bio 462 ch 1
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
overview of the nervous system
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
why brain
behavior, processing info
old conception
brain is part of a sensory motor system
output is the consequence of input (reflex loops)
exception to old conception (what made it wrong)
dreams and cognition
current conception
brain makes a representative model of our world through our senses
evidence for current conception
appearance of neurons coincided with appearance of movement during hunting
learning
prediction-action model = brain builds a virtual model of the future (prediction), which is compared with a movement physically entering the future (action)
some connections get stronger, others get weaker
neuronal ensembles
independent units of neurons that are grouped together and become activated together to build internal thoughts, memories, ideas, etc
organized into hierarchies
modules
specific diagrams that must be precise
wiring of neurons links different…
modules
precise connections
neurons connect only with set particular ones
distributed connectivity
many connections are pruned and tweaked through learning
neurons are lost until the perfect wiring is created
two types of wiring
precise and distributed
learning is which type of wiring?
distributed
Hebb’s rule
associative learning
when two or more neurons are activated at the same time, their connections are strengthened, which is how memories are built
associative learning
association of separate stimuli when neurons fire together and form a unit
spatial topographic maps
ex. position of object in space correlates to specific position in retina
wiring diagrams are organized in…
maps, which provide representations
control theory
compare output with the prediction
error signal causes fine-tuning of output
(feedback control)
optimization
work must be performed effectively at minimal energy cost
machinery of the nervous system is extremely optimize
how many of total genes are expressed in the nervous system
2/3
how many of total genes are expressed UNIQUELY in nervous system
1/3
signal in neurons
electricity provided by ion currents
axon
