Two-Dimensional Imaging (Basic Ultrasound Physics-Chapter 12)
1/208
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
209 Terms
Sound travels in a _____ line.
straight
Sound beams must be ____ to optimize lateral resolution.
narrow
Sound beams must be narrow to optimize _____ resolution.
lateral
How does an ultrasound system create high quality, dimensional images?
2 characteristics:
____
____
Sound travels in a straight line
Sound beams must be narrow to optimize lateral resolution
Ultrasound systems send _____ pulses into the body, receives reflections from those pulses, processes them, and then stores them
narrow
Ultrasound systems send narrow pulses into the body, receives ____ from those pulses, _____ them, and then ____ them
reflections ; processes ; stores
After the first beam is fired into the body, a second pulse is sent at (the same / a different) angle than the first, and so on thereafter
a different
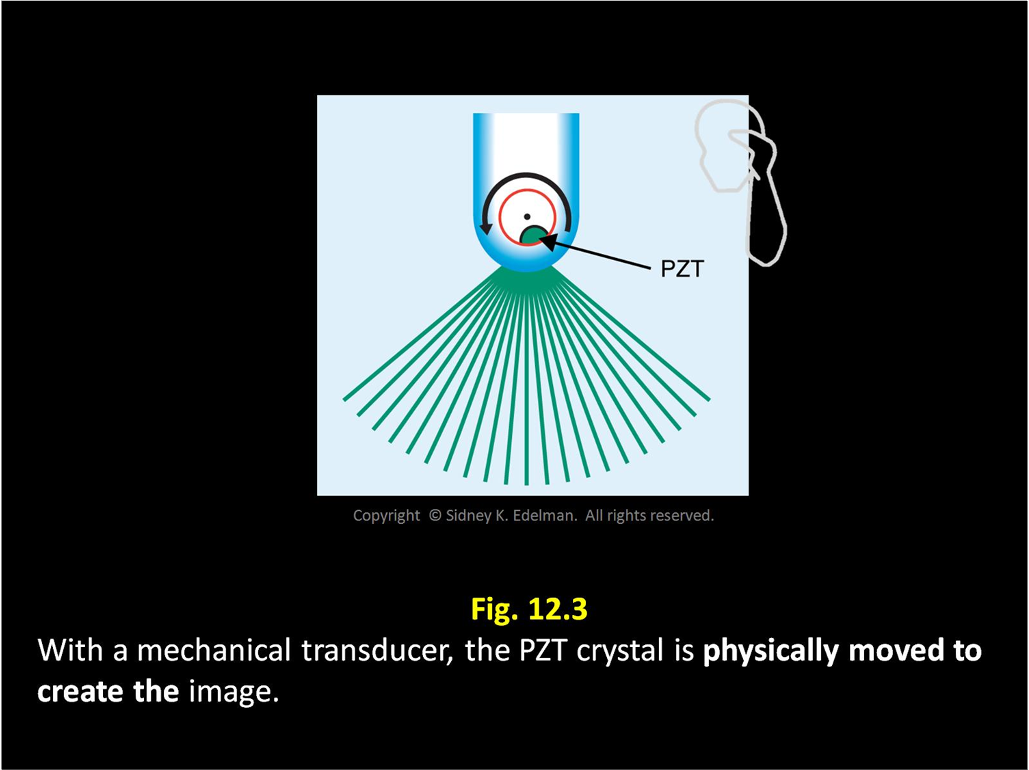
Mechanical transducers contains (single/multiple), ____, ____-shaped active element (Looks like a ____)
single ; circular ; disc ; coin
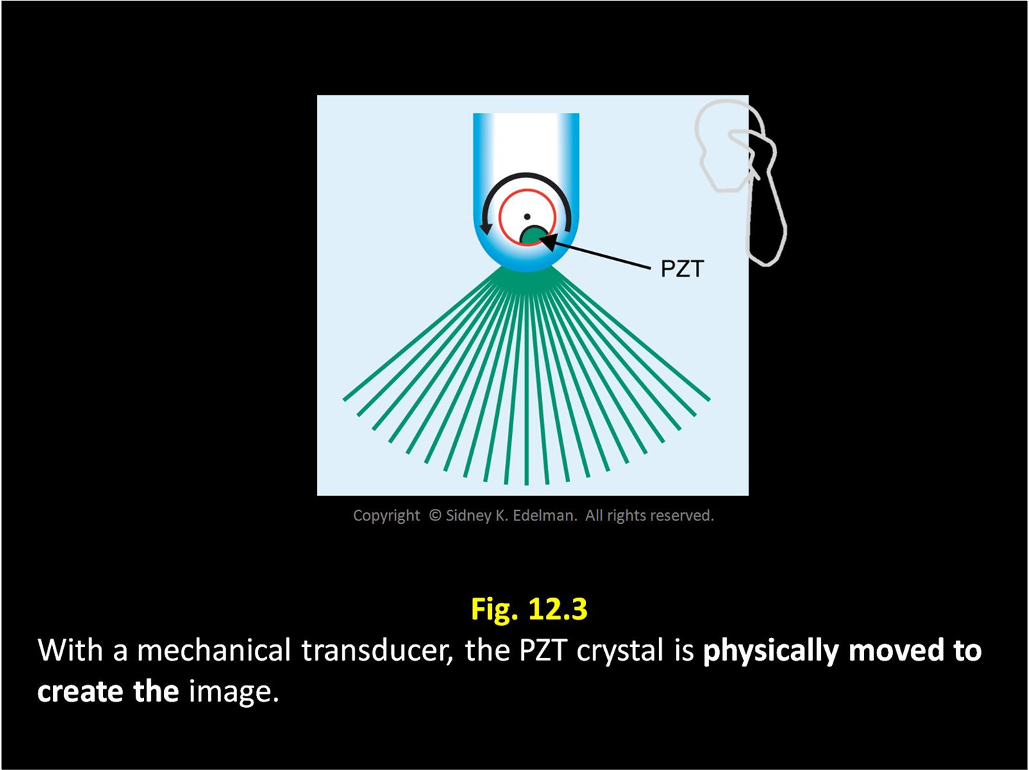
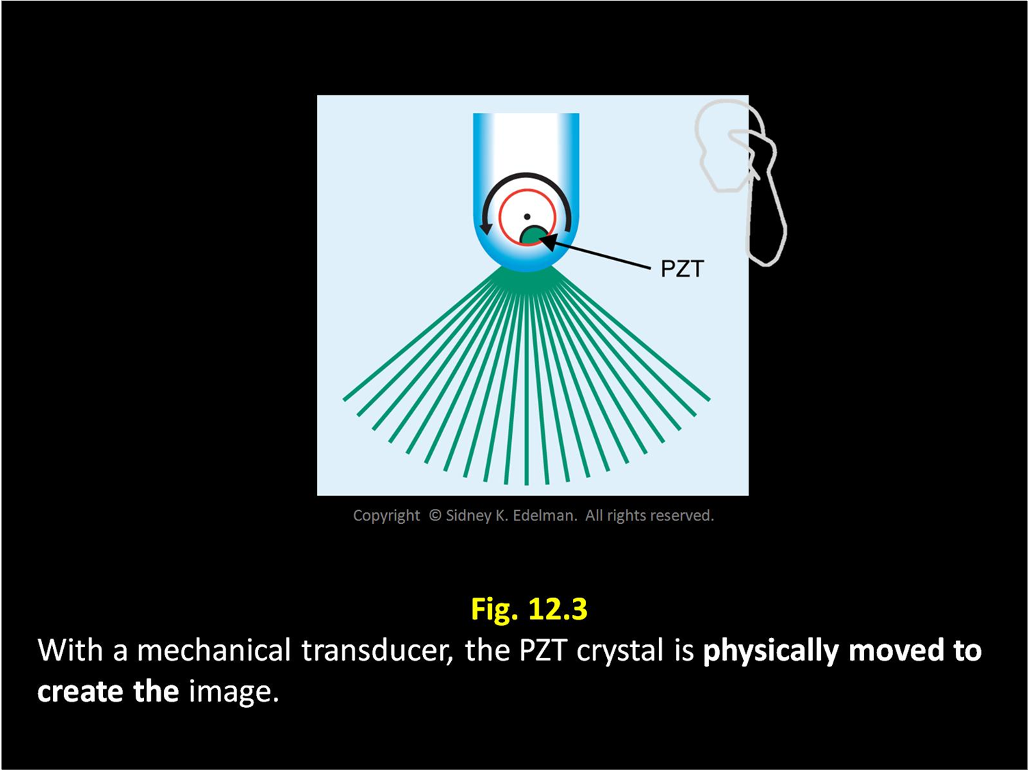
Mechanical transducers create a ___ or ___-shaped image, like the ____ of a ____ ___ ____.
fan ; sector ; sweeping of a windshield wiper blade
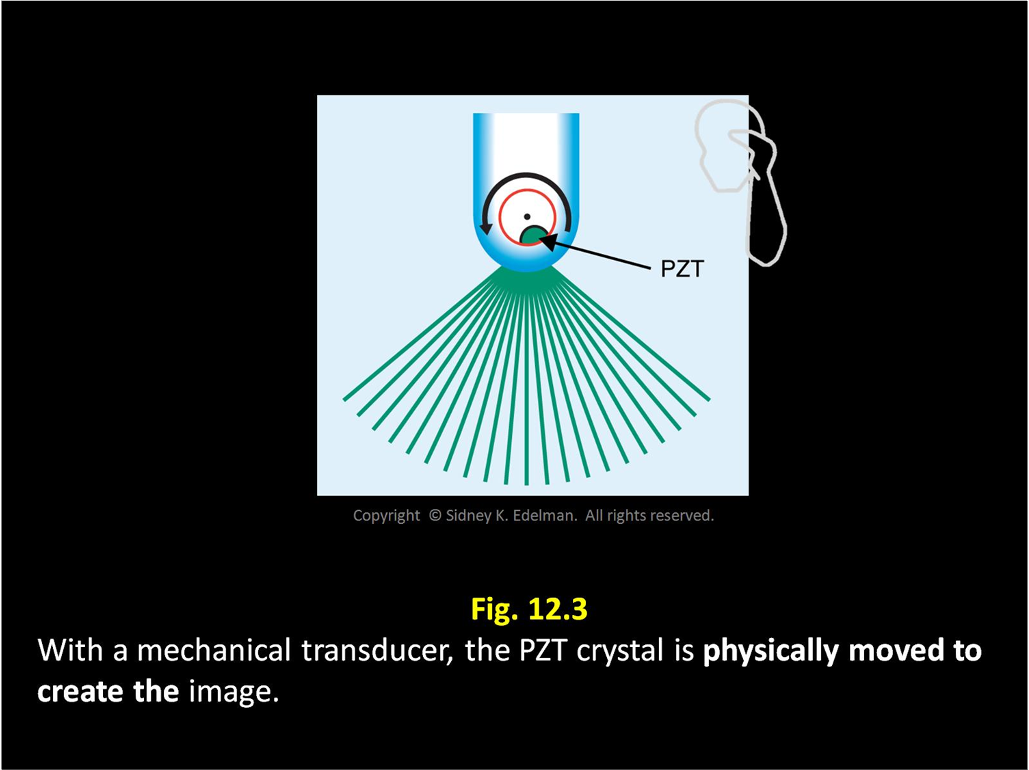
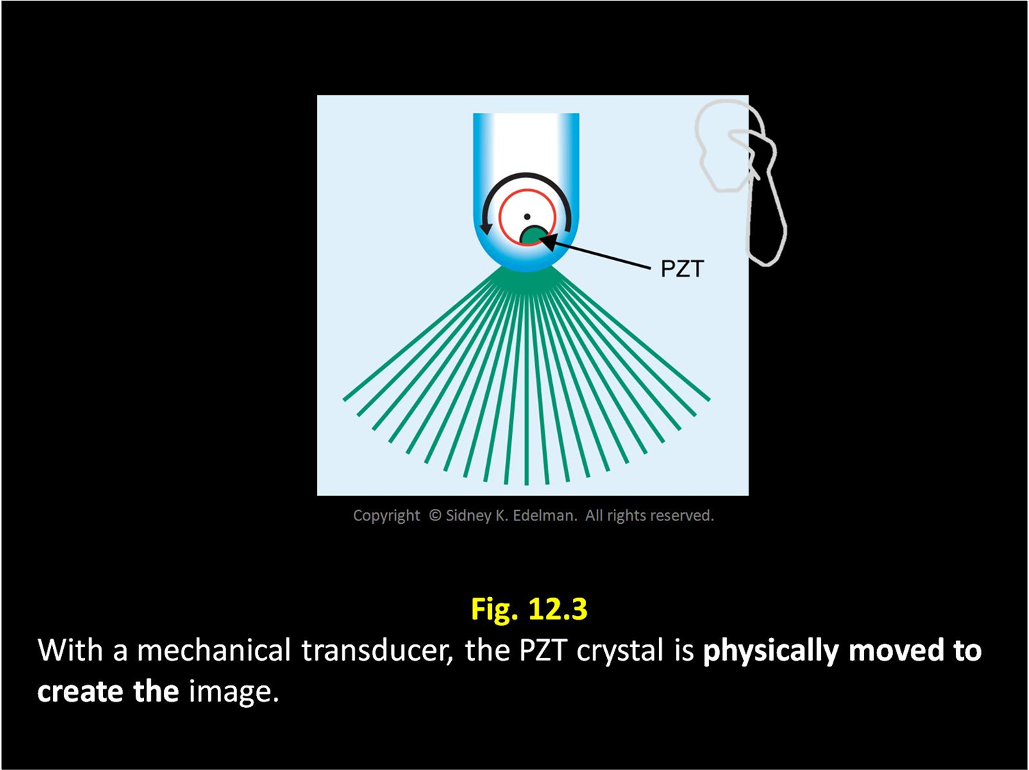
As the mechanical transducer rotates, pulses come from ____-like ____ on a ___ ____
PZT ; spokes ; bicycle wheel
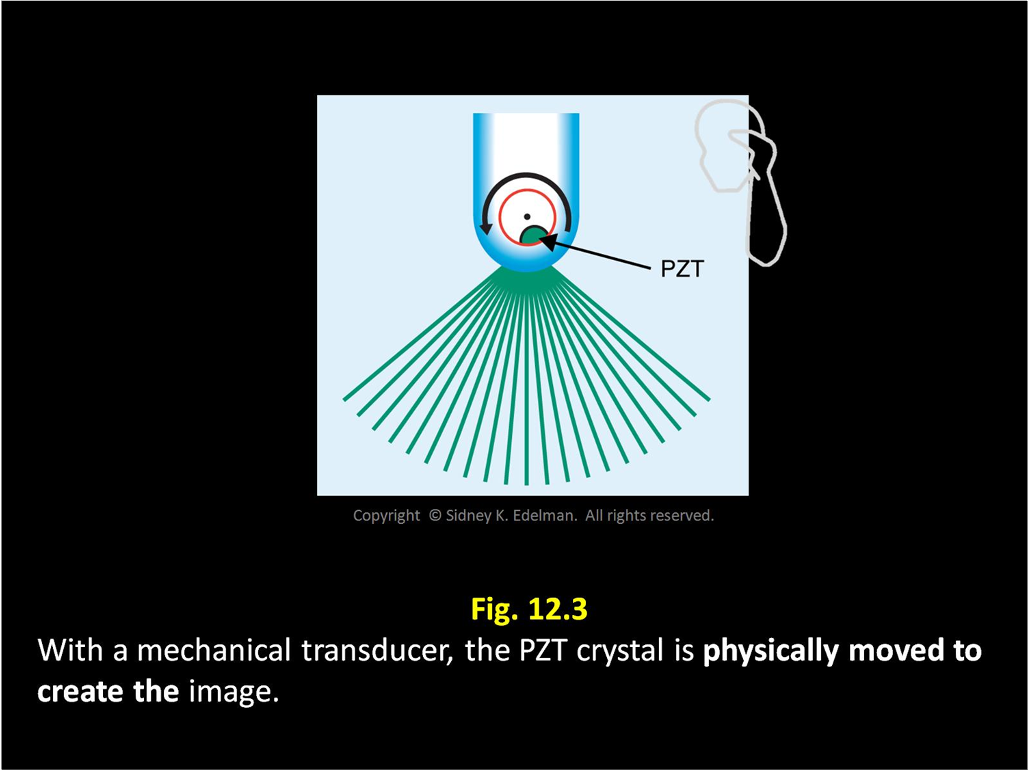
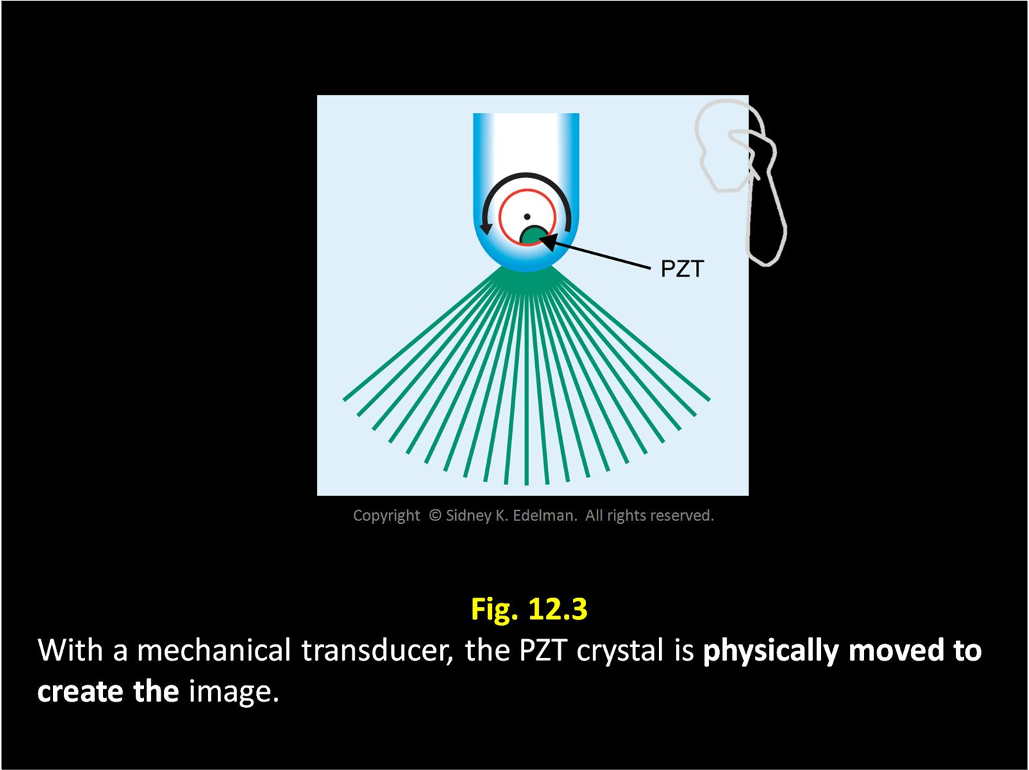
When using a mechanical transducer, the gaps between the pulses ____ with greater depth.
