; ex: cacti, which grow in extremely warm environments, can hold up to 70 kg of water)
overproduction; inherited variation; limits on population growth; differential reproductive success
Darwin's Premises of Evolution by Natural Selection
overproduction
each species produces more offspring than will survive to maturity
inherited variation
individuals within a population have slightly different inheritable traits
limits on population growth
limited resources in the environment produces a struggle for existence
differential reproductive success
offspring with the most favorable combination of characteristics are most likely to survive and reproduce, passing those genetic characteristics to the next generation
Darwin's Theory of Evolution
Darwin could not explain how traits were passed from one generation to another or why individuals vary within a population
modern synthesis
a comprehensive theory of evolution that incorporates genetics and includes most of Darwin's ideas and Mendelian genetics, focusing on populations as the fundamental units of evolution
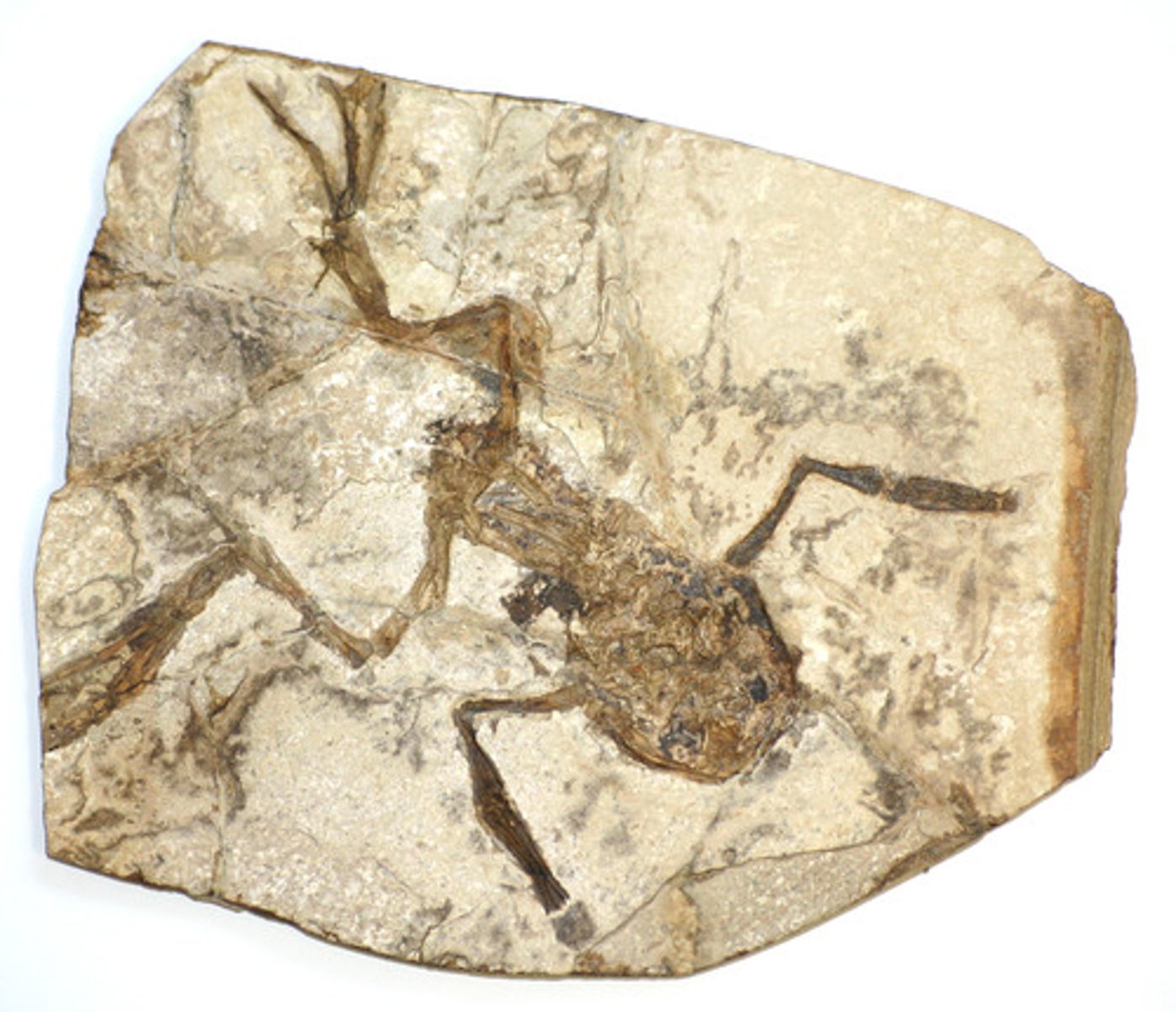
fossil
a trace of an ancient organism that has been preserved in rock

Populus
cottonwood

comparative anatomy
the study of similarities and differences among structures of living species
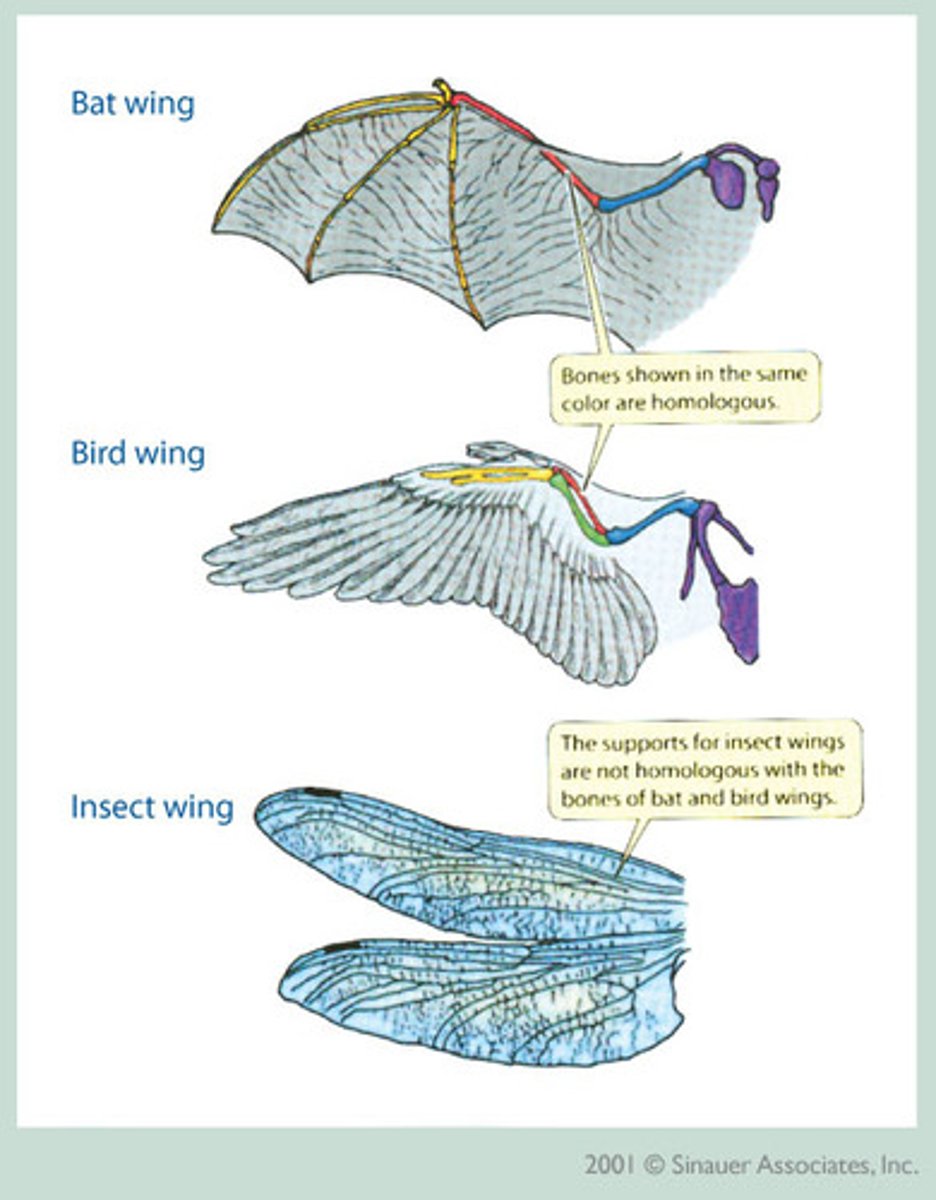
homologous features
features with similar structures but different functions; provide evidence for common ancestry

Ferocactus wislizenii
fishhook cactus

homoplastic features
structures in unrelated species that are similar in function and appearance but not in evolutionary origin; result of convergent evolution
