PSYC 372 GMU Exam 1
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
127 Terms
Division of nervous system
Central Nervous System (CNS) and Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Division of central nervous system (CNS)
brain and spinal cord
Division of the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Somatic and Autonomic
Division of Autonomic Nervous System
sympathetic and parasympathetic
Santiago Ramon y Cajal
Hispanic doctor awarded the Nobel Prize in 1906 for his work on the structure of the nervous system
Neurons are composed of
dendrites, cell body, axon
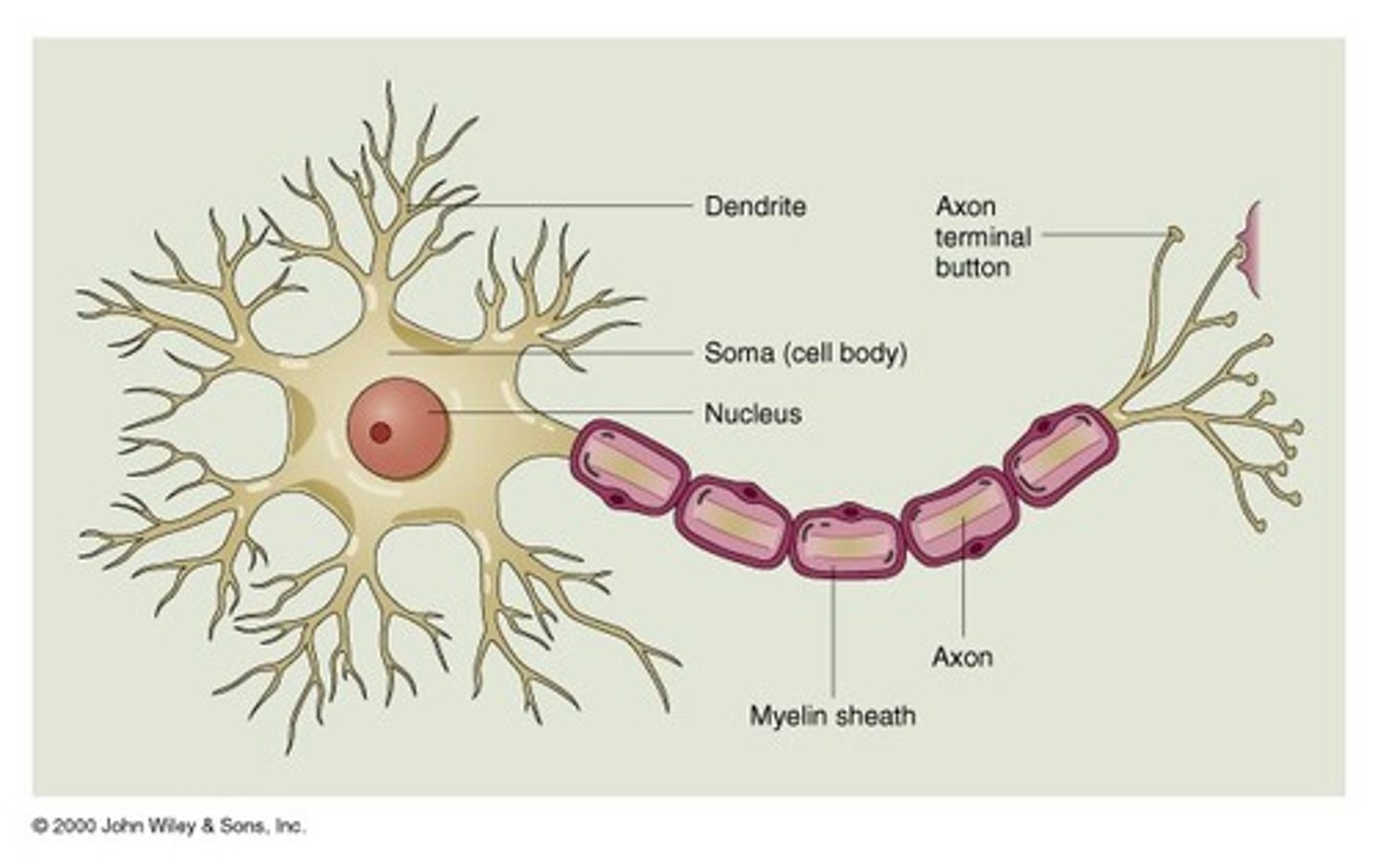
Types of Neurons
motor, sensory, interneurons
motor neurons
neurons that carry signals from the spinal cord to the muscles to produce movement
sensory neurons
neurons that receive information from the external world and convey this information to the brain via the spinal cord
afferent neurons
neurons that take information from the senses to the brain
efferent neurons
neurons that take information from the brain to the rest of the body
Sensory neurons are to _______________
as Motor neurons are to ______________
afferent; efferent
What are the types of glia
astrocytes, microglia, oligodendrocytes, schwann cells, radial glia
Radial Glia
Think: baby sitter
(guide) the migration of neurons and the growth of their axons and dendrites during (embryonic development)
Microglia
Think: platelets/white blood of the brain.