increase
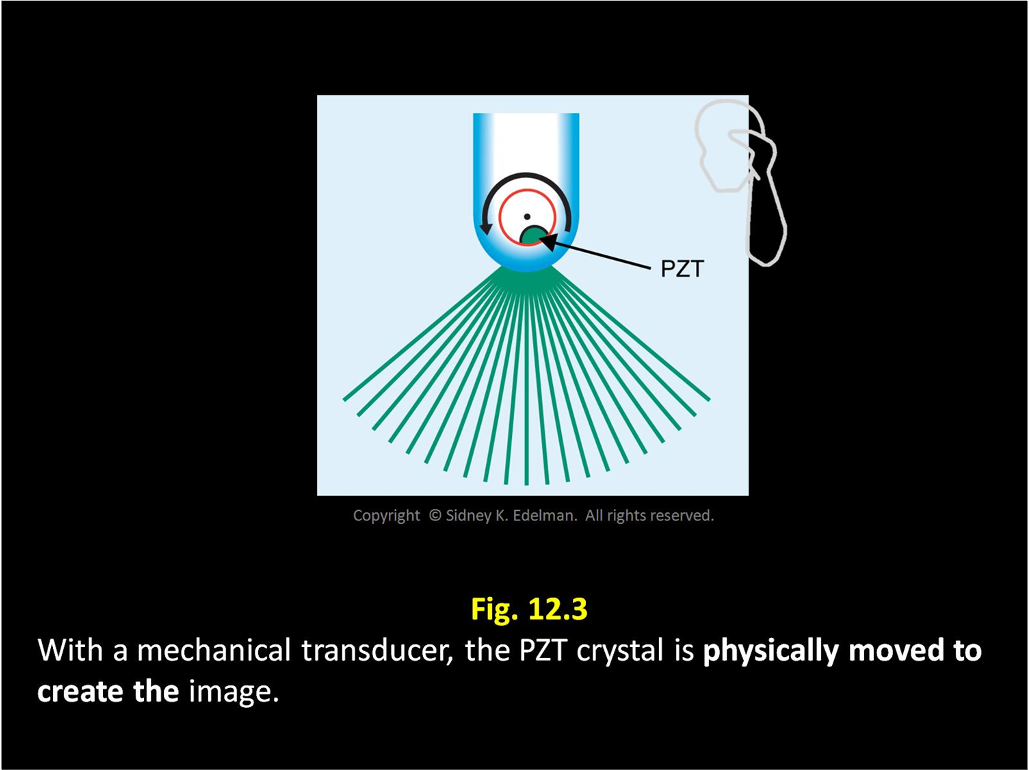
When using a mechanical transducer, the gaps between the pulses increase with greater ____.
depth
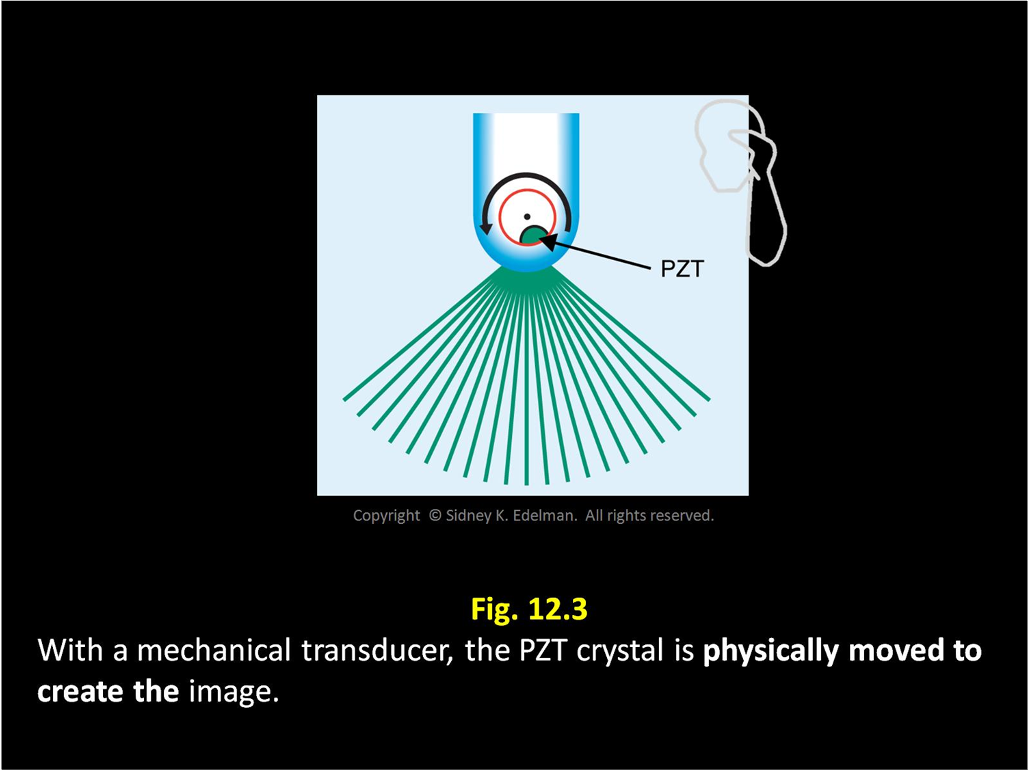
When using a mechanical transducer, the gaps between the pulses increase with (greater/lesser) depth.
Greater
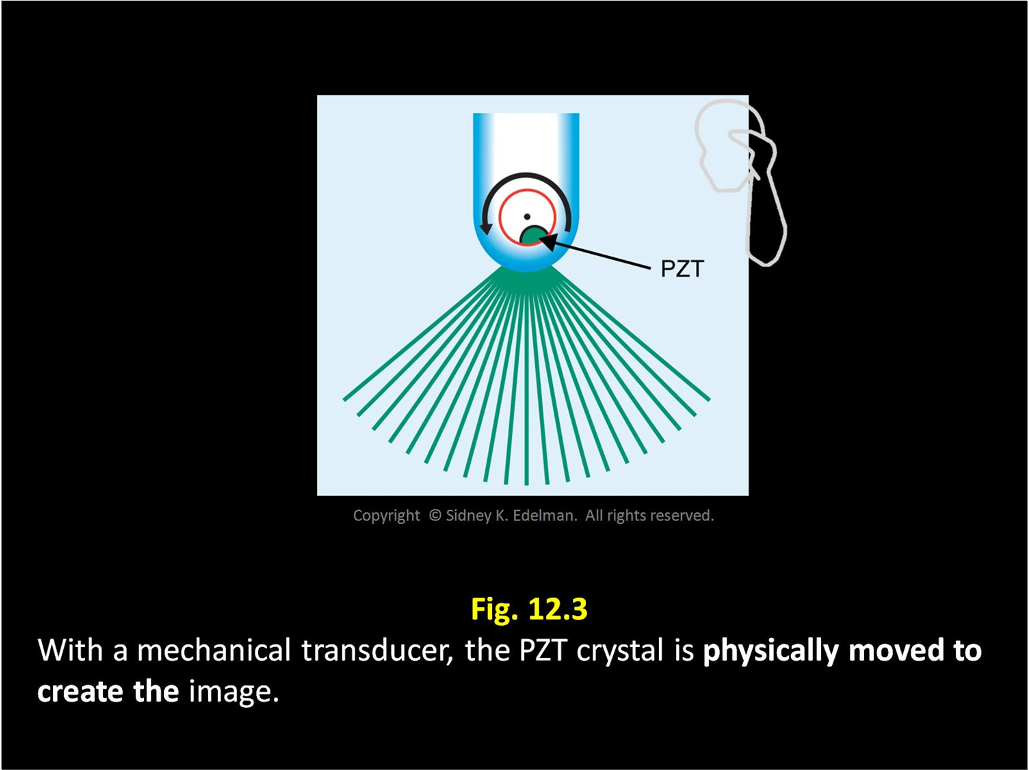
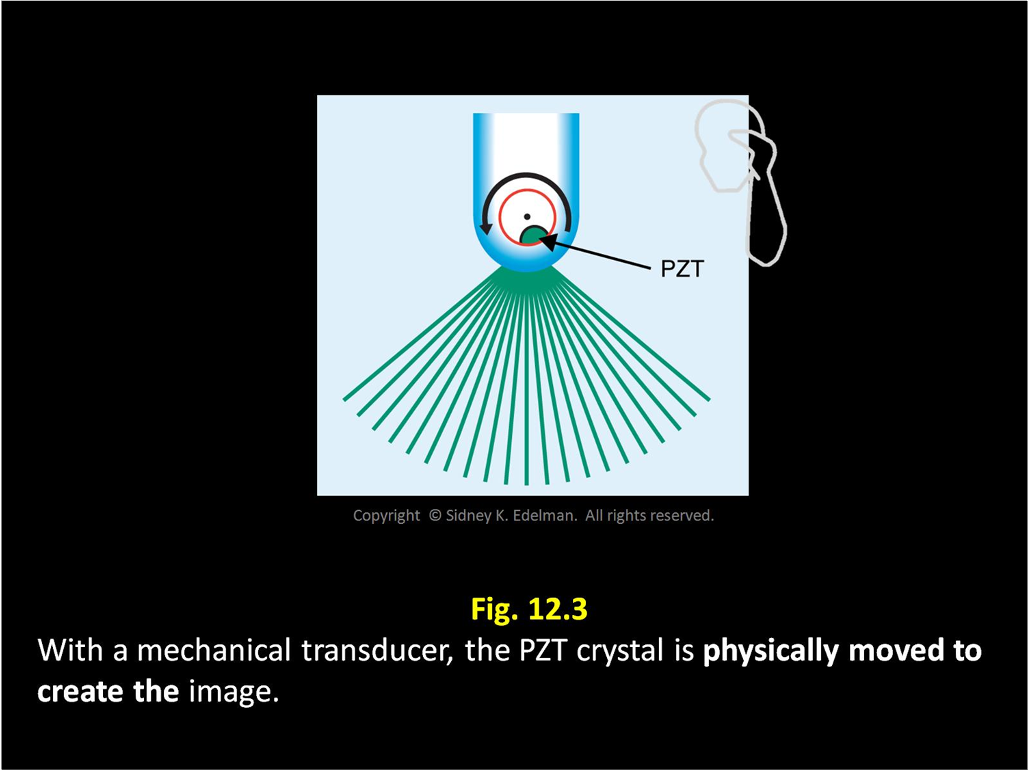
With mechanical transducers, the image is created by _____
rotating the crystal with a motor
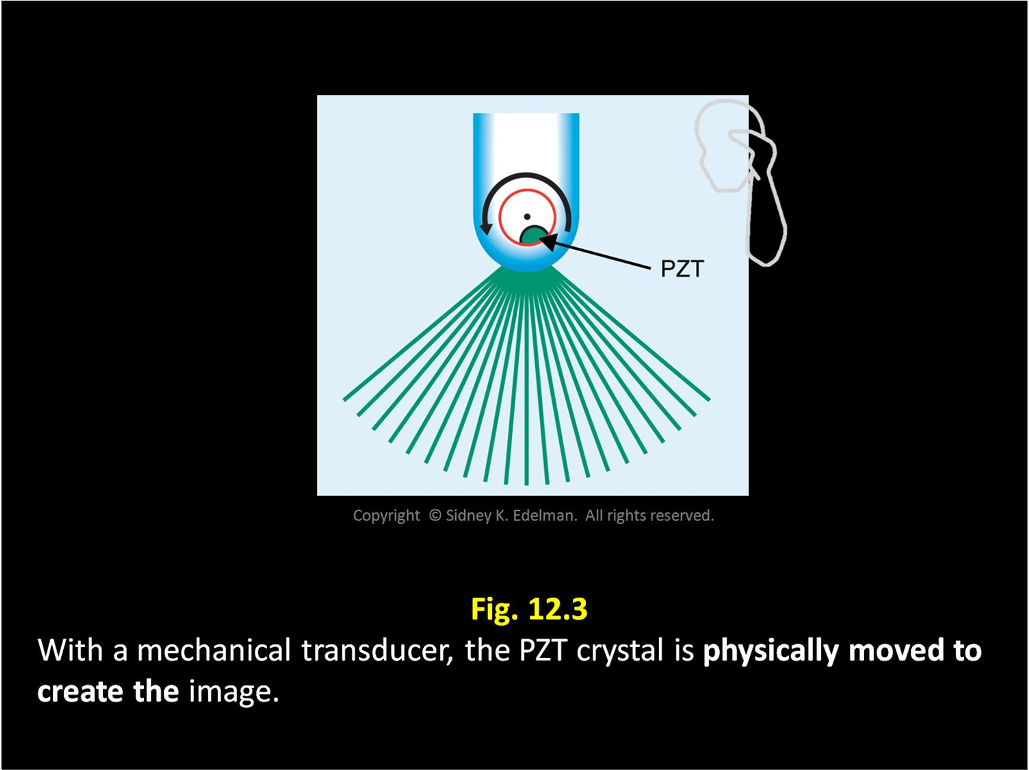
With mechanical transducer, the beams are emitted as the ____ ____. This is called ____ steering.
