4.4 Variation and Evolution
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Define continuous variation
A character within a population which shows a gradation from one extreme to another
Define discontinuous variation
Characters that are clear cut and easy to tell apart because they are controlled by a single gene
Define variation
The differences between organisms of the same species
Word for a character controlled by a single gene
monogenic
Word for a character controlled by many genes
polygenic
is discontinuous variation heritable and non heritable
It is heritable
It is not non heritable
Is continuous variation heritable and non heritable
It is heritable and non heritable
Define selection pressure
An environmental factor that can alter the frequency of alleles in a population, when it is limiting
Define natural selection
The increased chance of survival and reproduction of organisms with phenotypes suited to their environment. enhancing the transfer of favourable alleles from one generation to the other
Examples of selection pressure
Predation
Overcrowding
Availability of nesting sites
Define gene pool
The total of all the alleles of all the genes in a population at a given time
Define frequency
Proportion of an allele in the gene pool
State the Hardy-Weinberg equations
P2 + 2pq + q2
p + q = 1
What are the ideal conditions for the Hardy Weinberg principle
Organisms are diploid
The allele frequencies are equal in both sexes
They reproduce sexually
Mating is random
Generations do not overlap
The population size is very large
There is no immigration or emigration
There is no mutation
There is no selection
What is genetic drift
When variations in gene frequencies in populations occur by chance
Define speciation
The formation of a new species
Define evolution
A change in the average phenotype of a population
Explain genetic drift and founder
A small number of individuals become isolated and start a new population.
The founder members are a small sample of the original population
By chance they have very different allele frequency from the original population
Founder population may undergo genetic drift and become even more different
In a small population chance variation in allele frequency from one generation to the next can represent a large change in phenotype for a larger proportion of the population
Name the three types of natural selection
Stabilising selection, directional selection and disruptive selection
What is the theory of natural selection based on
In any population there is variation
Individuals within a population have the potential to produce large numbers of offspring yet the number of adults tends to stay the same from one generation to the next.
From the observations above, what deductions were made on natural selection
There is a struggle for survival (competition) with only the ‘fittest’ surviving
The individuals that survive and reproduce pass on to their offspring the characteristics that enable them to succeed (that is a selection advantage
In time, a group of individuals that once belonged to the same species may give rise to two different groups that are sufficiently distinct to belong to two separate species
Two ways new species rise
Abruptly
Gradually
How do new species arise abruptly
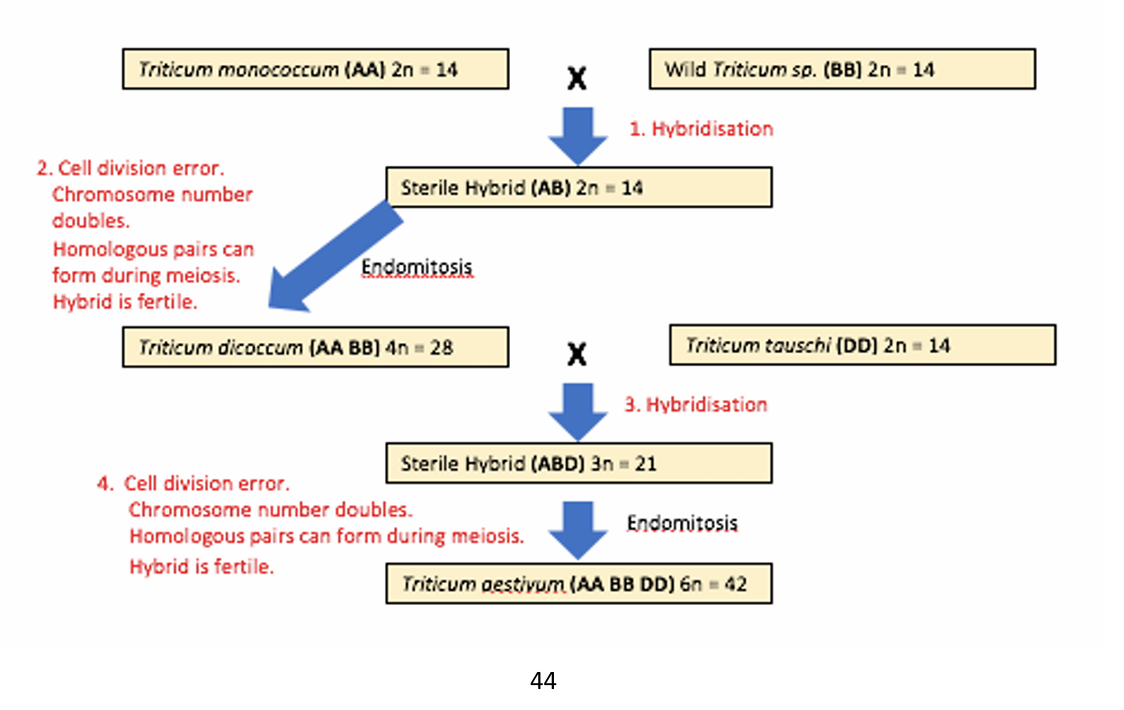
by polyploidy when their chromosome number doubles by endomitosis
How do new species arise gradually
by isolating groups of individuals
What are demes
Sub groups within a population that breed with each other more often than the rest of the population
Describe reproduction isolation
If a deme becomes isolated, it cannot breed with members of other demes and so the gene flow in and out is prevented. The mechanism prevents gene flow and the groups are reproductively isolated
How does specification occur
If demes are isolated for many generation, they undergo changes in allele frequency and accumulate so many different mutations that they are no longer able to interbreed successfully with members of the initial population
Name the two different types of reproductive isolation
Pre-zygotic
Post zygotic
Pre-zygotic
gametes are prevented from fusing and so a zygote is never formed
Post zygotic
gametes fuse and a zygote forms. Even if the organism develops and grows, it is sterile and so the genes of the parent species are kept separate and the species do not merge
When does geographical isolation occur
When the population becomes split by a physical barrier into separate demes.
Name examples of geographical isolation
mountain, a river, desert
Allopatric speciation
The evolution of new species from demes isolate in different geographical locations
Sympatric isolation
The evolution of new species from demes sharing a geographical location
What is behavioural isolation
in animals with elaborate courtship behaviour, the steps in the display of one organism fails to attract the necessary response in a potential partner of another group.
What is morphological isolation
the genitalia of the two groups may be incompatible.
What is gametic isolation
in flowering plants pollination may be prevented because the pollen grain fails to germinate on the stigma whereas in animals, sperm may fail to survive in the oviduct of the female
What is seasonal isolation
If the breeding season of two groups (demes) does not coincide, they cannot interbreed.
Describe hybrid inviability
Fertilisation occurs but incompatibility between the genes of the parents prevents the development of an embryo
Can an embryo formed from the gametes of two species develop in hybrid sterility
yes
How is the hybrid sterile in hybrid sterility
The chromosomes are not sufficiently similar.
Prophase I does not occur
gametes cannot form