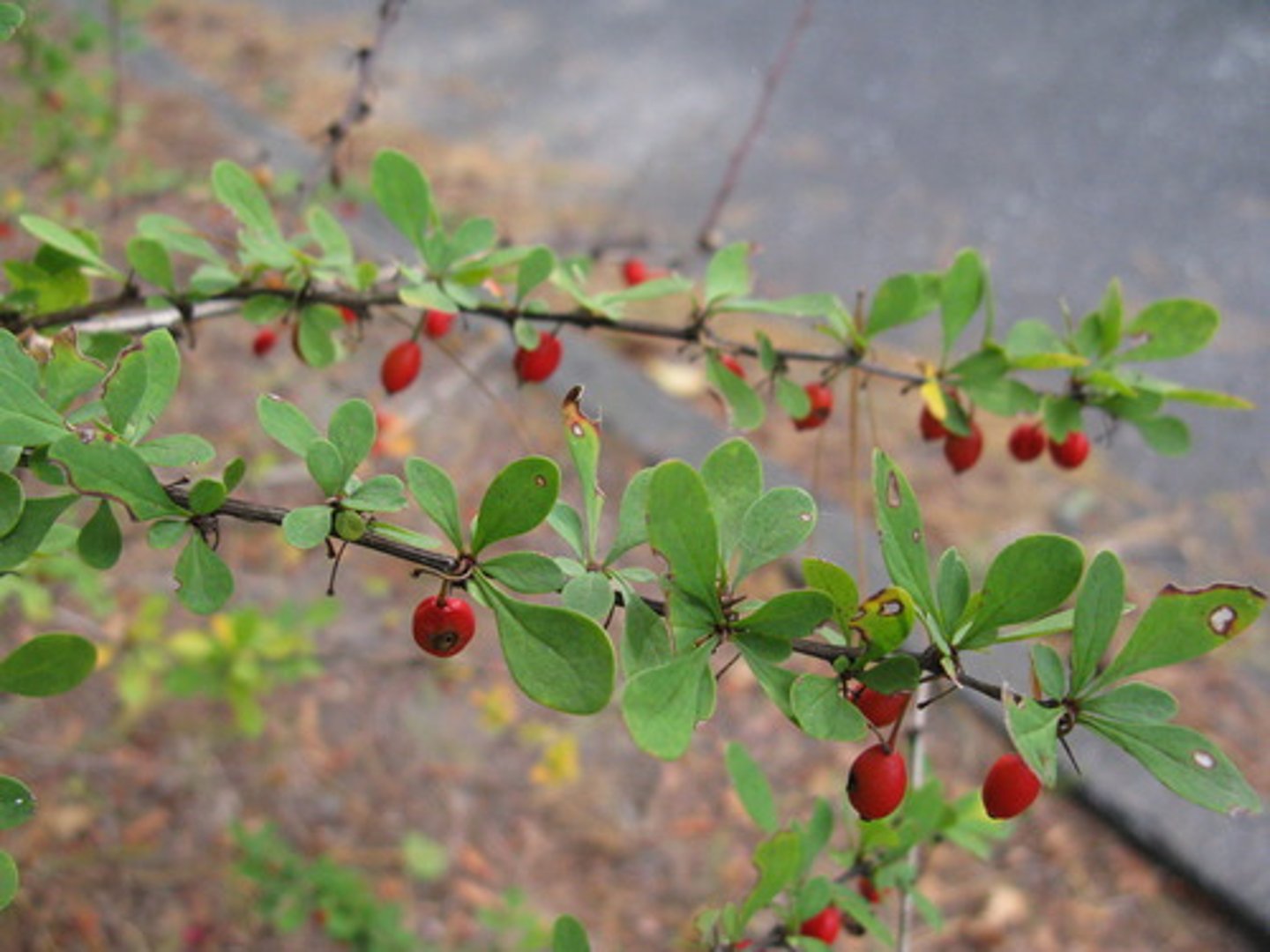
Berberis thunbergii
Japanese barberry

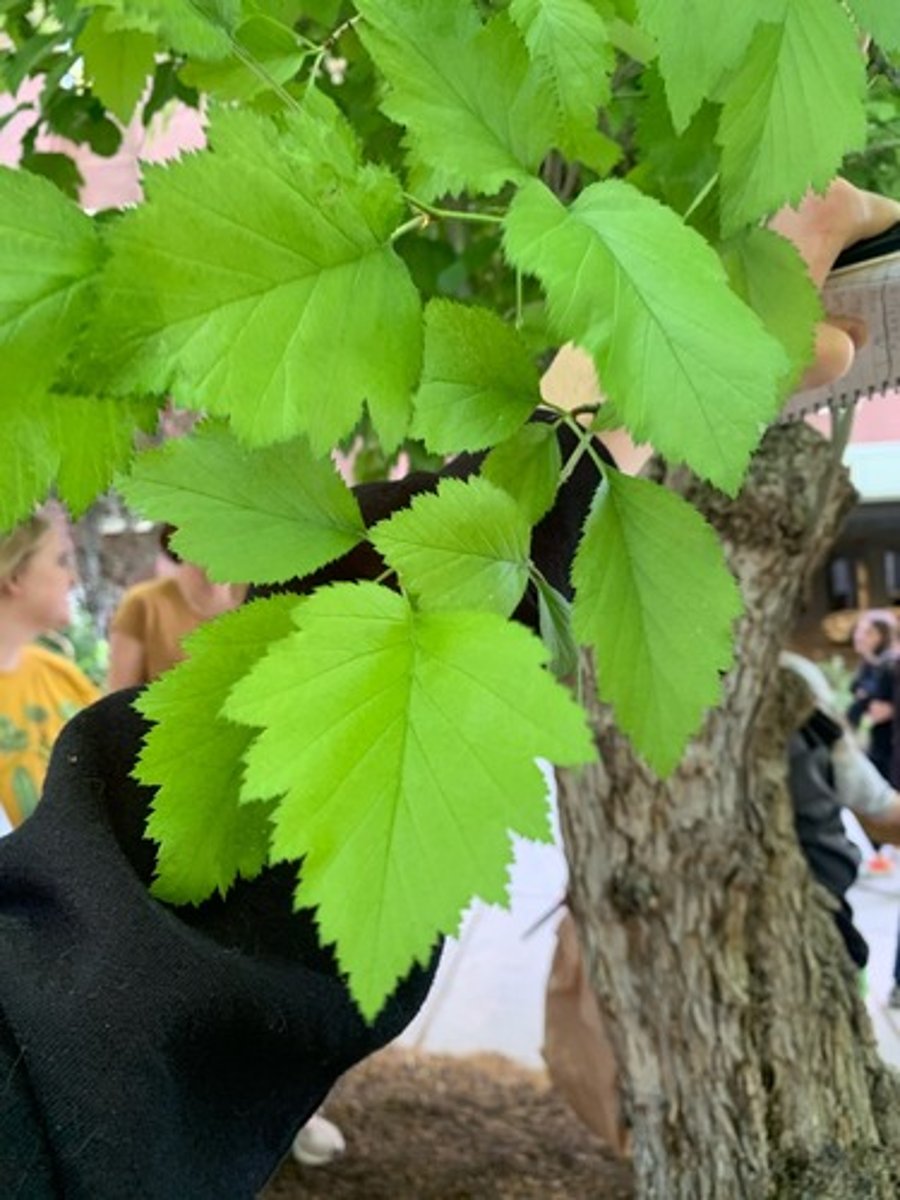
Crataegus mollis
downy hawthorn

convergent evolution
independent evolution of similar adaptations in unrelated species living in similar environments
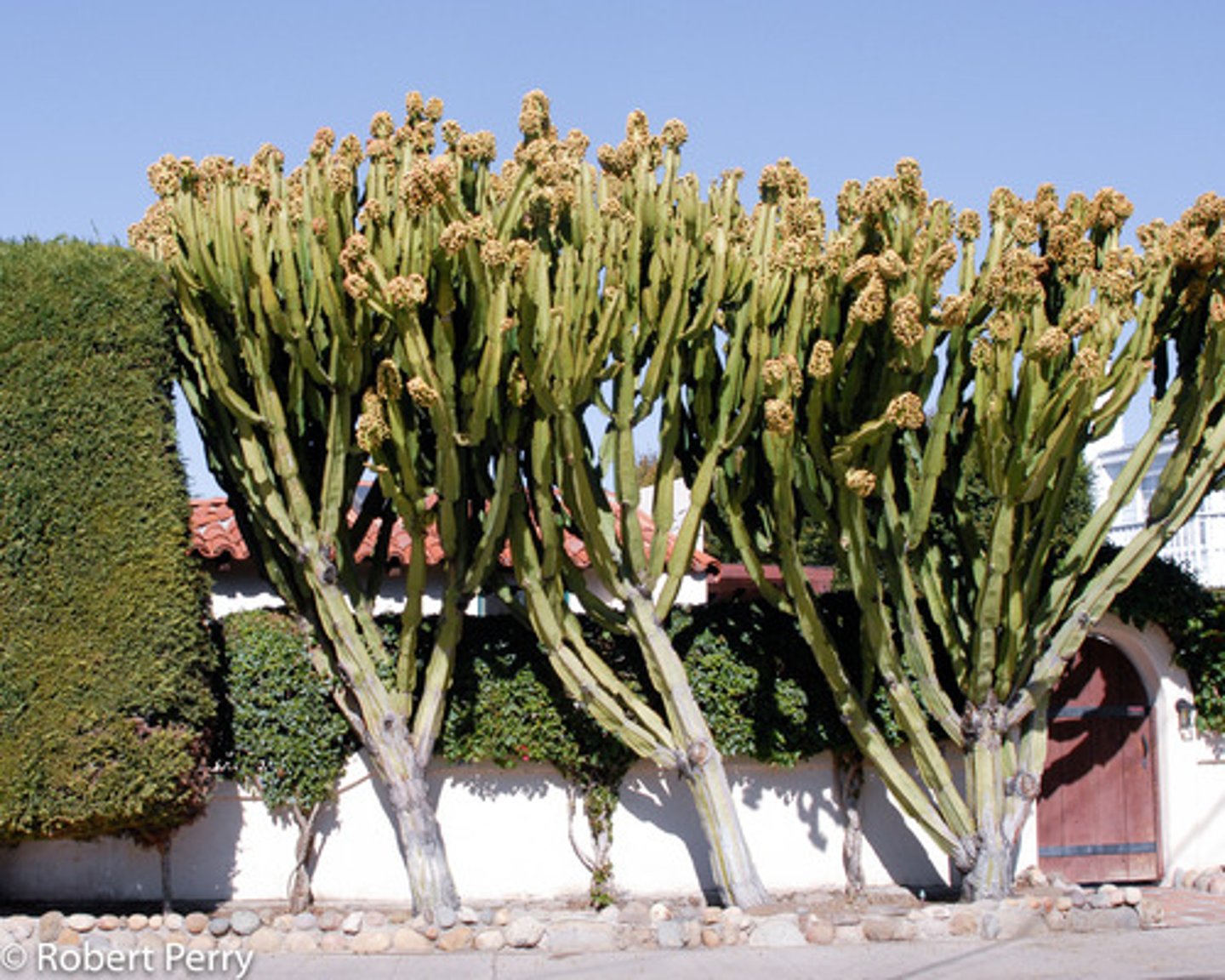
Euphorbia ingens
Candelabra Tree; member of the spurge family; native to Africa

Cereus hankeanus
member of the cactus family; native to North America
vestigial structure