PZT moves ; mechanical
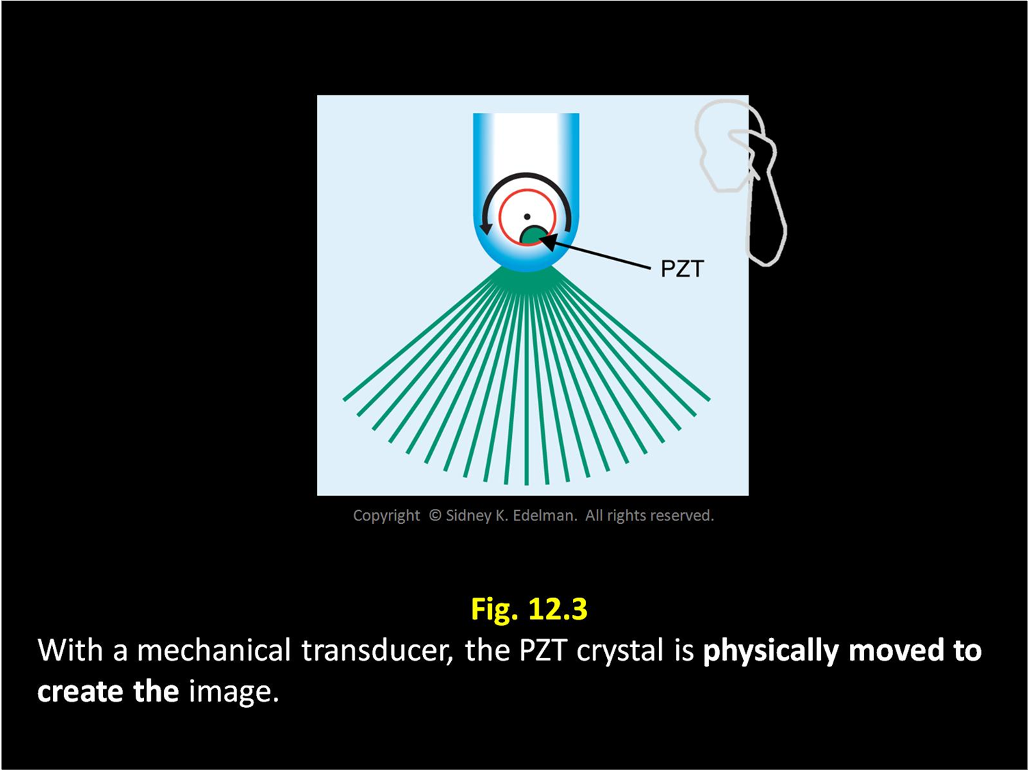
Mechanical transducers have a ____ focal depth which is called conventional, mechanical, or fixed focusing.
fixed
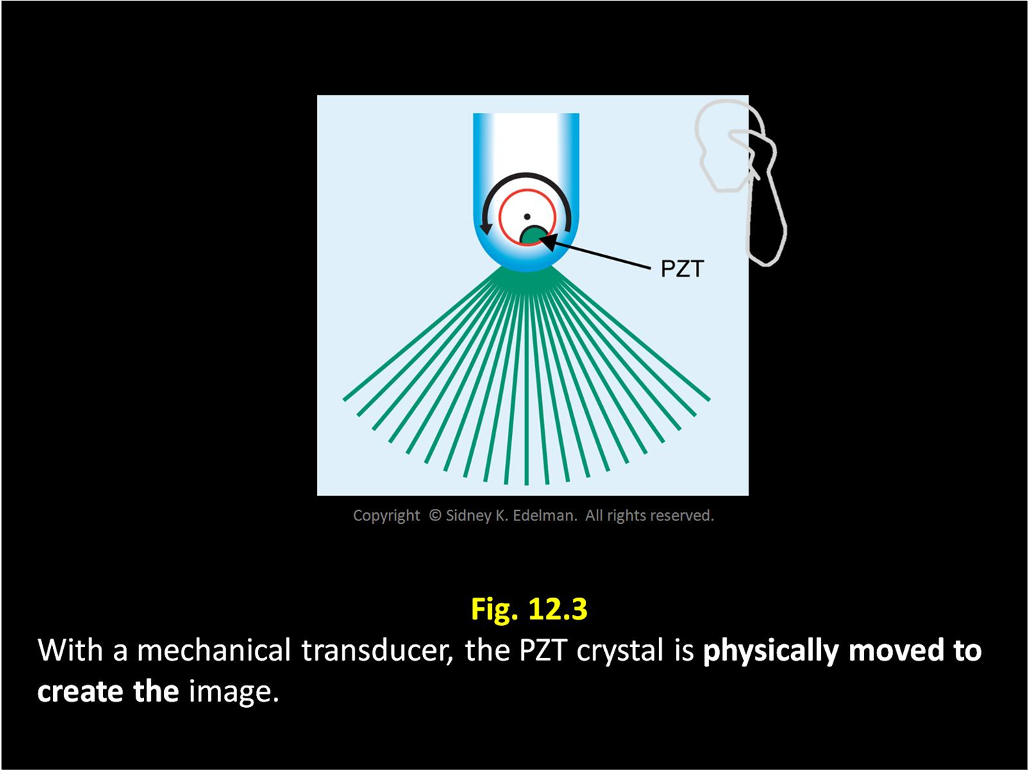
Mechanical transducers have a fixed focal depth which is called ____, ____, or _____ focusing.
conventional ; mechanical ; fixed
Mechanical transducers utilize 2 methods of fixed focusing, which are:
_
_
Internal - using curved active elements
External - using an acoustic lens
What happens to the mechanical transducer if the PZT is damaged? Why?
The entire image is lost.
Because there is only one PZT in the transducer
Transducer arrays contain (multiple / a single) active element/s.
multiple
An array consists of a single slab of _____ that is ___ into ___ ____ called __
PZT ; cut ; separate pieces ; elements
In transducer arrays, each element is connected by a ____ to ____ it from its ____ _____ and also connecting it to ___ _____.
wire ; isolate ; neighboring crystal ; system electronics
In transducer arrays, the combination of the active element, the wire, and the system electronics is called a ____.
Channel
In transducer arrays, the combination of the ____ , the ____, and the _____ is called a channel.
active element, the wire, and the system electronics

Linear probes have a (small/large) footprint but contain as many as ____-____ elements
small ; 100-300

In linear probes, each element is ____ and _____ and placed ____-____-____.
rectangular ; narrow ; side-by-side

In linear probes, the width of each element is ____ to ____ of the sound’s wavelength
¼ to ½

In linear probes, the width of each element is ¼ to ½ of the sound’s ______
wavelength
In linear probes, the image created is ___ or _____-shaped, which is similar to the mechanical transducers
fan ; sector
In linear probes, the image created is fan or sector-shaped, which is similar to the ____ transducers
Mechanical
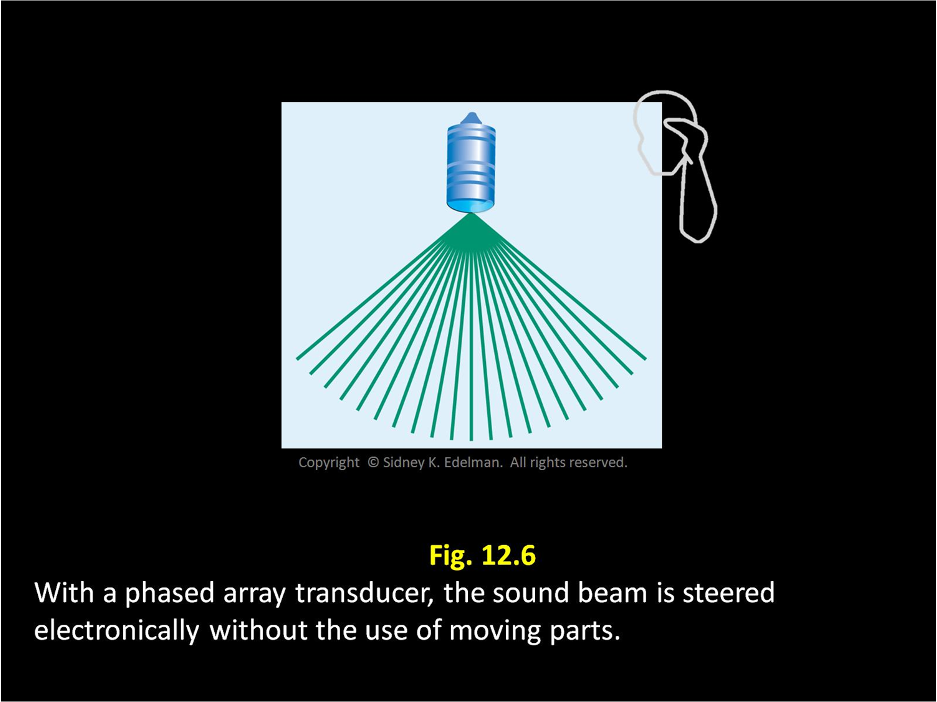
In ____ probes, the image created is fan or sector-shaped, which is similar to the mechanical transducers
linear
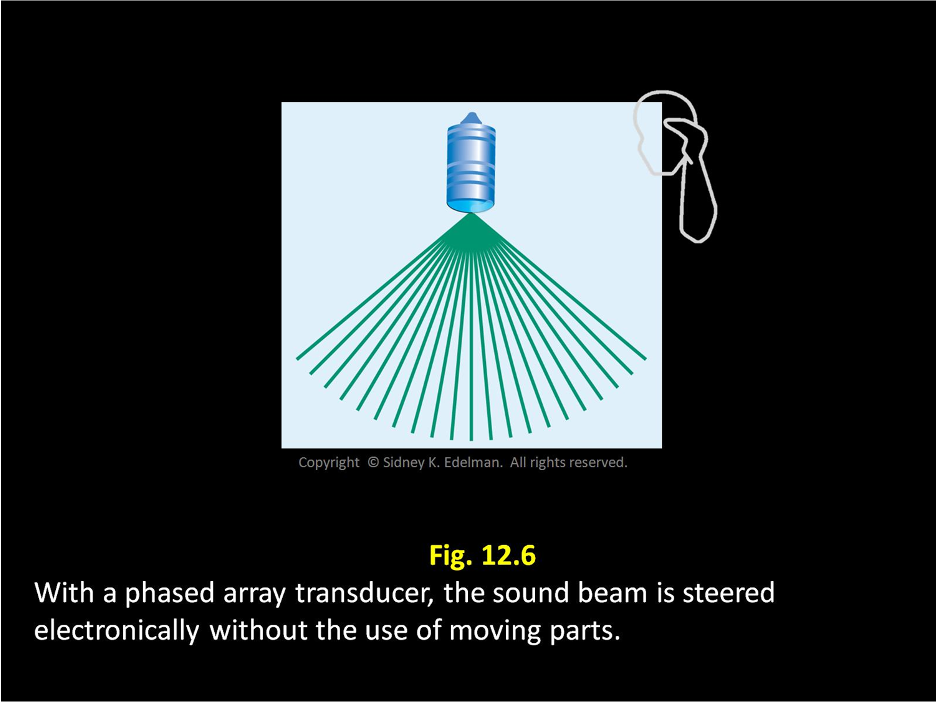
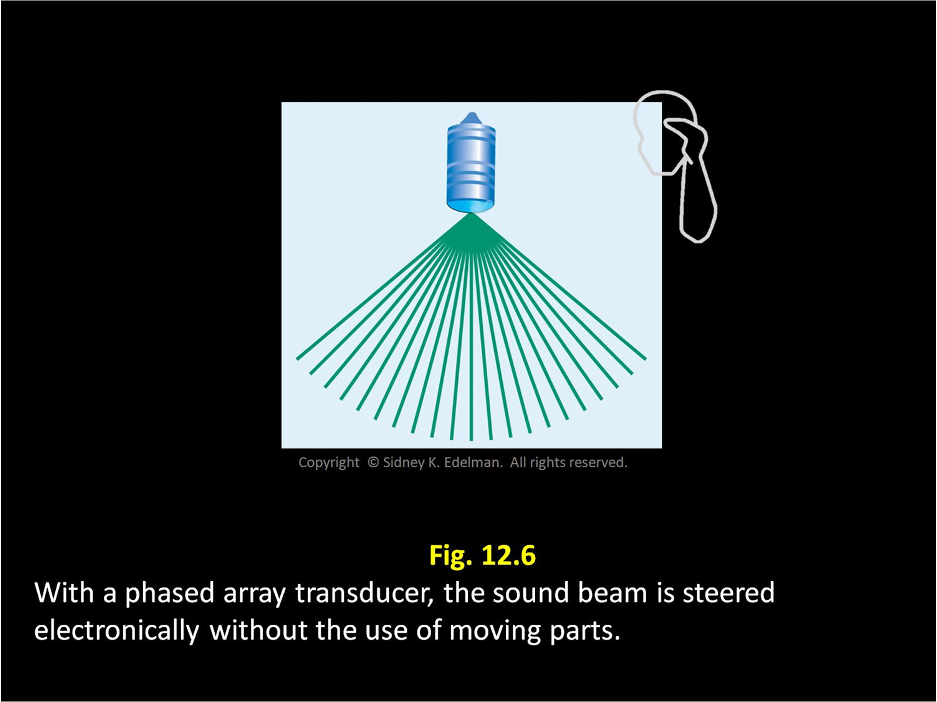
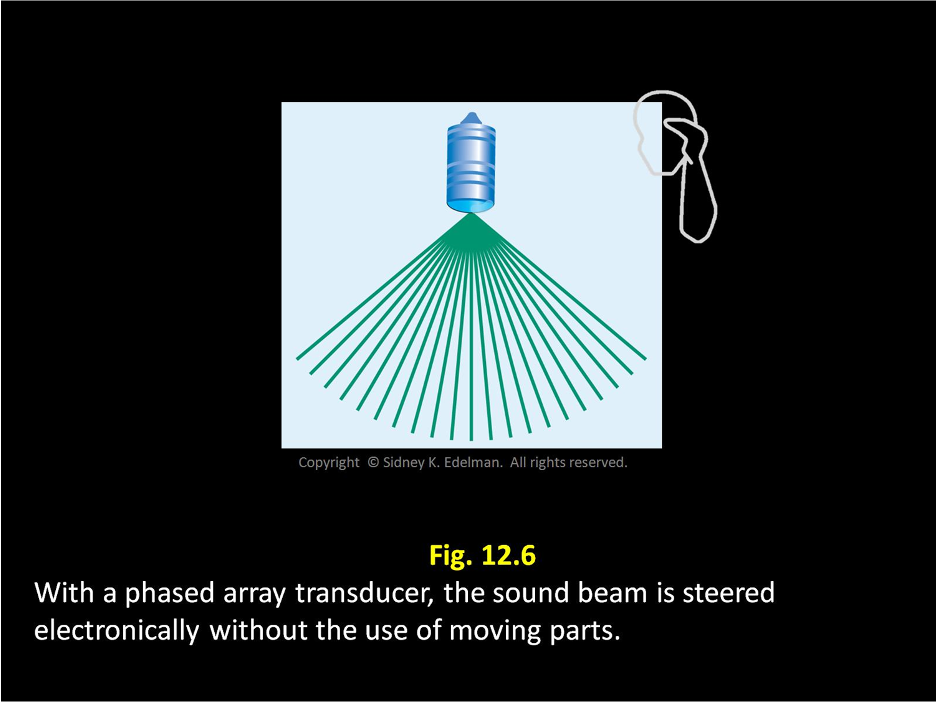
Linear phased arrays use electronic steering called ____.
phasing
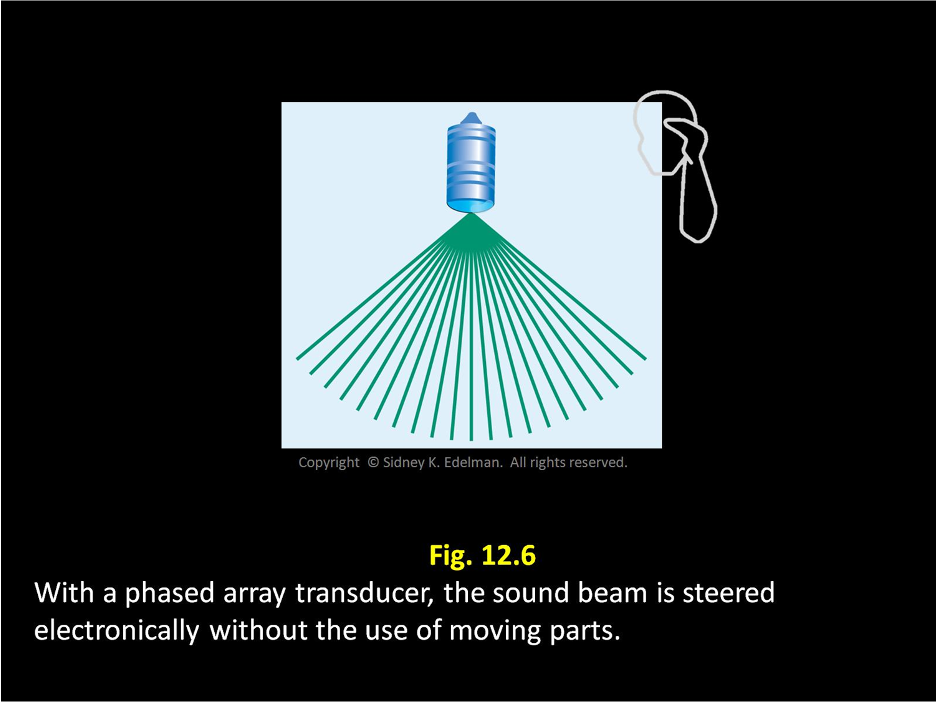
Linear phased arrays use ____ steering called phasing.
