lec 8.2 - translation (initiation and elongation)
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
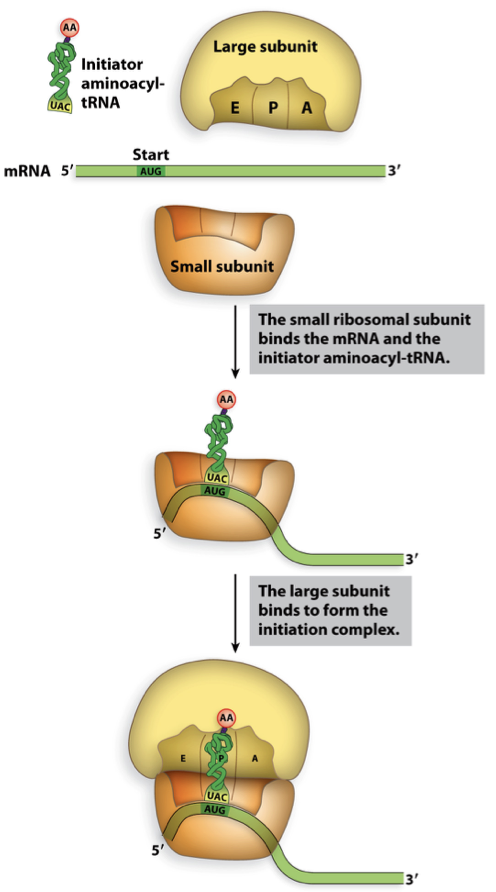
initiation in prokaryotes required components
need both ribosomal subunits, initiator amnioacyl tRNA and mRNA
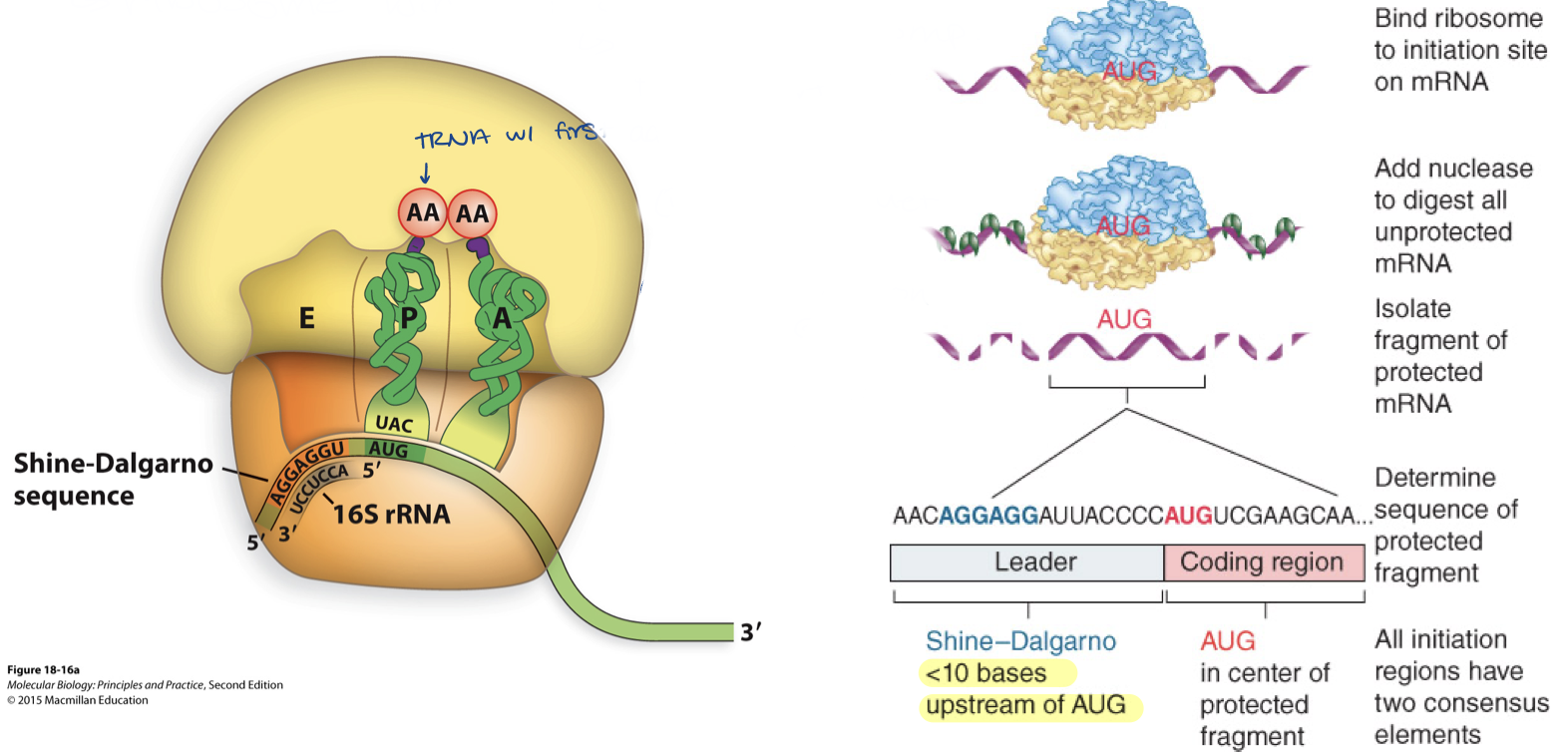
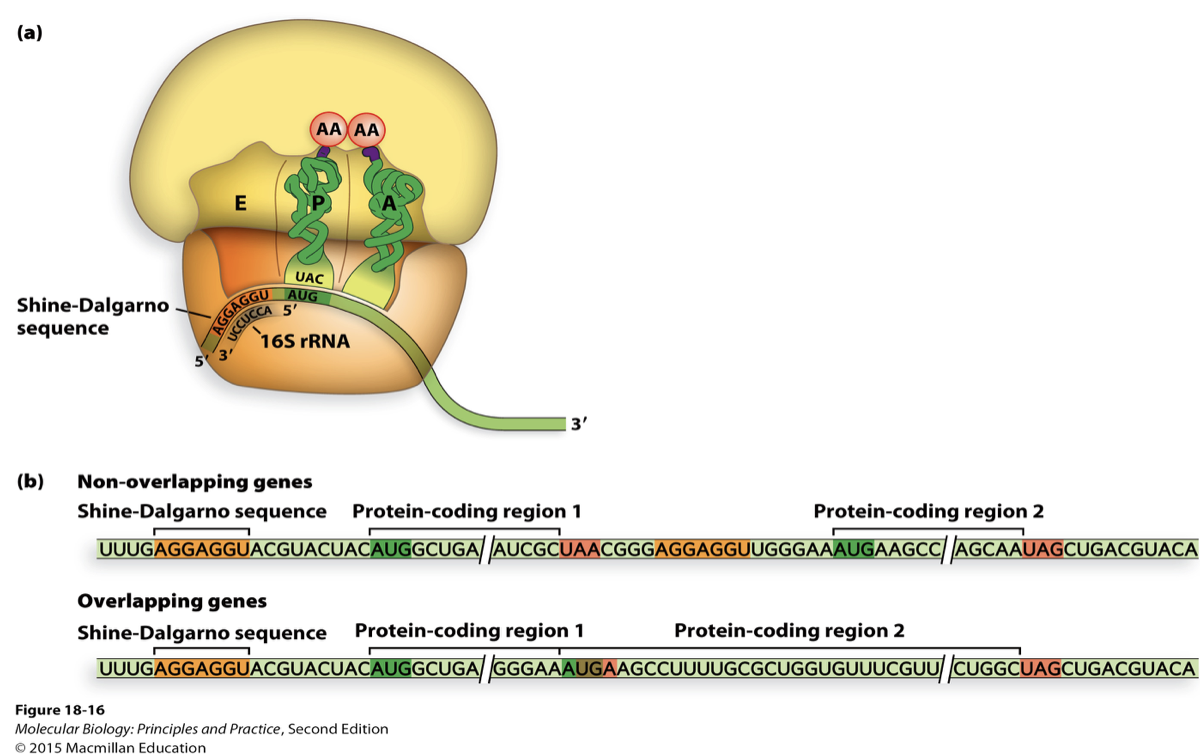
needs ribosome binding site (RBS) - shine dalgarno sequence
AGGAGGU (upstream of AUG)