extends out for long distance signaling
usually connect to dendrites of another neuron
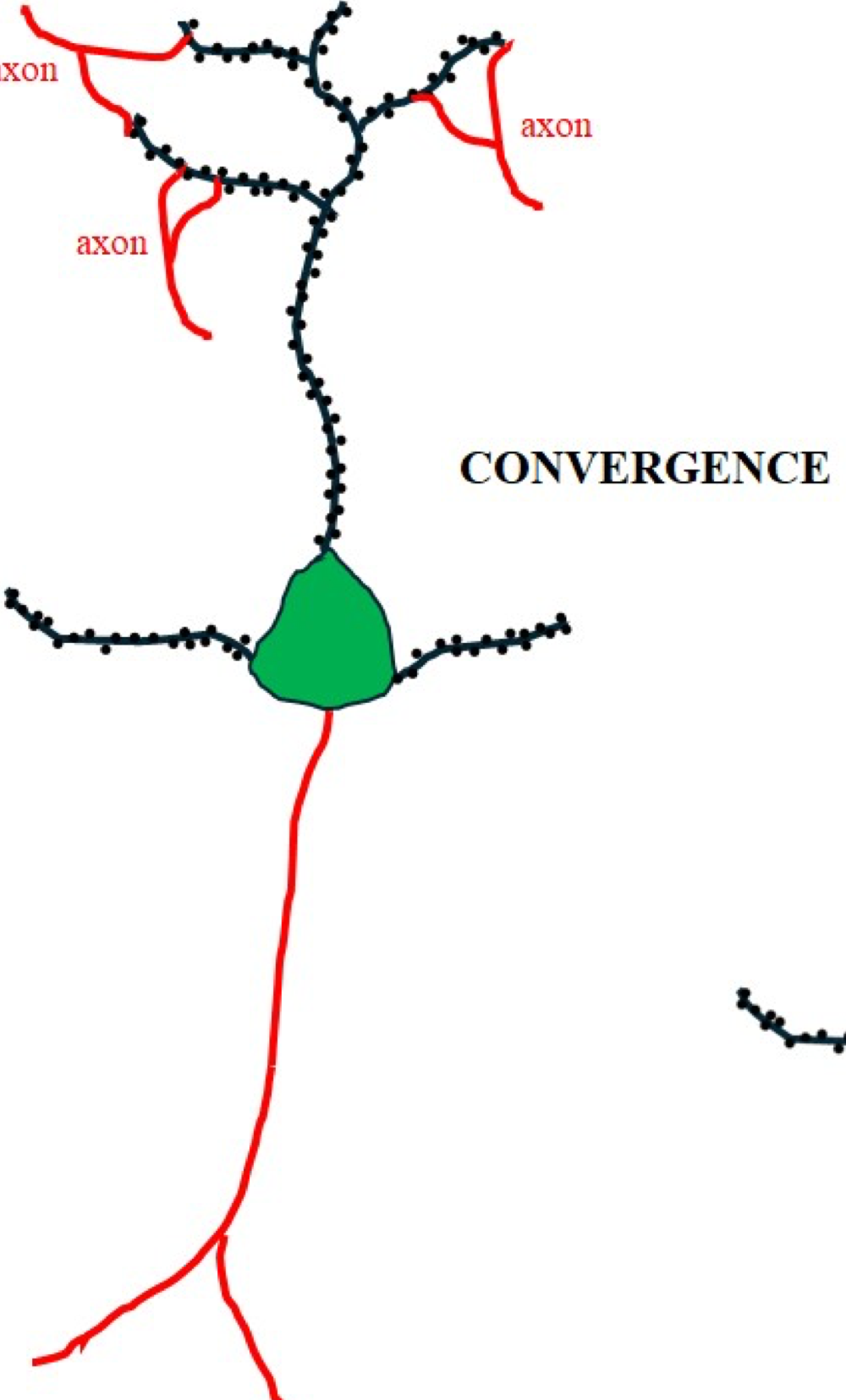
converge
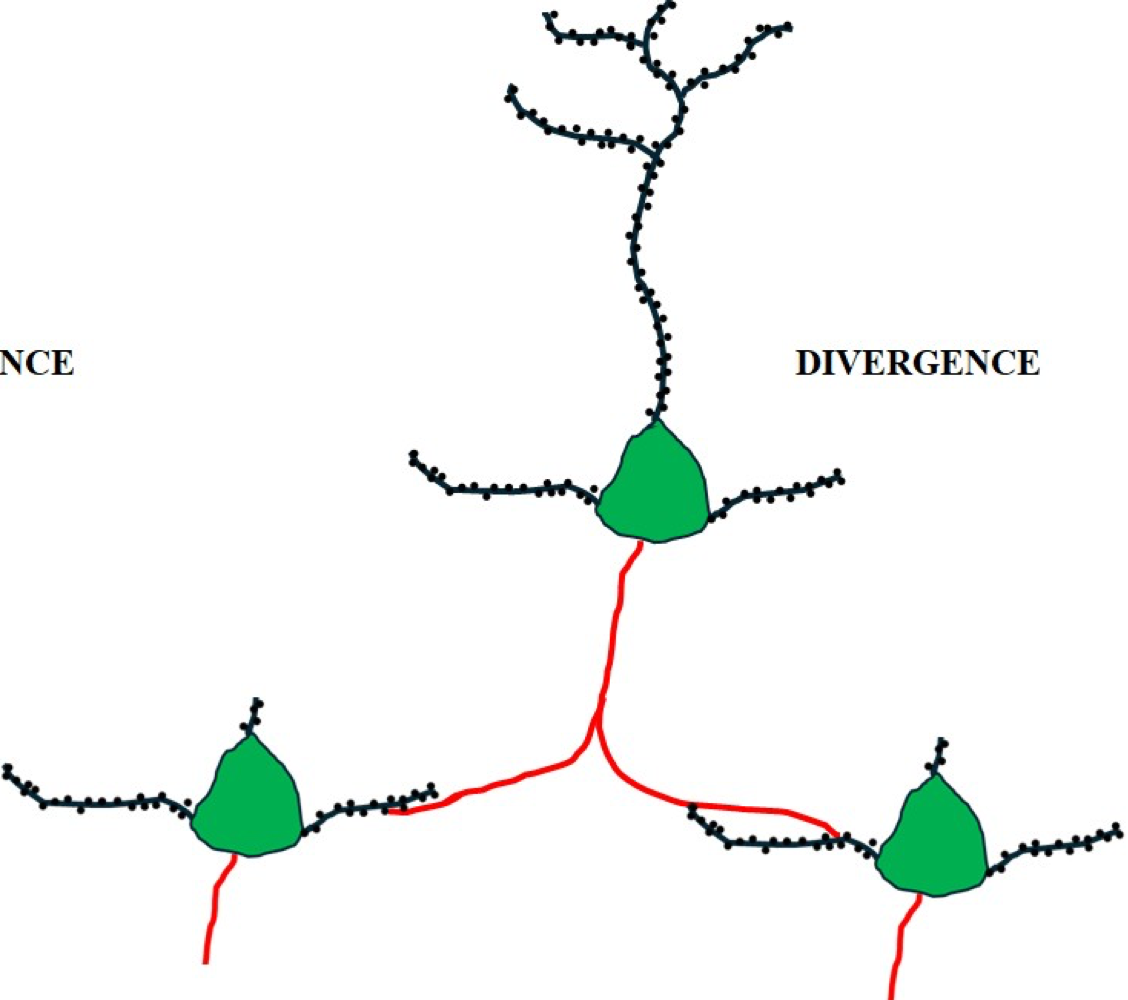
diverge
action potential
generated as a signal for the neuron
all or none, on or off
shape is similar in many species
results from integration of several inputs if threshold of depolarization is reached
constant amplitude
neurons connect to other neurons through…
synapses
chemical synapse
secretion of neurotransmitter between a pre-synaptic and a post-synaptic terminal
vesicles carrying neurostransmitter exocytose through membrane into synapse and bind to receptors
post-synaptic cell
expresses the receptor of the neurotransmitter
electrical synapse
direct link between neighboring cytoplasms
gap junction
closer joining of the two membranes, much faster
local potentials
slow and graded
amplitude depends on intensity of the input
ionotropic receptors
ion channels open with ligand binding
fast acting
metabotropic receptors
coupled to second messengers that cause chemical cascades
slow acting
EPSP
local excitatory post-synaptic potential caused by the movement of ions
IPSP
local inhibitory post-synaptic potential caused by the movement of ions
dendritic spines
contact of axons of excitatory terminals
soma
contact of axons of inhibitory terminals
central nervous system (CNS)
brain and spinal cord
cell bodies
peripheral nervous system (PNS)
cell bodies outside of brain and spinal cord
sensory systems
receive and process information from environment (input)
sensory ganglia and nerves, sensory receptors
motor systems
generate movement (output)
sympathetic, parasympathetic, enteric
autonomic ganglia and nerves
motor nerves
associational systems
complex brain functions
astrocytes
maintain a balanced environment around neurons and synapses
oligodendrocytes
form myelin around axons in CNS
multiple axons at once
schwann cells
form myeling around axons in PNS
one axon at once
myelin
multilayered membrane around axons
provides insulation and structural support, speeds up electrical signal
microglia
immune cells of CNS
mediate inflammation
same origin as macrophages (mesoderm)
prune synapses