electronic
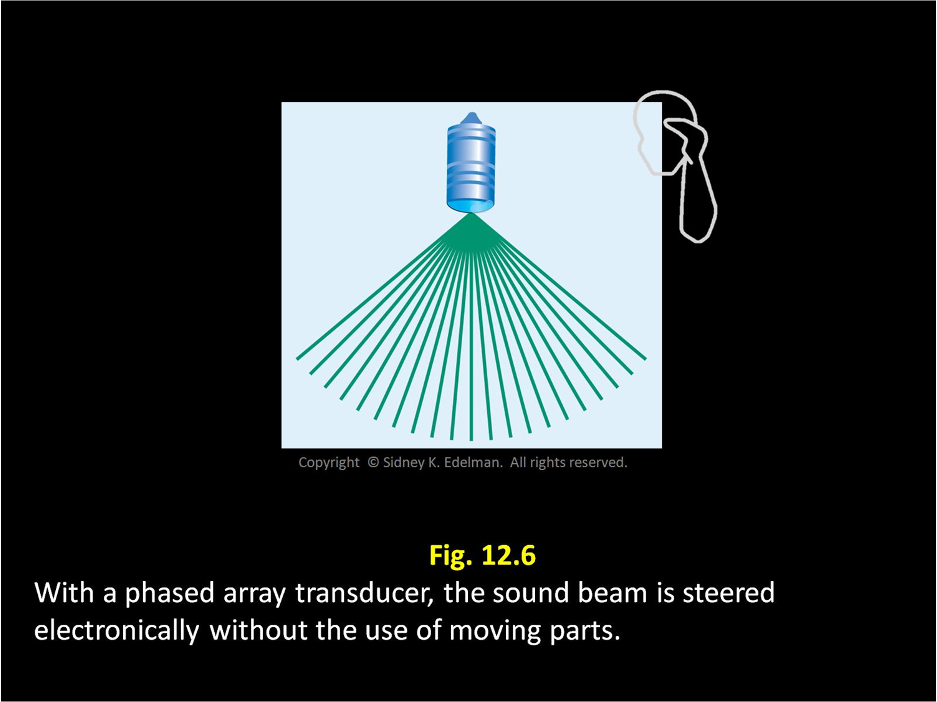
____ ____ ___ use electronic steering called phasing.
linear phased arrays
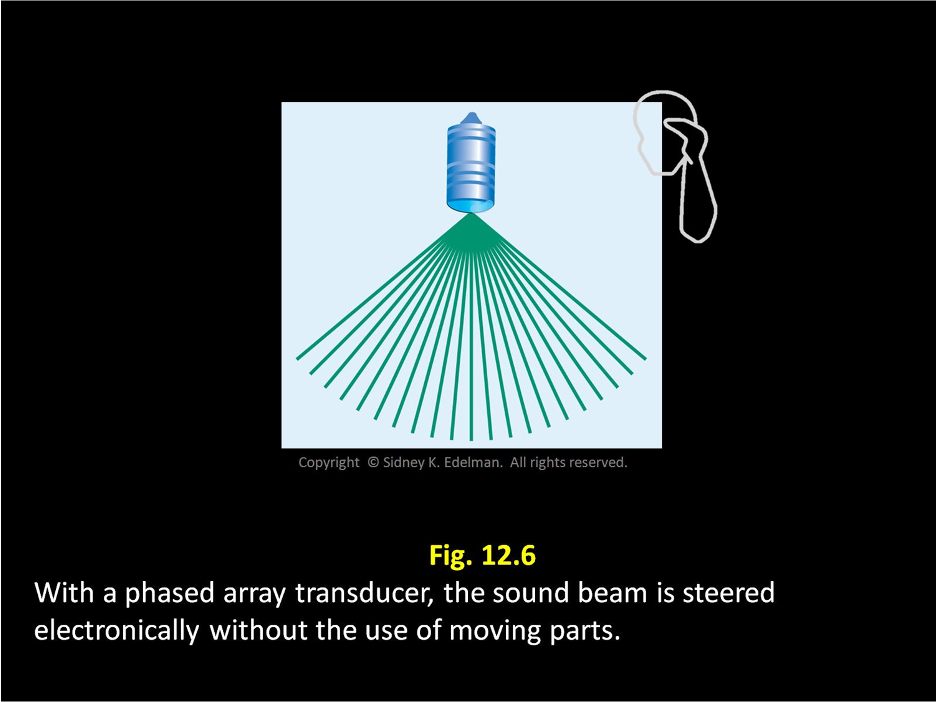
In linear phased array, beams are electronically transmitted in (the same/different) directions without the use of moving parts
different
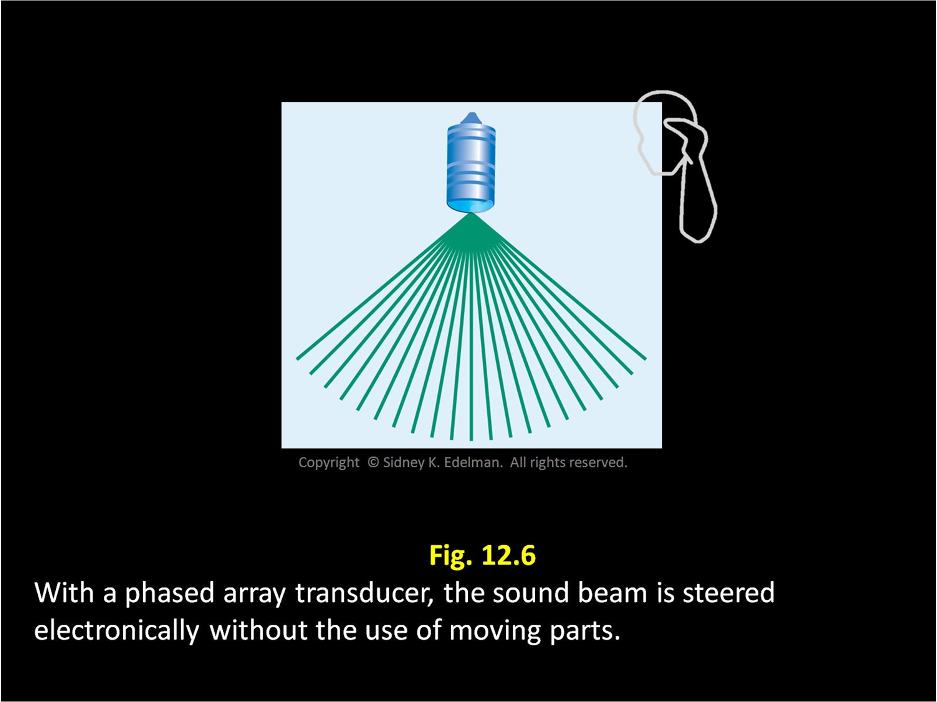
In linear phased array, beams are electronically transmitted in different directions without the use of ___ ____.
moving parts
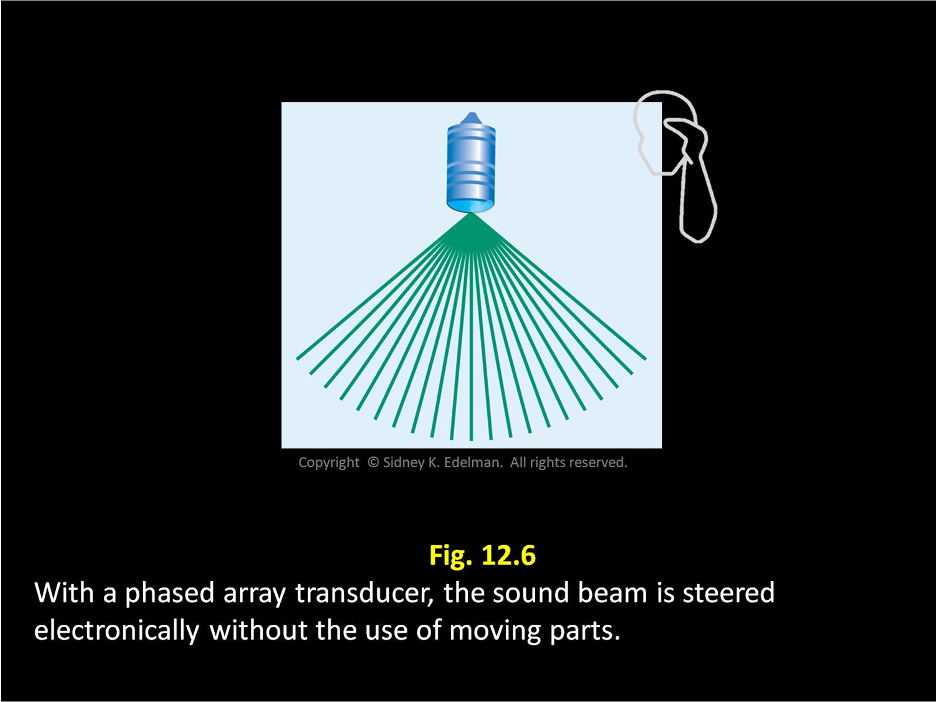
In linear phased array, beams are electronically transmitted in different directions (with/without) the use of moving parts
without
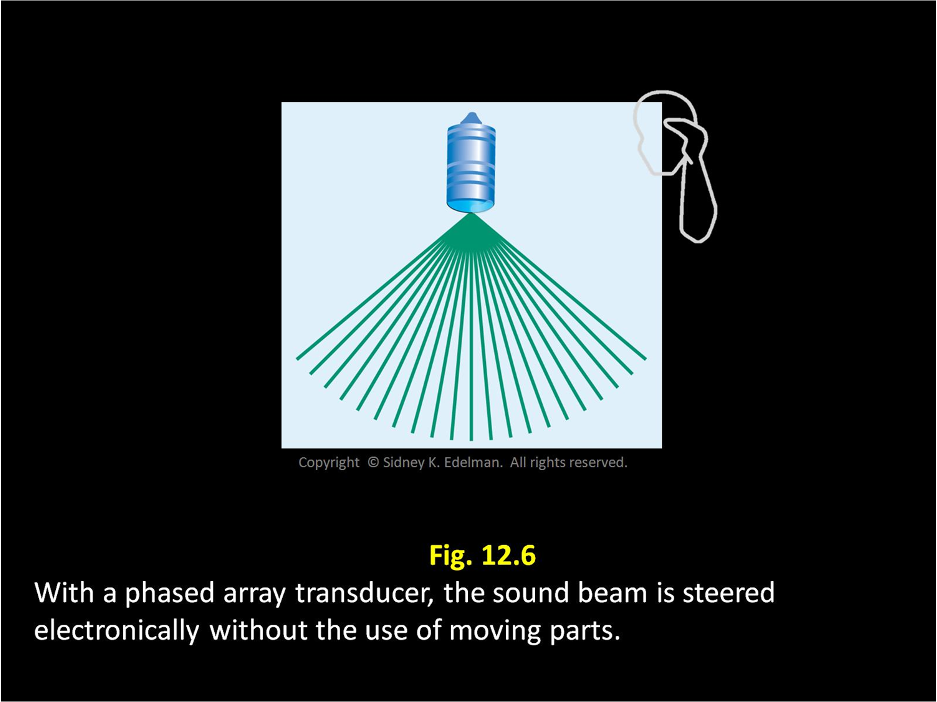
The linear phased array transducer is similar to the ____ transducer and has a pattern similar to the spokes on a bicycle wheel.
mechanical
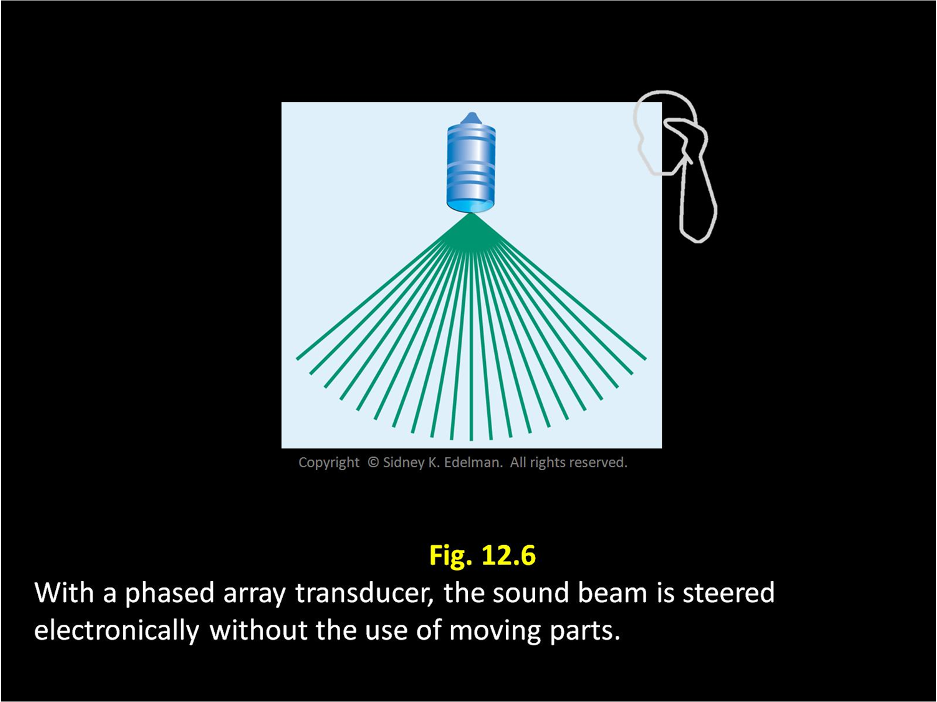
The linear phased array transducer is similar to the mechanical transducer and has a pattern similar to the ____ on a ___ ____
spokes on a bicycle wheel.

An advantage of linear phased arrays is that they can be focused ____, which means that the sonographer can change the depth of focus.
electronically

An advantage of linear phased arrays is that they can be focused electronically, which means that the sonographer can change the ___ of ____.
depth of focus.

Phased array systems can send ____ beams down the ____ ____ allowing for ___ focal zones.
multiple ; same line ; multiple

Phased array systems can send multiple beams down the same line allowing for multiple ___ ____.
focal zones

Damage to PZT in a linear phased array transducer causes ____
inconsistent or erratic beam steering or focusing

How many elements in a phased array probe are used to create a single sound pulse?