positions ribosome small subunit at correct position to find the first AUG
bacteria sometimes has internal mRNA
shine-dalgarno – upstream of AUG by 8-13 nucleotides
sequence is complementary to rRNA
tRNA w/ fMet at P site
second aa on tRNA at A site
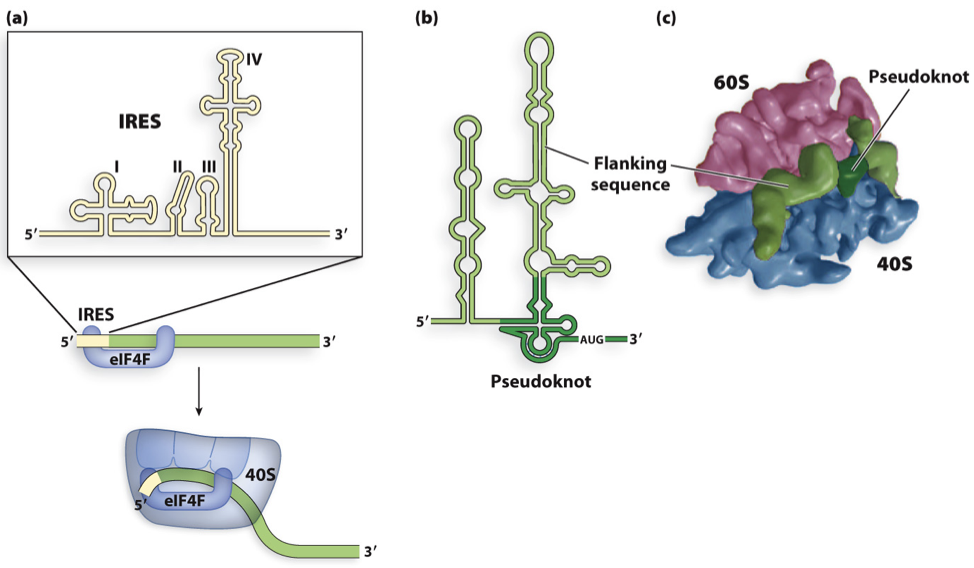
ribosome can also use internal ribosome entry sites (IRES)
besides the shine dalgarno RBS, what else can ribosomes use?