an evolutionary remnant of a formerly functional structure; occasionally present as an ancestral species adapts to a different mode of life

mimicry
morphological adaptation in which one species evolves to resemble another species for protection or other advantages
Ophrys scolopax
bee orchid
biogeography
study of the geographic distribution of living organisms and fossils; geographic distribution affects organism's evolution; areas isolated for a long time have plants and animals unique to those areas
Amino acids in common proteins
sequence is more similar in closely related species than in remotely related species
amino acids
building blocks of proteins
nucleic acids
nucleotides
Cytochrome C
is a protein carrier in the ETF, common in many living organisms, used for genetic relation
Sequence of nucleotides in DNA
greater proportion identical in closely related organisms than in remotely related organisms
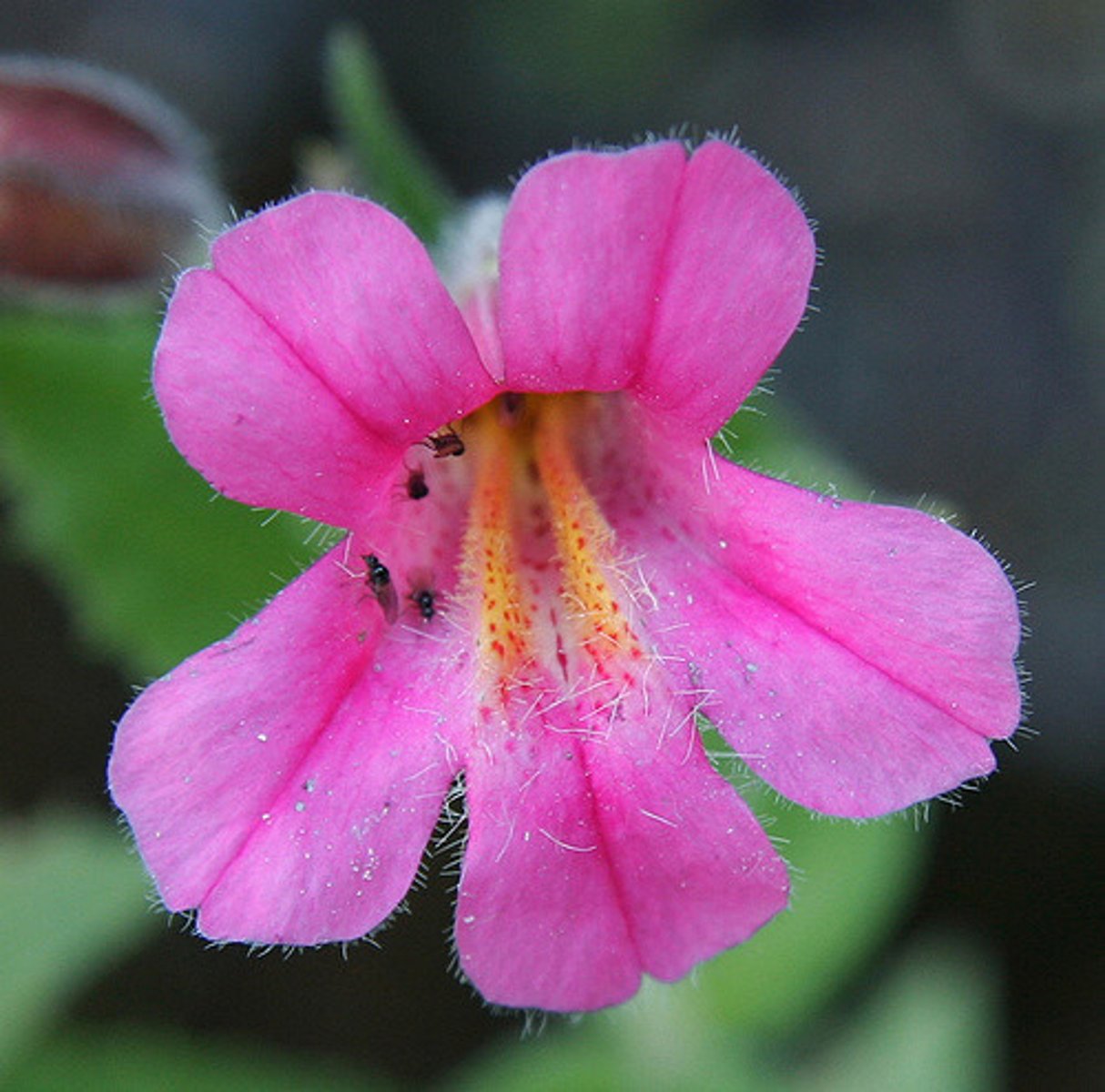
Mimulus lewisii
pink; attracts bees (more on smell)

Mimulus cardinalis
red; attracts hummingbirds (more on visual)