All 100-300 of them

In linear phased arrays, wavelets interfere ____ and ____ which creates a sound pulse with ____ _____.
constructively & destructively ; particular characteristics
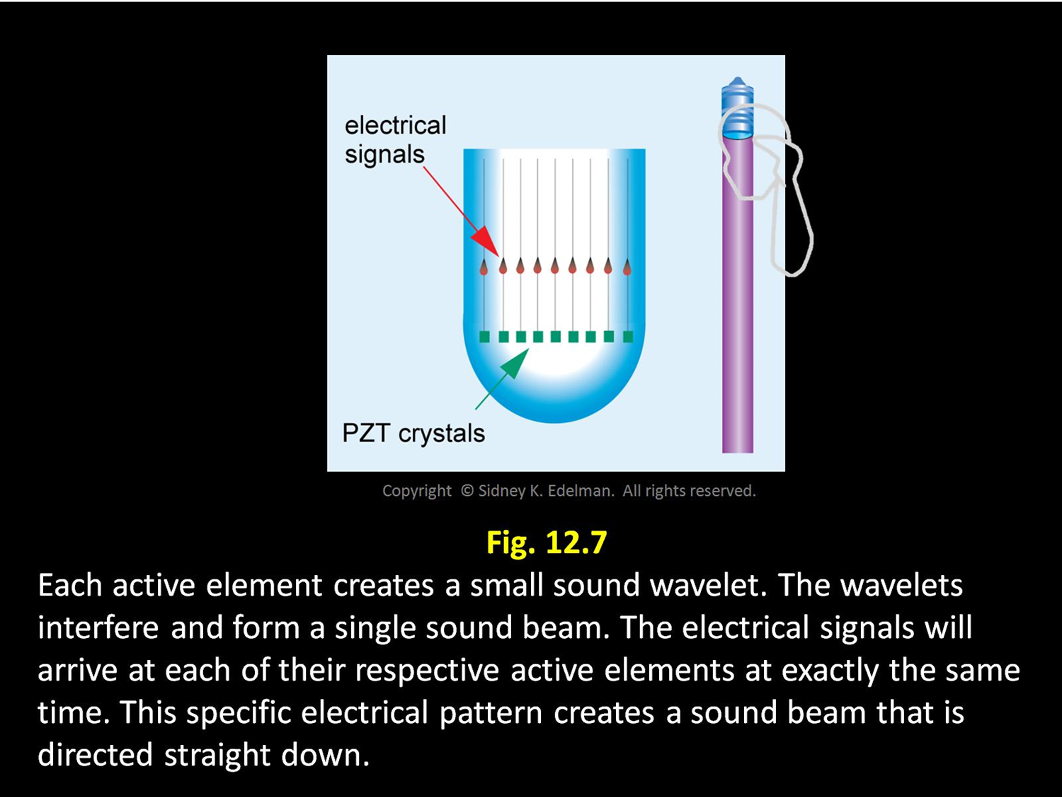
In Linear Phased Arrays,
How does the pattern of electrical spikes steer the sound beam?
______
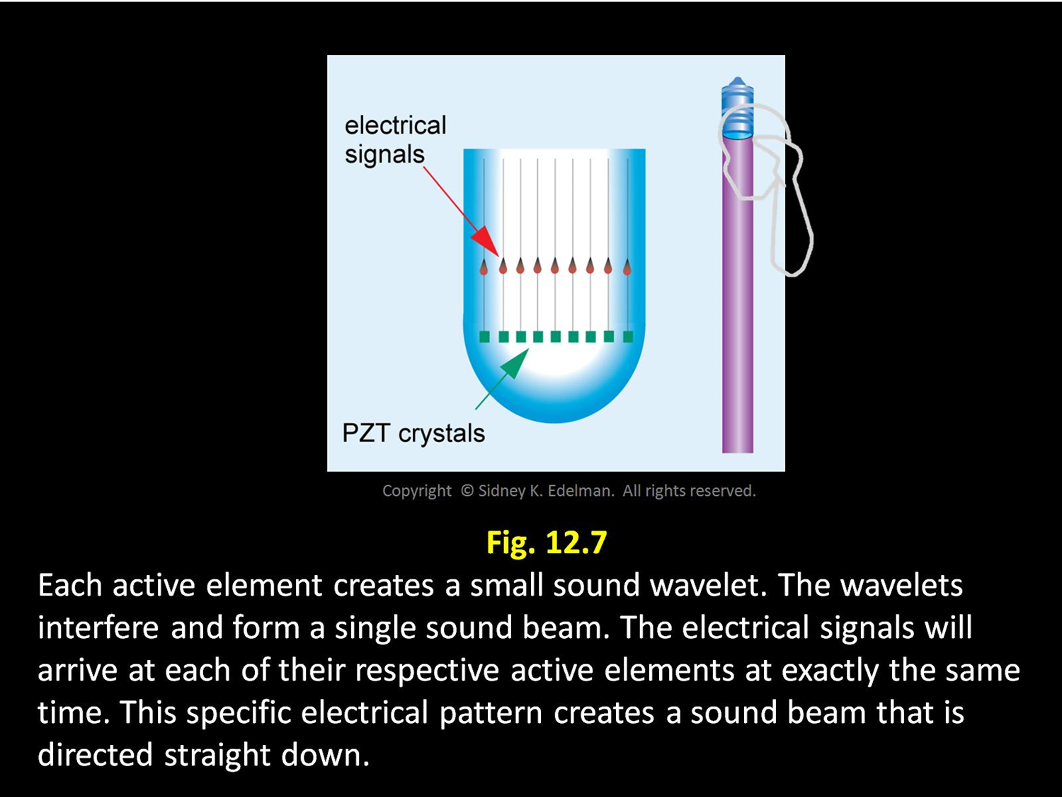
Each of the spikes excites the corresponding elements at the exact same time causing them to emit a sound wave that interfere forming a single sound beam
Spikes travel down the channels to each element
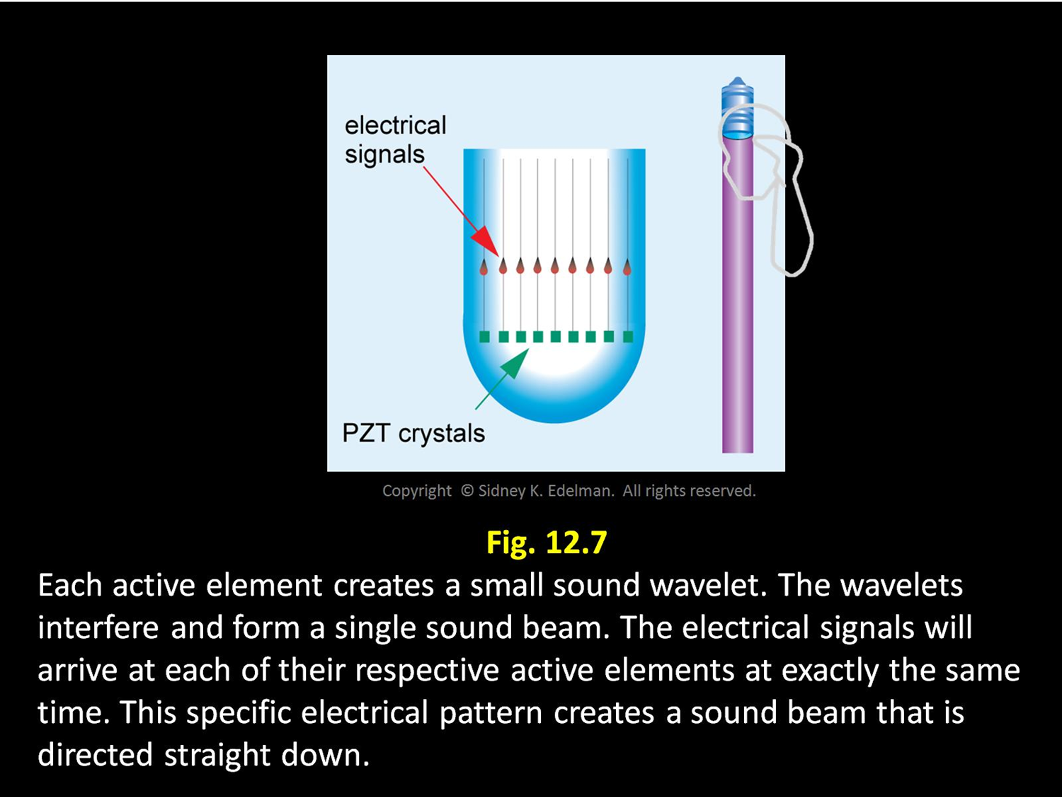
In Linear Phased Arrays,
How does the pattern of electrical spikes steer the sound beam?
Spikes travel down the channels to each element
Each of the spikes excites the corresponding elements at ____ causing them to emit a sound wave that _____ forming
the exact same time ; interfere forming a single sound beam
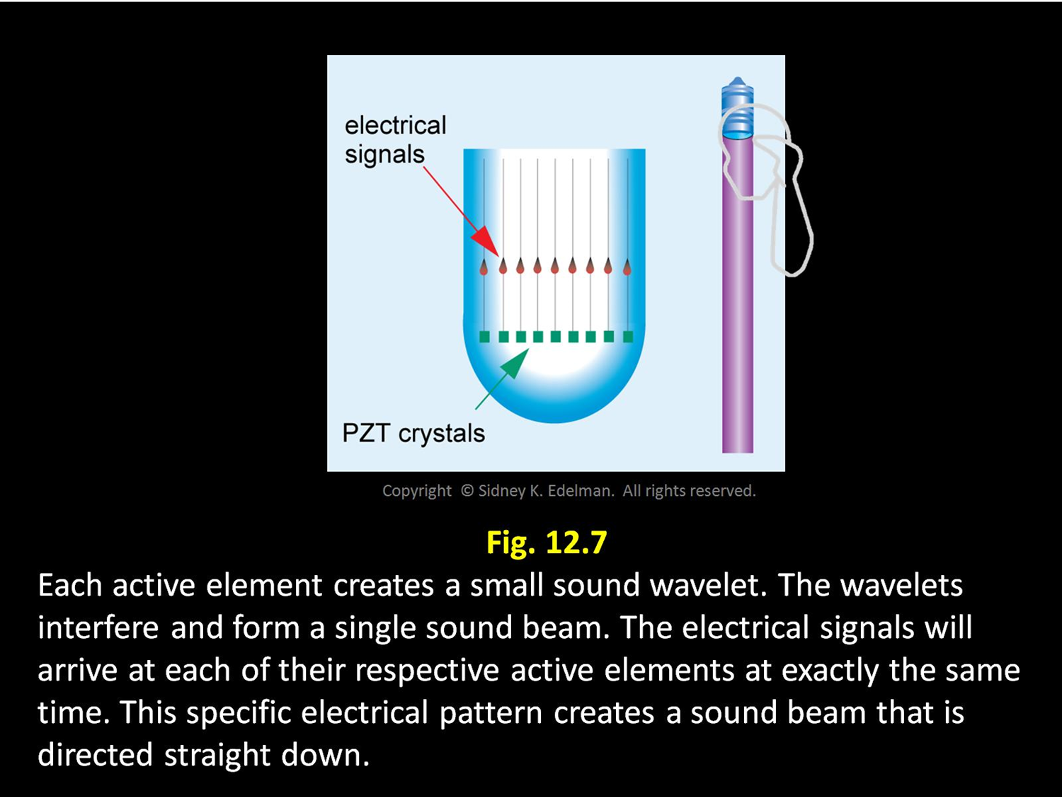
In Linear Phased Arrays,
How does the pattern of electrical spikes steer the sound beam?
Spikes travel down the channels to each element
______
Each of the spikes excites the corresponding elements at the exact same time causing them to emit a sound wave that interfere forming a single sound beam
In Linear Phased Arrays,
How can we determine the direction that the sound beam will transmit?
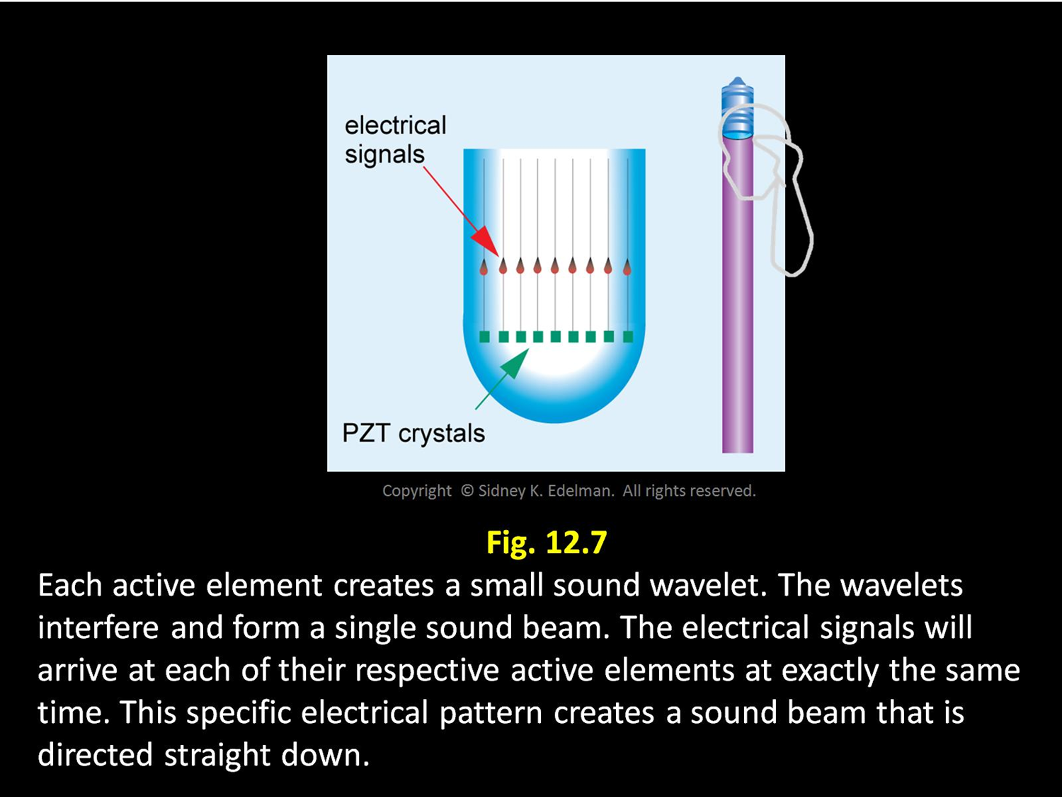
Two step approach
1: _______
2: draw another line perpendicular to the first line
draw a line that connects the electrical spikes, if this line has a slope then the beam will be steered
In Linear Phased Arrays,
How can we determine the direction that the sound beam will transmit?
Two step approach
1: draw a line that connects the electrical spikes, if this line has a slope then the beam will be steered
2: ______
draw another line perpendicular to the first line
In Linear Phased Arrays,
How can we determine the direction that the sound beam will transmit?