ribosomes can also used IRES (internal ribosome entry sites)
these allow another gene to be translated at once (2 in total)
polycistronic genes in bacteria
can have overlapping polycistronic genes in bacteria
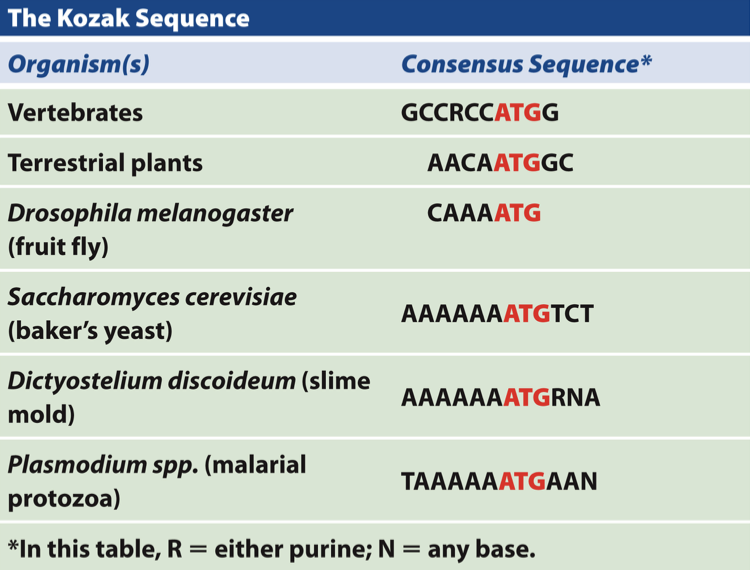
what do eukaroytes have instead of shine dalgarno?
describe it
Kozak sequence
usually a purine - 3 residues before the start codon and a G immediately following the start codon
