BIO120 CH5
1/185
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
186 Terms
what things make up amino acids
central (alpha) carbon atom
amino group
carboxyl group
R group (side chain)
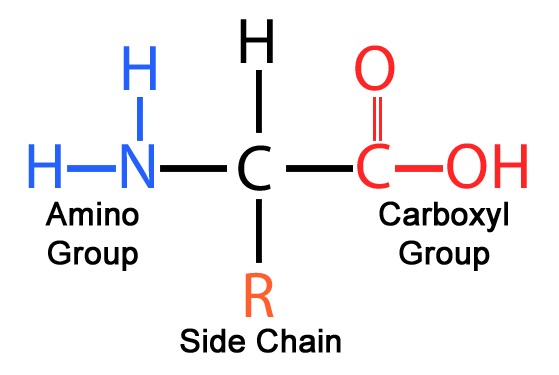
how are the structures of amino acids connected
with covalent bonds
in a neutral cell environment, the amino group gains what and the carboxyl group loses what
the amino group gains a proton and the carboxyl group loses a proton to become charged
who gains/loses a proton? the amino acid or the carboxyl group
amino group=gains a proton
carboxyl group=loses a proton
is the R group of an mino acid the same in every amino acid
no the R group is different from one amino acid to the next
how are R groups grouped
based on properties (hydrophilic, hydrophobic, etc.)
amino acids link together to form
proteins
what is the bond between amino acids called
peptide bond
in a peptide bond (each amino acid has a carboxyl group and hydroxide) the carboxyl group of one amino acid reacts with what
another amide group of another amino acid
what is the carbonyl group in the peptide bond
C=O group
what is the amide group in peptide bond
N-H group
when a peptide bond is formed as a result of a carboxyl group from one amino acid bonding to the amino group of another what is released
a molecule of water
what is a polypeptide
a polymer of amino acids or peptides
how is a peptide bond formed
a carboxyl group from one amino acid bonds to the amide group of another
how many amino cells make up polypeptides in cells
several hundred amino acids
what makes up the primary structure
the sequence of amino acids (3 letter abbreviation) in a protein
what structure determines how a protein folds
the primary structure
what makes up the secondary structure
interactions between amino acids
what is the tertiary structure
longer range interactions between secondary structures support 3D shape of the polypeptide
what is the quaternary structure
proteins are made up of several polypeptides which interact with each other and make up this structure
what are three brand functions of proteins in a cell
structural elements
communicate with environment
accelerate chem reactions
the ability of a protein to carry out its function depends on what
its 3D shape
what enables protein folding
the primary-quaternary structures of a protein
what’s so important about protein folding
its an important part of cellular function and health
what happens if proteins are misfolded
can cause diseases like Alzheimers and parkinsons
what are prions
the misfiled form of a normal protein found in the body, prion-protein
what type of bonds form between carbonyl and amide groups in different amino acid molecules
hydrogen bonds
hydrogen bonds form between what two molecules in two different amino acid molecules
carbonyl and amide groupswh
what do hydrogen bonds do to DNA
help stabilize helix structure
what are the two types of secondary structure found in DNA
alpha helix
beta sheet
what are alpha helix and beta sheets
two types of secondary structures found in DNA
in which secondary structure is the polypeptide backbone twisted tightly in a coil with 3.6 amino acids per turn, R groups project outward from helix
alpha helices
describe the structure of alpha helices
polypeptide backbone is twisted tightly in a coil
3.6 amino acids per turn
R groups project outward from helix
what is the polypeptide structure that folds back and forth on itself, R groups project alternately above and below the pleated beta sheet
beta sheet
describe the beta sheet
polypeptide structure that folds back and forth on itself
R groups project alternately above and below pleated beta sheet
what are secondary structures
how amino acids in polypeptide chain interact with each other and Alpha and beta and how they interactw
what is the tertiary structure of a protein
3D conformation of a polypeptide chain, composed of several secondary structural elements
what is the tertiary structure made of
several secondary structural elements
how is the tertiary structure determined
by spatial distribution of R groups
what determines the secondary and tertiary structures
the primary structure
the primary structure determines what
the secondary and tertiary structure
the tertiary structure determines what
function
what is included in the 3D shape of the tertiary structure
contours, distribution of charges and pockets
what does the shape of tertiary structure do for the protein
enables proteins to serve as structural support, membrane channels, enzymes, or signaling molecules
what is denaturation
the process by which molecules are unfolded and lose their structure
what is the process by which molecules are unfolded and lose their structure
denaturation
how can proteins be denatured
by heat or thru chem reaction
what must happen in order for a protein to denature
the ionic and hydrogen bonds within proteins must be broken to disrupt their tertiary structure
some proteins are complete as a single polypeptide chain with
tertiary structure
many protein include multiple polypeptide chains that come together to form a
quaternary structure
what makes up the quaternary structure
multiple polypeptide chains that come together
can the smaller subunits that make up a protein be different or need to be identical?