Two step approach
1: draw a line that connects the electrical spikes, if this line has a slope then the beam will be steered
2: draw another line perpendicular to the first line
If the first line is slanted in a particular direction, then the beam will _____
steer to the side instead of straight down
In linear phased arrays, beam steering is created by sending electrical signals with a ____ ____, AKA ___ _____, to ___ ____, which are seperated by ___ ____ of a ____.
slight delay ; phase delays ; each element ; ten billionths of a second
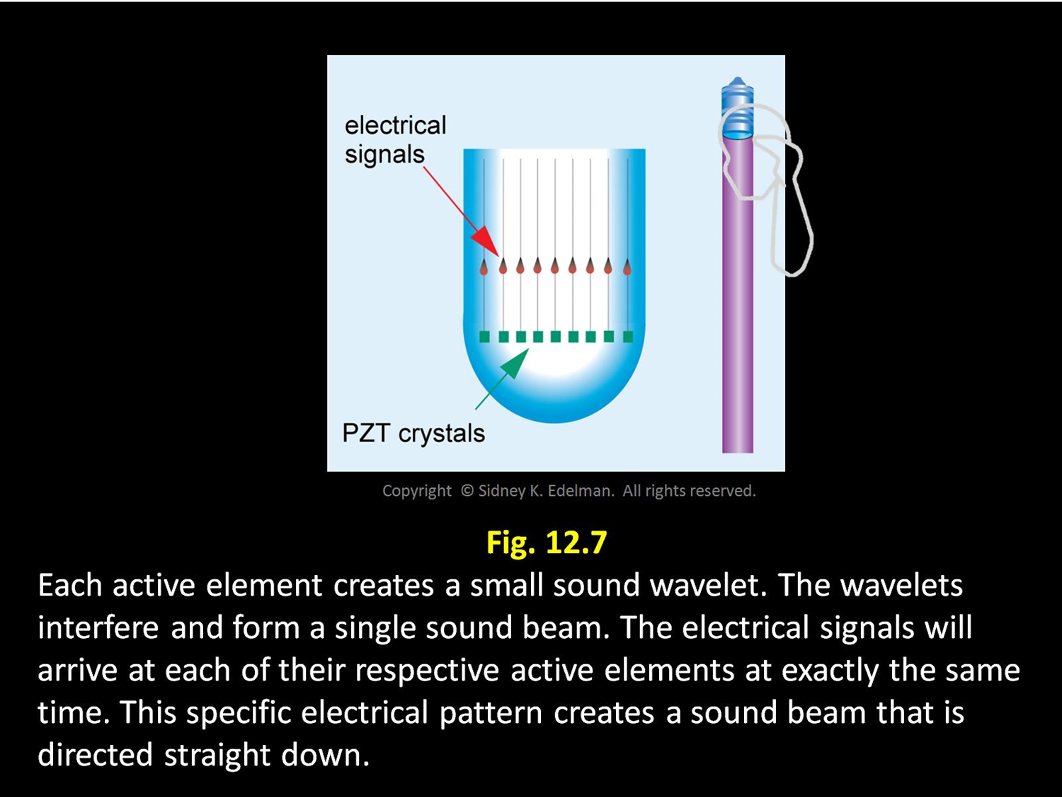
The electronics that steer the beam are called the _____ _____
beam former
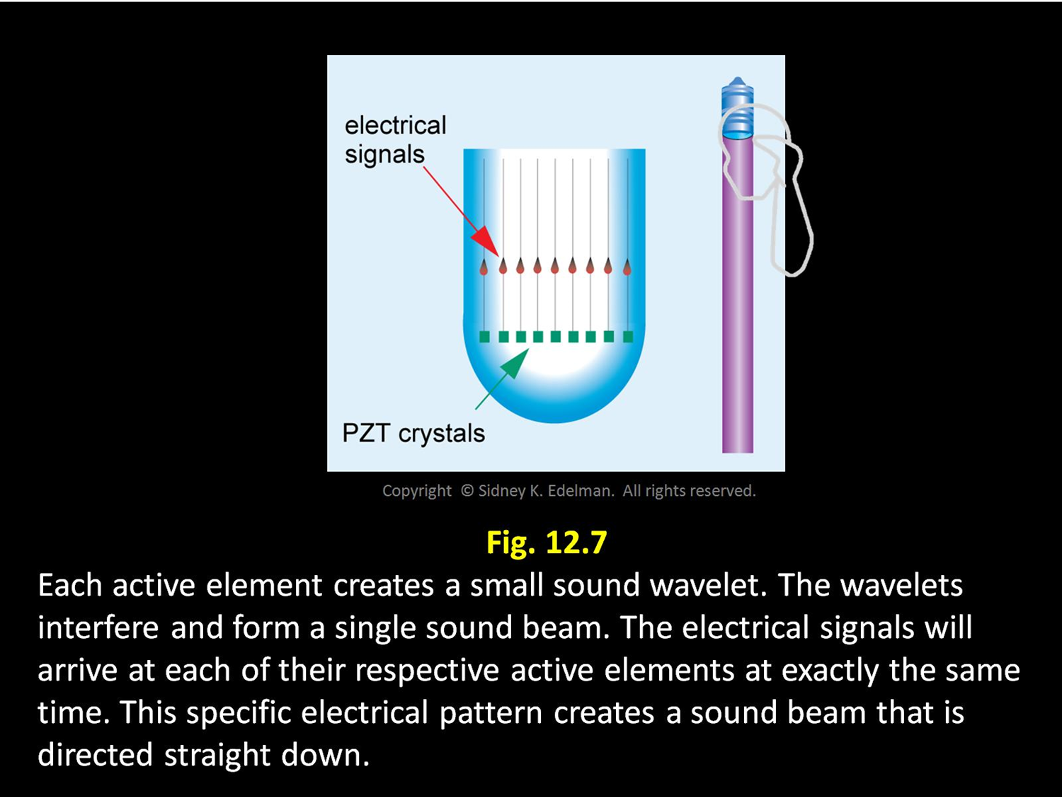
The ____ that ___ the ______ are called the beam former
electronics that steer the beam
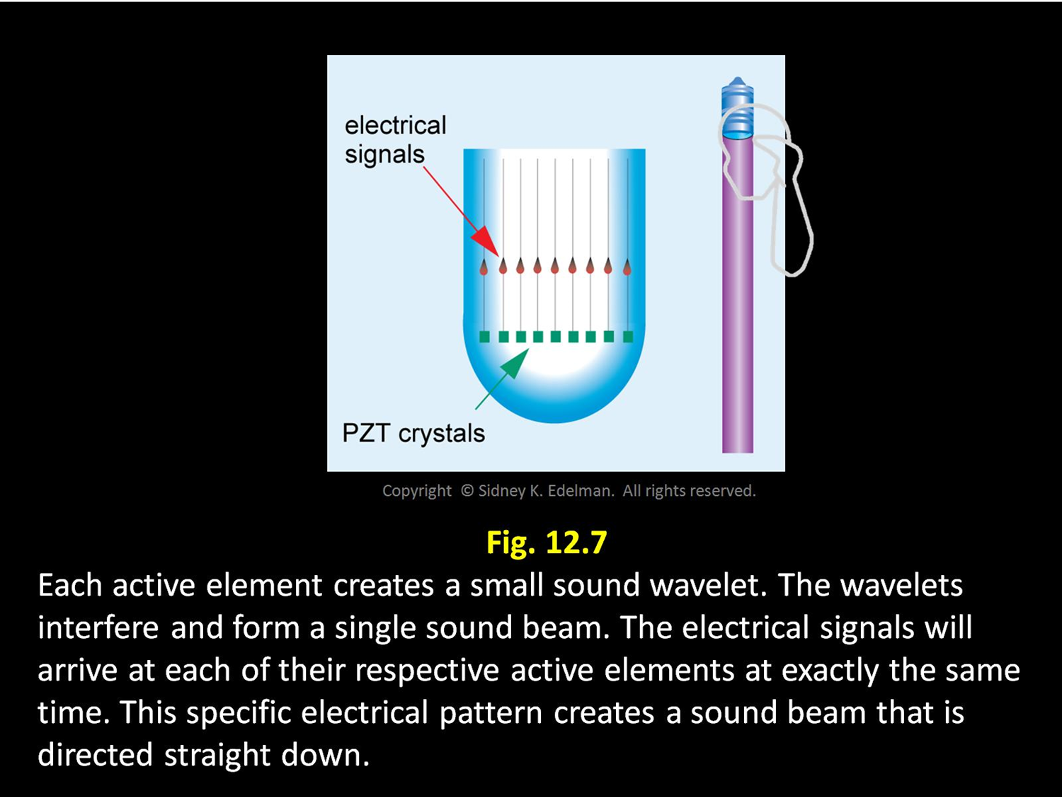
The _____ is what causes the sector-shaped image.
steering
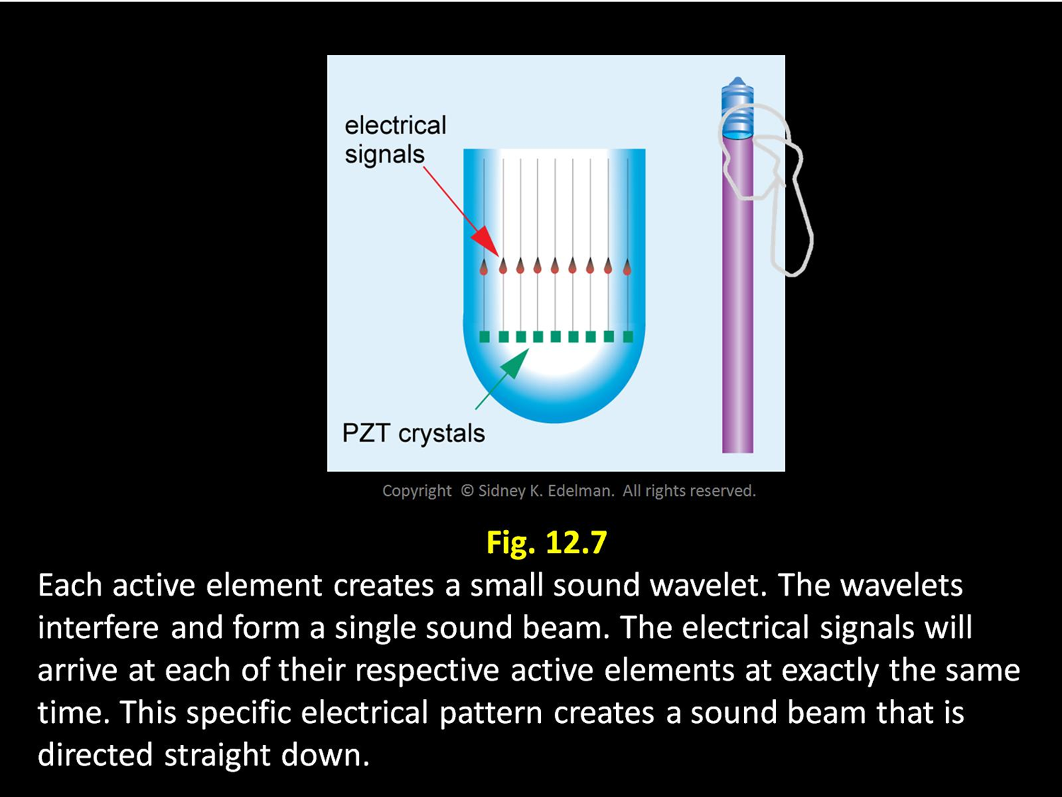
The steering is what causes the ____-shaped image.
sector