Kozak sequence makes contact with tRNA → enhances translation (not an RBS like Shine-dalgarno)
contact w/ initiator tRNA
enhances translation
correct AUG in eukaryotes is AUG closest to 5’ cap (first one after), not like this in prokaryotes
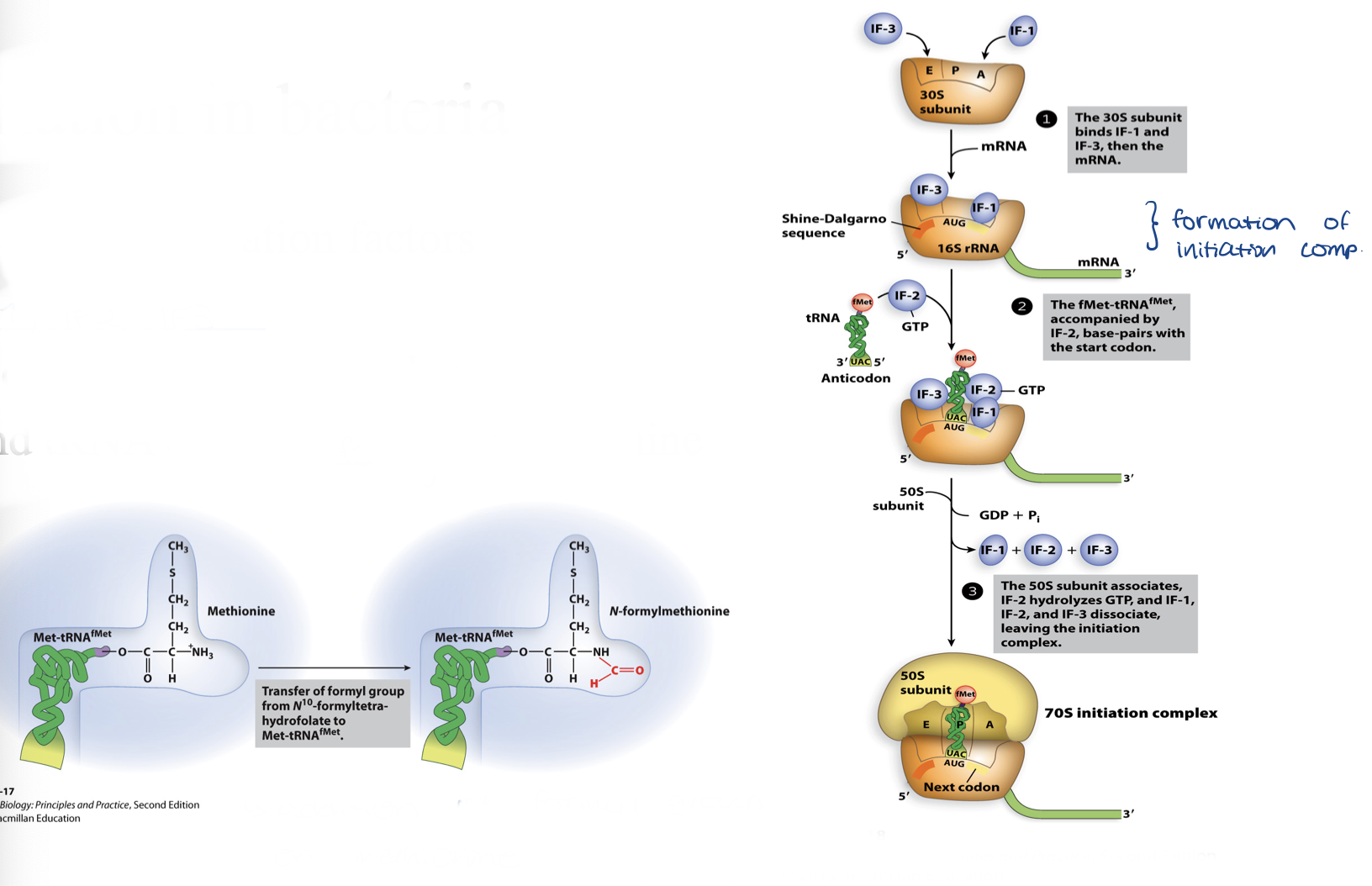
initiation in bacteria
requirements
products
requires 3 initiation factors
IF1, IF2, IF3