Act as phagocytes, eating damaged cells and bacteria, act as the brains immune system.
Schwan cells
Form myelin sheath in PNS
Oligodendrocytes
Form myelin sheath in CNS
Astrocytes
Think: supplier/ dealer
-Regulates chemical composition of extracellular fluid:Surrounds synapses, takes up or releases ions released by axons
-Remove waste when neurons die
-Control blood flow to brain areas, dilate blood vessels
action potential
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon.
6 ion movement process of action potential propagation
1. Na+ channels open, Na+ enters cell
2. K+ channels open, K+ leaves cell
3. Na+ channels become refactory no more no less (peak is hit)
4. Voltage gated channels open. K+ continues to leave cell, causing membrane potential to return to resting
5. K+ channels close, Na+ channels reopen.
6. Extra K+ diffuses away causing hyperpolerization
absolute refractory period
The minimum length of time after an action potential during which another action potential cannot begin.
relative refractory period
the period of time following an action potential, when it is possible, but difficult, for the neuron to fire a second action potential, due to the fact that the membrane is further from threshold potential (hyperpolarized)
Saltatory conduction
action potentials jump from node to node
How do neurons communicate?
By transmitting chemicals at junctions (synapse)
Who is Sherrington?
Studied reflexes: Dog in harness and pinched its feet.
- The Reflex arc
Reflex arc
A relatively direct connection between a sensory neuron and a motor neuron that allows an extremely rapid response to a stimulus, often without conscious brain involvement.
Three important points about Reflexes made by Sherrington
(1) Reflexes are slower than conduction along an axon
(2) Several weak stimuli present at slightly different times or slightly different locations produce a stronger reflex than a single stimulus
(3) As one set of muscles becomes excited, another set relaxes
How does length and number of neuron effect communication speed?
E1: (a)-------------< (b) shorter time
E2: (c)----<(d)-----< (e) longer time
temporal summation
Summation by a postsynaptic cell of input from a single source over time.
spatial summation
The sum of multiple synapses firing at different locations at one time to create a net effect.
excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP)
a slight depolarization of a postsynaptic cell, bringing the membrane potential of that cell closer to the threshold for an action potential
inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP)
temporary hyperpolarization of a membrane
presynaptic neuron
neuron that sends the signal
postsynaptic neuron
neuron that receives the signal
IPSP are both EPSP
Graded Potentials
Otto Loewi's experiment
- Frog heart experiment
- Realized that he was collecting and transferring chemicals, not loose electricity
types of neurotransmitters (NT)
Amino Acids
A modified amino acid
Monoamines
Neuropeptides
Purines
Gases
NT: Amino acid
Glutamate, GABA, glycine
Asparate
NT: A modified amino acid
Acetylcholine
NT: monoamines
indoleamines: serotonin
Catecholamines: Dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine
NT: Neuropeptides
Endorphines, substance P,
neuropeptide Y
NT: Purines
ATP, adenosine
Gases
NO (nitric oxide)
ionotropic effects
synaptic effects that depend on the rapid opening of some kind of gate in the membrane
Quick
metabotropic effects
effect at a synapse that produces a relatively slow but long-lasting effect through metabolic reactions
Long lasting and slow
Pain and smell is to __________
as vision and hearing is to _________.