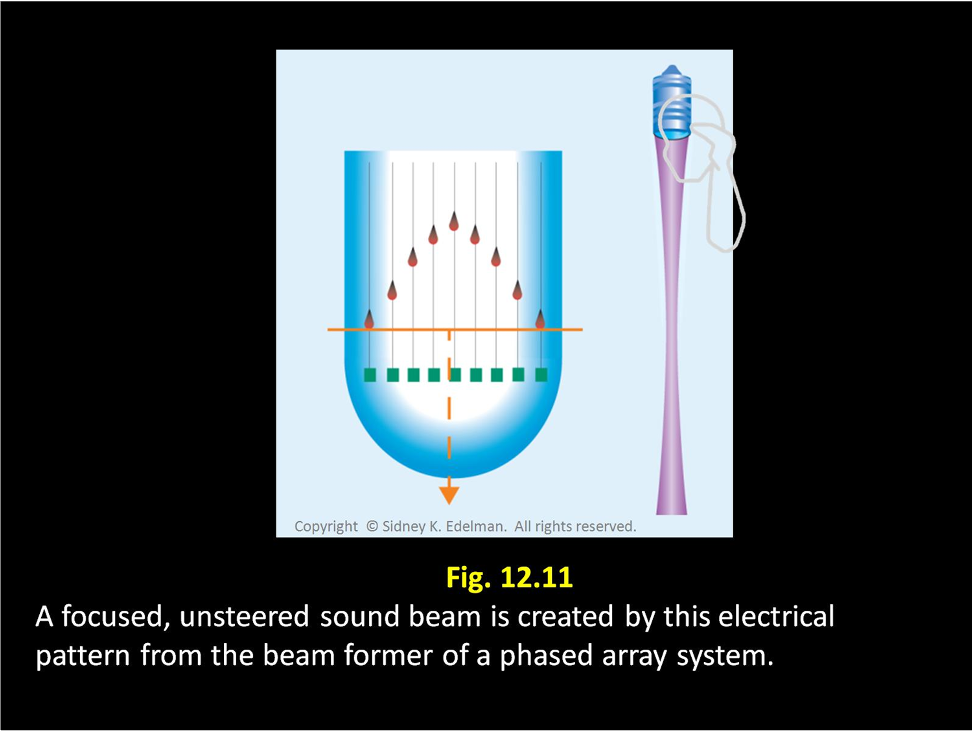
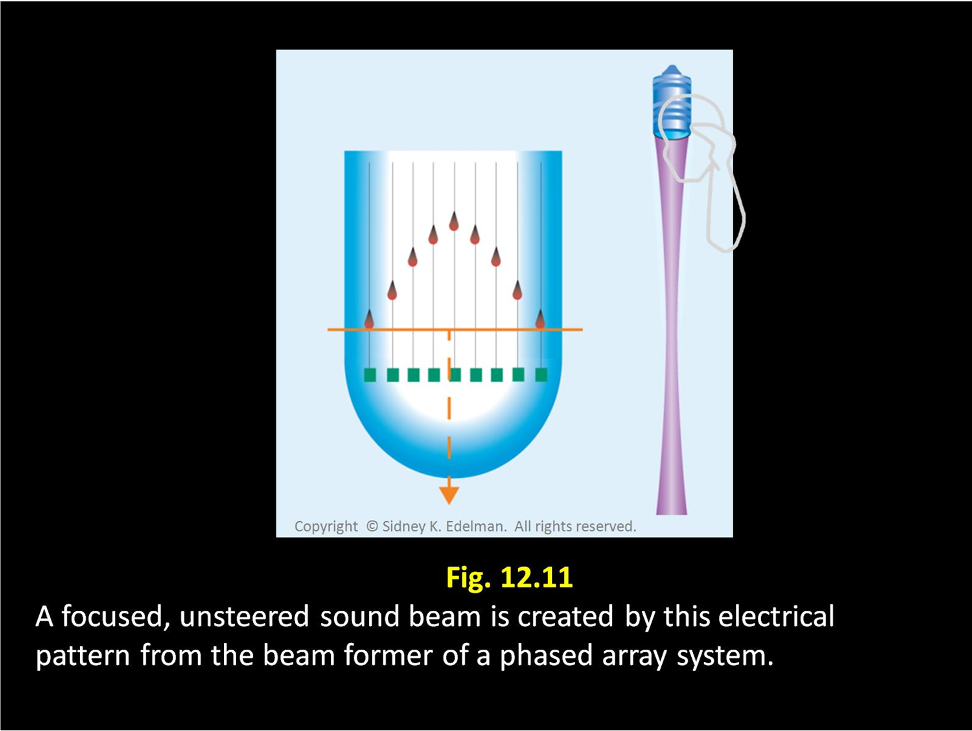
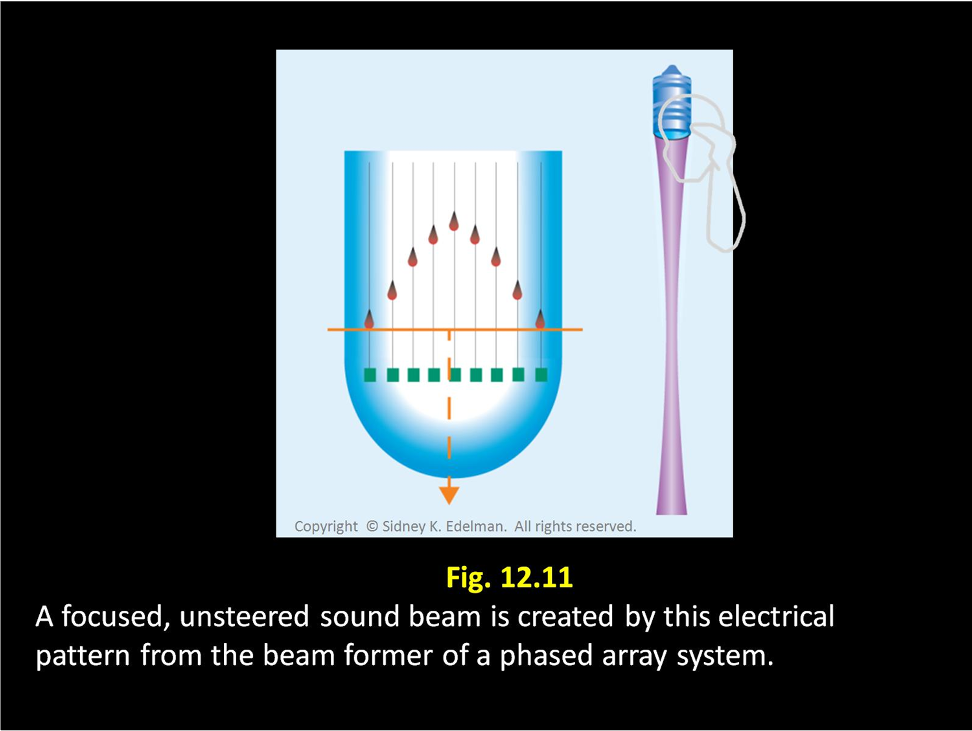
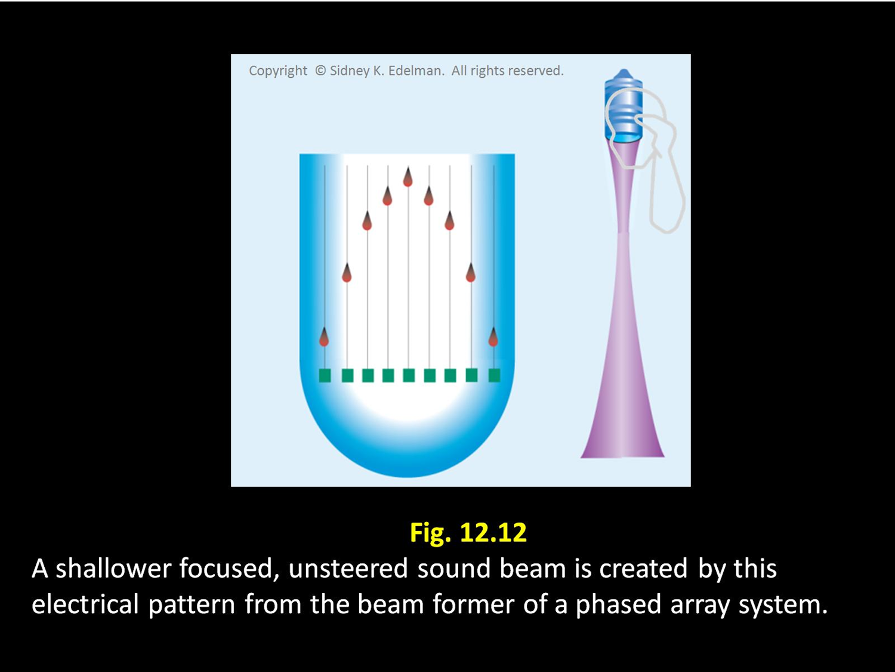
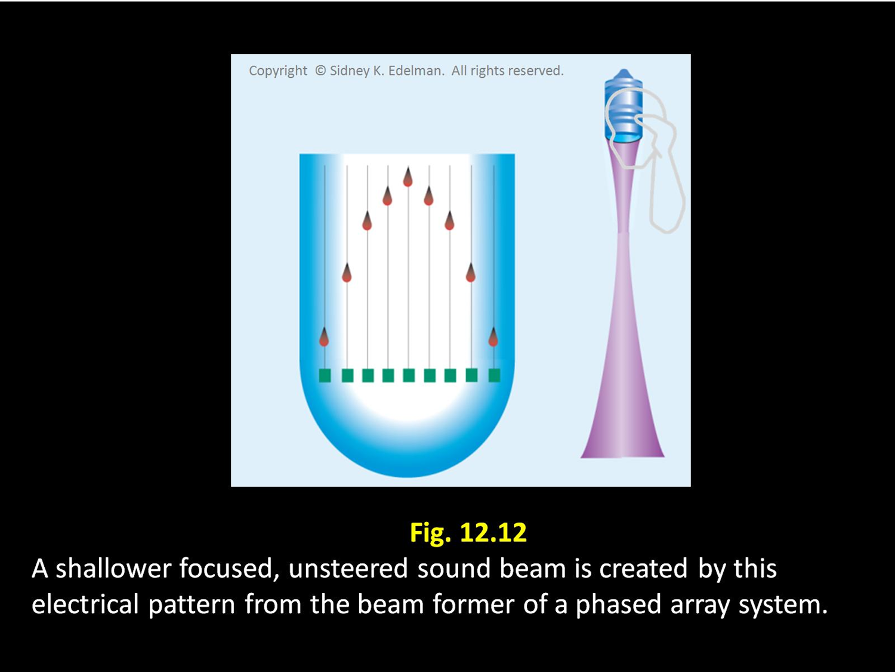
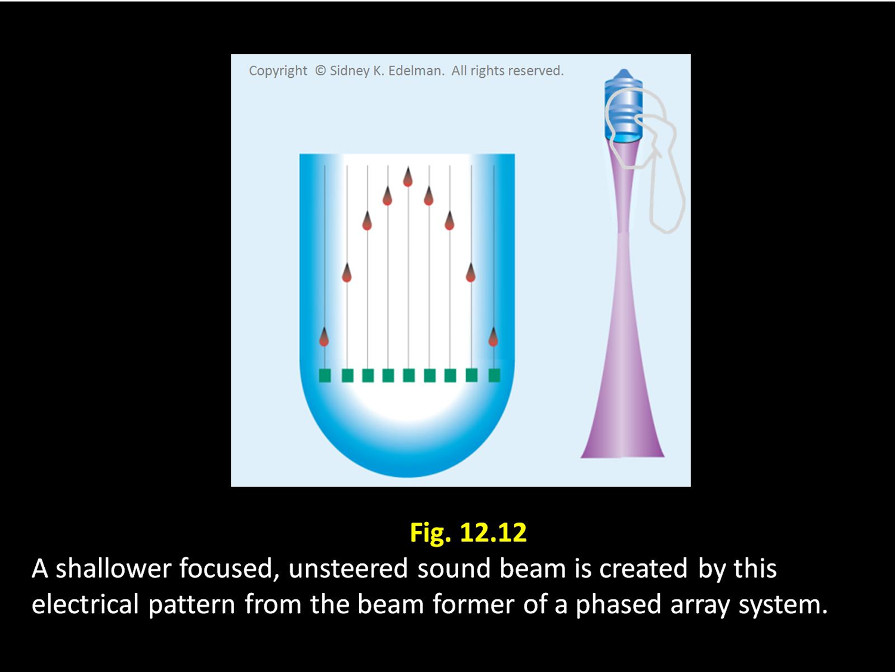
If the spike pattern is in a ___ ____ then an unfocused beam will be formed.
straight line
If the spike pattern is in a straight line then an _____ beam will be formed.
unfocused
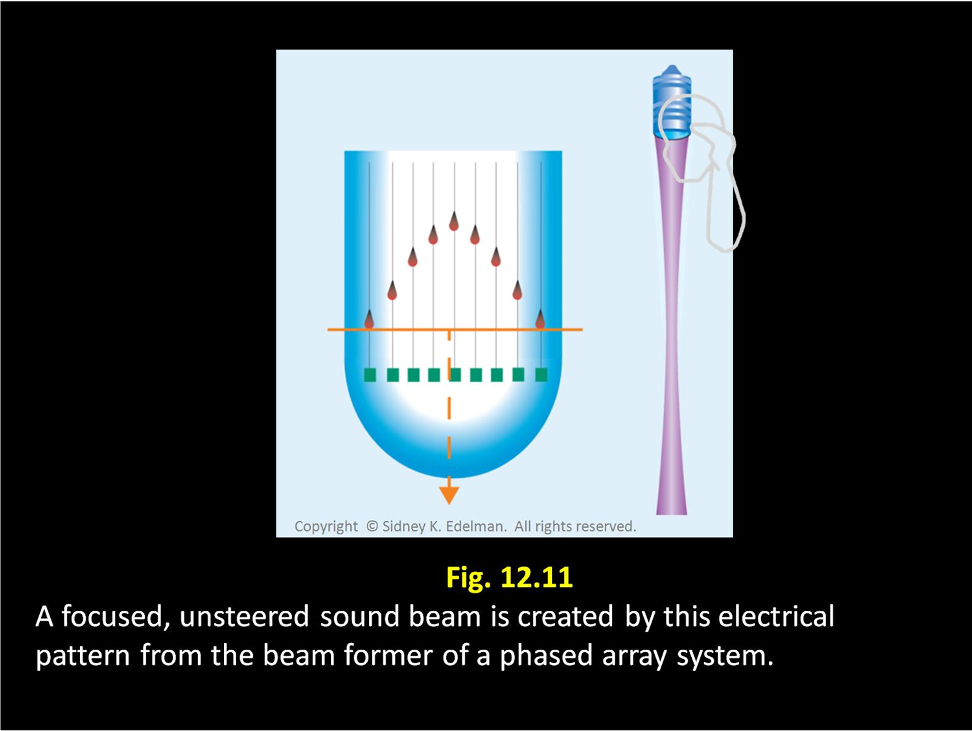
If the spike pattern is ____ then the beam will be focused
curved
If the spike pattern is curved then the beam will be _____
focused
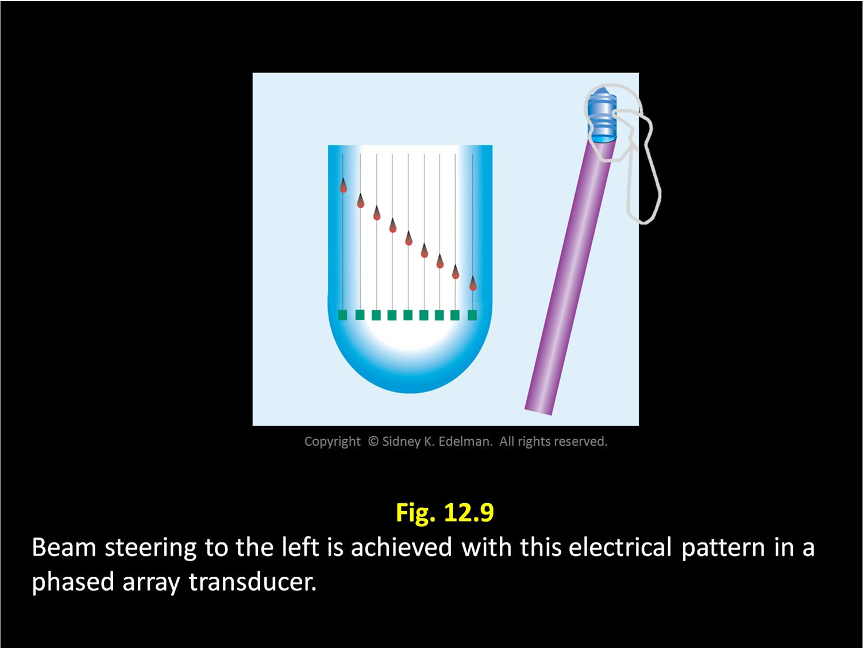
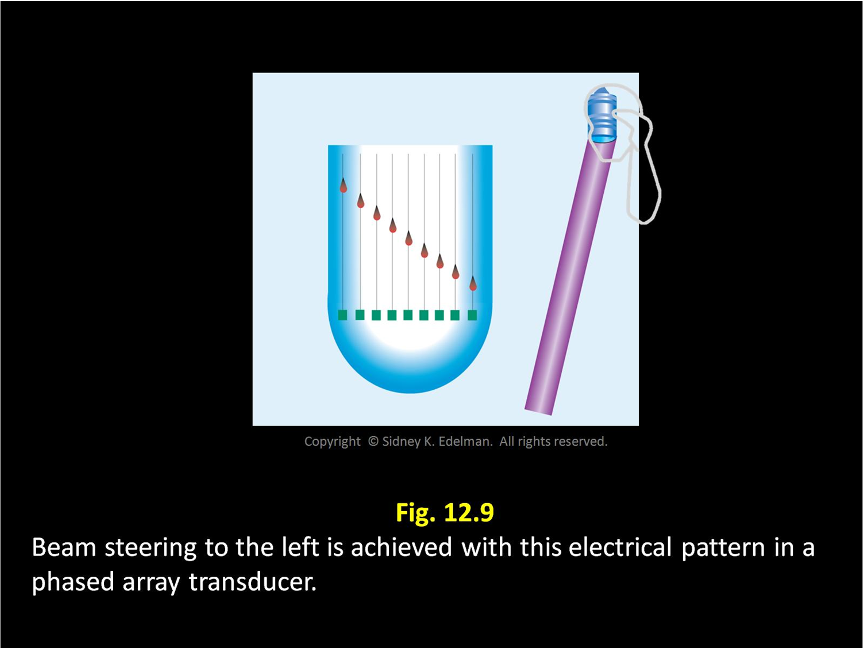
Describe this beam.
Unfocused ; Steered to the left
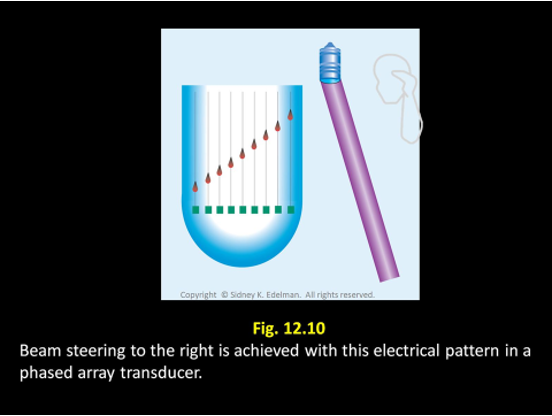
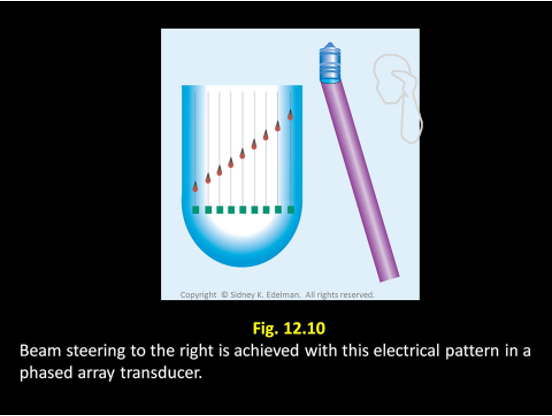
Describe this beam.
Unfocused ; Steered to the right
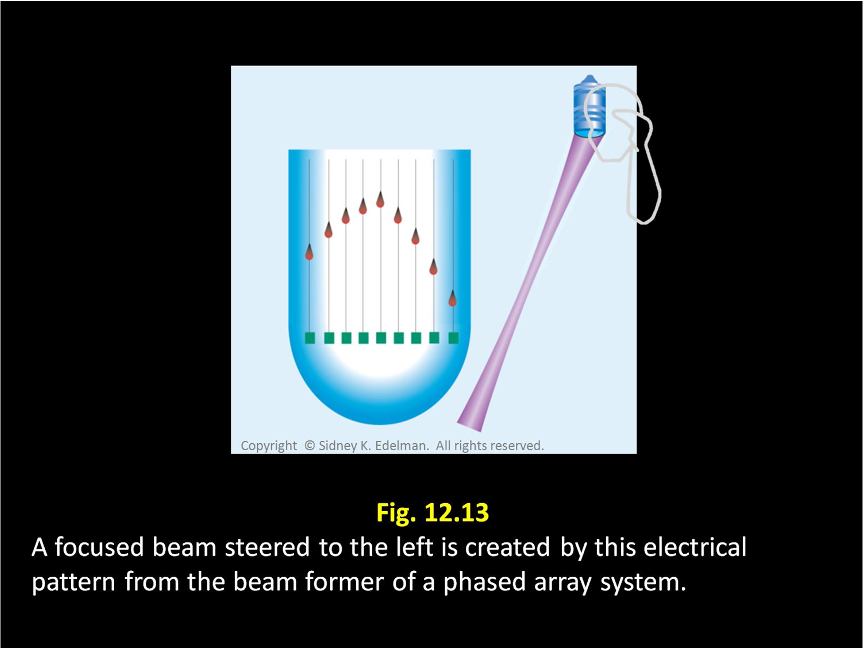
Describe this beam.
Focused ; Left Steered
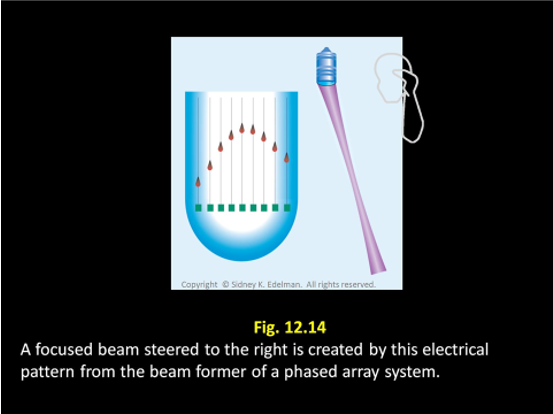
Describe this beam.
