Lipids
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
two types of fatty acids found in triglycerides
unsaturated and saturated
saturated “fats”
no double bond between carbons
completely saturated with H bonds
unsaturated “fats”
one or more double bond between carbons
why is saturated fats solid at room temperature? (food form)
have straight chains of fatty acid
why is unsaturated fats liquid at room temperature? (food form)
due to double bonds
bends in the fatty acid
monounsaturated fats
unsaturated fat with one double bond
polyunsaturated fats
unsaturated fat with multiple double bonds
why are saturated fats considered unhealthy/ bad
causes an increase in low density lipids (LDL), molecules that carry bad cholesterol
cause heart disease
makes cell membranes rigid and prevents signals from flowing
three types of unsaturated fats
monounsaturated (good to eat)
polyunsaturated (good to eat)
trans unsaturated fats (bad to eat)
trans unsaturated fats
man-made
has been processed and modified
monounsaturated fats benefits
increases high density lipoprotein (HDL), which carries good cholesterol
reduces heart attacks and diabetes
cis/trans unsaturated fats
cis - hydrogens are on same side, causing bend in db
trans - hydrogens are on opposite side of the db, straight
lipids
macromolecule made of mostly carbon, hydrogen, and few oxygen atoms
hydrophobic molecules due to non-polar regions of hydrocarbons which is majority
4 classes of lipids
Triglycerides
Phospholipids
Steroids
Waxes
function of triglycerides
long term energy storage because their C-H bonds are rich in energy
insulates and cushions vital organs by surrounding it
provide important components for cell membranes
where are triglycerides stored
adipose cells aka fat cells
how do adipose cells manages energy storage and use
when the body needs energy, adipose cells break down and release, causing it to shrink
excess energy from triglycerides are stored in adipose cells, causing swelling
triglycerides structure
consists of glycerol bonded to 3 fatty acids
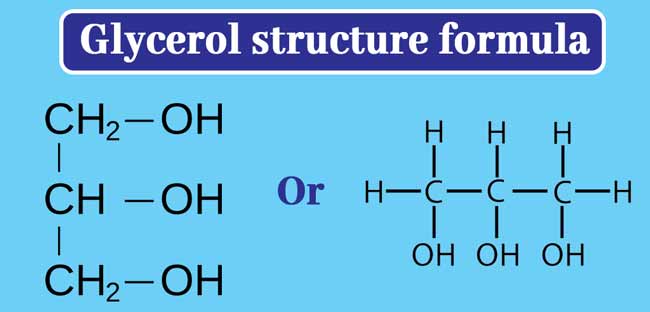
glycerol structure
molecule made of a three-carbon chain, each carbon is attached to a hydroxyl group (–OH)
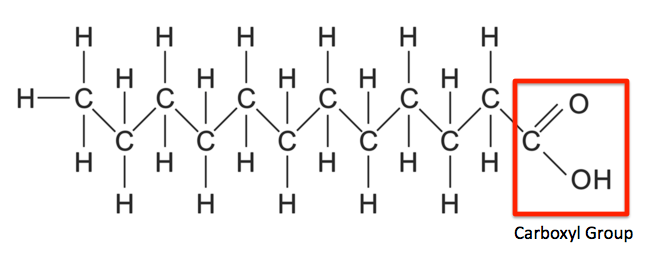
fatty acids structure
hydrocarbons with a carbon bonded to a carboxyl group (COOH) at one end
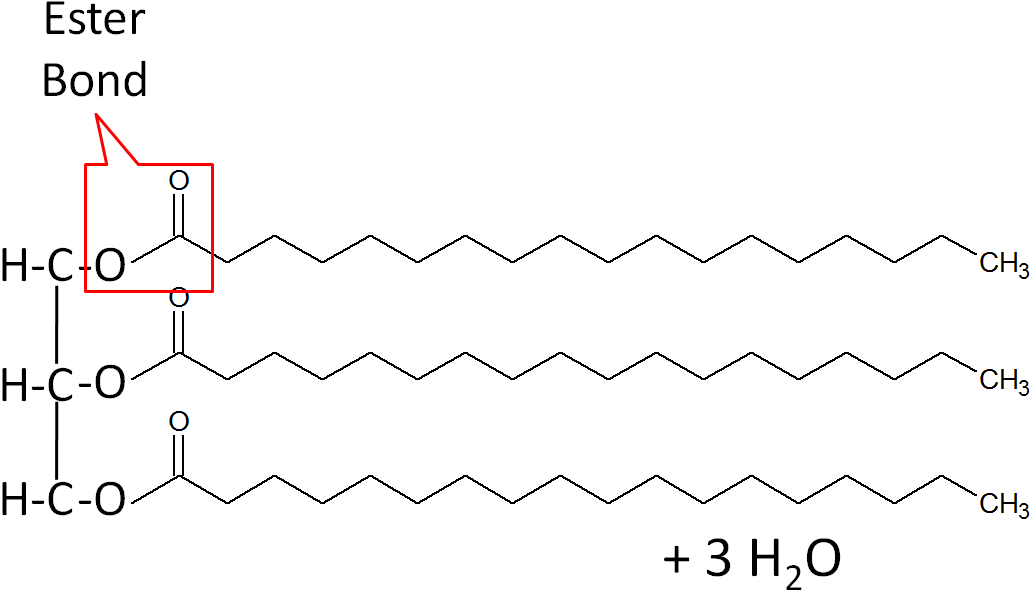
triglycerides - condensation reaction
bonds the glycerol and fatty acid chain with an ester linkage
3 water molecules are created as byproduct
do lipids have monomers
no true monomer
made up in random combinations
how are trans fats created
manufactured through a hydrogenation process
the process changes the unsaturated cis form to trans by changing the location of the H
phospholipids
major components of cell membranes, makes the lipid bilayer
only two fatty chains
hydrophilic polar heads (fatty acid chains), hydrophobic non-polar tails (phosphate)
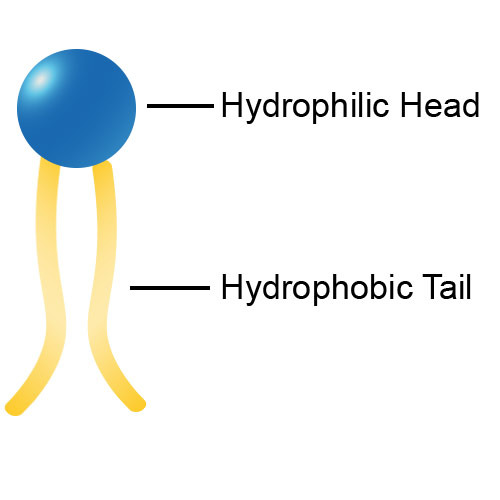
function of phospholipid bilayer in a cell
surrounds the cells as a protective boundary
semi-permeable, letting some substances into the cell and not others
what substances are not allowed in the cell
hydrophobic substances because the cell contains water
steriods
lipids with 4 fused carbon rings
functional groups attached will vary depending on the steroid
cholesterol
steroid found in animal cell membranes
produces many hormones (ex. sex hormones)
waxes
type of lipid
diverse structures with long carbon chains
solid at room temperature
waxes in plants
coats surfaces of leaves to prevent water loss
waxes in animals
coats skin, fur, feathers, and exoskeleton to prevent water from entering