produces initiation complex and tRNA carrying formyl-methionine
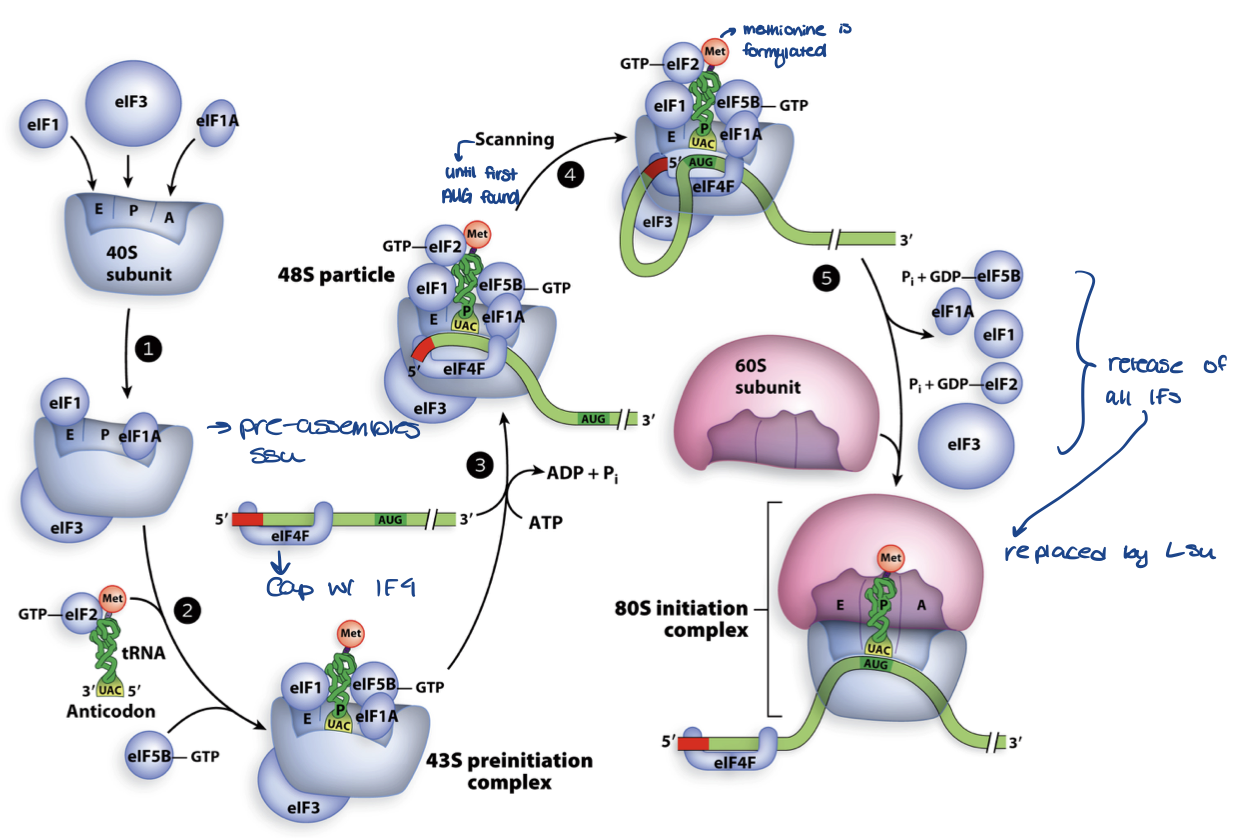
initiation in eukaryotes
requirements
products
uses 5’ cap to recognize, then scan to find first AUG
12 initiation factors
binding and hydrolysis of GTP and ATP
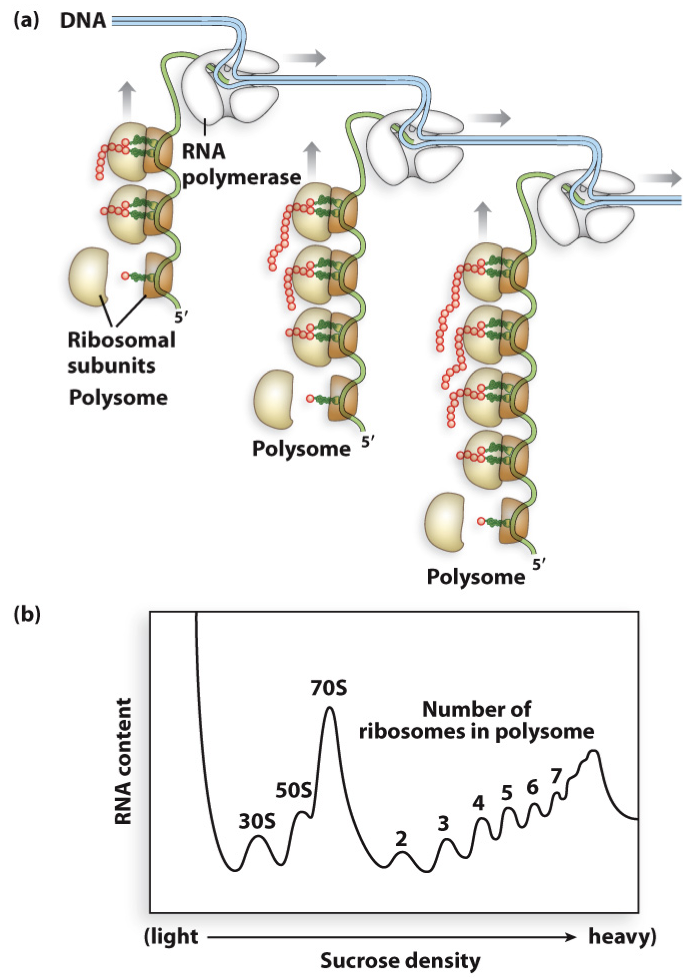
polysome - in prokaryotes
what is it?
what does it do?
what allows for this phenomenon?