Focused ; Right steered
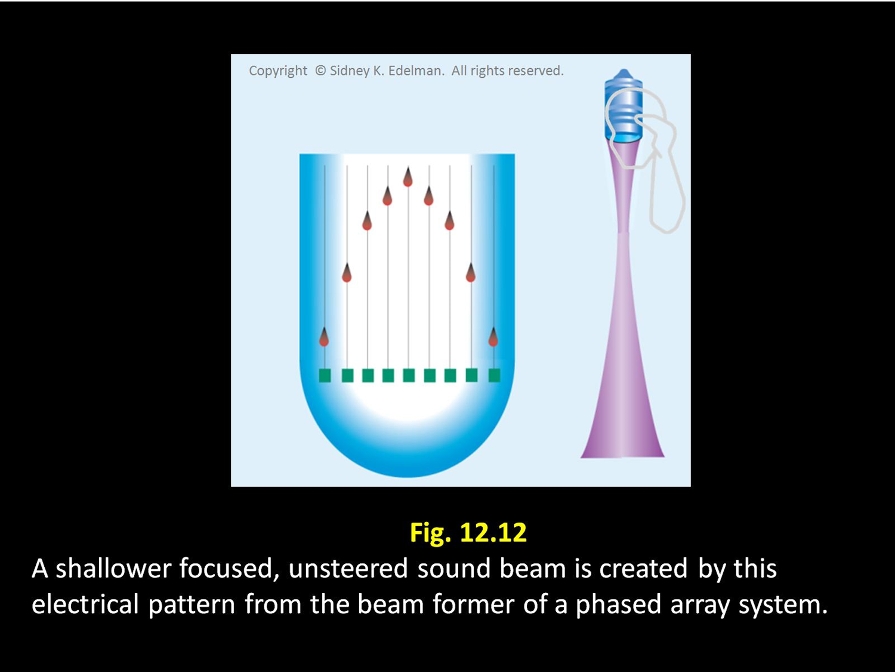
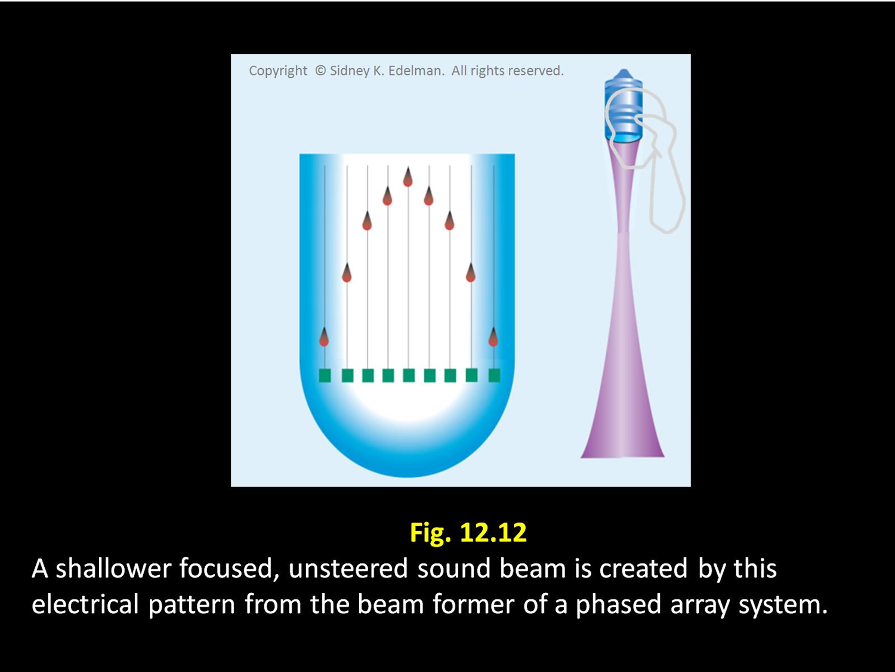
The more severe the ____, the more shallow the focus of the beam
curvature
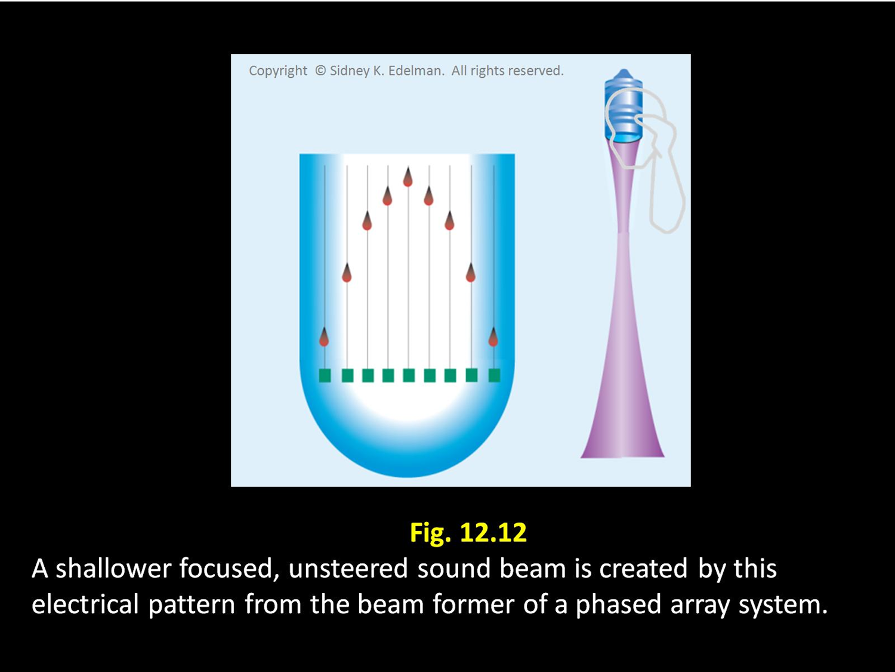
The more severe the curvature, the more ____ the focus of the beam
shallow
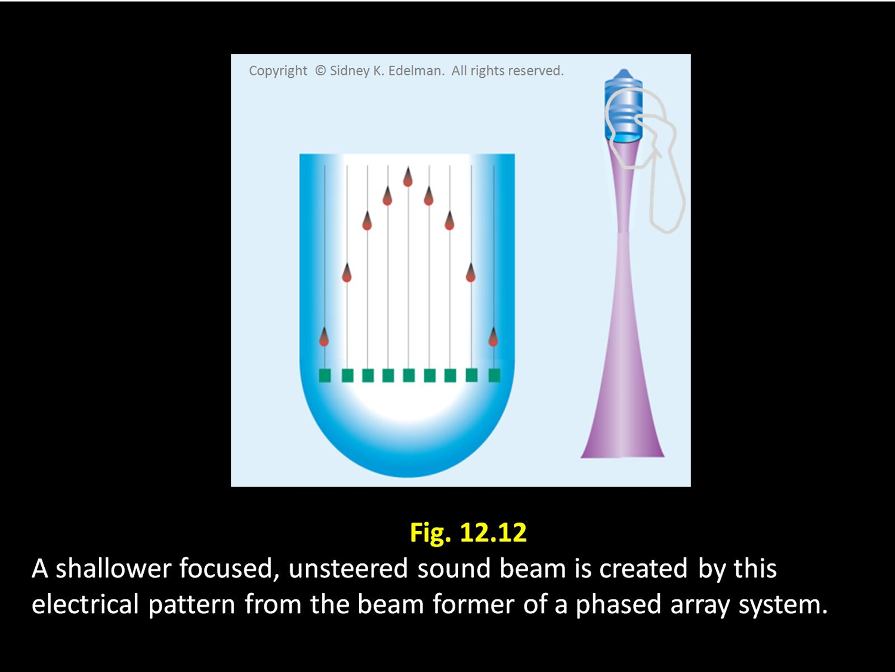
The more severe the curvature, the more shallow the ____ of the beam
focus
The D-shape spike pattern is of (great / no) use to diagnostic imaging due to the fact that it creates a defocused sound beam.
no
The D-shape spike pattern is of no use to diagnostic imaging due to the fact that it creates a ___ sound beam.
defocused
The ____ spike pattern is of no use to diagnostic imaging due to the fact that it creates a defocused sound beam.
D-shape
Describe this sound beam.
Defocused ; D-shaped
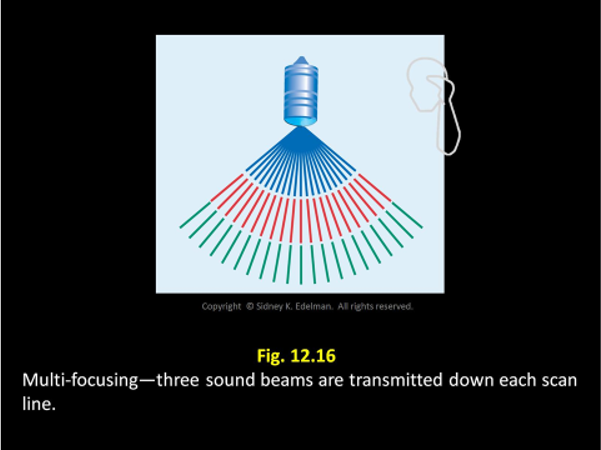
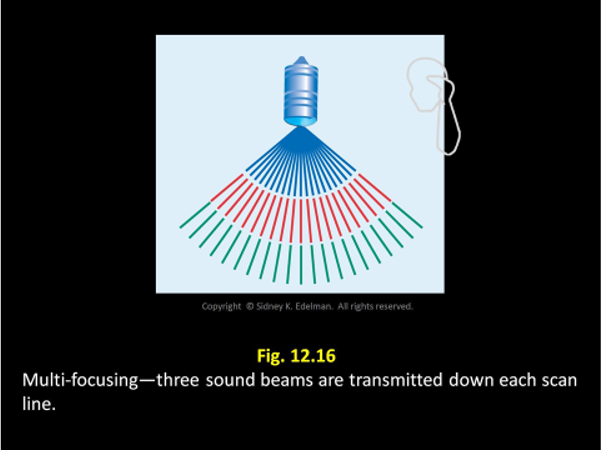
Each sound beam has its own focus, so to increase the number of foci in an image the US system must ____
send multiple pulses down the same scan line.
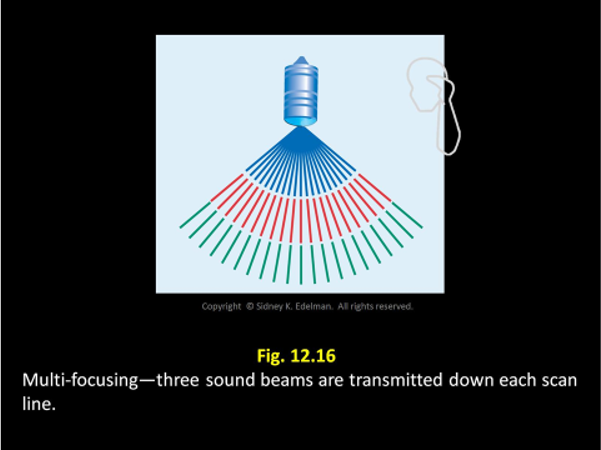
Each sound beam has its own focus, so to increase the number of _____, the US system must send multiple pulses down the same scan line.
foci in an image
To create different focal zones the ____ of each ___ ____ ____ must be different
curvature ; pulse spike pattern
To create different focal zones the curvature of each pulse spike pattern must be ____
different
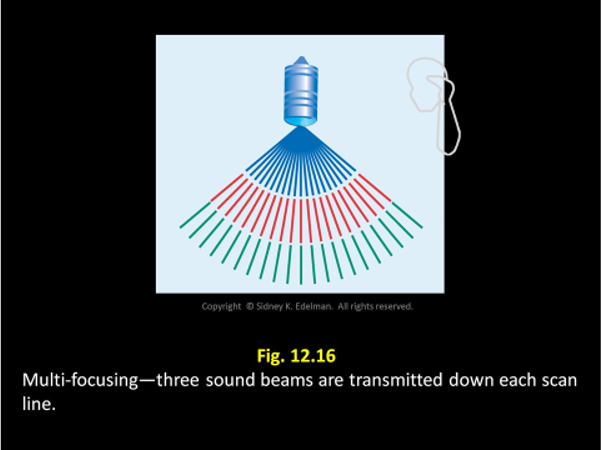
For a shallow focus, the curvature has to be ___
severe
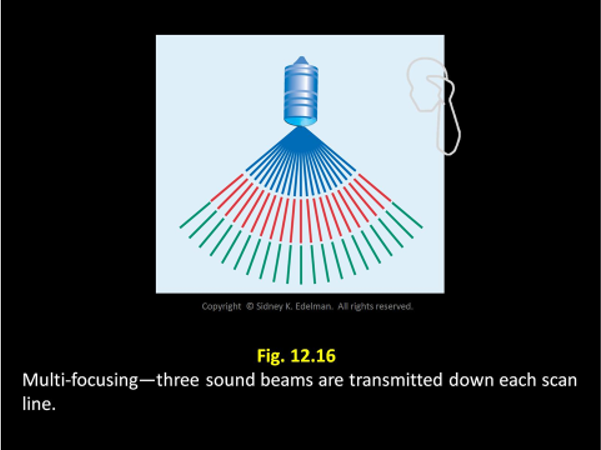
For a ___ focus, the curvature has to be severe
shallow
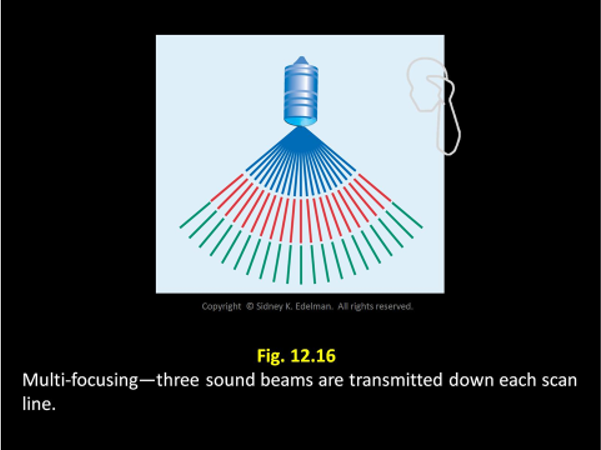
The pattern with the least amount of curvature will have the ____ focus.
deepest
The pattern with the ___ amount of curvature will have the deepest focus.
least
Focusing can also occur during ____
reception
____ can also occur during reception
Focusing
For more accurate imaging, the US system creates ___ ___ ___ during reception
variable time delays
For more accurate imaging, the US system creates variable time delays during ____
reception
For more accurate imaging, the US system creates variable time delays during reception
The reflected sounds during imaging arrive back to the transducer and excite ___ ____.
These excited elements create signals that are sent back to the system via the channels
multiple elements
For more accurate imaging, the US system creates variable time delays during reception
The reflected sounds during imaging arrive back to the transducer and excite multiple elements
These excited elements create ____ that are sent back to the ___ via the ____
signals ; system ; channels
Images will be more accurate if the US system creates ___ ____ ___ for the returning signals
variable time delays
Images will be more accurate if the US system creates variable time delays for the returning signals
These delays depend on the ___ of the ___ which makes the delay patterns change continuously while listening
depth of the reflectors
Images will be more accurate if the US system creates variable time delays for the returning signals
These delays depend on the depth of the reflectors which makes the ___ ____ change continuously while listening
delay patterns
Images will be more accurate if the US system creates variable time delays for the returning signals
These delays depend on the depth of the reflectors which makes the delay patterns ____ continuously while listening
change
Images will be more accurate if the US system creates variable time delays for the returning signals
These delays depend on the depth of the reflectors which makes the delay patterns change continuously while _____
listening
What is the major difference between receiving and transmitting?
Receiving = multiple focal point
Transmitting = one focal point
During reception, there (are multiple / is one) focal point/s.
are multiple
Dynamic receive focusing is done ____ by the US system and cannot be controlled by the sonographer
automatically
Dynamic receive focusing is done automatically by the US system and (can/cannot) be controlled by the sonographer
cannot
Dynamic receive focusing is done automatically by the US system and cannot be ___
controlled by the sonographer
Dynamic receive focusing is done automatically by the ___ ____ and cannot be controlled by the sonographer
US system

In ___ ____ ____ transducers, the active element is disc-like in shape comprising of multiple ring-shaped elements with a common center
annular phased array

In annular phased array transducers, the active element is ____-like in shape comprising of multiple ____-shaped elements with a ___ ____.
disc ; ring ; common center

The active element is annular phased array transducers are similar to a ___
bull’s-eye target