Income statement part 2
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
lecture 5
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
What does depreciation show
a way of showing how non-current assets lose value over time
why do we need to know about depreciation
most non-current assets have a finite life because they get used to generate wealth for the business
what does depreciation attempt to do?
measure the proportion of non-current asset used to generate the revenue for the current period
is depreciation cash or not?
it is a non-cash expense
how often is depreciation recorded in the income statement
annually
what do we need to know to calculate the annual depreciation expense? (4)
the purchase cost of the asset
the useful life of the asset
the residual life of the asset
the depreciation method to be used
what are the two most common methods to measure depreciation?
straight line method
reducing balance method
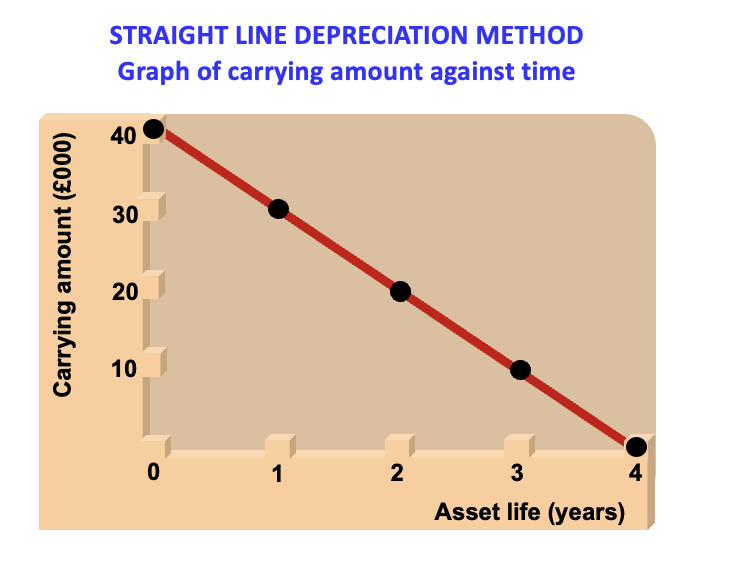
how do we do the straight line method and van example?
deduct the same amount each year
e.g. cost of van is £12,000, useful life is 5 years, residual value is £2000
depreciation charge = 12,000-2000 = 10,000/5 = 2000 each year
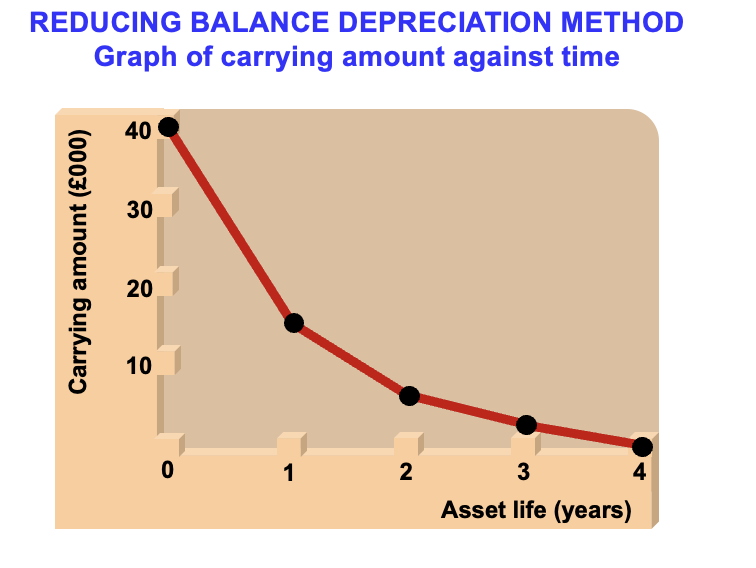
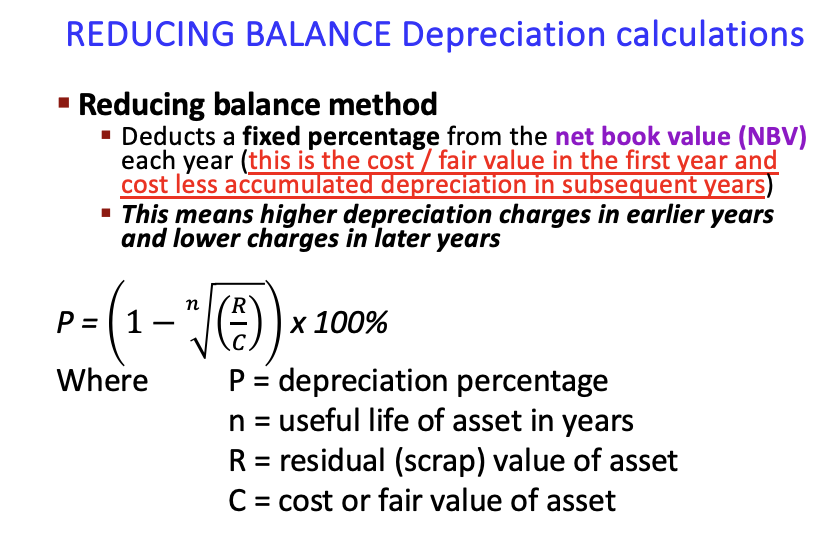
how do we do the reducing balance method?
deduct same % every year, but you deduct from a reducing amount each year e.g. in year 1 you deduct 30% of 10,000 but in year 2 you deduct 30% of 7000
straight line method graph
reducing balance method graph
formula for straight line method?
cost - residual value/number of expected years’ life
what is GP?
gross profit
what is OP?
operating profit
what list does depreciation come under?
operating expenses
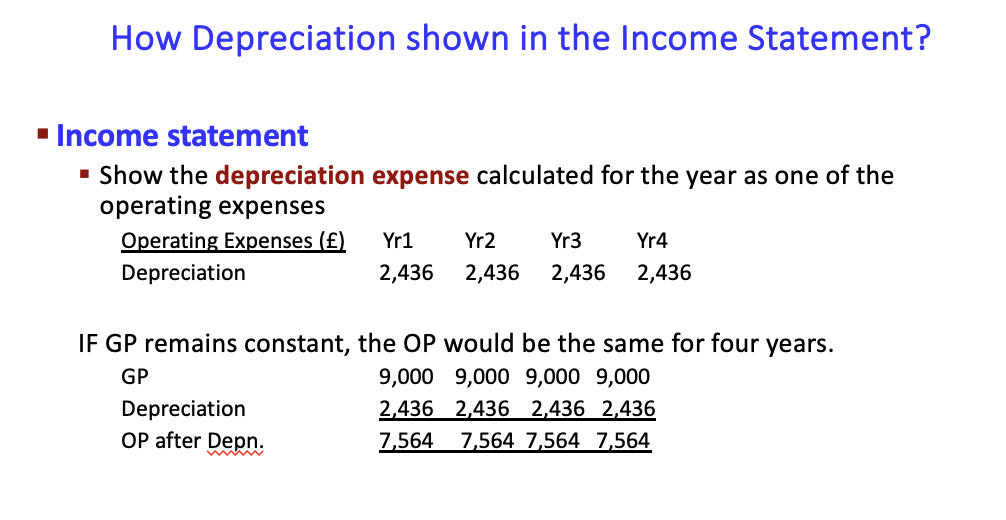
how is it shown in the income statement?