many ribosomes on a single mRNA (which is still being transcribed)
increases rate of translation
can happen because both transcription and translation occur in the cytoplasm (no nucleus so mRNA does not have to travel out of it) and no introns need splicing
where does translation start in viruses
can start translation at IRES site (internal ribosome entry site) when 5’cap missing – used by viruses and bacteria
IRES recognized by eIF4F initiation factor
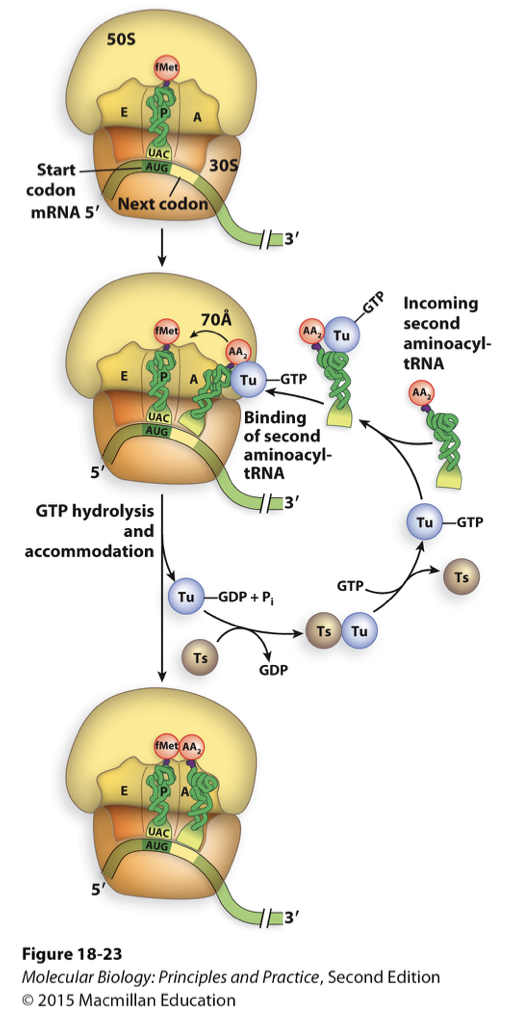
elongation in prokaryotes
requirements/factors
3 elongation factors in bacteria
EF-Tu
EF-Ts
EF-G
Tu and Ts helps with binding of new tRNA with aa and peptidyl transferase reaction