Metabotropic effect; Ionotropic
Drugs that bind to receptors
- Many hallucinogenic drugs
- Nicotine
- Antipsychotic drugs
- Opiates
Nicotine stimulates the ________ receptors. Resulting in a ___________ feeling
acetylcholine; rewarding
Antipsychotic drugs block --------- receptors.
Side effects: decreased pleasure and motivation
Dopamine
Opiates bind to _______________ receptors , thus reliving ___________.
endorphin; pain
Dorsal (posterior)
toward the back or spine
Ventral (anterior)
Toward the belly or front
Superior
toward the head, Above
Inferior
away from the head, towards to feet, down/ below
Lateral
Away from the midline of the body
Medial
Toward the midline of the body
Proximal
Closer to the point of attachment
Distal
away from the point of attachment
Ipsilateral
on the same side of the body
Contralateral
on the opposite side of the body
Coronal plane
divides body into front and back
saggital plane
divides the body into a right and left side
Horizontal plane (transverse plane)
divides body into top and bottom
gyrus (gyri)
rounded elevation on the surface of the brain
Lamina
Row or layer of cell bodies separated from other cell bodies by layer of axons and dendrites
Suclus
A fold or groove that separates one gyrus from another
Fissure
a long, deep sulcus
Spinal cord consist of what two types of matter
Grey and white Matter
White matter
Whitish nervous tissue of the CNS consisting of neurons and their myelin sheaths.
Grey Matter
- The portions of the central nervous system that are abundant in cell bodies of neurons rather than axons. - Unmyelinated.
autonomic nervous system
Sends and receives messages to regulate the automatic behaviors of the body (heart rate, blood pressure, respiration, digestion, etc.)
Sympathetic Nervous System
- A network of nerves that prepares the organs for rigorous activity
- (fight or flight)
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Facilitates vegetative and nonemergency responses
- Rest and Relaxation
Neurotransmitters in the ANS:
parasympathetic mostly uses ___________ as Sympathetic mostly uses ______________
Acetylochine; norepinephrine
Major division of the brain
Fore-brain; mid-brain; Hind-brain
Major structures in the forebrain
thalamus, hypothalamus, cerebral cortex, hippocampus, basal ganglia
Major structures in the Midbrain
tectum, tegmentum, superior colliculus, inferior colliculus, substantia nigra
Major structures in the Hindbrain
medulla, pons, cerebellum
- they combine to make up brain stem
medulla oblongata
hint: gotta go long
Responsible for vital life-sustaining functions such as heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure, digestion, and vomiting
Cranial Nerves
Allow the medulla to control sensations from the head, muscle movements in the head, and many parasympathetic outputs
Cranial Nerve I: Olfactory
smell
Cranial Nerve III: Oculomotor
eyelid movement, pupil constriction and accommodation
Cranial Nerve II: Optic
vision
Cranial Nerve IV: Trochlear
eye movement
Cranial Nerve V: Trigeminal
Skin sensations from most of the face; control of jaw muscles for chewing and swallowing
Cranial Nerve VI: Abducens
eye movement
Cranial Nerve VII: Facial
facial expression; taste - anterior 2/3 of tongue; eyelid and lip closure
Cranial nerve VIII: Vestibulocochlear
hearing and equilibrium
Cranial Nerve IX: Glossopharyngeal
gagging; swallowing - sensory; taste
Cranial Nerve X: Vagus
Sensation from neck and thorax; control of throat, esophagus, and larynx parasympathetic nerves to stomach, intestines and other organs
Cranial Nerve XI: Accessory
Control of neck and shoulder movement
Cranial Nerve XII: Hypoglossal
movement of tongue
Mnemonic for cranial nerves
(rated R)
Oh Oh Oh To Touch And Feel Virgin Girl Vagina Ah Heaven
Pons (bridge)
the part of the brainstem that links the medulla oblongata and the thalamus.
Cerebellum (Bella Balance)
Balance and coordination
Tectum
roof of the midbrain
superior colliculus is to ___________
as inferior colliculus is to __________
vision; hearing or eye movement ; auditory information processing
Tegmentum
contains nuclei for cranial nerves and part of the reticular formation
substantia nigra
gives rise to the dopamine-containing pathway facilitating readiness for movement
limbic system
Associated with motivation emotions, such as eating, drinking, sexual activity, anxiety, and aggression