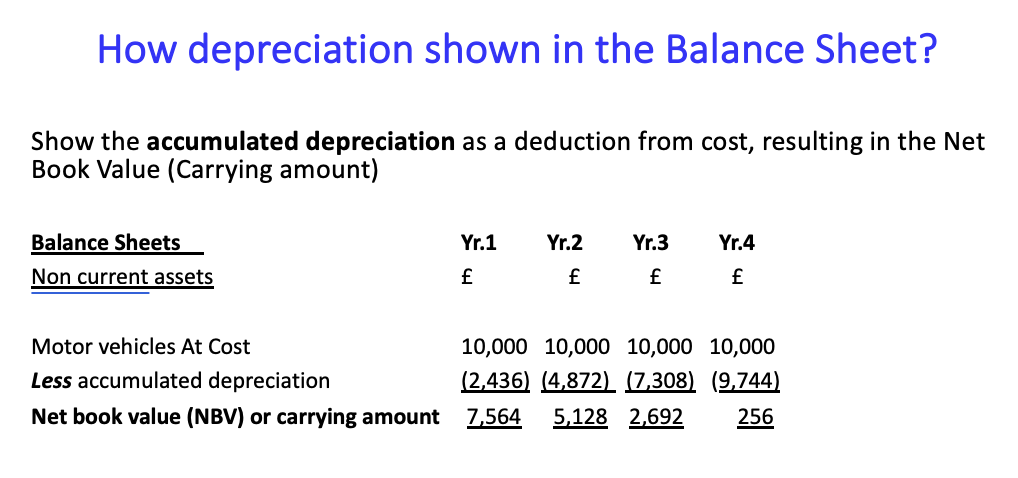
how is it shown in the balance sheet?
formula for reducing balance method
what happens when a non-current asset is sold?
the sale value is unlikely to be the same as the net book value of that asset, we need ton calculate a profit or loss on disposal
how do we calculate profit or loss on a disposal of an NCA? (4)
Determine NBV of asset at date of the sale and compare with selling price to see profit/loss
record profit/loss as a non-operating income/expense in IS
remove the asset and its accumulated depreciation from the BS
depending on how sale is paid for record cash or payable receivables
what are the two things the business need to determine in relation to inventories at the end of each accounting period? (valuing inventories)
the cost of the inventories sold or used up during the period
the cost of the inventories remaining at the end of the period
how do you determine the two things?
the business must make an assumption about how inventories are physically handled e.g. which inventories should the business assume sells first?
what are the 3 methods to value inventories?
FIFO (First in, first out)
LIFO (Last in, first out)
AVCO (Weighted average cost)
What is FIFO? (First in, first out)
the earliest inventories bought are the first to be sold
what is LIFO (last in, first out)
the latest inventories to be bought are first to be sold, not allowed in UK
what is AVCO (Weighted average cost)
the average purchase cost weighted by the volume of inventory purchased at different times is used as the cost of inventories
How is FIFO unique? (how does choosing this affect profit and closing inventory value on B/S)
will give highest profit and highest closing inventory value
How is LIFO unique? (how does choosing this affect profit and closing inventory value on B/S)
will give lowest profit and lowest closing value
how is AVCO unique? (how does choosing this affect profit and closing inventory value on B/S)
will give a value in-between
what are problems with trade receivables? (2)
bad debts and doubtful debts
how to bad debts arise?
sales made on credit, occur when the customer is unable to pay
how are bad debts treated in accounting e.g. the company who owes has gone bankrupt (4)
decrease trade receivables by the bad debt amount in BS
Increase expenses ‘bad debt written off’
we do not cancel original sale
what is a doubtful debt
company doesn’t know whether they will pay yet
what comes about on the B/S due to doubtful debts
allowance for trade receivables
how are doubtful debts treated in accounting (2)
decrease trade receivables on the B/S by required allowance
increase expenses on the I/S as ‘allowance for trade receivables’ by the same amount
what can businesses choose?
depreciation and inventory valuation methods
what does the business choice affect
profit and asset values, can make comparisons between firms difficult
what judgement does a business need to make about non-current assets
the useful life and residual value
what judgement is needed in terms of inventories
whether they should be valued at cost value or net realisable value, if NRV then an estimate must be made
what judgement is needed when considering the amount of doubtful debts to fill in allowance for trade receivables
the proportion of trade receivables that are deemed doubtful