can be identical OR different
what is the primary structure
sequence of amino acids
how fast do proteins fold
quickly in a matter of milliseconds
when are proteins vulnerable to improper folding
in unfolded denatured state
what is exposed in the unfolded state of a protein
hydrophobic groups are exposed to other macromolecules
where does protein folding occur
in cells cytoplasm
what can prevent the protein from folding properly
when hydrophobic group interact with other molecules before folding
what are chaparones
specialized proteins that protect the protein as it undergoes folding process
what protects proteins during the folding process
chaperones
secondary structure refers to
hydrogen bonding between amino acids forming alpha helix and beta sheet structures
tertiary structures make up
3D shape of proteins due to interactions between R groups
when is the sequence of bases in DNA used for template for RNA
during transcription
what happens during transcription
sequence of bases in DNA is used for template for RNA
when is the sequence of bases in RNA (or mRNA) is used to specify the order of amino acids added to new polypeptide chain
during translation
what happens during translation
the sequence of bases in RNA (mRNA) is used to specify the order of amino acids added to a new polypeptide chain
what are the components needed for translation
Ribosomes
small subunit
large subunit
what are ribosomes
made of RNA and proteins that bind with RNA
where is the site of translation
ribosomes
how many types of ribosomal RNA are contained in ribosomes
1-3
how many types of ribosomal proteins are contained in ribosomes
20-50
what is the order or binding sites for tRNA
EPA (environmental protection agency)
what does the small subunit do
read mRNA to make sure genetic code is translated correctly into proteins
aligns the genetic code
where are the 3 binding sites for tRNA
in the large subunit
what is the a site (name)
aminoacyle A site
what is the name of the p site
peptide site
what is the name of the E site
exit site
when mRNA is in place on the ribosome, the mRNA sequence is read in groups of what
3 nucleotides or codons
each codon in the mRNA codes for what in the polypeptide chain
a single amino acid
what in the mRNA codes for a single amino acid in the polypeptide chain
each codon
what establishes the correct reading frame for codons
ribosome
the ribosome will establish what
the correct reading frame for codons
translation of each codon in mRNA into an amino acid is carried out by what
tRNA
what does tRNA do
tRNA translates each codon in mRNA into an amino acid
what are tRNAs
small RNA molecules
what makes up a tRNA
70-90 nucleotides with a self-pairing structure
what makes up the anticodon
three bases in the anticodon loop
what is the anticodon
3 nucleotide sequences that are complementary to mRNA codon
what connects specific amino acids to tRNA
enzymes called aminoacyl tRNA synthetases
what is aminoacyl tRNA synthetases
enzymes
what is aminoacyl tRNA synthetases responsible for
translating codon sequence in a nucleic acid to a specific amino acid in a polypeptide chain
how many aminoacyl tRNA synthetases do most organisms have
most have only one for each amino acid
where does aminoacyl tRNA synthetases bind
to multiple sites on any tRNA molecules that have an anticodon corresponding to an amino acid
aminoacyl tRNA synthetases binds to multiple sites on any tRNA molecule that has what
an anticodon corresponding to an amino acid
a tRNA that has no amino acid attached to it is (charged/uncharged)
unchargeda
a tRNA that has an amino acid attached is (charged/uncharged)
charged
how accurate is aminoacyl tRNA synthetases
very accurate and rarely attach the wrong amino acid
which is there more of, codons or amino acids
codons
amino acids are specified by
more than one codon
is genetic code redundant?
yes