transfer new aa on growing peptide chain
if tRNA has wrong anti-codon it gets rejected
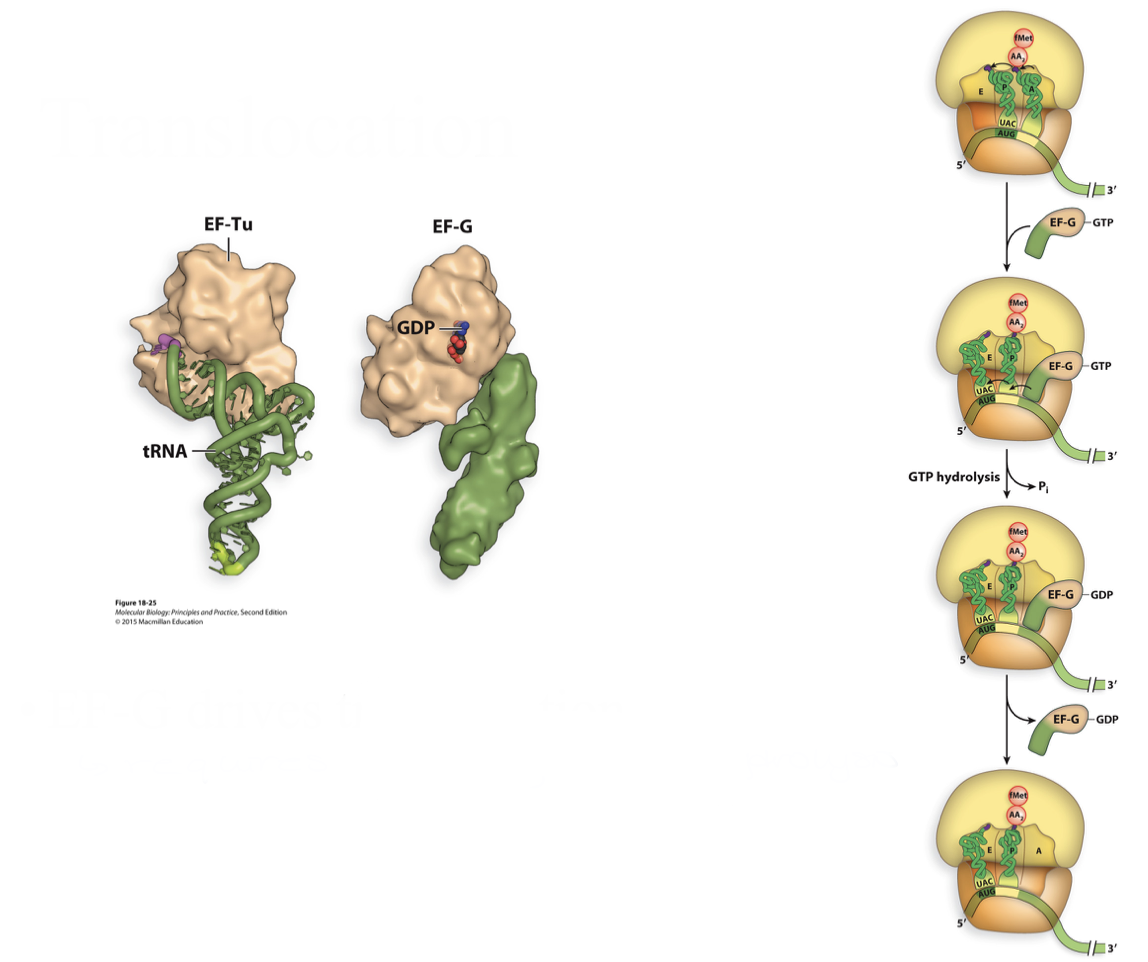
translocation in prokaryotes
EF-G (elongation factor G) drives translocation
requires energy → GTP hydrolysis
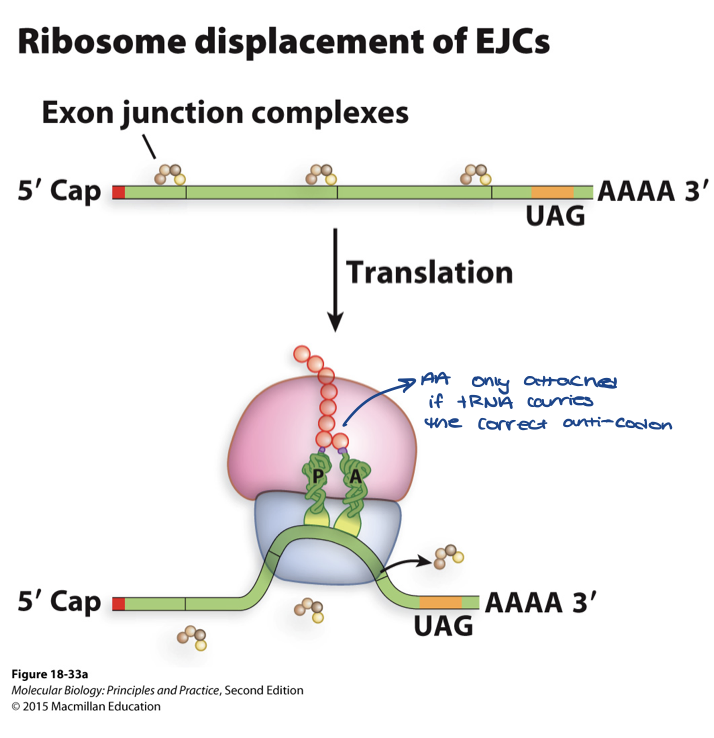
elongation in eukaryotes
ribosome removes the exon junction complex (EJC) complex as it proceeds along the mRNA
requirements of termination in prokaryotes
requires 3 termination or release factors
RF1, RF2, RF3
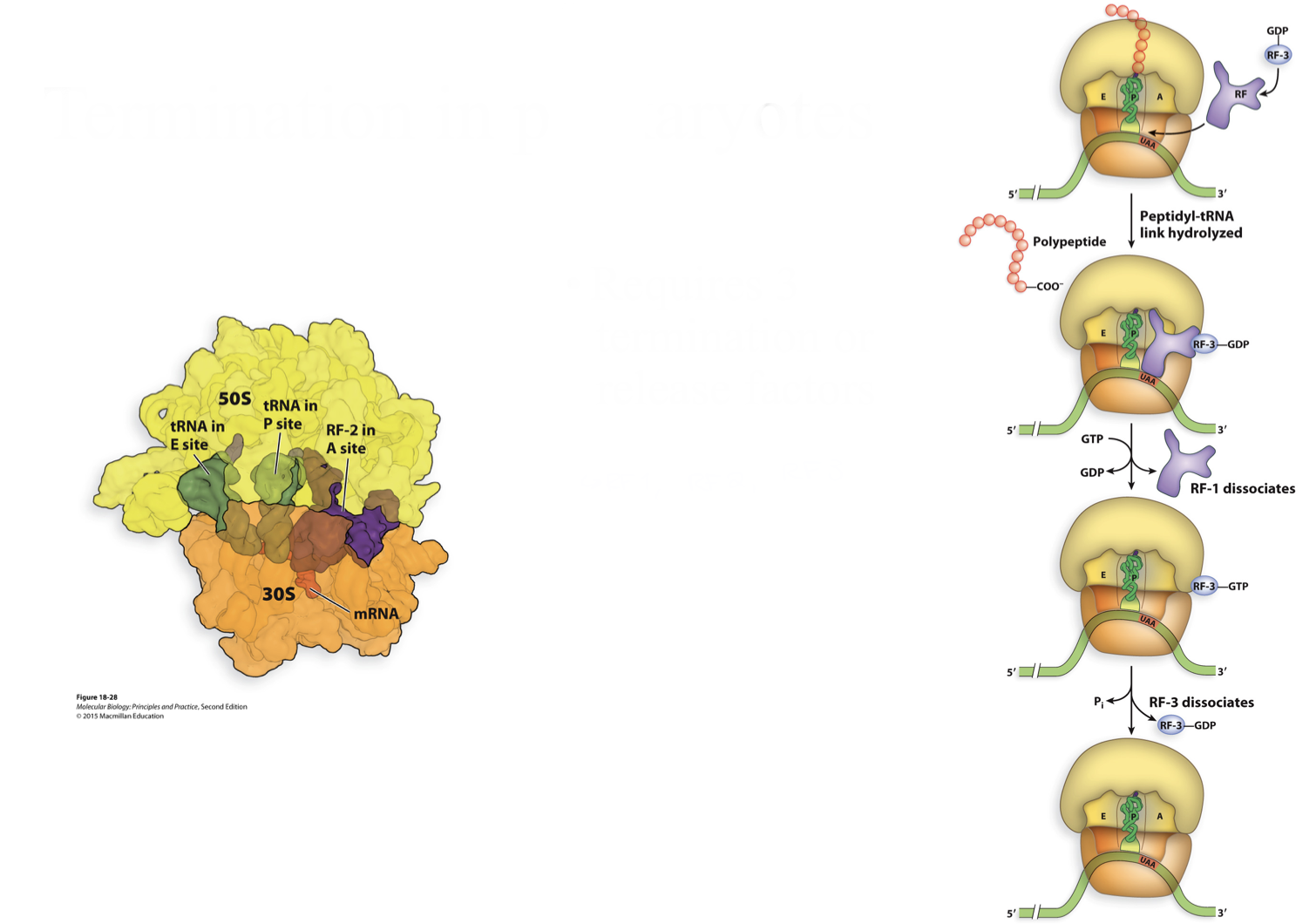
steps of termination in prokaryotes
happens in 2 steps, needs RF1, RF2 and RF3
step 1
RF1 recognizes stop codons UAA and UAG
RF2 recognizes stop codons UAA and UGA
they activate ribosome to hydrolyse peptidyl tRNA
step 2
RF3 (GTPase) releases RF1 and RF2, binds GDP → hydrolyzes GTP to signal termination is done
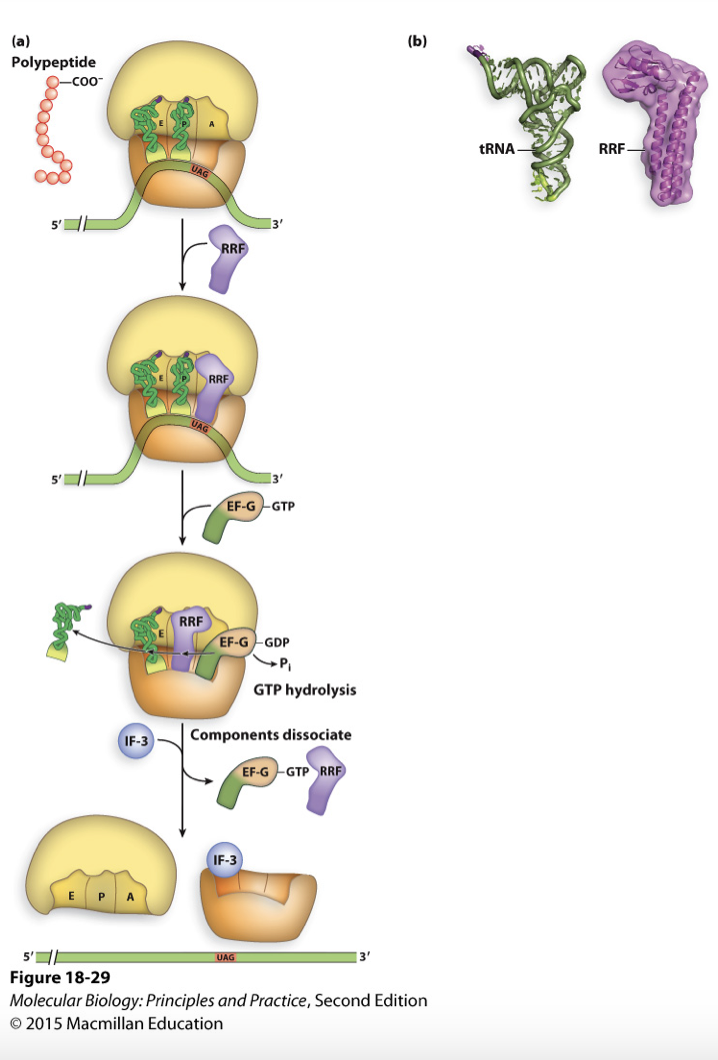
at the end of this step translation is terminated but ribosome complex is still together therefore need RRF along with EF-G to dissociate complex
ribosome recycling
uses RRF (ribosome recycling factor) to dissociate ribosome complex by wedging the ribosome apart
RRF mimics tRNA shape and recognizes stop codon
use EF-G-GTP and GTP hydrolysis (energy) to move RRF into P site